文章目录
- 0. 代码仓库
- 代码编译时候可能出现的错误
- 1. 哈希
- 1.1 哈希算法的种类:
- 1.2 使用的头文件
- 1.3 哈希算法API
- 1.3.1 详解md5 API
- 1.3.2 sha1/sha224/sha256/sha384/sha512常用API
- 1.5 sha1代码测试
- 1.4 在VS中添加预处理器定义
- 1.5 哈希算法C++代码封装的思路
- 2. 非对称加密RSA
- 2.1 特点
- 2.2 应用场景:
- 2.3 生成RSA密钥对:常用的API
- 2.4 生成密钥对:测试代码
- 2.4.1 将密钥对写入磁盘 - 代码主要部分
- 2.4.2 使用bio方式将秘钥写入磁盘
- 2.5 加密和解密
- 2.5.1 加密解密常用API
- 2.5.2 加密解密:测试代码
- 2.6 RSA签名和校验签名
- 2.6.1 签名和校验签名API
- 2.6.2 签名和校验:测试代码
- 2.7 RSA封装成C++类
- 3.对称加密AES
- 3.1 AES 加解密的API:
- 3.1.1 生成加密/解密的Key
- 3.1.2 CBC方式加密 - 密码分组链接模式
- 3.2 AES代码测试
0. 代码仓库
Openssl_Test:项目中要单独添加main.cpp或者test.cpp
代码编译时候可能出现的错误
-
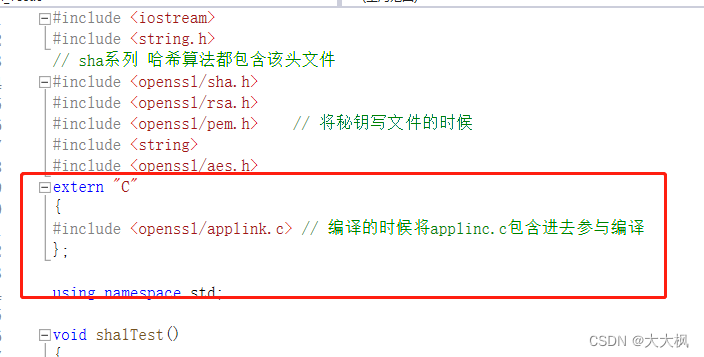
OPENSSL_Uplink no OPENSSL_Applink 错误
Applink()函数不属于openssl的dll内部函数的一部分(通过dll分析器看出这个函数不存在), 所以必须把applink.c文件应用程序的一部分编译.
-
解决方案
extern "C" { #include <openssl/applink.c> };
1. 哈希
1.1 哈希算法的种类:
- md5 - 散列值: 16byte
- sha1 - 散列值: 20byte
- sha224- 散列值: 28byte
- sha256- 散列值: 32byte
- sha384- 散列值: 48byte
- sha512- 散列值: 64byte
以上说的散列值长度是二进制数据长度, 一般散列值使用 16 进制格式的数字串表示的, 看到的字符串长度是原来的2倍长.
