背景
CPU:AST2500
驱动里实现GPIO模拟MDIO驱动,参考内核驱动mdio-bitbang.c和mdio-gpio.c,当前项目不支持设备树,驱动需要改成platform注册
MDIO介绍
SMI接口
SMI是MAC内核访问PHY寄存器接口,它由两根线组成,双工,MDC为时钟,MDIO为双向数据通信,原理上跟I2C总线很类似,也可以通过总线访问多个不同的phy。
MDC/MDIO基本特性:
- 两线制:MDC(时钟线)和MDIO(数据线)。
- 时钟频率:2.5MHz
- 通信方式:总线制,可同时接入的PHY数量为32个
- 通过SMI接口,MAC芯片主动的轮询PHY层芯片,获得状态信息,并发出命令信息。
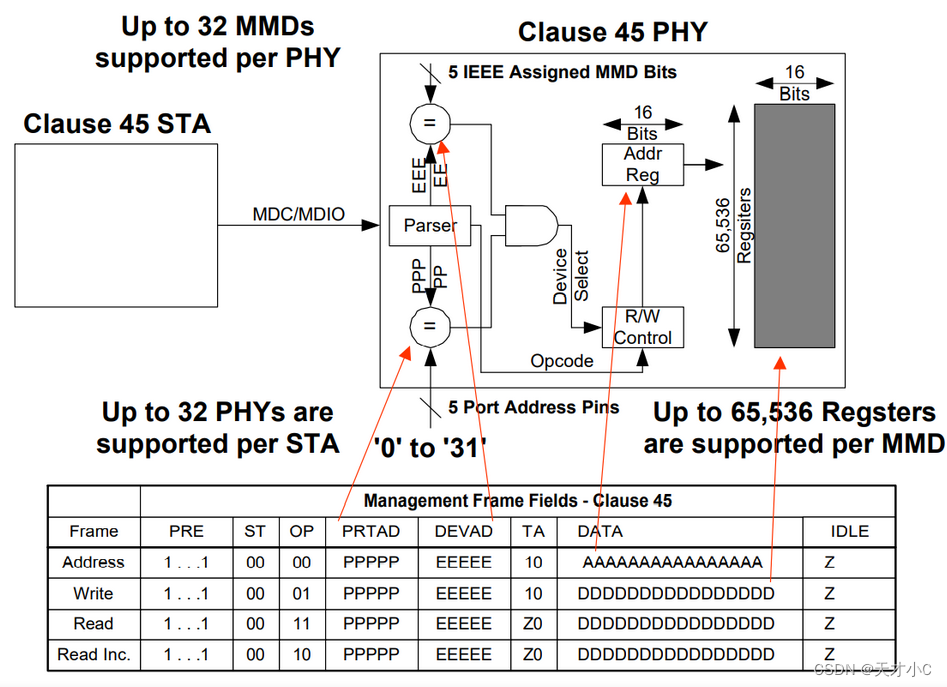
Clause22

Clause45
内核源码
修改后的源码不方便放上来,这里放的是内核源码
mdio-gpio.c
// SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-2.0
/*
* GPIO based MDIO bitbang driver.
* Supports OpenFirmware.
*
* Copyright (c) 2008 CSE Semaphore Belgium.
* by Laurent Pinchart <laurentp@cse-semaphore.com>
*
* Copyright (C) 2008, Paulius Zaleckas <paulius.zaleckas@teltonika.lt>
*
* Based on earlier work by
*
* Copyright (c) 2003 Intracom S.A.
* by Pantelis Antoniou <panto@intracom.gr>
*
* 2005 (c) MontaVista Software, Inc.
