今天,我带来二叉树的基础oj题
目录
- 单值二叉树:[链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/univalued-binary-tree/)
- 相同的树:[链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/same-tree/)
- 对称二叉树:[链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/symmetric-tree/)
- 二叉树的前序遍历:[链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-preorder-traversal/)
- 二叉树的中序遍历:[链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/)
- 二叉树的后序遍历:[链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-postorder-traversal/)
- 另一棵树的子树:[链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/subtree-of-another-tree/)
- 二叉树的构建和遍历:[链接](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/4b91205483694f449f94c179883c1fef?tpId=60&&tqId=29483&rp=1&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/tsing-kaoyan/question-ranking)
- 翻转二叉树:[链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/invert-binary-tree/)
单值二叉树:链接
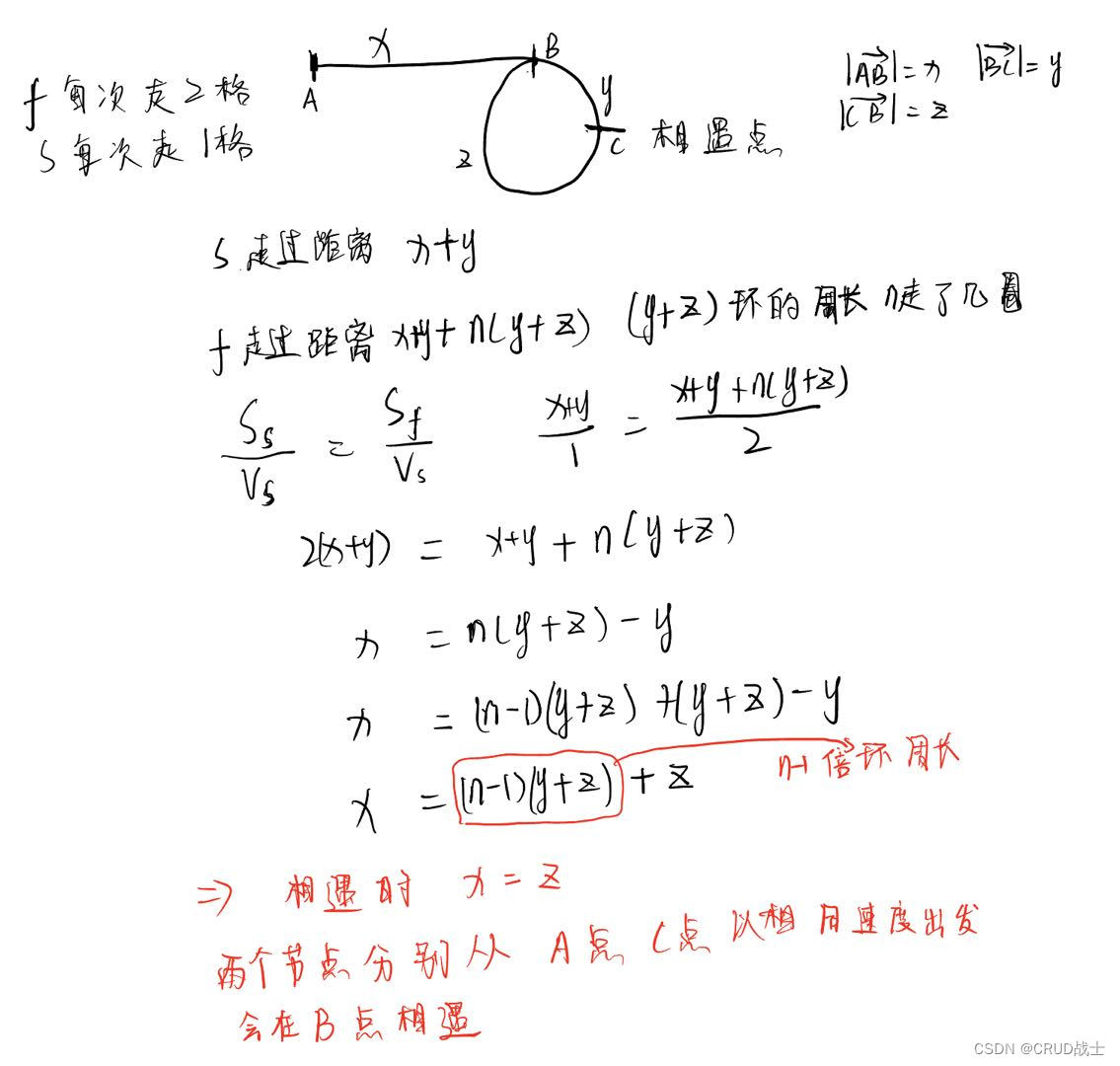
题目要求:如果二叉树每个节点都具有相同的值,那么该二叉树就是单值二叉树。
只有给定的树是单值二叉树时,才返回 true;否则返回 false。
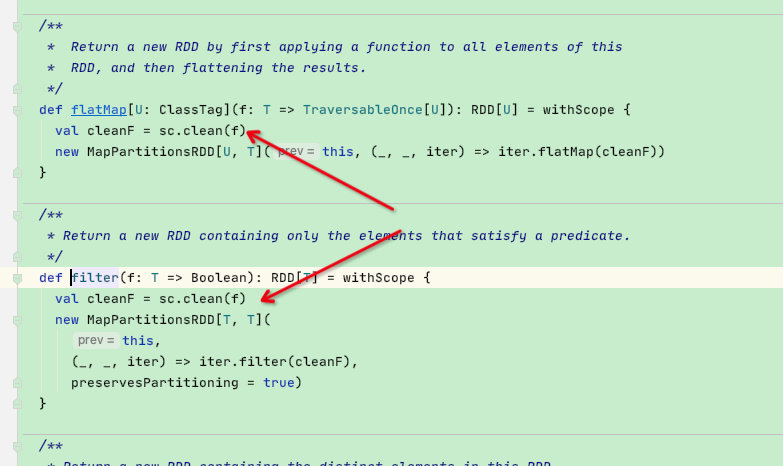
如下图为单值二叉树。
//依次比较左右结点和根节点
bool isUnivalTree(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
return true;
if(root->left && root->left->val != root->val)
return false;