1.2 使用的头文件
#include <openssl/md5.h>
#include <openssl/sha.h>
1.3 哈希算法API
1.3.1 详解md5 API
# define MD5_DIGEST_LENGTH 16 // md5哈希值长度
// 初始化函数, 初始化参数 c
int MD5_Init(MD5_CTX *c);
参数c: 传出参数
// 添加md5运算的数据-> 没有计算
// 该函数可以进行多次数据添加 -> 函数多次调用
int MD5_Update(MD5_CTX *c, const void *data, size_t len);
参数:
- c: MD5_Init() 初始化得到的
- data: 传入参数, 字符串
- len: data数据的长度
// 对添加的数据进行md5计算
int MD5_Final(unsigned char *md, MD5_CTX *c);
参数:
- md: 传出参数, 存储得到的哈希值
- c: MD5_Init() 初始化得到的
// 通过传递的参数, 直接生成一个md5哈希值
// 只能添加一次数据
unsigned char *MD5(const unsigned char *d, size_t n, unsigned char *md);
参数:
- d: 传入, 要进行md5运算的字符串
- n: 字符串的的长度
- md: 传出, 存储md5的哈希值
返回值: 这个地址的函数第三个参数md地址
1.3.2 sha1/sha224/sha256/sha384/sha512常用API
# define SHA_DIGEST_LENGTH 20
# define SHA224_DIGEST_LENGTH 28
# define SHA256_DIGEST_LENGTH 32
# define SHA384_DIGEST_LENGTH 48
# define SHA512_DIGEST_LENGTH 64
int SHA1_Init(SHA_CTX *c);
int SHA1_Update(SHA_CTX *c, const void *data, size_t len);
int SHA1_Final(unsigned char *md, SHA_CTX *c);
unsigned char *SHA1(const unsigned char *d, size_t n, unsigned char *md);
int SHA224_Init(SHA256_CTX *c);
int SHA224_Update(SHA256_CTX *c, const void *data, size_t len);
int SHA224_Final(unsigned char *md, SHA256_CTX *c);
unsigned char *SHA224(const unsigned char *d, size_t n, unsigned char *md);
int SHA256_Init(SHA256_CTX *c);
int SHA256_Update(SHA256_CTX *c, const void *data, size_t len);
int SHA256_Final(unsigned char *md, SHA256_CTX *c);
unsigned char *SHA256(const unsigned char *d, size_t n, unsigned char *md);
int SHA384_Init(SHA512_CTX *c);
int SHA384_Update(SHA512_CTX *c, const void *data, size_t len);
int SHA384_Final(unsigned char *md, SHA512_CTX *c);
unsigned char *SHA384(const unsigned char *d, size_t n, unsigned char *md);
int SHA512_Init(SHA512_CTX *c);
int SHA512_Update(SHA512_CTX *c, const void *data, size_t len);
int SHA512_Final(unsigned char *md, SHA512_CTX *c);
