目录
1 模拟大规模充电汽车充电行为
2 Matlab部分代码实现
3 Matlab代码实现
1 模拟大规模充电汽车充电行为
电动汽车EV(Electric Vehicle)具有清洁环保、高效节能的优点,不仅能缓解化石能源危机,而且能够有效地减少温室气体的排放。2015年10月,国务院发布加快EV充电基础设施建设的指导意见,指出到2020年充电基础设施能满足500万辆EV充电需求,预计未来几年我国EV的保有量将大幅增长。然而,规模化EV的无序充电会加大电网负荷的峰谷差,并对电力系统的规划、配电网的电能质量和经济运行以及稳定性带来显著的影响,反之.对EV的充电行为进行有序优化控制,充分发挥EV作为分布式储能元件的优势,能够实现削峰填谷、平抑可再生能源出力波动的功能,并为电网提供调峰、调频等辅助服务。
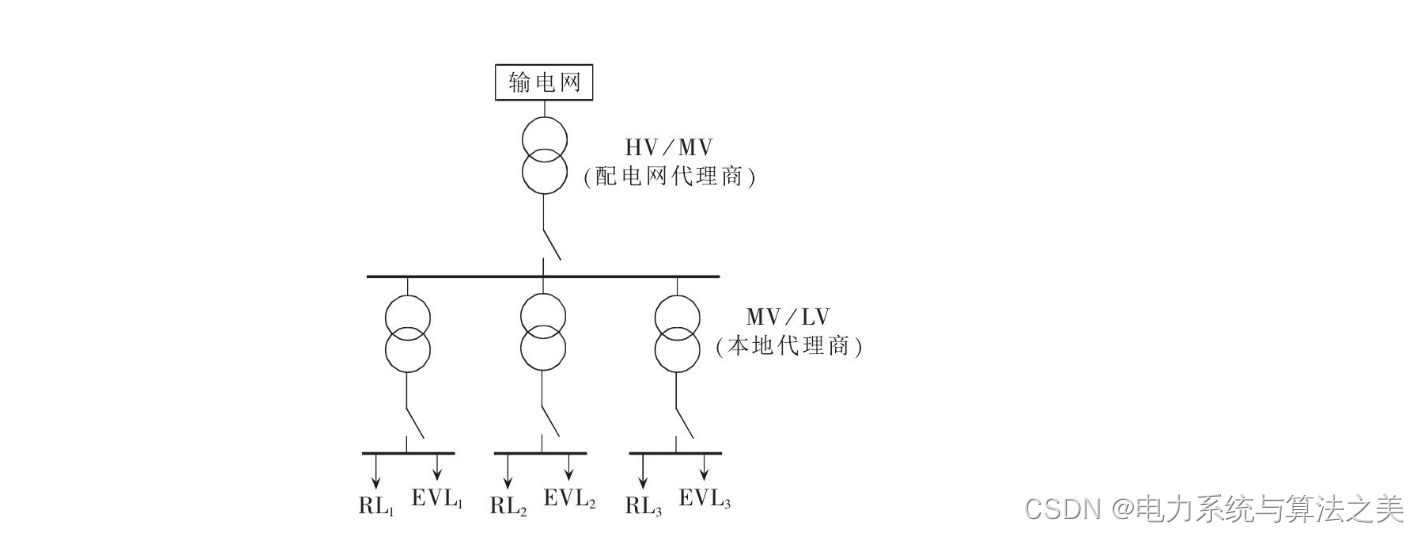
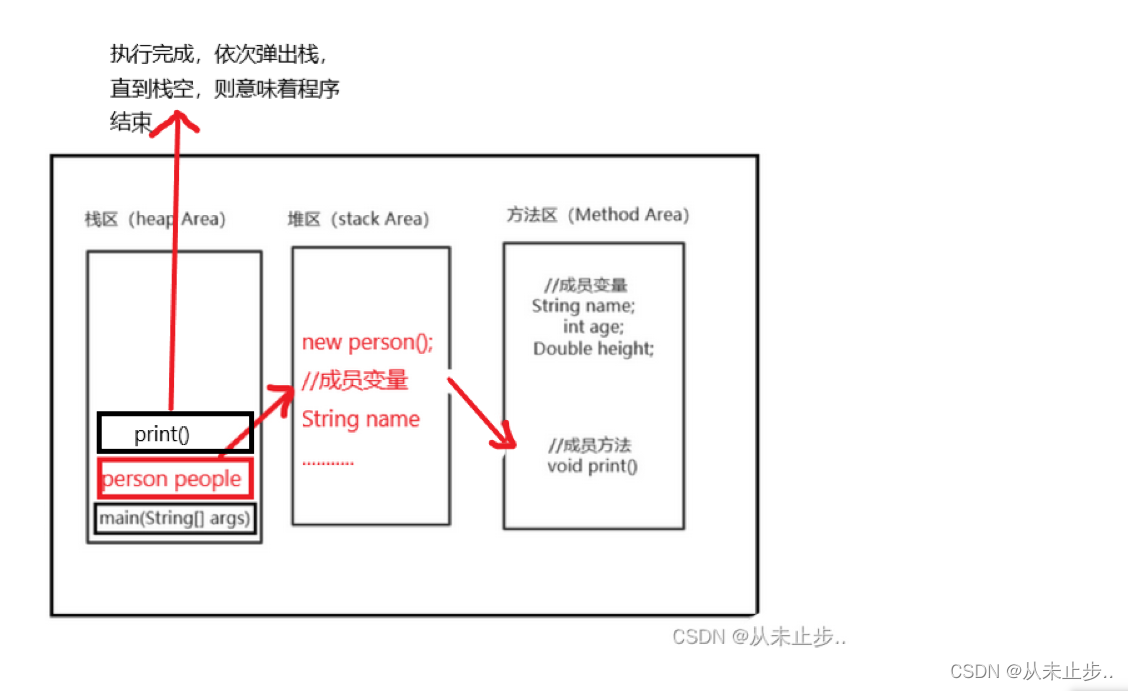
下图为大规模EV分散接入配电网的场景示意图。EV的管理框架分为配电网代理商、本地代理商和EV 3个层次。配电网代理商分布在高中压HVIMV(High VoltageMedium Voltage)变电层中,负责配电网的安全稳定控制以及EV的有序协调控制;本地代理商分布在中低压MVLV(Mediuim VoltageLow Voltage)变电层中,负责区域EV充电负荷的管控。充电站连接在配电变压器下,配电变压器下除了EV负荷EVL(EV Load)外,还有常规的居民负荷RL(Residential Load)。
EV进入充电站后,充电智能终端可以获取电池的总容量、荷电状态SoC(State Of Charge)等信息,并通过以太网或专用无线网络提交给本地代理商;用户设置取车时刻以及充电预期荷电状态,充电结束后按实际充电电量向本地代理商支付费用。本地代理商将EV的状态信息和电量需求信息汇集后上传给配电网代理商。配电网代理商采取分时段实时滚动优化的控制策略,当有新的EV接入电网时,更新EV的充电需求信息,执行优化,控制算法,并将充电计划分区下达给各个本地代理商,由本地代理商执行对管控区域内EV的充电控制。
2 Matlab部分代码实现
function [will_charge, best_prior, best_idx] = ...
CalChargingPrior(is_necessary, cur_soc, arrMCost, ...
