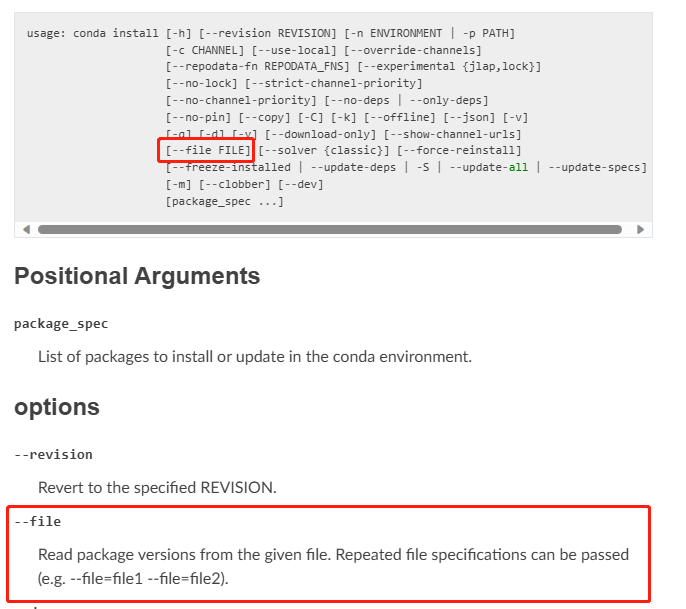
文章目录
- 0、整体框架
- 1、imageProjection —— 点云分割
- 0. main()
- 1. cloudHandler()
- 2. copyPointCloud()
- 3. findStartEndAngle()
- 4. projectPointCloud()
- 5. groundRemoval()
- 6. cloudSegmentation()
- 7. labelComponents()
- 8. publishCloud()
- 9. resetParameters()
- 2、featureAssociation —— 特征提取与匹配
- 0. main()
- 1. runFeatureAssociation()
- 2. adjustDistortion()
- 3. calculateSmoothness()
- 4. markOccludedPoints()
- 5. extractFeatures()
- 6. updateInitialGuess()
- 7. updateTransformation()
- 8. findCorrespondingSurfFeatures()
- 9. calculateTransformationSurf()
- 10. integrateTransformation()
- 11. publishOdometry()
- 12. publishCloudsLast()
- 3、mapOptimization —— 图的优化
- 0. main()
- 1. run()
- 2. transformAssociateToMap()
- 3. extractSurroundingKeyFrames()
- 4. downsampleCurrentScan()
- 5. scan2MapOptimization()
- cornerOptimization()
- surfOptimization()
- LMOptimization()
- 6. saveKeyFramesAndFactor()
- 7. correctPoses()
- 8. loopClosureThread() —— 回环检测
- detectLoopClosure()
- performLoopClosure()
- 4、transformFusion —— 融合粗、精配准的里程计信息
- 0. main()
- 1. laserOdometryHandler()
- 2. odomAftMappedHandler()
A lightweight and ground optimized lidar odometry and mapping (LeGO-LOAM) system for ROS compatible UGVs. The system takes in point cloud from a Velodyne VLP-16 Lidar (placed horizontal) and optional IMU data as inputs. It outputs 6D pose estimation in real-time.
LeGO-LOAM(激光SLAM,IMU+LiDAR),以LOAM为基础,实现与其同等的精度同时大大提高了速度。利用点云分割区分噪声,提取平面与边特征,使用两步LM优化方法求解位姿,并且添加回环检测减小漂移。
github:https://github.com/RobustFieldAutonomyLab/LeGO-LOAM
0、整体框架
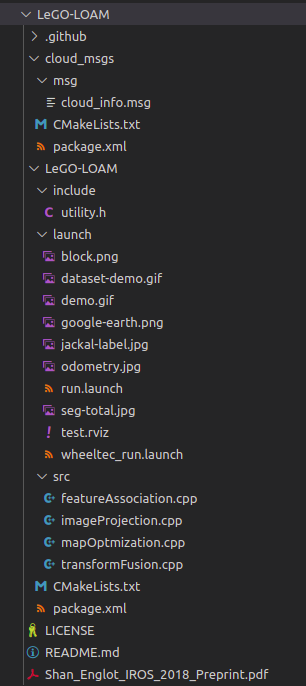
首先看一下代码结构,cloud_msgs、launch、include、src(核心程序),接下来具体看一下:
- CMakeList.txt
...
find_package(GTSAM REQUIRED QUIET)
find_package(PCL REQUIRED QUIET)
find_package(OpenCV REQUIRED QUIET)
...