if(root->right && root->right->val != root->val)
return false;
return isUnivalTree(root->left) && isUnivalTree(root->right);
}

相同的树:链接
题目要求:给你两棵二叉树的根节点 p 和 q ,编写一个函数来检验这两棵树是否相同。
如果两个树在结构上相同,并且节点具有相同的值,则认为它们是相同的。
//比较根节点
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q)
{
if(p == NULL && q == NULL)
return true;
if(p == NULL || q == NULL)
return false;
if(p->val != q->val)
return false;
return isSameTree(p->left,q->left) && isSameTree(p->right,q->right);
}

对称二叉树:链接
题目要求:给你一个二叉树的根节点 root , 检查它是否轴对称。
bool _isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root1,struct TreeNode* root2)
{
if(root1 == NULL && root2 == NULL)
return true;
if(root1 == NULL || root2 == NULL)
return false;
if(root1->val != root2->val)
return false;
return _isSymmetric(root1->left,root2->right) && _isSymmetric(root1->right,root2->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root)
{
return !root || _isSymmetric(root->left,root->right);
}

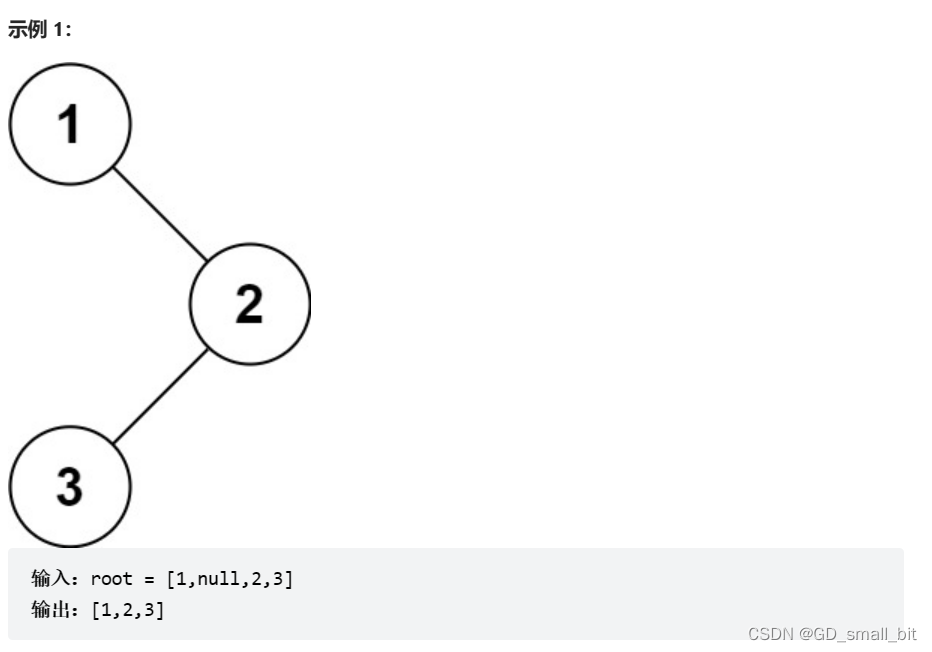
二叉树的前序遍历:链接
题目要求:给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它节点值的 前序 遍历。
void _preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root,int* arr,int* returnSize)
{
if(root == NULL)
return;
arr[(*returnSize)++] = root->val;
_preorderTraversal(root->left,arr,returnSize);
