一、IIC子系统
两根线: scl:时钟线 sda:数据线
iic有4种信号:
起始信号(start):scl是高电平,sda下降沿
终止信号(stop):scl高电平,sda上升沿
应答信号(ack):第9个周期,sda是低电平
非应答信号(NACK:)第9个周期,sda维持高电平
iic总线特点: 串行同步半双工
iic总线的时序:
1)写时序
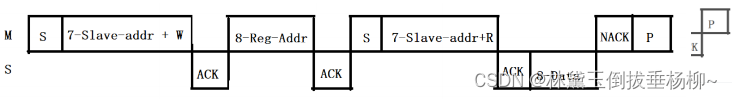
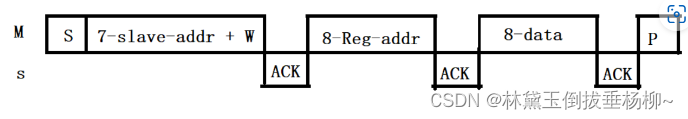 2)读时序
2)读时序
二、IIC设备驱动层API
struct device_driver
{
const char *name;
const struct of_device_id *of_match_table;
};
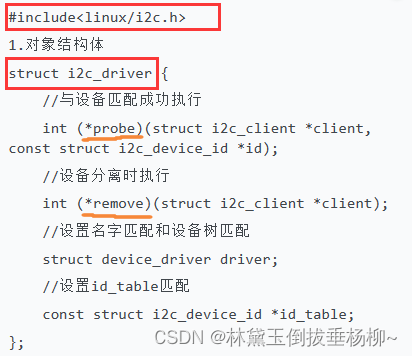
2.给对象分配空间并且初始化

3.注册
#define i2c_add_driver(struct i2c_driver *driver) \
i2c_register_driver(THIS_MODULE, driver)
4.注销
void i2c_del_driver(struct i2c_driver *driver)
5.一键注册宏
module_i2c_driver(__i2c_driver)
三、修改I2C1设备树节点以及添加si7006的子节点

四、struct i2c_client结构体
当驱动匹配设备信息成功后内核中就会存在一个struct i2c_client 对象,对象内部保存的是匹配成功的设备的信息以及总线相关的信息

五、i2c数据传输的函数
基于I2C总线进行数据传输
int i2c_transfer(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num)
adap:用于索引总线驱动的对象指针 client->adapter
msgs:要传输的一个或者多个消息, 一个消息是以起始信号作为出发点
num:传输的消息的数量
六、消息结构体 struct i2c_msg
一条消息中要包含从机地址、读写标志位以及消息的正文

根据时序来,有几个起始信号就要有几条消息
1)写消息的封装

2)读消息的封装

七、读取温湿度传感器
1.温湿度的读取时序:

2.温度和湿度的计算公式

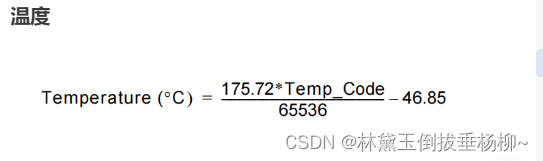
3.代码
head.h
#ifndef __HEAD_H__
#define __HEAD_H__
#define GET_HUM _IOR('m',1,int)//获取湿度的功能码
#define GET_TEM _IOR('m',0,int)//获取温度的功能码
#endifpdrv.c
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/i2c.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include "head.h"
unsigned int major;
struct class *cls;
struct device *dev;
struct i2c_client *client1;
// 封装函数读取温度和湿度
int read_hum_tem(char reg)
{
// 封装传输的消息
char r_buf[] = {reg};
short value;
struct i2c_msg r_msg[] = {
[0] = {
.addr = client1->addr,
.flags = 0,
.len = sizeof(r_buf),
.buf = r_buf,
},
[1] = {
.addr = client1->addr,
.flags = 1,
.len = 2,
.buf = (char *)&value,
},
};
//传输消息
int ret=i2c_transfer(client1->adapter,r_msg,2);
if(ret!=2)
{
printk("传输消息失败\n");
return -EIO;
}
return value;
}
// 封装操作方法
int si7006_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk("%s:%s:%d\n", __FILE__, __func__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
long si7006_ioctl(struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
int tem, hum;
int ret;
switch (cmd)
{
case GET_HUM: // 读取湿度
// 读取湿度的逻辑
hum = read_hum_tem(0XE5);
ret = copy_to_user((void *)arg, &hum, 4);
if (ret)
{
printk("copy_to_user err\n");
return ret;
}
break;
case GET_TEM: // 读取温度
// 读取温度的逻辑
tem = read_hum_tem(0XE3);
ret = copy_to_user((void *)arg, &tem, 4);
if (ret)
{
printk("copy_to_user err\n");
return ret;
}
break;
}
return 0;
}
int si7006_close(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk("%s:%s:%d\n", __FILE__, __func__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
// 定义操作方法结构体遍历并且初始化
struct file_operations fops = {
.open = si7006_open,
.unlocked_ioctl=si7006_ioctl,
.release = si7006_close,
};
// 给对象分配空间并且初始化
int i2c_probe(struct i2c_client *client, const struct i2c_device_id *id)
{
client1=client;
int ret;
// 字符设备驱动的注册
major = register_chrdev(0, "si7006", &fops);
if (major < 0)
{
printk("注册字符设备驱动失败\n");
ret = major;
goto out1;
}
printk("注册字符设备驱动成功\n");
// 设备节点的创建
// 向上提交目录
cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "si7006");
if (IS_ERR(cls))
{
printk("向上提交目录失败\n");
ret = PTR_ERR(cls);
goto out2;
}
printk("向上提交目录信息成功\n");
// 向上提交设备节点信息
dev = device_create(cls, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "si7006");
if (IS_ERR(dev))
{
printk("向上提交设备节点信息失败\n");
ret = PTR_ERR(dev);
goto out3;
}
printk("向上提交设备节点信息成功\n");
return 0;
out3:
class_destroy(cls);
out2:
unregister_chrdev(major, "si7006");
out1:
return ret;
}
int i2c_remove(struct i2c_client *client)
{
// 设备信息的注销
// 设备节点的销毁
// 驱动的注销
return 0;
}
// 定义设备树匹配的表
struct of_device_id oftable[] = {
{
.compatible = "hqyj,si7006",
},
{},
}; // 名字表的构建
// 分配驱动信息对象
struct i2c_driver i2c_drv = {
.probe = i2c_probe,
.remove = i2c_remove,
.driver = {
.name = "si7006",
.of_match_table = oftable,
},
};
// 一键注册宏
module_i2c_driver(i2c_drv);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
test.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include"head.h"
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
int tem,hum;
float tem1,hum1;
int fd=open("/dev/si7006",O_RDWR);
if(fd<0)
{
printf("设备文件打开失败\n");
exit(-1);
}
while(1)
{
//获取数据
ioctl(fd,GET_HUM,&hum);
ioctl(fd,GET_TEM,&tem);
//大小端转换
hum=ntohs(hum);
tem=ntohs(tem);
//计算数据
hum1=125.0*hum/65536-6;
tem1=175.72*tem/65536-46.85;
printf("tem=%f,hum=%f\n",tem1,hum1);
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}