依赖库:GTSAM、PCL、OPenCV
GTSAM 是一个在机器人领域和计算机视觉领域用于平滑(smoothing)和建图(mapping)的C++库,采用因子图(factor graphs)和贝叶斯网络(Bayes networks)的方式最大化后验概率。
- launch/run.launch
节点:rviz、camera_init_to_map、base_link_to_camera、imageProjection、featureAssociation、mapOptmization、transformFusion
主要节点就是后4个,也是对应src目录下的核心程序。
- include/utility.h
定义数据结构:点云、话题、激光雷达参数、图像分割参数、特征提取参数、优化参数、建图参数
...
/*
* A point cloud type that has "ring" channel
*/
struct PointXYZIR
{
PCL_ADD_POINT4D;
PCL_ADD_INTENSITY;
uint16_t ring;
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
} EIGEN_ALIGN16;
POINT_CLOUD_REGISTER_POINT_STRUCT (PointXYZIR,
(float, x, x) (float, y, y)
(float, z, z) (float, intensity, intensity)
(uint16_t, ring, ring)
)
...
这里定义了一种包含 ring_id 的点云数据类型,velodyne 的激光雷达是有这个数据的,其它厂商的不一定有;区别于laser_id,ring_id是指从最下面的激光线依次向上递增的线号(0-15 for VLP-16)。
...
// Using velodyne cloud "ring" channel for image projection (other lidar may have different name for this channel, change "PointXYZIR" below)
extern const bool useCloudRing = false; // if true, ang_res_y and ang_bottom are not used
// VLP-16
extern const int N_SCAN = 16;//number of lasers
extern const int Horizon_SCAN = 1800;//number of points from one laser of one scan
extern const float ang_res_x = 0.2;//angle resolution of horizon
extern const float ang_res_y = 2.0;//angle resolution of vertical
extern const float ang_bottom = 15.0+0.1;
extern const int groundScanInd = 7;//表示地面需要的线圈数;
...
针对不同激光雷达的参数设置,要根据自己的实际情况去调整,假如使用数据集的数据,比如KITTI,就需要针对HDL-64E进行调整,而且由于该雷达垂直角分辨率不是均匀的,还需要自己编写后续的投影程序。

1、imageProjection —— 点云分割
将激光点云处理成图像
总体流程:订阅点云数据回调处理 -> 点云转换到pcl预处理 -> 截取一帧激光数据 -> 投影映射到图像 -> 地面移除 -> 点云分割 -> 发布点云数据 -> 重置参数;
0. main()
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "lego_loam");
ImageProjection IP;
ROS_INFO("\033[1;32m---->\033[0m Image Projection Started.");
ros::spin();
return 0;
}
在 main 函数中,只是实例化了一个对象 IP ,所以 一旦创建了一个对象,就进入到了 Class 中去执行构造函数。
ImageProjection() : nh("~")
{
// 订阅原始的激光点云
subLaserCloud = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>(pointCloudTopic, 1, &ImageProjection::cloudHandler, this);
// 转换成图片的点云
pubFullCloud = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/full_cloud_projected", 1);
// 转换成图片的并带有距离信息的点云
pubFullInfoCloud = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/full_cloud_info", 1);
// 发布提取的地面特征
pubGroundCloud = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/ground_cloud", 1);
// 发布已经分割的点云
pubSegmentedCloud = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/segmented_cloud", 1);
// 具有几何信息的分割点云
pubSegmentedCloudPure = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/segmented_cloud_pure", 1);
pubSegmentedCloudInfo = nh.advertise<cloud_msgs::cloud_info>("/segmented_cloud_info", 1);
// 含有异常信息的点云
pubOutlierCloud = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/outlier_cloud", 1);
nanPoint.x = std::numeric_limits<float>::quiet_NaN();
nanPoint.y = std::numeric_limits<float>::quiet_NaN();
nanPoint.z = std::numeric_limits<float>::quiet_NaN();
nanPoint.intensity = -1;
allocateMemory();
resetParameters();
}
class 中的构造函数中,订阅了原始的激光点云数据(subLaserCloud)然后就进入到了 回调函数(ImageProjection::cloudHandler)对点云数据进行处理。
1. cloudHandler()
订阅激光雷达点云信息之后的回调函数
void cloudHandler(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr& laserCloudMsg){
// 1. Convert ros message to pcl point cloud 将ros消息转换为pcl点云
copyPointCloud(laserCloudMsg);
// 2. Start and end angle of a scan 扫描的起始和结束角度
findStartEndAngle();
// 3. Range image projection 距离图像投影
projectPointCloud();
// 4. Mark ground points 标记地面点
groundRemoval();
// 5. Point cloud segmentation 点云分割
cloudSegmentation();
// 6. Publish all clouds 发布点云