_preorderTraversal(root->right,arr,returnSize);
}
int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize)
{
int* arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 101);
*returnSize = 0;
_preorderTraversal(root,arr,returnSize);
return arr;
}

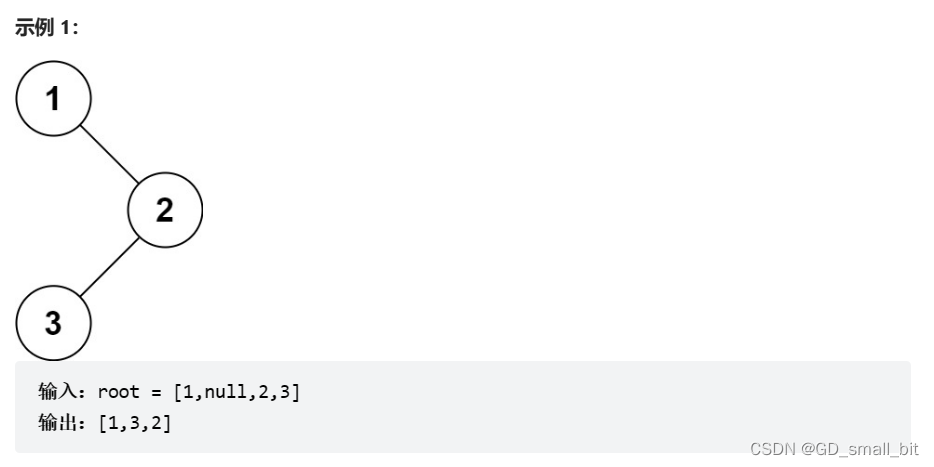
二叉树的中序遍历:链接
题目要求:给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回 它的 中序 遍历 。
void _inorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root,int* arr,int* returnSize)
{
if(root == NULL)
return;
_inorderTraversal(root->left,arr,returnSize);
arr[(*returnSize)++] = root->val;
_inorderTraversal(root->right,arr,returnSize);
}
int* inorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize)
{
int* arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 101);
*returnSize = 0;
_inorderTraversal(root,arr,returnSize);
return arr;
}

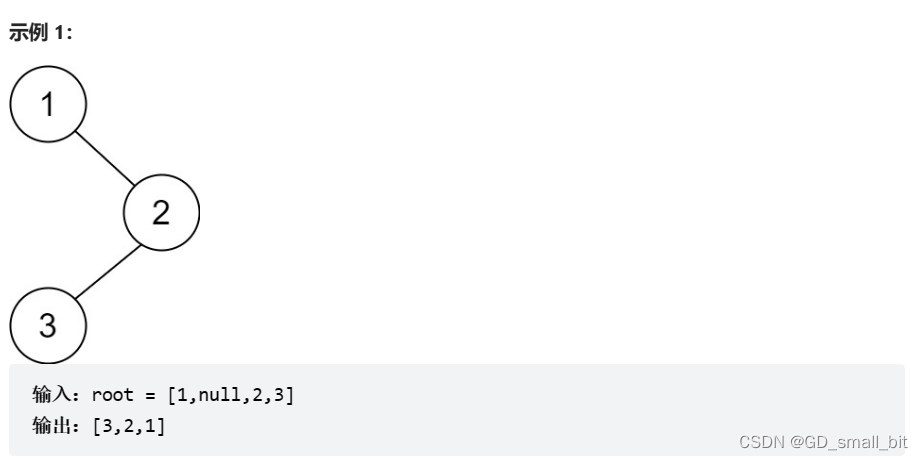
二叉树的后序遍历:链接
题目要求:给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 后序遍历 。
void _postorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root,int* arr,int* returnSize)
{
if(root == NULL)
return;
_postorderTraversal(root->left,arr,returnSize);
_postorderTraversal(root->right,arr,returnSize);
arr[(*returnSize)++] = root->val;
}
int* postorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize)
{
int* arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 101);
*returnSize = 0;
_postorderTraversal(root,arr,returnSize);
return arr;
}
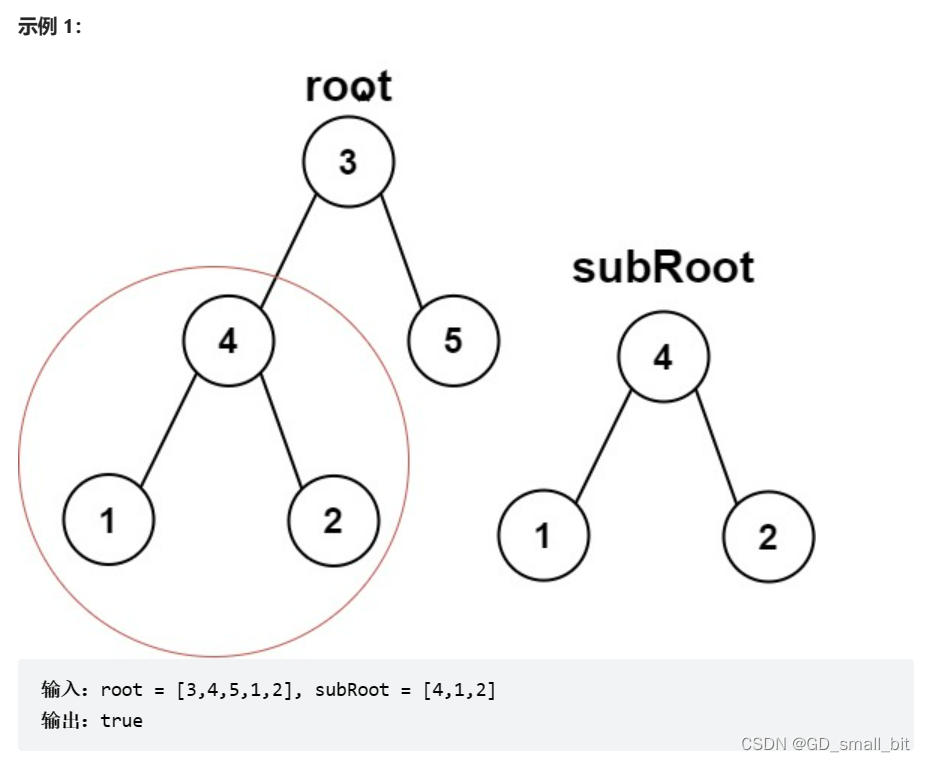
另一棵树的子树:链接
题目要求:给你两棵二叉树 root 和 subRoot 。检验 root 中是否包含和 subRoot 具有相同结构和节点值的子树。如果存在,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
二叉树 tree 的一棵子树包括 tree 的某个节点和这个节点的所有后代节点。tree 也可以看做它自身的一棵子树。
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* root1,struct TreeNode* root2)
{
if(root1 == NULL && root2 == NULL)
return true;
if(root1 == NULL || root2 == NULL)
return false;
if(root1->val != root2->val)
return false;
return isSameTree(root1->left,root2->left) && isSameTree(root1->right,root2->right);
}
bool isSubtree(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* subRoot)
{
if(root == NULL)
return false;
if(isSameTree(root,subRoot))
return true;
return isSubtree(root->left,subRoot) || isSubtree(root->right,subRoot);
}
二叉树的构建和遍历:链接
题目要求:描述
编一个程序,读入用户输入的一串先序遍历字符串,根据此字符串建立一个二叉树(以指针方式存储)。
例如如下的先序遍历字符串: ABC##DE#G##F### 其中“#”表示的是空格,空格字符代表空树。建立起此二叉树以后,再对二叉树进行中序遍历,输出遍历结果。
输入描述:
输入包括1行字符串,长度不超过100。
输出描述:
可能有多组测试数据,对于每组数据, 输出将输入字符串建立二叉树后中序遍历的序列,每个字符后面都有一个空格。 每个输出结果占一行。