unsigned char *SHA512(const unsigned char *d, size_t n, unsigned char *md);
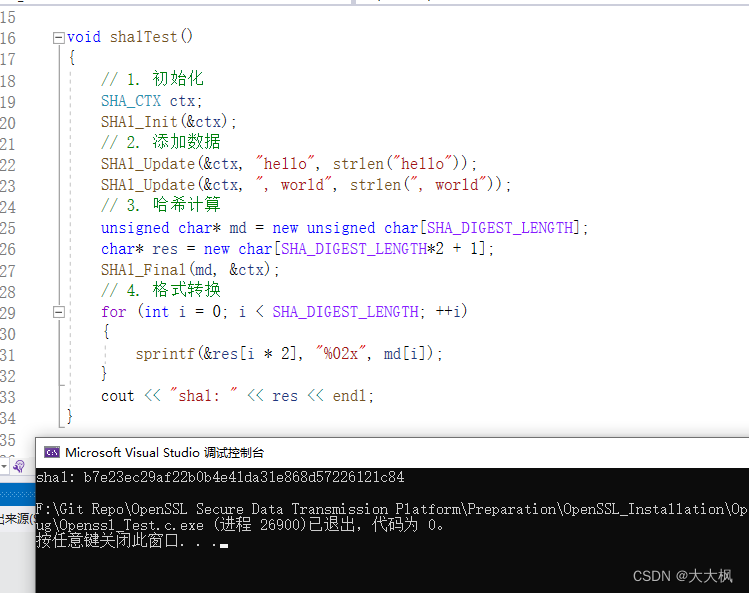
1.5 sha1代码测试
void sha1Test()
{
// 1. 初始化
SHA_CTX ctx;
SHA1_Init(&ctx);
// 2. 添加数据
SHA1_Update(&ctx, "hello", strlen("hello"));
SHA1_Update(&ctx, ", world", strlen(", world"));
// 3. 哈希计算
unsigned char* md = new unsigned char[SHA_DIGEST_LENGTH];
char* res = new char[SHA_DIGEST_LENGTH*2 + 1];
SHA1_Final(md, &ctx);
// 4. 格式转换
for (int i = 0; i < SHA_DIGEST_LENGTH; ++i)
{
sprintf(&res[i * 2], "%02x", md[i]);
}
cout << "sha1: " << res << endl;
}
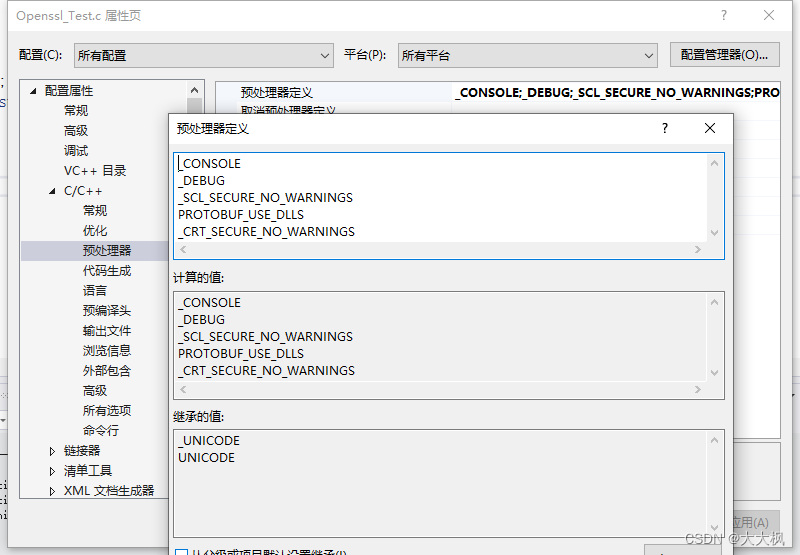
1.4 在VS中添加预处理器定义
_CONSOLE
_DEBUG
_SCL_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
PROTOBUF_USE_DLLS
_CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
1.5 哈希算法C++代码封装的思路
c++中不建议使用宏,因为容易出bug,而且这种bug不好找,可以使用 常量/枚举/内联->用空间换时间。
class MyHash
{
public:
enum HashType{M_MD5, M_SHA1, M_SHA224, M_SHA512, M_SHA384, M_SHA512};
MyHash(HashType type) // 得到一个哈希对象, 创建不同的哈希对象
{
m_type = type;
switch(type)
{
case M_MD5:
MD5_Init();
break;
case M_sha1:
SHA1_Init();
break;
}
}
~MyHash();
// 添加数据
void addData(string str)
{
switch(m_type)
{
case M_MD5:
MD5_Update();
break;
case M_sha1:
SHA1_Update();
break;
}
}
// 计算哈希值
string result()
{
switch(m_type)
{
xxx_Final();
// 转换 -> 16进制格式
}
}
private:
HashType m_type;
MD5_CTX m_md5;
}
2. 非对称加密RSA
RSA 算法密钥长度越长,安全性越好,加密解密所需时间越长。
密钥长度
增长1倍,公钥操作所需时间增加约4倍,私钥操作所需时间增加约8倍,公私钥生成时间约增长16倍;
2.1 特点
- 秘钥是一个密钥对:
公钥,私钥- 公钥加密, 必须私钥解密
- 私钥加密, 必须公钥解密
- 加密强度比较高, 效率低
- 不会使用非对称加密, 加密特别大的数据
2.2 应用场景:
- 2.2.1 秘钥分发 -> 对称加密
- 核心思想: 加密的时候,
公钥加密, 私钥解密 - 分发步骤:
- 假设A, B两端
- A端生成了一个密钥对, 分发公钥, B端有了公钥
- B端生成一个对称加密的秘钥, 使用公钥加密 -> 密文
- B将密文发送给A
- A接收数据 -> 密文, 使用私钥对密文解密 -> 对称加密的秘钥
- 核心思想: 加密的时候,
- 2.2.2 签名 -> 验证数据是否被篡改, 验证数据的所有者
- 核心思想:
私钥加密, 公钥解密 - A, B两端, 假设A要发送数据
- A端生成一个密钥对, 将公钥进行分发, 自己留私钥
- 签名
- A对原始数据进行
哈希运算-> 哈希值 - A使用私钥对哈希值加密 -> 密文
- 将原始数据+密文发送给B
- A对原始数据进行
- 校验签名