pindex_start, pindex_end)
global TOU_EPrice
global solutions
global battery_features
% debug by fei
if (pindex_end - pindex_start + 1) < battery_features.fcharge_periods
error
end
% 优先权重系数
if solutions.start_charging == 4 %如果是组合策略,用上所有系数
W = solutions.w_coeff;
% 剩余SOC/最低SOC
u_s = 1.5 - cur_soc / battery_features.lowest_soc;
else
W = zeros(1, 4);
W(solutions.start_charging) = 1;
W(4) = 1;
end
% 是否必须充电
if is_necessary
u_s = 10000; %inf
else
u_s = 0;
end
nPrior = length(arrMCost);
% 从某个时刻开始充电的平均电价:元/(瓦*时段)
%arrMCost = [];
% TOC平均电价:元/(瓦*时段)
nMTOC = TOU_EPrice.mprice;
% 充电需用时段
nTch = single( battery_features.fcharge_periods );
% 剩余空闲时段
nTidle = pindex_end - pindex_start + 1;
arrTidle = single(nTidle) : -1 : nTch;
% 随机优先 [0 1]
nRndPr = round(rand);
arrRndPr = single( nRndPr * rand(1, nPrior) );
% 计算不同时段的充电优先程度
arrPrior = W(1)*arrRndPr + ...
W(2)*(1.5 - arrMCost ./ nMTOC) + ...
W(3)*(1.5 - nTch ./ arrTidle) + ...
u_s + W(4);
% 最优充电级别与时段
[p, i] = max(arrPrior);
best_prior = p;
best_idx = pindex_start + i - 1;
% 是否建议充电
will_charge = (best_prior > 0.5);
end% 根据不同策略,计算起始充电时段
function [start_cperiod, end_cperiod] = CalChargingPeriods(is_necessary, cur_soc, ...
pindex_start, pindex_end)
%global solutions
global battery_features
%global mc_params
%global TOU_EPrice
% 初始参数
start_cperiod = 0;
end_cperiod = 0;
earliest = pindex_start;
latest = pindex_end - battery_features.fcharge_periods + 1;
% 计算从某一时段起充电所需平均电价
arrMCost = CalChargePrices(earliest:latest);
% 根据策略,计算每一时段充电优先级
[will_charge, best_prior, best_idx] = ...
CalChargingPrior(is_necessary, cur_soc, arrMCost, pindex_start, pindex_end);
% 计算策略下的最佳充电起止时间
if will_charge
start_cperiod = best_idx;
end_cperiod = start_cperiod + battery_features.fcharge_periods - 1;
end
end% m_w_load: 一天中电网各时段负荷平均值,periods_per_day X mean_load
% m_w_charged: 一天中EV各时段充电平均值,periods_per_day X mean_charge
% m_real_trv:一天中EV各时段出行次数平均值,periods_per_day X mean_real_travel
% m_plan_trv:一天中EV各时段计划出行次数平均值,periods_per_day X mean_plan_travel
function [Y, Rmp, Rsc, Rt] = CalIndices(m_w_load, m_w_charged, ...
m_real_trv, m_plan_trv, is_print)
global TOU_EPrice
% W1 + W2 + W3 = 1.0
% W1 * 0.275 = W2 * 0.440 = W3 * 0.975 = Si
%
% Mi = [0.275 0.440 0.975]
% Wi = [0.5455 0.3409 0.1538]
% Si = [0.15 0.15 0.15]
% 指标统计范围 及 权重系数
RAGmp = [0.05 0.25]; RAGsave=[0.15 0.75]; RAGtrip=[0.95 1.0];
Wi = [0.4 0.3 0.3];
% 谷峰比 = 充电谷值/充电峰值
% nWValley = min(m_w_load);
% nWPeak = max(m_w_load);
% Rpv = nWValley / nWPeak;
% 均峰比 = 充电均值/充电峰值
nWMeanLoad = mean(m_w_load);
nWPeakLoad = max(m_w_load);
Rmp = nWMeanLoad / nWPeakLoad;
% 用户节省电费率 = 1 - 实际电费/最高电费
nRealCost = sum(m_w_charged .* TOU_EPrice.day_prices);
nMaxCost = sum(m_w_charged .* max(TOU_EPrice.day_prices));
Rsc = 1 - nRealCost / nMaxCost;
% 顺利出行率 = 实际里程/计划里程
nRealTrv = sum(m_real_trv);
nPlanTrv = sum(m_plan_trv);
Rt = nRealTrv / nPlanTrv;
% Rmp = 0.218;
% Rsc = 0.193;
% Rt = 0.972;
% 综合指标:均峰比,节能率,出行率
Y = Wi(1) * (Rmp - min(RAGmp)) / (max(RAGmp) - min(RAGmp)) + ...