publishCloud();
// 7. Reset parameters for next iteration 重置下一次迭代的参数
resetParameters();
}
回调函数中按照以上 7 个逻辑步骤对点云进行处理,主要的逻辑步骤通过一个个封装好的函数呈现出来。
2. copyPointCloud()
由于激光雷达点云消息在传递过程中使用的是ROS 类型的消息,所以在处理的过程中统一需要对消息类型转换,通常的办法就是使用 PCL 库
// 复制点云 将ros消息转换为pcl点云
// 使用pcl库函数;
void copyPointCloud(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr& laserCloudMsg){
// 1. 读取ROS点云转换为PCL点云
cloudHeader = laserCloudMsg->header;
// cloudHeader.stamp = ros::Time::now(); // Ouster lidar users may need to uncomment this line
pcl::fromROSMsg(*laserCloudMsg, *laserCloudIn);
//2.移除无效的点云 Remove Nan points
std::vector<int> indices;
pcl::removeNaNFromPointCloud(*laserCloudIn, *laserCloudIn, indices);
// 3. have "ring" channel in the cloud or not
// 如果点云有"ring"通过,则保存为laserCloudInRing
// 判断是不是使用了 velodyne 的激光雷达
if (useCloudRing == true){
pcl::fromROSMsg(*laserCloudMsg, *laserCloudInRing);
if (laserCloudInRing->is_dense == false) {
ROS_ERROR("Point cloud is not in dense format, please remove NaN points first!");
ros::shutdown();
}
}
}
这个函数主体内容分为三个步骤,其中的第三步注意区分自己使用的激光雷达是否存在 CloudRing,没有这个的激光雷达接下来的步骤都不会去执行,所以在实际跑这个框架的时候一定要注意这个地方
3. findStartEndAngle()
// 找到开始结束角度
// 1.一圈数据的角度差,使用atan2计算;
// 2.注意计算结果的范围合理性
void findStartEndAngle(){
// start and end orientation of this cloud
// 1.开始点和结束点的航向角 (负号表示顺时针旋转)
segMsg.startOrientation = -atan2(laserCloudIn->points[0].y, laserCloudIn->points[0].x);
// 加 2 * M_PI 表示已经转转了一圈
segMsg.endOrientation = -atan2(laserCloudIn->points[laserCloudIn->points.size() - 1].y,
laserCloudIn->points[laserCloudIn->points.size() - 1].x) + 2 * M_PI;
// 2.保证所有角度落在 [M_PI , 3M_PI] 上
if (segMsg.endOrientation - segMsg.startOrientation > 3 * M_PI) {
segMsg.endOrientation -= 2 * M_PI;
} else if (segMsg.endOrientation - segMsg.startOrientation < M_PI)
segMsg.endOrientation += 2 * M_PI;
segMsg.orientationDiff = segMsg.endOrientation - segMsg.startOrientation;
}
这个函数在 LOAM 代码里面也存在。
首先通过一个反正切函数,找到一帧激光点云起始时刻和结束时刻的航向角,第二步的作用是将一帧激光点云的航向角度限制在 [pi , 3pi] 之间,方便后续计算出一帧激光点云的时间。
4. projectPointCloud()
距离图像投影
将3D point cloud投影映射到2D range image
将激光雷达数据投影成一个16x1800(依雷达角分辨率而定)的点云阵列
// 距离图像投影
// 将3D point cloud投影映射到2D range image
// 将激光雷达数据投影成一个16x1800(依雷达角分辨率而定)的点云阵列
void projectPointCloud(){
// range image projection
float verticalAngle, horizonAngle, range;
size_t rowIdn, columnIdn, index, cloudSize;
PointType thisPoint;
cloudSize = laserCloudIn->points.size();
// 遍历整个点云
for (size_t i = 0; i < cloudSize; ++i){
// 提取点云中 x y z 坐标数值
thisPoint.x = laserCloudIn->points[i].x;
thisPoint.y = laserCloudIn->points[i].y;
thisPoint.z = laserCloudIn->points[i].z;
// find the row and column index in the iamge for this point
// 判断是不是使用了 velodyne 的雷达
if (useCloudRing == true){
// 提取激光雷达线束到 rowIdn
rowIdn = laserCloudInRing->points[i].ring;
}
// 是其他的雷达 就通过俯仰角 确定当前的激光点是来自哪个线束 index
else{
verticalAngle = atan2(thisPoint.z, sqrt(thisPoint.x * thisPoint.x + thisPoint.y * thisPoint.y)) * 180 / M_PI;
rowIdn = (verticalAngle + ang_bottom) / ang_res_y; //确定行索引
}
if (rowIdn < 0 || rowIdn >= N_SCAN)
continue;
horizonAngle = atan2(thisPoint.x, thisPoint.y) * 180 / M_PI;
// 保证 columnIdn 的大小在 [0 , 1800)
columnIdn = -round((horizonAngle-90.0)/ang_res_x) + Horizon_SCAN/2; //确定列索引
if (columnIdn >= Horizon_SCAN)
columnIdn -= Horizon_SCAN;
if (columnIdn < 0 || columnIdn >= Horizon_SCAN)
continue;
// 如果距离小于 1米 则过滤掉 通常是过滤自身(距离传感器比较近的点)
range = sqrt(thisPoint.x * thisPoint.x + thisPoint.y * thisPoint.y + thisPoint.z * thisPoint.z); //确定深度
if (range < sensorMinimumRange)
continue;
// 将计算下来的距离传感器的 数值保存到 rangeMat 中
// 这是一个 16 * 1800 的矩阵 rowIdn为线束数值 columnIdn 是 一圈圆形 滩平之后的数值
// range 是特征点云点到原点的数值
// 这样就将一个三维的坐标 转换到一个 矩阵中了.