- B接收数据: 密文 + 收到的原始数据
- 使用公钥对密文解密 -> 哈希值old
- 使用has算法对收到的数据进行哈希运算 -> 哈希值new
- 比较这两个哈希值
- 相同: 校验成功
- 不同: 失败
- 核心思想:
2.3 生成RSA密钥对:常用的API
#include <openssl/rsa.h>
// 申请一块内存, 存储了公钥和私钥
// 如果想得到RSA类型变量必须使用 RSA_new();
RSA *RSA_new(void);
void RSA_free(RSA *);
BIGNUM* BN_new(void);
void BN_free(BIGNUM*);
// 生成密钥对, 密钥对存储在内存中
int RSA_generate_key_ex(RSA *rsa, int bits, BIGNUM *e, BN_GENCB *cb);
参数:
- rsa: 通过RSA_new()获得
- bits: 秘钥长度, 单位: bit, 常用的长度 1024*n (n正整数)
- e: 比较大的数(5位以内)
- 通过 BN_new 得到对应的变量
- 初始化: BN_set_word(e, 12345);
- cb: 回调函数, 用不到, 直接写NULL
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
2.4.2 使用bio方式将秘钥写入磁盘
// 创建bio对象
// 密钥对写磁盘文件的时候, 需要编码 -> base64
// 封装了fopen
BIO *BIO_new_file(const char *filename, const char *mode);
参数:
- filename: 文件名
- mode: 文件打开方式和fopen打开方式的指定相同
int PEM_write_bio_RSAPublicKey(BIO* bp, const RSA* r);
int PEM_write_bio_RSAPrivateKey(BIO* bp, const RSA* r, const EVP_CIPHER* enc,
unsigned char* kstr, int klen, pem_password_cb *cb, void* u);
2.5 加密-读取秘钥
RSA* PEM_read_bio_RSAPublicKey(BIO* bp, RSA** r, pem_password_cb *cb, void* u);
RSA* PEM_read_bio_RSAPrivateKey(BIO* bp, RSA** r, pem_password_cb *cb, void* u);
参数:
- bp: 通过BIO_new_file();函数得到该对象
- r: 传递一个RSA* rsa指针的地址, 传出参数-> 公钥/私钥
- cb: 回调函数, 用不到, 指定为NULL
- u: 给回调传参, 用不到, 指定为NULL
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
RSA* PEM_read_RSAPublicKey(FILE* fp, RSA** r, pem_password_cb *cb, void* u);
RSA* PEM_read_RSAPrivateKey(FILE* fp, RSA** r, pem_password_cb *cb, void* u);
2.4.1 将密钥对写入磁盘
// 写入文件中的公钥私钥数据不是原始数据, 写入的编码之后的数据
// 是一种pem的文件格式, 数据使用base64进行编码
int PEM_write_RSAPublicKey(FILE* fp, const RSA* r);
int PEM_write_RSAPrivateKey(FILE* fp, const RSA* r, const EVP_CIPHER* enc,
unsigned char* kstr, int klen, pem_password_cb *cb, void* u);
参数:
- fp: 需要打开一个磁盘文件, 并且指定写权限
- r: 存储了密钥对
//////////////// - 私钥独有的参数
- enc: 指定的加密算法 -> 对称加密 -> NULL
- kstr: 对称加密的秘钥 -> NULL
- klen: 秘钥长度 -> 0