Wi(2) * (Rsc - min(RAGsave)) / (max(RAGsave) - min(RAGsave)) + ...
Wi(3) * (Rt - min(RAGtrip)) / (max(RAGtrip) - min(RAGtrip));
if isnan(Y)
Y = 0.0;
end
% 输出结果
if is_print
fprintf('----电网负荷:峰值= %d 瓦;均值= %d 瓦;均峰比= %f----\n', nWPeakLoad, nWMeanLoad, Rmp);
fprintf('----居民用电费用:实际电费= %f 元;最高电费= %d 元;节省率= %f----\n', nRealCost, nMaxCost, Rsc);
fprintf('----顺利出行情况:实际出行里程= %f 公里;计划出行里程= %d 公里;出行率= %f----\n', nRealTrv, nPlanTrv, Rt);
fprintf('----综合指标:Y= %f----\n', Y);
end
endfunction [all_indices, mday_indices] = EVPowerLoad(varargin)
global solutions
global mc_params
%% 初始化变量
[nTerms, nEVs] = Initial(varargin);
%% 模拟 n天 m辆电动汽车
if ~mc_params.only_show_results
for t=1:nTerms
% for ev_id=1:total_EV
all_indices = Simulate(t);
% end
end
end
%% 结果统计: 峰谷差,出行受影响概率,充电价格,加入噪声出行等
result = TempResult('load');
[grid, ev_behaviour, mday_indices] = StatisticPowerLoad(result);
end
%% initial parameters
function [nTerms, nEVs] = Initial(params)
%% 定义常量
global mc_params % MC 参数
global battery_features % 电池特性
global pile_power % 电桩特性
global solutions % 策略
global behaviours % 一天用户行为(EVs X Day_Periods)
%global all_behaviours % 所有统计时间的用户行为(EVs X All_Periods)
global t_periods % 所有统计时段
global g2v_features % 充电特性
global TOU_EPrice % 分时电价
global PDF_Travel % 服从一定概率分布的出行行为
%% 指定参数运行
if size(params, 2) > 0
nTerms = params{1};
nDaysPT = params{2};
nEVs = params{3};
chargingStrategy = params{4};
chargingWCoeff = params{5};
chargingMinSOC = params{6};
isOutput = params{7};
% 用于存储中间结果,而不用保存成文件
saveResult = false;
showResultOnly = false;
else % default values
% clear all
clc
close all
% 自定义参数值
nTerms = 4;
nDaysPT = 25;
nEVs = 240000; %EV数量: 2800 5000 62500 240000
chargingStrategy = 4;
chargingWCoeff = [0.1512,0.7384,0.1105,0.0196];%ones(1, 4) * 0.25;
chargingMinSOC = 0.5686;%0.2;
isOutput = true;
saveResult = true; %default:true;
showResultOnly = true; %default:false;
seed=15;
randn('state',seed);
rand('state',seed);
end
%% 初始化常量
mc_params.output = isOutput; %是否输出结果
mc_params.cur_day = 1; %当前天数
%mc_params.cur_ev = 1; %当前汽车ID
mc_params.periods_per_day = 96; %一天划分为若干时段
mc_params.total_days = nDaysPT; %每期模拟天数
mc_params.all_days = nTerms * mc_params.total_days; %总共模拟天数
mc_params.mins_per_period = (24 * 60) / ...
mc_params.periods_per_day; %每个时段的时长
mc_params.total_periods = mc_params.periods_per_day * ...