* Vitaly Bordug <vbordug@ru.mvista.com>
*/
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/platform_data/mdio-gpio.h>
#include <linux/mdio-bitbang.h>
#include <linux/mdio-gpio.h>
#include <linux/gpio/consumer.h>
#include <linux/of_mdio.h>
struct mdio_gpio_info {
struct mdiobb_ctrl ctrl;
struct gpio_desc *mdc, *mdio, *mdo;
};
static int mdio_gpio_get_data(struct device *dev,
struct mdio_gpio_info *bitbang)
{
bitbang->mdc = devm_gpiod_get_index(dev, NULL, MDIO_GPIO_MDC,
GPIOD_OUT_LOW);
if (IS_ERR(bitbang->mdc))
return PTR_ERR(bitbang->mdc);
bitbang->mdio = devm_gpiod_get_index(dev, NULL, MDIO_GPIO_MDIO,
GPIOD_IN);
if (IS_ERR(bitbang->mdio))
return PTR_ERR(bitbang->mdio);
bitbang->mdo = devm_gpiod_get_index_optional(dev, NULL, MDIO_GPIO_MDO,
GPIOD_OUT_LOW);
return PTR_ERR_OR_ZERO(bitbang->mdo);
}
static void mdio_dir(struct mdiobb_ctrl *ctrl, int dir)
{
struct mdio_gpio_info *bitbang =
container_of(ctrl, struct mdio_gpio_info, ctrl);
if (bitbang->mdo) {
/* Separate output pin. Always set its value to high
* when changing direction. If direction is input,
* assume the pin serves as pull-up. If direction is
* output, the default value is high.
*/
gpiod_set_value_cansleep(bitbang->mdo, 1);
return;
}
if (dir)
gpiod_direction_output(bitbang->mdio, 1);
else
gpiod_direction_input(bitbang->mdio);
}
static int mdio_get(struct mdiobb_ctrl *ctrl)
{
struct mdio_gpio_info *bitbang =
container_of(ctrl, struct mdio_gpio_info, ctrl);
return gpiod_get_value_cansleep(bitbang->mdio);
}
static void mdio_set(struct mdiobb_ctrl *ctrl, int what)
{
struct mdio_gpio_info *bitbang =
container_of(ctrl, struct mdio_gpio_info, ctrl);
if (bitbang->mdo)
gpiod_set_value_cansleep(bitbang->mdo, what);
else
gpiod_set_value_cansleep(bitbang->mdio, what);
}
static void mdc_set(struct mdiobb_ctrl *ctrl, int what)
{
struct mdio_gpio_info *bitbang =
container_of(ctrl, struct mdio_gpio_info, ctrl);
gpiod_set_value_cansleep(bitbang->mdc, what);
}
static const struct mdiobb_ops mdio_gpio_ops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.set_mdc = mdc_set,
.set_mdio_dir = mdio_dir,
.set_mdio_data = mdio_set,
.get_mdio_data = mdio_get,
};
static struct mii_bus *mdio_gpio_bus_init(struct device *dev,
struct mdio_gpio_info *bitbang,
int bus_id)
{
struct mdio_gpio_platform_data *pdata = dev_get_platdata(dev);
struct mii_bus *new_bus;
bitbang->ctrl.ops = &mdio_gpio_ops;
new_bus = alloc_mdio_bitbang(&bitbang->ctrl);
if (!new_bus)
return NULL;
new_bus->name = "GPIO Bitbanged MDIO";
new_bus->parent = dev;
if (bus_id != -1)
snprintf(new_bus->id, MII_BUS_ID_SIZE, "gpio-%x", bus_id);
else
strncpy(new_bus->id, "gpio", MII_BUS_ID_SIZE);
if (pdata) {
new_bus->phy_mask = pdata->phy_mask;
new_bus->phy_ignore_ta_mask = pdata->phy_ignore_ta_mask;
}
dev_set_drvdata(dev, new_bus);
return new_bus;
}
static void mdio_gpio_bus_deinit(struct device *dev)
{
struct mii_bus *bus = dev_get_drvdata(dev);
free_mdio_bitbang(bus);
}
static void mdio_gpio_bus_destroy(struct device *dev)
{
struct mii_bus *bus = dev_get_drvdata(dev);
mdiobus_unregister(bus);
mdio_gpio_bus_deinit(dev);
}
static int mdio_gpio_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct mdio_gpio_info *bitbang;
struct mii_bus *new_bus;
int ret, bus_id;
bitbang = devm_kzalloc(&pdev->dev, sizeof(*bitbang), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!bitbang)
return -ENOMEM;