rangeMat.at<float>(rowIdn, columnIdn) = range;
// 将 index 和 横坐标存储在 intensity 中 整数部分是线束数值 小数部分是方向角度
thisPoint.intensity = (float)rowIdn + (float)columnIdn / 10000.0;
//深度图的索引值 index = 列号 + 行号 * 1800
index = columnIdn + rowIdn * Horizon_SCAN;
// fullCloud 存放的是坐标信息(二维的)
// fullInfoCloud 增加了点到传感器的距离信息(三维的)
fullCloud->points[index] = thisPoint;
fullInfoCloud->points[index] = thisPoint;
// intensity 中存放的是点云点到传感器的距离
fullInfoCloud->points[index].intensity = range; // the corresponding range of a point is saved as "intensity"
}
}
此处对激光点云的处理是 LEGO-LOAM 和 LOAM 的第一个区别。这里将一帧激光点云处理成一个 16 * 1800 像素的图片。 16代表的是激光雷达的线束,1800代表的是激光扫描一圈时候是 间隔0.5度发射一个激光束 所以 360 * 0.5 = 1800
再者,rangeMat.at(rowIdn, columnIdn) 这里调用了一个 opencv 的多维数组,数组中的行与列 对应的就是图片的长和宽,然后数组中存放的数值就是图片相应位置上面的点到激光雷达的距离。
最后将点云的坐标信息存储在 intensity 中,采用的方法是:整数+小数 存储。整数部分存储的是激光线束数值,小数部分存储的水平航向值。
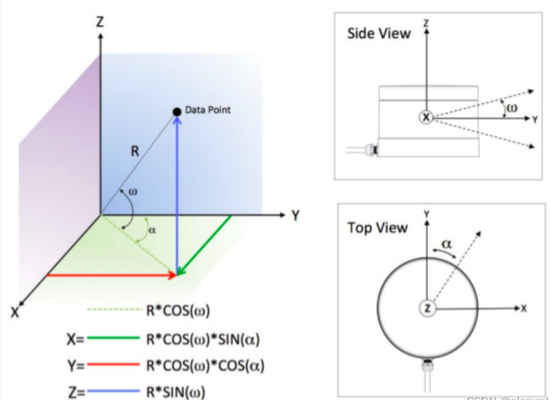
atan2(y,x);
反正切的角度等于X轴与通过原点和给定坐标点(x, y)的直线之间的夹角,结果为正表示从X轴逆时针旋转的角度,结果为负表示从X轴顺时针旋转的角度;

-
确定行索引
根据ring id或者根据坐标计算:
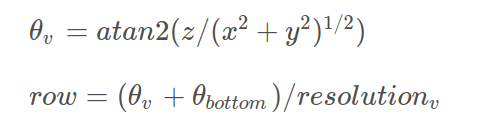
-
确定列索引([ − π , π ] 转换为 [ 0 , 1800 ]):
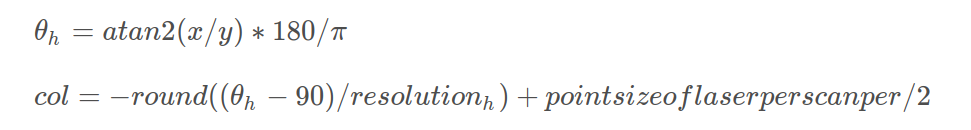
-
确定深度值:(注意数据的有效范围)
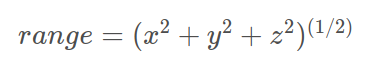
5. groundRemoval()
首先。判断地面点的标志就是相邻两个激光线束扫描到点的坐标,如果两个坐标之间的差值 或者两个坐标之间的斜率大于一个设定的值,则将该点
判断是地面点。所以此处用到了激光点云图片的深度信息
// 移除地面点
// 根据上下两线之间点的位置计算两线之间俯仰角判断,小于10度则为地面点
void groundRemoval(){
size_t lowerInd, upperInd;
float diffX, diffY, diffZ, angle;
// groundMat
// -1, no valid info to check if ground of not 没有有效的信息确认是不是地面
// 0, initial value, after validation, means not ground 确认不是地面点
// 1, ground
for (size_t j = 0; j < Horizon_SCAN; ++j){
// 前7个激光雷达扫描线束足够满足地面点的检测 所以只遍历 7 次
for (size_t i = 0; i < groundScanInd; ++i){
//groundScanInd定义打到地面上激光线的数目
lowerInd = j + ( i )*Horizon_SCAN;
upperInd = j + (i+1)*Horizon_SCAN;
// 如果之前计算过的 intensity 是 -1 则直接默认为是一个无效点
if (fullCloud->points[lowerInd].intensity == -1 ||
fullCloud->points[upperInd].intensity == -1){
// no info to check, invalid points 对这个无效点直接进行贴标签
groundMat.at<int8_t>(i,j) = -1;
continue;
}
diffX = fullCloud->points[upperInd].x - fullCloud->points[lowerInd].x;
diffY = fullCloud->points[upperInd].y - fullCloud->points[lowerInd].y;
diffZ = fullCloud->points[upperInd].z - fullCloud->points[lowerInd].z;
// 计算相邻两个线束之间的夹角
angle = atan2(diffZ, sqrt(diffX*diffX + diffY*diffY) ) * 180 / M_PI;
//垂直方向相邻两点俯仰角小于10度就判定为地面点;相邻扫描圈
if (abs(angle - sensorMountAngle) <= 10){
groundMat.at<int8_t>(i,j) = 1;
groundMat.at<int8_t>(i+1,j) = 1;
}
}
}
// extract ground cloud (groundMat == 1)
// mark entry that doesn't need to label (ground and invalid point) for segmentation
// note that ground remove is from 0~N_SCAN-1, need rangeMat for mark label matrix for the 16th scan