(mc_params.total_days + 1); %时段总数
mc_params.total_EVs = nEVs;
mc_params.cperiod_start_id = 0;
mc_params.cperiod_end_id = 0;
mc_params.cperiods = [];
mc_params.eday_soc = ones(nEVs, 1, 'single'); %初始所有EV的SOC为1.0
mc_params.save_result = saveResult;
mc_params.memory_result = []; %用于存储中间结果,而不用保存成文件
mc_params.only_show_results = showResultOnly; %只输出统计结果
battery_features.capacity = 100; %电池容量
battery_features.voltage = 230; %电池电压
battery_features.power = battery_features.capacity * ...
battery_features.voltage; %电池总能量
battery_features.efficiency = 0.3; %充电效率
battery_features.fcharge_duration = 5; %充满时间
battery_features.full_soc = 0.9; %soc > 此状态,即认为电池充满
battery_features.lowest_soc = chargingMinSOC; %soc < 此状态,必须充电
battery_features.power_consume_per_km = 0.125e3; %耗能
% 满充所需分钟数 及 时段数
battery_features.fcharge_minutes = battery_features.fcharge_duration * 60;
battery_features.fcharge_periods = ceil( battery_features.fcharge_minutes / mc_params.mins_per_period );
pile_power = 15e3; %充/放电功率
solutions.start_charging = chargingStrategy; %起始充电策略:1.随机充电;2.电价引导充电;3.停车即充电;4.组合策略
solutions.w_coeff = chargingWCoeff; %各种充电影响因素的权重
solutions.enable_discharge = false; %允许V2G的放电模式
% 电动汽车类型
%EV_type = {'bus', 'taxis', 'official_car', 'private_car'};
% 1 X (模拟天数 * 每天时段数)
t_periods = CreatePeriods();
% 计算每时段电网耗用能量 (Wh)
g2v_features.grid_w_consumed = mc_params.mins_per_period / 60 * pile_power;
% 计算每时段EV所充能量 (Wh)
g2v_features.ev_w_charged = g2v_features.grid_w_consumed * battery_features.efficiency;
% 加载分时电价表
TOU_EPrice = CreateEPriceList();
% 清除结果数据
if ~mc_params.only_show_results
ClearResults();
end
% 加载概率密度函数
load './data/fitness_travel.mat';
PDF_Travel = pdf_travel;
end
%% simulate one day
function all_indices = Simulate(t)
global mc_params
global behaviours
%global t_periods
mc_params.cur_day = t;
%mc_params.cur_ev = ev_id;
%w_day = mod( (d-1), 7 );
%% clear all behaviours
ClearAllBehaviours();
%fprintf('-----模拟第 %d 天-----\n', mc_params.cur_day);
%% make the driving & charging plan for all days
MakeDaysPlan();
%% update all EVs
UpdateEVs();
%% formating data
[grid, ev_behaviour, y_indices] = StatDataFormat();
%% combine data of everyday
all_indices = CombineData(grid, ev_behaviour, y_indices);
%% update params
UpdateMCParams();
end
function all_periods = CreatePeriods()
global mc_params
% construct the period array
all_periods = int32( 0 : (mc_params.total_periods - 1) ) * ...
mc_params.mins_per_period;
end
function ClearAllBehaviours()
global behaviours
% init array for EV behaviours
behaviours = [];
behaviours.v_is_driving = logical([]);
behaviours.v_plan_driving = logical([]);
behaviours.v_driving_km_pp = single([]);
behaviours.v_driving_cost_power = single([]);
behaviours.v_able_charge = logical([]);
behaviours.v_is_charging = logical([]);
behaviours.v_ev_w_charged = single([]);
behaviours.v_ev_w_discharged = single([]);
behaviours.grid_power_load = single([]);
behaviours.soc = single([]);
end
function ClearResults()
global mc_params
global solutions
ndays = mc_params.all_days;
% init & save temporary data
result.grid.power_load = zeros(ndays, mc_params.periods_per_day, 'single');
result.grid.power_charged = zeros(ndays, mc_params.periods_per_day, 'single');
result.grid.power_V2G = zeros(ndays, mc_params.periods_per_day, 'single');
result.ev_behaviour.trv_num_per_period = zeros(ndays, mc_params.periods_per_day, 'int32');
result.ev_behaviour.plan_trv_num_per_period = zeros(ndays, mc_params.periods_per_day, 'int32');
result.ev_behaviour.cha_num_per_period = zeros(ndays, mc_params.periods_per_day, 'int32');
result.ev_behaviour.dischar_num_per_period = zeros(ndays, mc_params.periods_per_day, 'int32');
result.y_indices = zeros(ndays, 1, 'single');
TempResult('save', result);
clear 'result';
end
function all_indices = CombineData(grid, ev_behaviour, y_indices)
global behaviours
%global all_behaviours
global solutions
global mc_params
ndays = mc_params.all_days;
cur_day = ((mc_params.cur_day - 1) * mc_params.total_days + 1) : ...