ret = mdio_gpio_get_data(&pdev->dev, bitbang);
if (ret)
return ret;
if (pdev->dev.of_node) {
bus_id = of_alias_get_id(pdev->dev.of_node, "mdio-gpio");
if (bus_id < 0) {
dev_warn(&pdev->dev, "failed to get alias id\n");
bus_id = 0;
}
} else {
bus_id = pdev->id;
}
new_bus = mdio_gpio_bus_init(&pdev->dev, bitbang, bus_id);
if (!new_bus)
return -ENODEV;
ret = of_mdiobus_register(new_bus, pdev->dev.of_node);
if (ret)
mdio_gpio_bus_deinit(&pdev->dev);
return ret;
}
static int mdio_gpio_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
mdio_gpio_bus_destroy(&pdev->dev);
return 0;
}
static const struct of_device_id mdio_gpio_of_match[] = {
{ .compatible = "virtual,mdio-gpio", },
{ /* sentinel */ }
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of, mdio_gpio_of_match);
static struct platform_driver mdio_gpio_driver = {
.probe = mdio_gpio_probe,
.remove = mdio_gpio_remove,
.driver = {
.name = "mdio-gpio",
.of_match_table = mdio_gpio_of_match,
},
};
module_platform_driver(mdio_gpio_driver);
MODULE_ALIAS("platform:mdio-gpio");
MODULE_AUTHOR("Laurent Pinchart, Paulius Zaleckas");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL v2");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("Generic driver for MDIO bus emulation using GPIO");
mdio-bitbang.c
// SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-2.0
/*
* Bitbanged MDIO support.
*
* Author: Scott Wood <scottwood@freescale.com>
* Copyright (c) 2007 Freescale Semiconductor
*
* Based on CPM2 MDIO code which is:
*
* Copyright (c) 2003 Intracom S.A.
* by Pantelis Antoniou <panto@intracom.gr>
*
* 2005 (c) MontaVista Software, Inc.
* Vitaly Bordug <vbordug@ru.mvista.com>
*/
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/mdio-bitbang.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#define MDIO_READ 2
#define MDIO_WRITE 1
#define MDIO_C45 (1<<15)
#define MDIO_C45_ADDR (MDIO_C45 | 0)
#define MDIO_C45_READ (MDIO_C45 | 3)
#define MDIO_C45_WRITE (MDIO_C45 | 1)
#define MDIO_SETUP_TIME 10
#define MDIO_HOLD_TIME 10
/* Minimum MDC period is 400 ns, plus some margin for error. MDIO_DELAY
* is done twice per period.
*/
#define MDIO_DELAY 250
/* The PHY may take up to 300 ns to produce data, plus some margin
* for error.
*/
#define MDIO_READ_DELAY 350
/* MDIO must already be configured as output. */
static void mdiobb_send_bit(struct mdiobb_ctrl *ctrl, int val)
{
const struct mdiobb_ops *ops = ctrl->ops;
ops->set_mdio_data(ctrl, val);
ndelay(MDIO_DELAY);
ops->set_mdc(ctrl, 1);
ndelay(MDIO_DELAY);
ops->set_mdc(ctrl, 0);
}
/* MDIO must already be configured as input. */
static int mdiobb_get_bit(struct mdiobb_ctrl *ctrl)
{
const struct mdiobb_ops *ops = ctrl->ops;
ndelay(MDIO_DELAY);
ops->set_mdc(ctrl, 1);
ndelay(MDIO_READ_DELAY);
ops->set_mdc(ctrl, 0);
return ops->get_mdio_data(ctrl);
}
/* MDIO must already be configured as output. */
static void mdiobb_send_num(struct mdiobb_ctrl *ctrl, u16 val, int bits)
{
int i;
for (i = bits - 1; i >= 0; i--)
mdiobb_send_bit(ctrl, (val >> i) & 1);
}
/* MDIO must already be configured as input. */
static u16 mdiobb_get_num(struct mdiobb_ctrl *ctrl, int bits)
{
int i;
u16 ret = 0;
for (i = bits - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
ret <<= 1;
ret |= mdiobb_get_bit(ctrl);
}
return ret;
}
/* Utility to send the preamble, address, and
* register (common to read and write).