// 给地面点 标记一个符号 为 -1
for (size_t i = 0; i < N_SCAN; ++i){
for (size_t j = 0; j < Horizon_SCAN; ++j){
if (groundMat.at<int8_t>(i,j) == 1 || rangeMat.at<float>(i,j) == FLT_MAX){
labelMat.at<int>(i,j) = -1;
}
}
}
// 发布点云信息,只发布地面点云信息
if (pubGroundCloud.getNumSubscribers() != 0){
for (size_t i = 0; i <= groundScanInd; ++i){
for (size_t j = 0; j < Horizon_SCAN; ++j){
if (groundMat.at<int8_t>(i,j) == 1)
groundCloud->push_back(fullCloud->points[j + i*Horizon_SCAN]);
}
}
}
}
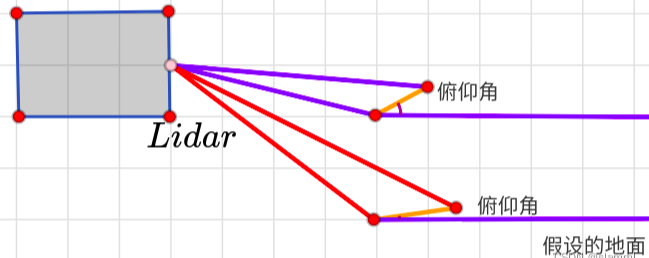
垂直相邻两点俯仰角小于10度就判定为地面点。
6. cloudSegmentation()
从论文中可以看到,分割函数的来源参考了两篇论文 ( Effificient Online Segmentation for Sparse 3D Laser Scans ,另外一篇 Fast Range Image-Based Segmentation of Sparse 3D Laser Scans for Online Operation)的方法 。方法的原理可以参考知乎文章 《地面点障碍物快速分割聚类》 。
// 点云分割
// 首先对点云进行聚类标记,根据标签进行对应点云块存储;
void cloudSegmentation(){
// segmentation process
for (size_t i = 0; i < N_SCAN; ++i) // 16线的 一个线束一个的遍历
for (size_t j = 0; j < Horizon_SCAN; ++j) // 水平 的 1800
if (labelMat.at<int>(i,j) == 0) // 对非地面点进行点云分割
labelComponents(i, j); // 调用这个函数对点云进行分割聚类
int sizeOfSegCloud = 0;
// extract segmented cloud for lidar odometry
// 提取分割点云 用于激光雷达里程计
for (size_t i = 0; i < N_SCAN; ++i) {
segMsg.startRingIndex[i] = sizeOfSegCloud-1 + 5;
for (size_t j = 0; j < Horizon_SCAN; ++j) {
if (labelMat.at<int>(i,j) > 0 || groundMat.at<int8_t>(i,j) == 1){
// outliers that will not be used for optimization (always continue)
// 勾勒出优化过程中不被使用的值
// 1. 如果label为999999则跳过
if (labelMat.at<int>(i,j) == 999999){
if (i > groundScanInd && j % 5 == 0){
outlierCloud->push_back(fullCloud->points[j + i*Horizon_SCAN]);
continue;
}else{
continue;
}
}
// majority of ground points are skipped
// 2. 如果为地,跳过index不是5的倍数的点
if (groundMat.at<int8_t>(i,j) == 1){
if (j%5!=0 && j>5 && j<Horizon_SCAN-5)
continue;
}
// mark ground points so they will not be considered as edge features later
segMsg.segmentedCloudGroundFlag[sizeOfSegCloud] = (groundMat.at<int8_t>(i,j) == 1);
// mark the points' column index for marking occlusion later
segMsg.segmentedCloudColInd[sizeOfSegCloud] = j;
// save range info
segMsg.segmentedCloudRange[sizeOfSegCloud] = rangeMat.at<float>(i,j);
// save seg cloud
segmentedCloud->push_back(fullCloud->points[j + i*Horizon_SCAN]);
// size of seg cloud
++sizeOfSegCloud;
}
}
segMsg.endRingIndex[i] = sizeOfSegCloud-1 - 5;
}
// extract segmented cloud for visualization
if (pubSegmentedCloudPure.getNumSubscribers() != 0){
for (size_t i = 0; i < N_SCAN; ++i){
for (size_t j = 0; j < Horizon_SCAN; ++j){
if (labelMat.at<int>(i,j) > 0 && labelMat.at<int>(i,j) != 999999){
segmentedCloudPure->push_back(fullCloud->points[j + i*Horizon_SCAN]);
