文章目录
- Spring的发展历史
- AOT
- GraalVM
- SpringBoot实战AOT
- RuntimeHints
- 案例分析
- RuntimeHintsRegistrar
- SpringBoot中AOT核心代码
Spring的发展历史
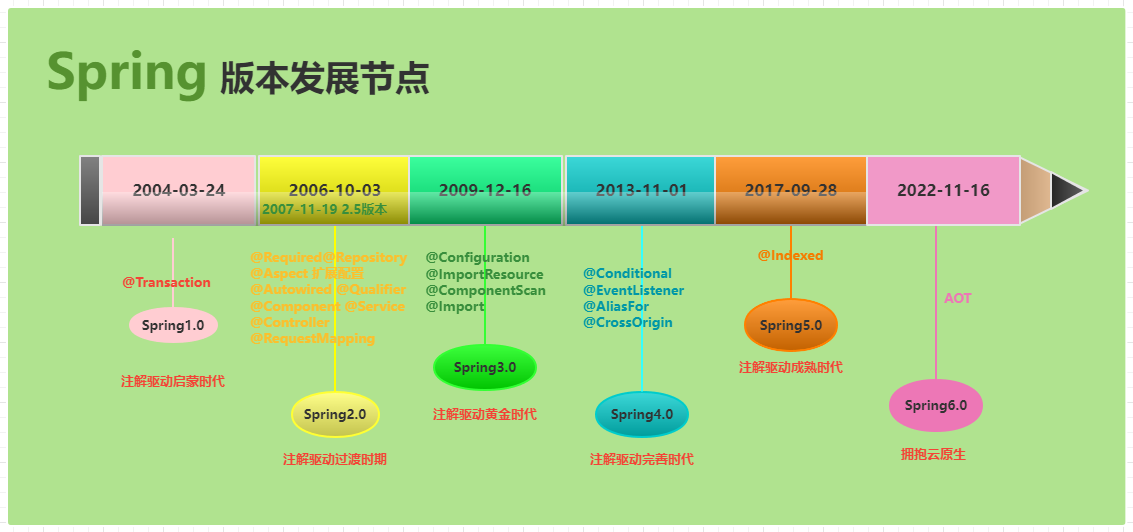
AOT
Spring 6.0的新特性Ahead of Time(AOT)编译是一种技术,可以提前将Spring应用程序编译成原生镜像,从而加快启动速度并降低内存消耗。AOT编译与传统的即时编译(JIT)相比,最大的优点是可以在程序运行前进行预编译,避免在程序运行时进行编译和内存消耗。
JIT(Just-in-time) 动态编译,即时编译,也就是边运行边编译,在程序运行时,动态生成代码,启动比较慢,编译时需要占用运行时的资源。
AOT,Ahead Of Time 指的是运行前编译,预先编译,AOT 编译能直接将源代码转化为机器码,内存占用低,启动速度快,可以无需 runtime 运行,直接将 runtime 静态链接至最终的程序中,但是无运行时性能加成,不能根据程序运行情况做进一步的优化,AOT 缺点就是在程序运行前编译会使程序安装的时间增加。
简单来讲:JIT即时编译的是在程序的运行过程中,将字节码转换为可在硬件上直接运行的机器码,并部署至托管环境中的过程。而 AOT 编译指的则是,在程序运行之前,便将字节码转换为机器码的过程。
GraalVM
Spring6 支持的 AOT 技术,GraalVM 就是底层的支持,Spring 也对 GraalVM 本机映像提供了一流的支持。GraalVM 是一种高性能 JDK,旨在加速用 Java 和其他 JVM 语言编写的应用程序的执行,同时还为 JavaScript、Python 和许多其他流行语言提供运行时。 GraalVM 提供两种运行 Java 应用程序的方法:在 HotSpot JVM 上使用 Graal 即时 (JIT) 编译器或作为提前 (AOT) 编译的本机可执行文件。 GraalVM 的多语言能力使得在单个应用程序中混合多种编程语言成为可能,同时消除了外语调用成本。GraalVM 向 HotSpot Java 虚拟机添加了一个用 Java 编写的高级即时 (JIT) 优化编译器。
GraalVM 具有以下特性:
- 一种高级优化编译器,它生成更快、更精简的代码,需要更少的计算资源
- AOT 本机图像编译提前将 Java 应用程序编译为本机二进制文件,立即启动,无需预热即可实现最高性能
- Polyglot 编程在单个应用程序中利用流行语言的最佳功能和库,无需额外开销
- 高级工具在 Java 和多种语言中调试、监视、分析和优化资源消耗
SpringBoot实战AOT
在SpringBoot项目中通过AOT来提前编译我们的项目。
新建一个Maven项目。添加相关的依赖
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.2</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
添加相关的SpringBoot插件