- cb: 回调函数, 用不到, NULL
- u: 给回调传参, 用不到, NULL
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
2.5 单独生成公钥或者私钥
// rsa公钥私钥类型是一样的: RSA类型
// 将参数rsa中的公钥提取出来
RSA *RSAPublicKey_dup(RSA *rsa);
- rsa参数: 秘钥信息
- 返回值: rsa公钥
// 将参数rsa中的私钥提取出来
RSA *RSAPrivateKey_dup(RSA *rsa);
- rsa参数: 秘钥信息
- 返回值: rsa私钥
2.4 生成密钥对:测试代码
2.4.1 将密钥对写入磁盘 - 代码主要部分
void generateRsaKey()
{
// 1. 创建rsa变量
RSA* rsa = RSA_new();
// 1.5 创建bignum对象, 并初始化
BIGNUM* e = BN_new();
BN_set_word(e, 12345);
// 2. 生成密钥对 -> 密钥对在内存中
RSA_generate_key_ex(rsa, 1024, e, NULL);
// 3. 将密钥对写入到磁盘
FILE* fp = fopen("public.pem", "w");
PEM_write_RSAPublicKey(fp, rsa);
fclose(fp);
// 写私钥
fp = fopen("private.pem", "w");
PEM_write_RSAPrivateKey(fp, rsa, NULL, NULL, 0, NULL, NULL);
fclose(fp);
}
运行成功之后生成公钥和私钥
2.4.2 使用bio方式将秘钥写入磁盘
BIO* bio = BIO_new_file("public-1.pem", "w");
PEM_write_bio_RSAPublicKey(bio, rsa);
// 释放资源
BIO_free(bio);
bio = BIO_new_file("private-1.pem", "w");
PEM_write_bio_RSAPrivateKey(bio, rsa, NULL, NULL, 0, NULL, NULL);
BIO_free(bio);
2.5 加密和解密
2.5.1 加密解密常用API
以块的方式进行加密的, 加密的数据长度, 不能大于秘钥长度
- 假设: 秘钥长度: 1024bit = 128byte
// 公钥加密
int RSA_public_encrypt(int flen, const unsigned char *from, unsigned char *to, RSA *rsa, int padding);
// 私钥解密
int RSA_private_decrypt(int flen, const unsigned char *from, unsigned char *to, RSA *rsa, int padding);
//////////////////////// 签名使用 /////////////////////////
// 私钥加密
int RSA_private_encrypt(int flen, const unsigned char *from, unsigned char *to, RSA *rsa, int padding);
// 公钥解密
int RSA_public_decrypt(int flen, const unsigned char *from, unsigned char *to, RSA *rsa, int padding);
参数:
- flen: 要加密/解密的数据长度
长度 0 < flen <= 秘钥长度-11
- from: 传入, 要加密/解密的数据
- to: 传出, 存储数据, 加密->存储密文, 解密->存储明文
- rsa: 秘钥: 公钥/私钥
- padding: 指定填充方案, 数据填充, 不需要使用者做
- RSA_PKCS1_PADDING -> 使用该方案会填充11字节
2.5.2 加密解密:测试代码
注意解密时候的返回值,容易出错
return string(buf,
len); //注意这里
// 公钥加密
string encryptPublicKey()
{
// 1. 准备要加密数据