#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
//二叉树的结点定义
typedef char BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTree
{
BTDataType val;
struct BinaryTree* left;
struct BinaryTree* right;
}BinaryTree;
//创建二叉树
BinaryTree* RebuildBinaryTree(char* arr,int* pi)
{
if(arr[(*pi)] == '#')
{
(*pi)++;
return NULL;
}
BinaryTree* root = (BinaryTree*)malloc(sizeof(BinaryTree));
if(root == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(1);
}
root->val = arr[(*pi)++];
root->left = RebuildBinaryTree(arr,pi);
root->right = RebuildBinaryTree(arr,pi);
return root;
}
//中序遍历
void InOrder(BinaryTree* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
return;
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%c ",root->val);
InOrder(root->right);
}
int main()
{
char arr[100];
scanf("%s",arr);
int i = 0;
BinaryTree* root = RebuildBinaryTree(arr,&i);
InOrder(root);
return 0;
}
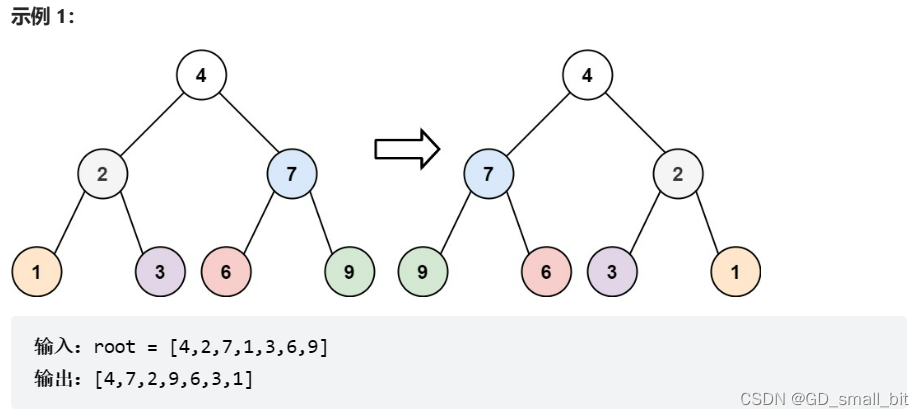
翻转二叉树:链接
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。
struct TreeNode* invertTree(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
return NULL;
invertTree(root->left);
invertTree(root->right);
struct TreeNode* tmp = root->left;
root->left = root->right;
root->right = tmp;
return root;
}

今天,二叉树的基础oj题就讲到这里,关注点一点,下期更精彩。