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.graalvm.buildtools</groupId>
<artifactId>native-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
编写一点简单的代码测试,打开 x64 Native Tools Command Prompt for VS 2019 ,切换到工程目录下
执行 mvn -Pnative native:compile 进行编译,编译成功就会在target目录下生成 EXE 文件,后续执行该文件就可以。
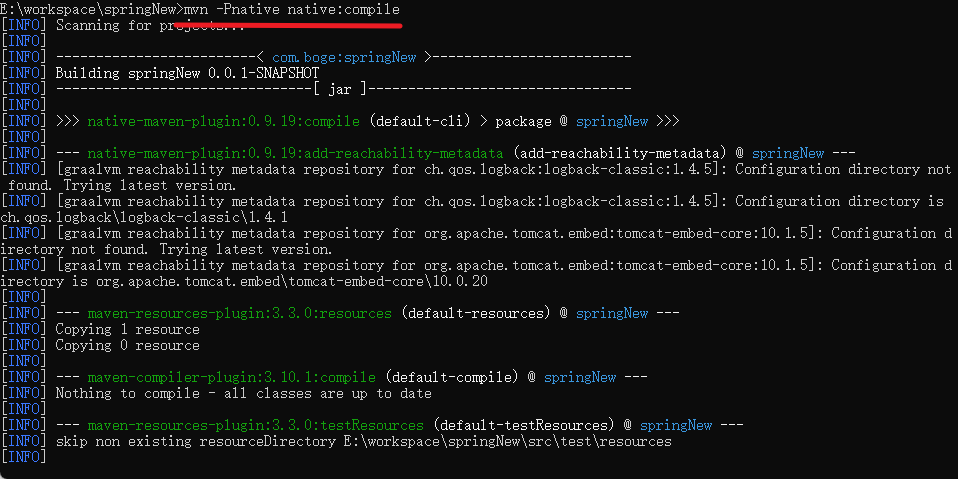
双击执行exe文件,会发现速度快很多
RuntimeHints
与常规 JVM 运行时相比,将应用程序作为本机映像运行需要额外的信息。例如,GraalVM 需要提前知道组件是否使用反射。同样,除非明确指定,否则类路径资源不会在本机映像中提供。因此,如果应用程序需要加载资源,则必须从相应的 GraalVM 原生图像配置文件中引用它。
APIRuntimeHints在运行时收集反射、资源加载、序列化和 JDK 代理的需求。
案例分析
声明个普通的实体类型
public class UserEntity {
public String hello(){
return "hello ...";
}
}
在控制器中通过反射来操作处理
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
String res = "hello";
try {
Method hello = UserEntity.class.getMethod("hello");
res = (String)hello.invoke(UserEntity.class.newInstance(),null);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return res;
}
通过命令编译为 exe 文件
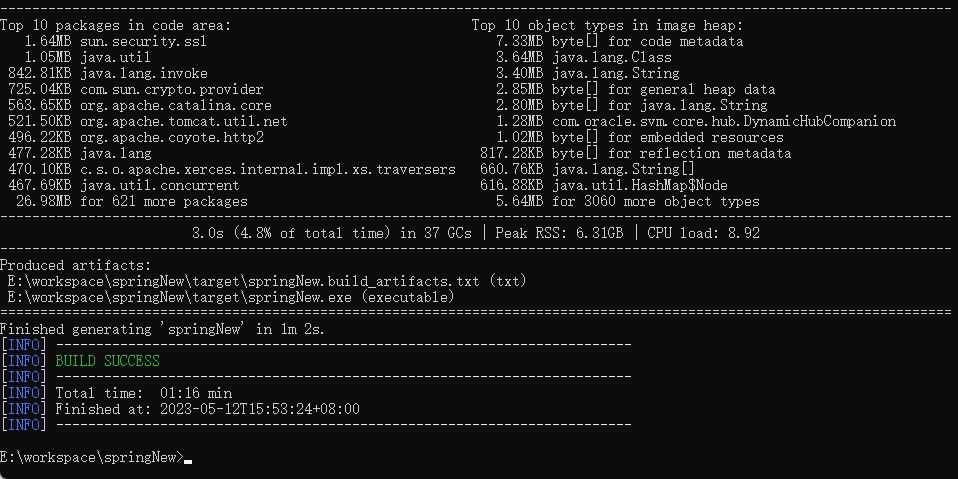
运行exe文件后,通过浏览器发起请求。
在HelloController中。通过反射的方式使用到了UserEntity的无参构造方法。如果不做任何处理。那么打成二进制可执行文件后是执行不了的,可以通过 Runtime Hints 机制来处理。
RuntimeHintsRegistrar
官网提供的解决方案,自定义一个RuntimeHintsRegistrar接口的实现类,然后把该实现类注入到Spring中
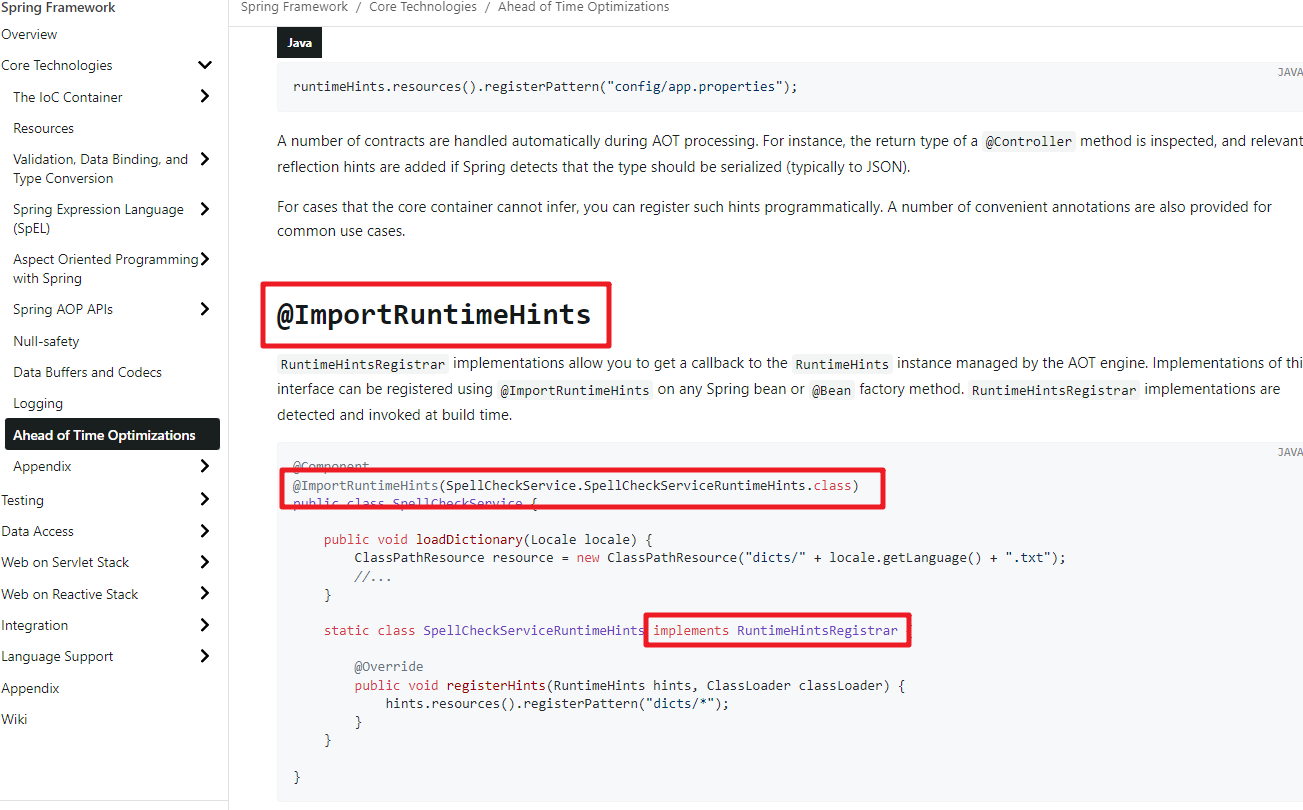
@RestController
@ImportRuntimeHints(HelloController.UserEntityRuntimeHints.class)
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
String res = "hello";
try {