string text = "让编程改变世界...";
// 2. 准备秘钥 -> 公钥
// 从磁盘文件读秘钥
// 使用bio的方式
BIO* bio = BIO_new_file("public-1.pem", "r");
RSA* pubKey = RSA_new();
if (PEM_read_bio_RSAPublicKey(bio, &pubKey, NULL, NULL) == NULL)
{
cout << "读公钥失败了..." << endl;
return string();
}
BIO_free(bio);
// 3. 加密 -> 密文
// 数据被加密之后, 长度和秘钥长度相同
// 通过函数计算秘钥长度
int keyLen = RSA_size(pubKey);
char *buf = new char[keyLen];
// 返回值就是密文长度
int len = RSA_public_encrypt(text.size(), (const unsigned char*)text.data(),
(unsigned char*)buf, pubKey, RSA_PKCS1_PADDING);
// 4. 将密文返回
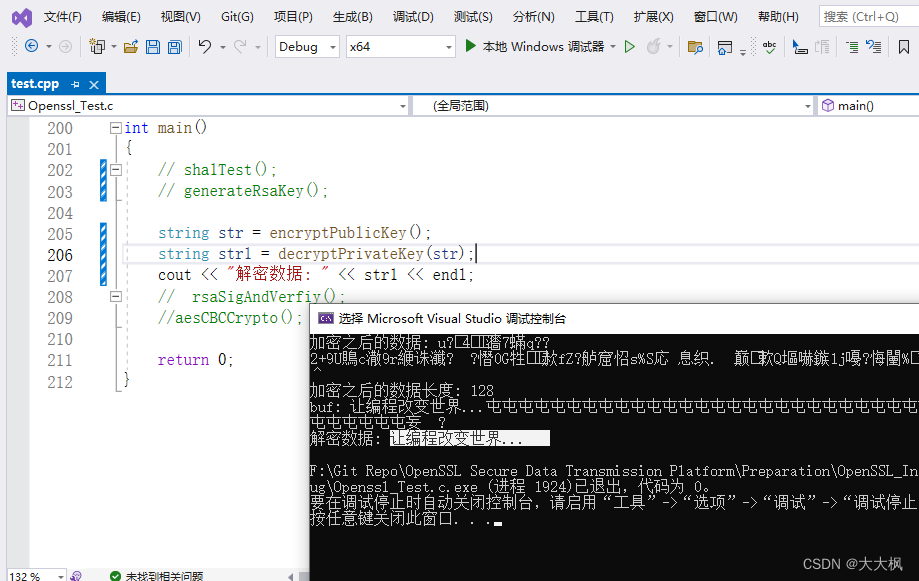
cout << "加密之后的数据: " << buf << endl;
cout << "加密之后的数据长度: " << len << endl;
return string(buf, len);
}
// 私钥解密
string decryptPrivateKey(string str)
{
// 1. 准备秘钥 ->私钥
// 从磁盘文件读秘钥
// 使用bio的方式
BIO* bio = BIO_new_file("private-1.pem", "r");
RSA* priKey = RSA_new();
if (PEM_read_bio_RSAPrivateKey(bio, &priKey, NULL, NULL) == NULL)
{
cout << "读私钥失败..." << endl;
return string();
}
BIO_free(bio);
// 解密 -> 明文
// 数据被加密之后, 长度和秘钥长度相同
// 通过函数计算秘钥长度
int keyLen = RSA_size(priKey);
char *buf = new char[keyLen];
// 返回值是解密之后的数据长度 == 原始数据长度
int len = RSA_private_decrypt(str.size(), (const unsigned char*)str.data(),
(unsigned char*)buf, priKey, RSA_PKCS1_PADDING);
// 4. 将明文返回
cout << "buf: " << buf << endl;
return string(buf, len); //注意这里
}
2.6 RSA签名和校验签名
2.6.1 签名和校验签名API
int RSA_sign(int type, const unsigned char *m, unsigned int m_length,
unsigned char *sigret, unsigned int *siglen, RSA *rsa);
参数:
- type: 使用的哈希算法
- NID_MD5
- NID_SHA1
- NID_SHA224
- .....
- m: 要进行签名的数据
- m_length: 要签名的数据长度
- 0 < m_length <= 秘钥长度-11
- sigret: 传出, 存储了签名之后的数据 -> 密文
- siglen: sigret密文长度
- rsa: 私钥
返回值: 判断函数状态
int RSA_verify(int type, const unsigned char *m, unsigned int m_length,
const unsigned char *sigbuf, unsigned int siglen, RSA *rsa);
参数:
- type: 使用的哈希算法, 和签名使用的哈希算法一致
- NID_MD5
- NID_SHA1
- NID_SHA224
- .....
- m: 进行签名的原始数据 -> 接收到的