*/
static void mdiobb_cmd(struct mdiobb_ctrl *ctrl, int op, u8 phy, u8 reg)
{
const struct mdiobb_ops *ops = ctrl->ops;
int i;
ops->set_mdio_dir(ctrl, 1);
/*
* Send a 32 bit preamble ('1's) with an extra '1' bit for good
* measure. The IEEE spec says this is a PHY optional
* requirement. The AMD 79C874 requires one after power up and
* one after a MII communications error. This means that we are
* doing more preambles than we need, but it is safer and will be
* much more robust.
*/
for (i = 0; i < 32; i++)
mdiobb_send_bit(ctrl, 1);
/* send the start bit (01) and the read opcode (10) or write (01).
Clause 45 operation uses 00 for the start and 11, 10 for
read/write */
mdiobb_send_bit(ctrl, 0);
if (op & MDIO_C45)
mdiobb_send_bit(ctrl, 0);
else
mdiobb_send_bit(ctrl, 1);
mdiobb_send_bit(ctrl, (op >> 1) & 1);
mdiobb_send_bit(ctrl, (op >> 0) & 1);
mdiobb_send_num(ctrl, phy, 5);
mdiobb_send_num(ctrl, reg, 5);
}
/* In clause 45 mode all commands are prefixed by MDIO_ADDR to specify the
lower 16 bits of the 21 bit address. This transfer is done identically to a
MDIO_WRITE except for a different code. To enable clause 45 mode or
MII_ADDR_C45 into the address. Theoretically clause 45 and normal devices
can exist on the same bus. Normal devices should ignore the MDIO_ADDR
phase. */
static int mdiobb_cmd_addr(struct mdiobb_ctrl *ctrl, int phy, u32 addr)
{
unsigned int dev_addr = (addr >> 16) & 0x1F;
unsigned int reg = addr & 0xFFFF;
mdiobb_cmd(ctrl, MDIO_C45_ADDR, phy, dev_addr);
/* send the turnaround (10) */
mdiobb_send_bit(ctrl, 1);
mdiobb_send_bit(ctrl, 0);
mdiobb_send_num(ctrl, reg, 16);
ctrl->ops->set_mdio_dir(ctrl, 0);
mdiobb_get_bit(ctrl);
return dev_addr;
}
static int mdiobb_read(struct mii_bus *bus, int phy, int reg)
{
struct mdiobb_ctrl *ctrl = bus->priv;
int ret, i;
if (reg & MII_ADDR_C45) {
reg = mdiobb_cmd_addr(ctrl, phy, reg);
mdiobb_cmd(ctrl, MDIO_C45_READ, phy, reg);
} else
mdiobb_cmd(ctrl, MDIO_READ, phy, reg);
ctrl->ops->set_mdio_dir(ctrl, 0);
/* check the turnaround bit: the PHY should be driving it to zero, if this
* PHY is listed in phy_ignore_ta_mask as having broken TA, skip that
*/
if (mdiobb_get_bit(ctrl) != 0 &&
!(bus->phy_ignore_ta_mask & (1 << phy))) {
/* PHY didn't drive TA low -- flush any bits it
* may be trying to send.