segmentedCloudPure->points.back().intensity = labelMat.at<int>(i,j);
}
}
}
}
}
7. labelComponents()
// 标签组件
// 局部特征检测聚类
// 平面点与边缘点
void labelComponents(int row, int col){
// use std::queue std::vector std::deque will slow the program down greatly
float d1, d2, alpha, angle;
int fromIndX, fromIndY, thisIndX, thisIndY;
bool lineCountFlag[N_SCAN] = {false};
// 传进来的两个参数,按照坐标不同分别给他们放到 X 与 Y 的数组中
queueIndX[0] = row;
queueIndY[0] = col;
int queueSize = 1; // 需要计算角度的点的数量
int queueStartInd = 0;
int queueEndInd = 1;
allPushedIndX[0] = row;
allPushedIndY[0] = col;
int allPushedIndSize = 1;
while(queueSize > 0){
// Pop point
fromIndX = queueIndX[queueStartInd];
fromIndY = queueIndY[queueStartInd];
--queueSize;
++queueStartInd;
// Mark popped point
labelMat.at<int>(fromIndX, fromIndY) = labelCount;
// Loop through all the neighboring grids of popped grid
// 遍历整个点云,遍历前后左右四个邻域点,求点之间的角度数值
for (auto iter = neighborIterator.begin(); iter != neighborIterator.end(); ++iter){
// new index
thisIndX = fromIndX + (*iter).first;
thisIndY = fromIndY + (*iter).second;
// index should be within the boundary
if (thisIndX < 0 || thisIndX >= N_SCAN)
continue;
// at range image margin (left or right side)
if (thisIndY < 0)
thisIndY = Horizon_SCAN - 1;
if (thisIndY >= Horizon_SCAN)
thisIndY = 0;
// prevent infinite loop (caused by put already examined point back)
if (labelMat.at<int>(thisIndX, thisIndY) != 0)
continue;
//比较得出较大深度与较小深度
d1 = std::max(rangeMat.at<float>(fromIndX, fromIndY),
rangeMat.at<float>(thisIndX, thisIndY));
d2 = std::min(rangeMat.at<float>(fromIndX, fromIndY),
rangeMat.at<float>(thisIndX, thisIndY));
if ((*iter).first == 0)
alpha = segmentAlphaX;
else
alpha = segmentAlphaY;
angle = atan2(d2*sin(alpha), (d1 -d2*cos(alpha))); //平面聚类公式,角度越大两点越趋向于平面
//segmentTheta=60度
if (angle > segmentTheta){
queueIndX[queueEndInd] = thisIndX;
queueIndY[queueEndInd] = thisIndY;
++queueSize;
++queueEndInd;
labelMat.at<int>(thisIndX, thisIndY) = labelCount;
lineCountFlag[thisIndX] = true;
allPushedIndX[allPushedIndSize] = thisIndX;
allPushedIndY[allPushedIndSize] = thisIndY;
++allPushedIndSize;
}
}
}
// check if this segment is valid
bool feasibleSegment = false;
// 如果是 allPushedIndSize 累加的数量增加到了30 个 则判断这部分点云属于一个聚类
if (allPushedIndSize >= 30)
feasibleSegment = true; //面点
// 如果垂直 方向上点的数量大于 5个 默认是一个有效的聚类
else if (allPushedIndSize >= segmentValidPointNum){
int lineCount = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < N_SCAN; ++i)
if (lineCountFlag[i] == true)
++lineCount;
if (lineCount >= segmentValidLineNum)
feasibleSegment = true; //边点
}
// segment is valid, mark these points
if (feasibleSegment == true){
++labelCount;