mc_params.cur_day * mc_params.total_days;
% 加载临时数据
result = TempResult('load');
% 合并每天的电网负荷及EV行为
result.grid.power_load(cur_day, :) = grid.power_load;
result.grid.power_charged(cur_day, :) = grid.power_charged;
result.grid.power_V2G(cur_day, :) = grid.power_V2G;
result.ev_behaviour.trv_num_per_period(cur_day, :) = ev_behaviour.trv_num_per_period;
result.ev_behaviour.plan_trv_num_per_period(cur_day, :) = ev_behaviour.plan_trv_num_per_period;
result.ev_behaviour.cha_num_per_period(cur_day, :) = ev_behaviour.cha_num_per_period;
result.ev_behaviour.dischar_num_per_period(cur_day, :) = ev_behaviour.dischar_num_per_period;
result.y_indices(cur_day, :) = y_indices;
% save temporary data
TempResult('save', result);
% clear data from memory
all_indices = result.y_indices;
clear 'result';
end
function UpdateMCParams()
global mc_params
global behaviours
% clear mc prams
mc_params.total_periods = mc_params.periods_per_day * ...
(mc_params.total_days + 1); %时段总数
mc_params.cperiod_start_id = 0;
mc_params.cperiod_end_id = 0;
mc_params.cperiods = [];
% record soc for all EVs when one day is ending
mc_params.eday_soc = behaviours.soc(:, end);
end
function [is_necessary, soc_start] = IsNecessaryCharge(ev_id, pindex_start, pindex_end)
%global behaviours
global battery_features
% soc低于0.2时必须充电
soc_start = GetPreviousSOC(ev_id, pindex_start);
is_necessary = (soc_start < battery_features.lowest_soc);
end电动汽车EV(Electric Vehicle)具有清洁环保、高效节能的优点,不仅能缓解化石能源危机,而且能够有效地减少温室气体的排放。2015年10月,国务院发布加快EV充电基础设施建设的指导意见,指出到2020年充电基础设施能满足500万辆EV充电需求,预计未来几年我国EV的保有量将大幅增长。然而,规模化EV的无序充电会加大电网负荷的峰谷差,并对电力系统的规划、配电网的电能质量和经济运行以及稳定性带来显著的影响,反之.对EV的充电行为进行有序优化控制,充分发挥EV作为分布式储能元件的优势,能够实现削峰填谷、平抑可再生能源出力波动的功能,并为电网提供调峰、调频等辅助服务。
下图为大规模EV分散接入配电网的场景示意图。EV的管理框架分为配电网代理商、本地代理商和EV 3个层次。配电网代理商分布在高中压HVIMV(High VoltageMedium Voltage)变电层中,负责配电网的安全稳定控制以及EV的有序协调控制;本地代理商分布在中低压MVLV(Mediuim VoltageLow Voltage)变电层中,负责区域EV充电负荷的管控。充电站连接在配电变压器下,配电变压器下除了EV负荷EVL(EV Load)外,还有常规的居民负荷RL(Residential Load)。
3 Matlab代码实现
完整Matlab代码实现:

![[附源码]计算机毕业设计Node.jsBuff饰品交易平台论文(程序+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2f052b5af5ef4a12ab836dc771753bea.png)



![[附源码]Nodejs计算机毕业设计焦作旅游网站Express(程序+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3ad172350b35487681b6d91d493a42c4.png)