*/
for (i = 0; i < 32; i++)
mdiobb_get_bit(ctrl);
return 0xffff;
}
ret = mdiobb_get_num(ctrl, 16);
mdiobb_get_bit(ctrl);
return ret;
}
static int mdiobb_write(struct mii_bus *bus, int phy, int reg, u16 val)
{
struct mdiobb_ctrl *ctrl = bus->priv;
if (reg & MII_ADDR_C45) {
reg = mdiobb_cmd_addr(ctrl, phy, reg);
mdiobb_cmd(ctrl, MDIO_C45_WRITE, phy, reg);
} else
mdiobb_cmd(ctrl, MDIO_WRITE, phy, reg);
/* send the turnaround (10) */
mdiobb_send_bit(ctrl, 1);
mdiobb_send_bit(ctrl, 0);
mdiobb_send_num(ctrl, val, 16);
ctrl->ops->set_mdio_dir(ctrl, 0);
mdiobb_get_bit(ctrl);
return 0;
}
struct mii_bus *alloc_mdio_bitbang(struct mdiobb_ctrl *ctrl)
{
struct mii_bus *bus;
bus = mdiobus_alloc();
if (!bus)
return NULL;
__module_get(ctrl->ops->owner);
bus->read = mdiobb_read;
bus->write = mdiobb_write;
bus->priv = ctrl;