}else{ // segment is invalid, mark these points
for (size_t i = 0; i < allPushedIndSize; ++i){
labelMat.at<int>(allPushedIndX[i], allPushedIndY[i]) = 999999;
}
}
}
取去除地面的 labelMat,逐点开始计算邻域4点(邻域的索引要注意有效范围),与中心点比较出距离的最大值与最小值,通过下面公式结合阈值π / 3,大于该值则构成平面特征为平面点,队列存储索引,labelMat 存储标签值,同时 lineCountFlag 置 true,直到不满足阈值跳出进行下步。
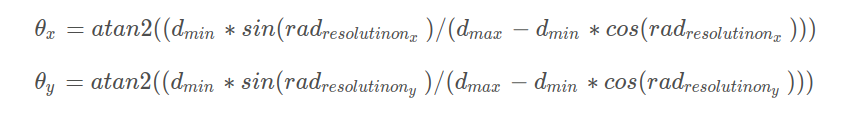
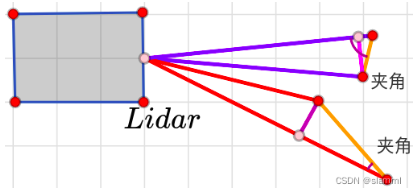
聚类,超过30个点聚为一类,labelCount++;
小于30超过5,统计垂直方向聚类点数,超过3个也标记为一类;
若都不满足,则赋值999999表示需要舍弃的聚类点。
8. publishCloud()
发布各类点云数据
9. resetParameters()
参数重置
LeGO-LOAM首先进行地面分割,找到地面之后,对地面之上的点进行聚类。聚类的算法如下图,主要是根据斜率对物体做切割,最后得到地面和分割后的点云。上述步骤的关键是要理解如何进行地面分割和点云分割。
点云分割完成之后,接下来对分割后的点云提取特征,提取的特征的目的是进行点云配准,从而得出当前位姿。
2、featureAssociation —— 特征提取与匹配
订阅分割点云、外点、imu数据,总体流程:
- (特征提取部分)订阅传感器数据 -> 运动畸变去除 -> 曲率计算 -> 去除瑕点 -> 提取边、平面特征 -> 发布特征点云;
- (特征关联部分)将IMU信息作为先验 -> 根据线特征、面特征计算位姿变换 -> 联合IMU数据进行位姿更新 -> 发布里程计信息
0. main()
主函数内部做了两件事情,一个是实例化一个对象,一个是循环执行类方法
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "lego_loam");
ROS_INFO("\033[1;32m---->\033[0m Feature Association Started.");
// 1. 在构造函数中订阅消息和消息回调函数
FeatureAssociation FA;
ros::Rate rate(200);
// 2. 循环调用runFeatureAssociation,函数的主流程所在
while (ros::ok())
{
ros::spinOnce();
FA.runFeatureAssociation();
rate.sleep();
}
ros::spin();
return 0;
}
主函数里面首选实例化了一个对象 FA ,所以和之前的ImageProjection 处理过程一样,执行构造函数的内容,所以在构造函数中会订阅上一个cpp 文件中 pub 出来的消息。然后转到回调函数中处理数据,此处的回调函数都是将相应的信息存储到buff 中,所以不做详细分析。
消息回调主要是接收上一个步骤(点云分割)中分割好的点云消息。
FeatureAssociation():
nh("~")
{
// 1. 接收消息,上一步分割好的点云
// 订阅了分割之后的点云
subLaserCloud = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/segmented_cloud", 1, &FeatureAssociation::laserCloudHandler, this);
// 订阅的分割点云含有图像的深度信息
subLaserCloudInfo = nh.subscribe<cloud_msgs::cloud_info>("/segmented_cloud_info", 1, &FeatureAssociation::laserCloudInfoHandler, this);
// 非聚类的点
subOutlierCloud = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/outlier_cloud", 1, &FeatureAssociation::outlierCloudHandler, this);
// IMU传感器的消息
subImu = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::Imu>(imuTopic, 50, &FeatureAssociation::imuHandler, this);
// 2. 发布消息
// 发布面特征点 和 边特征点
pubCornerPointsSharp = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/laser_cloud_sharp", 1);
pubCornerPointsLessSharp = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/laser_cloud_less_sharp", 1);
pubSurfPointsFlat = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/laser_cloud_flat", 1);
pubSurfPointsLessFlat = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/laser_cloud_less_flat", 1);
pubLaserCloudCornerLast = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/laser_cloud_corner_last", 2);
pubLaserCloudSurfLast = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/laser_cloud_surf_last", 2);