- m_length: m参数字符串的长度
- sigbuf: 接收到的签名数据
- siglen: sigbuf接收到的签名数据的长度
- rsa: 公钥
返回值:
如果!=1: 失败
如果==1: 成功
2.6.2 签名和校验:测试代码
void rsaSigAndVerfiy()
{
// 1. 签名数据
string text = "让编程改变世界...";
// 2. 秘钥
RSA* pubKey = RSA_new();
RSA* priKey = RSA_new();
BIO* pubBio = BIO_new_file("public.pem", "r");
PEM_read_bio_RSAPublicKey(pubBio, &pubKey, NULL, NULL);
BIO_free(pubBio);
BIO* prilBio = BIO_new_file("private.pem", "r");
PEM_read_bio_RSAPrivateKey(prilBio, &priKey, NULL, NULL);
BIO_free(prilBio);
// 3. 签名
int len = RSA_size(priKey);
unsigned int outLen = 0;
unsigned char* out = new unsigned char[len];
RSA_sign(NID_sha1, (const unsigned char*)text.data(), text.size(), out, &outLen, priKey);
// 要给到用户的数据
string sigbuf((char*)out, outLen);
// 4. 验证签名
int ret = RSA_verify(NID_sha1, (const unsigned char*)text.data(), text.size(), (const unsigned char*)sigbuf.data(), sigbuf.size(), pubKey);
cout << "ret : " << ret << endl;
}
2.7 RSA封装成C++类
class MyRSA
{
public:
MyRSA();
~MyRSA;
// 生成密钥对
// 公钥加密
// 私钥解密
// 数据签名
// 验证签名
private:
RSA* pubkey;
RSA* pirKey;
}
3.对称加密AES
分组加密: 每组长度 -> 16byte, 128bit
秘钥长度: 16byte, 24byte, 32byte
每组明文和加密之后的密文长度相同
- 分组加密有不同的加密方式
- 五种密码分组模式
- 最常用: cbc -> 密文分组链接
- 需要一个初始化向量 -> 数组 -> 存储一个随机字符串 -> 分组长度相同
- 加密的和解密的时候都需要这个初始化向量
- 加解密的时候初始化向量的值必须相同
- 最常用: cbc -> 密文分组链接
- 五种密码分组模式
AES是一套对称密钥的密码术,目前已广泛使用,用于替代已经不够安全的DES算法。所谓对称密钥,就是说加密和解密用的是同一个密钥,消息的发送方和接收方在消息传递前需要享有这个密钥。和非对称密钥体系不同,这里的密钥是双方保密的,不会让任何第三方知道。
对称密钥加密法主要==基于块加密,选取固定长度的密钥,去加密明文中固定长度的块,生成的密文块与明文块长度一样。显然密钥长度十分重要,块的长度也很重要。如果太短,则很容易枚举出所有的明文-密文映射;如果太长,性能则会急剧下降。AES中规定块长度为128 bit,而密钥长度可以选择128, 192或256 bit== 。暴力破解密钥需要万亿年,这保证了AES的安全性。
3.1 AES 加解密的API:
3.1.1 生成加密/解密的Key
#include <openssl/aes.h>
# define AES_BLOCK_SIZE 16 // 明文分组的大小
// 加密的时候调用
// aes中的秘钥格式 AES_KEY
AES_KEY key;
// 封装加密时候使用的秘钥
int AES_set_encrypt_key(const unsigned char *userKey, const int bits, AES_KEY *key);
// 封装解密时候使用的秘钥