Method hello = UserEntity.class.getMethod("hello");
res = (String)hello.invoke(UserEntity.class.newInstance(),null);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return res;
}
static class UserEntityRuntimeHints implements RuntimeHintsRegistrar{
@Override
public void registerHints(RuntimeHints hints, ClassLoader classLoader) {
try {
hints.reflection().registerConstructor(UserEntity.class.getConstructor(), ExecutableMode.INVOKE);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
SpringBoot中AOT核心代码
执行 mvn -Pnative native:compile时会执行GraalVM中的相关指令。最终会调用SpringApplicationAotProcessor中的main 方法来完成相关提前编译操作。
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int requiredArgs = 6; // 调用main方法接收的有6个参数
Assert.isTrue(args.length >= requiredArgs, () -> "Usage: " + SpringApplicationAotProcessor.class.getName()
+ " <applicationName> <sourceOutput> <resourceOutput> <classOutput> <groupId> <artifactId> <originalArgs...>");
// 获取SpringBoot项目的入口class
Class<?> application = Class.forName(args[0]);
// 通过传递过来的参数完成相关生成目录的配置
Settings settings = Settings.builder().sourceOutput(Paths.get(args[1])).resourceOutput(Paths.get(args[2]))
.classOutput(Paths.get(args[3])).groupId((StringUtils.hasText(args[4])) ? args[4] : "unspecified")
.artifactId(args[5]).build();
String[] applicationArgs = (args.length > requiredArgs) ? Arrays.copyOfRange(args, requiredArgs, args.length)
: new String[0];