return bus;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(alloc_mdio_bitbang);
void free_mdio_bitbang(struct mii_bus *bus)
{
struct mdiobb_ctrl *ctrl = bus->priv;
module_put(ctrl->ops->owner);
mdiobus_free(bus);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(free_mdio_bitbang);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL v2");
移植注意点
注意一
查看发送端和接收端的datasheet确认读写数据时是上升沿还是下降沿,AST2500是下降沿,phy端是上升沿,所以写的时候需要上升沿,读取数据时是下降沿采集
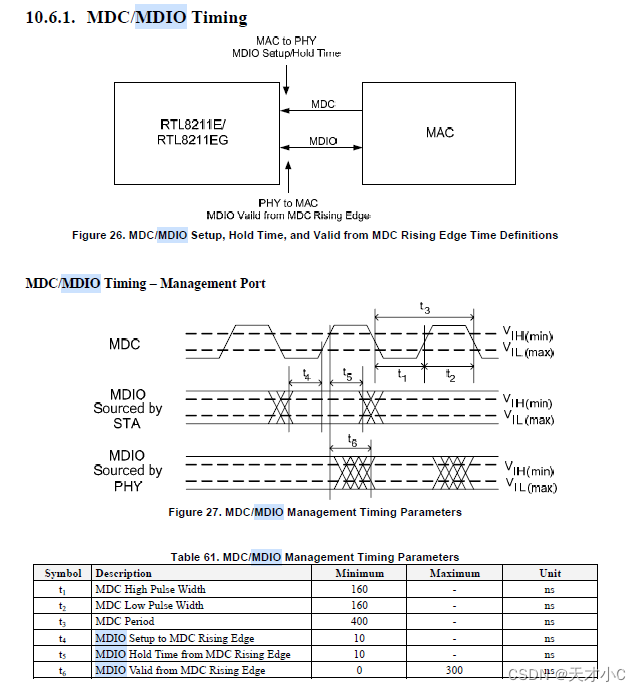
注意二
模拟MDIO的两个GPIO属于同一个寄存器,同一时间快速操作影响clk和data时序
注意三
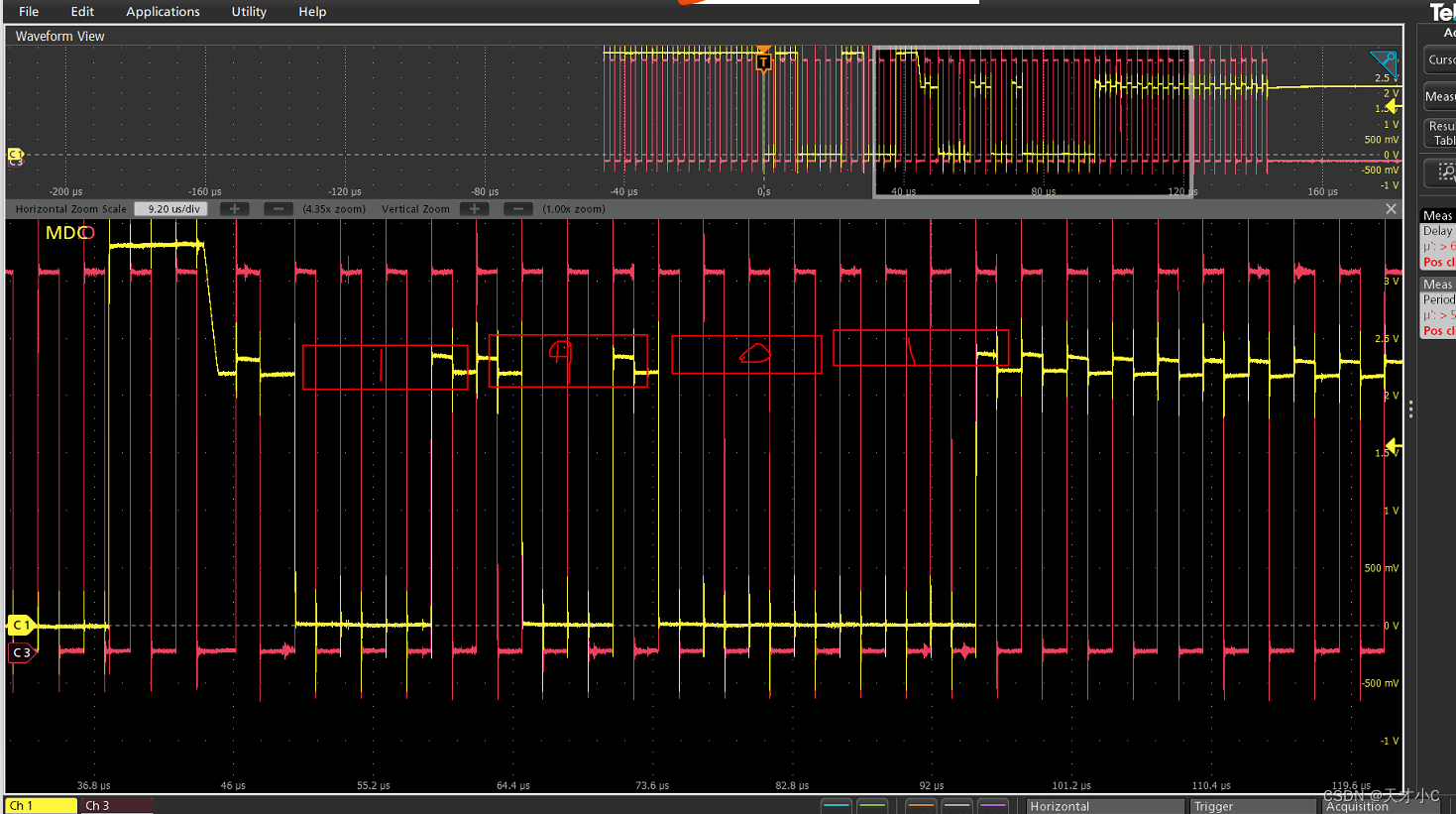
实际读的时候从波形来看,发现phy端在TA时没有拉低,导致读取数据失败,workaround就是跳过这一时序
注意四
OS里是无法直接看到类似eth0这样的设备,所以不能用传统注册MDIO bus,直接模拟通信
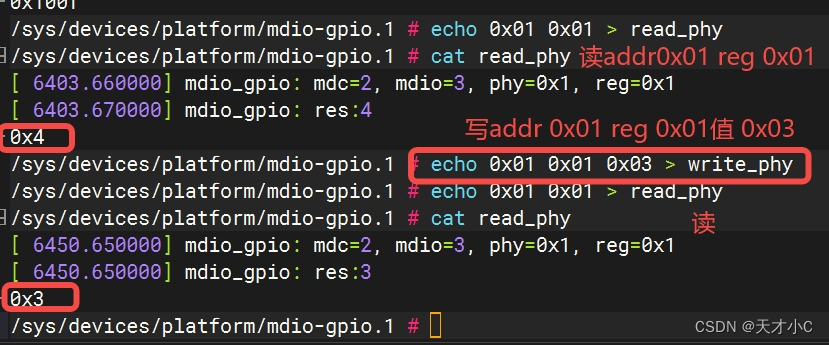
用例展示
读取芯片型号和版本





![[GWCTF 2019]我有一个数据库1](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/9f25e89dde5847a4a4b8d92d58a1bd55.png)