int AES_set_decrypt_key(const unsigned char *userKey, const int bits, AES_KEY *key);
| 参数名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| userkey | 对称加密的秘钥-> 字符串, 长度: 16, 24, 32byte |
| bites | 指定秘钥的长度: 单位->bit |
| key | 传出参数 |
3.1.2 CBC方式加密 - 密码分组链接模式
由最后一个参数决定是加密还是解密。
重点:length是16的整数倍
void AES_cbc_encrypt(const unsigned char *in, unsigned char *out,
size_t length, const AES_KEY *key,
unsigned char *ivec, const int enc);
参数:
- in: 要加密/解密的数据
- out: 传出参数
- 加密: 存储密文
- 解密: 存储明文
- length: 修改第一个参数in的长度
- (len = (字符串长度 + \0) % 16) == 0
- 如果不是在函数内部会自动填充
- 实际长度: ((len / 16) + 1 ) * 16
- key: 初始化之后的秘钥
- ivec: 初始化向量, 字符串 ==> 长度和分组长度相同
- enc: 指定数据要解密还是解密
- # define AES_ENCRYPT 1 -> 加密
- # define AES_DECRYPT 0 -> 解密
3.2 AES代码测试
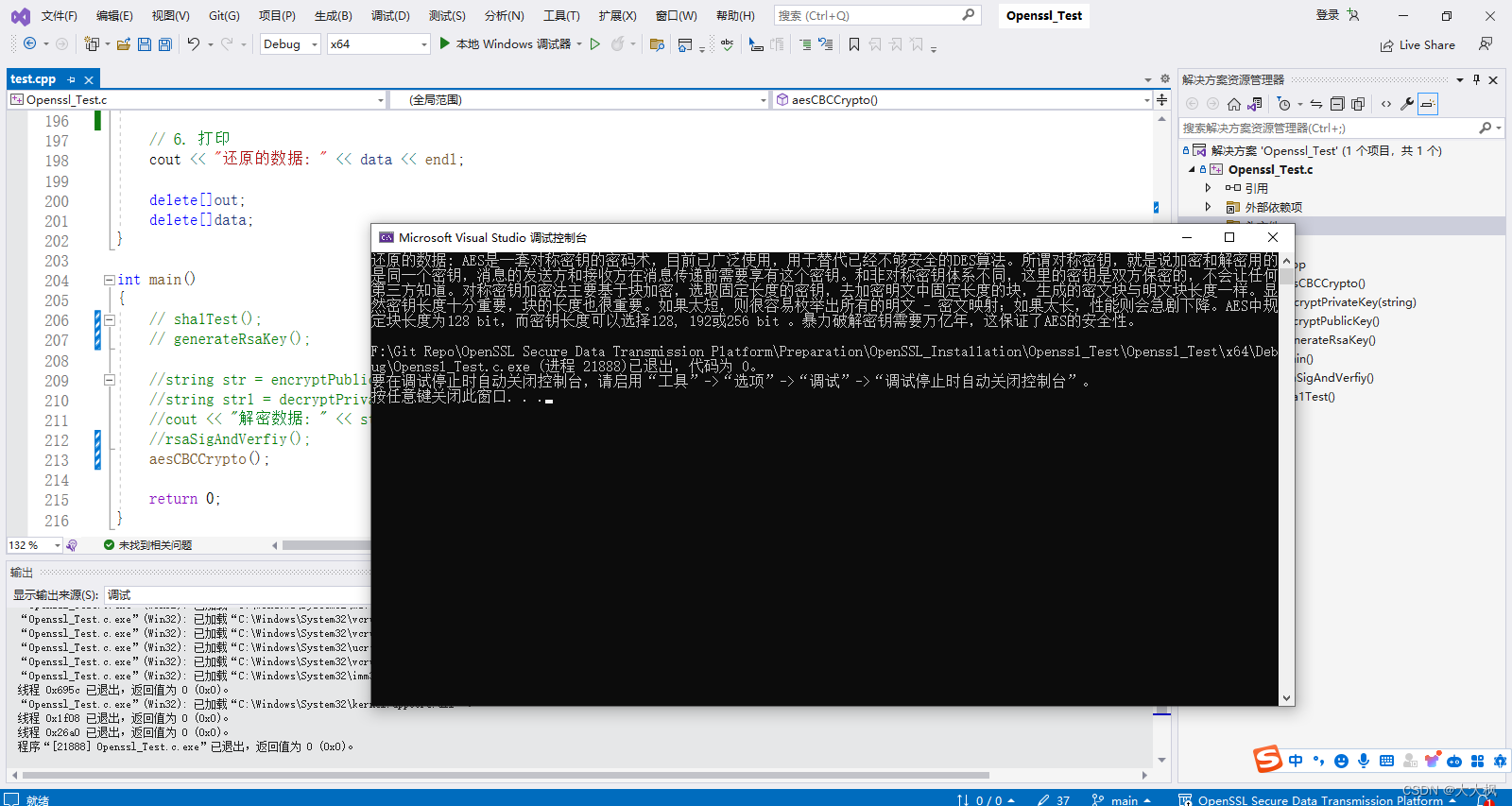
void aesCBCCrypto()
{
// 1. 准备数据
const char* pt = "AES是一套对称密钥的密码术,目前已广泛使用,用于替代已经不够安全的DES算法。所谓对称密钥,就是说加密和解密用的是同一个密钥,消息的发送方和接收方在消息传递前需要享有这个密钥。和非对称密钥体系不同,这里的密钥是双方保密的,不会让任何第三方知道。对称密钥加密法主要基于块加密,选取固定长度的密钥,去加密明文中固定长度的块,生成的密文块与明文块长度一样。显然密钥长度十分重要,块的长度也很重要。如果太短,则很容易枚举出所有的明文 - 密文映射;如果太长,性能则会急剧下降。AES中规定块长度为128 bit,而密钥长度可以选择128, 192或256 bit 。暴力破解密钥需要万亿年,这保证了AES的安全性。";
// 2. 准备秘钥
const char* key = "1234567887654321";
// 3. 初始化秘钥
AES_KEY encKey;
AES_set_encrypt_key((const unsigned char*)key, 128, &encKey);
// 4. 加密
// 计算长度
int length = 0;
int len = strlen((char*)pt) + 1;
if (len % 16 != 0)
{
length = ((len / 16) + 1) * 16;
}
else
{
length = len;
}
unsigned char* out = new unsigned char[length];
unsigned char ivec[AES_BLOCK_SIZE];
memset(ivec, 9, sizeof(ivec));
// 密文存储在out中
AES_cbc_encrypt((const unsigned char*)pt, out, length, &encKey, ivec, AES_ENCRYPT);
// 5. 解密
unsigned char* data = new unsigned char[length];
AES_KEY deckey;
memset(ivec, 9, sizeof(ivec));
AES_set_decrypt_key((const unsigned char*)key, 128, &deckey);
AES_cbc_encrypt(out, data, length, &deckey, ivec, AES_DECRYPT);
// 6. 打印
cout << "还原的数据: " << data << endl;
delete[]out;
delete[]data;
}