// 执行 process 方法
new SpringApplicationAotProcessor(application, settings, applicationArgs).process();
}
public final T process() {
try {
// 设置状态
System.setProperty(AOT_PROCESSING, "true");
return doProcess(); // 处理的核心方法
}
finally {
System.clearProperty(AOT_PROCESSING);
}
}
@Override
protected ClassName doProcess() {
deleteExistingOutput(); // 删除已经存在的目录
// 启动SpringBoot服务 但是不会做扫描bean
GenericApplicationContext applicationContext = prepareApplicationContext(getApplicationClass());
return performAotProcessing(applicationContext);
}
@Override
protected GenericApplicationContext prepareApplicationContext(Class<?> application) {
return new AotProcessorHook(application).run(() -> {
Method mainMethod = application.getMethod("main", String[].class);
return ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod(mainMethod, null, new Object[] { this.applicationArgs });
});
}
此时会执行启动类中的main方法来启动SpringBoot
在启动中创建Spring上下文对象时会做如下的处理
private ConfigurableApplicationContext createContext() {
if (!AotDetector.useGeneratedArtifacts()) {
return new AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext();
}
return new ServletWebServerApplicationContext();
}
如果没有使用AOT,那么就会创建AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext,它里面会添ConfigurationClassPostProcessor,从而会解析配置类。而如果使用了AOT,则会创建ServletWebServerApplicationContext,它就是一个空容器,它里面没有ConfigurationClassPostProcessor,所以后续不会触发扫描了。