pubOutlierCloudLast = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/outlier_cloud_last", 2);
pubLaserOdometry = nh.advertise<nav_msgs::Odometry> ("/laser_odom_to_init", 5);
initializationValue();
}
下面我们具体看这4个消息
- segmented_cloud 分割好的点云。
- segmented_cloud_info 分割好的点云,和segmented_cloud的区别是,cloud_info的强度信息是距离,而segmented_cloud的是range image的行列信息。
- outlier_cloud 离群点,也就是分割失败的点。
- imuTopic 接收imu的消息。
在理解了上述4个消息之后,我们分别看下他们的回调,点云消息的回调主要是把ROS的消息转换为点云,IMU的回调主要是把IMU的消息放入buffer中。
// 1. 接收"/segmented_cloud"消息,保存到segmentedCloud
void laserCloudHandler(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr& laserCloudMsg){
cloudHeader = laserCloudMsg->header;
timeScanCur = cloudHeader.stamp.toSec();
timeNewSegmentedCloud = timeScanCur;
segmentedCloud->clear();
pcl::fromROSMsg(*laserCloudMsg, *segmentedCloud);
newSegmentedCloud = true;
}
// 2. 接收"/outlier_cloud"消息,保存到outlierCloud
void outlierCloudHandler(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr& msgIn){
timeNewOutlierCloud = msgIn->header.stamp.toSec();
outlierCloud->clear();
pcl::fromROSMsg(*msgIn, *outlierCloud);
newOutlierCloud = true;
}
// 3. 接收"/segmented_cloud_info"消息,并且保存到segInfo中
// 注意这里没有转换为PCL点云,而是直接保存的消息cloud_msgs::cloud_info segInfo
void laserCloudInfoHandler(const cloud_msgs::cloud_infoConstPtr& msgIn)
{
timeNewSegmentedCloudInfo = msgIn->header.stamp.toSec();
segInfo = *msgIn;
newSegmentedCloudInfo = true;
}
接下来看IMU回调函数,接收到IMU消息之后保存到数组。IMU还做了一些角度的转换,这里暂时不做深究。
void imuHandler(const sensor_msgs::Imu::ConstPtr& imuIn)
{
double roll, pitch, yaw;
tf::Quaternion orientation;
tf::quaternionMsgToTF(imuIn->orientation, orientation);
tf::Matrix3x3(orientation).getRPY(roll, pitch, yaw);
float accX = imuIn->linear_acceleration.y - sin(roll) * cos(pitch) * 9.81;
float accY = imuIn->linear_acceleration.z - cos(roll) * cos(pitch) * 9.81;
float accZ = imuIn->linear_acceleration.x + sin(pitch) * 9.81;
imuPointerLast = (imuPointerLast + 1) % imuQueLength;
imuTime[imuPointerLast] = imuIn->header.stamp.toSec();
imuRoll[imuPointerLast] = roll;
imuPitch[imuPointerLast] = pitch;
imuYaw[imuPointerLast] = yaw;
imuAccX[imuPointerLast] = accX;
imuAccY[imuPointerLast] = accY;
imuAccZ[imuPointerLast] = accZ;
imuAngularVeloX[imuPointerLast] = imuIn->angular_velocity.x;
imuAngularVeloY[imuPointerLast] = imuIn->angular_velocity.y;
imuAngularVeloZ[imuPointerLast] = imuIn->angular_velocity.z;
AccumulateIMUShiftAndRotation();
}
接着分别对位置、速度和角度做积分,计算出当前的位置、速度和角度。
void AccumulateIMUShiftAndRotation()
{
float roll = imuRoll[imuPointerLast];
float pitch = imuPitch[imuPointerLast];
float yaw = imuYaw[imuPointerLast];
float accX = imuAccX[imuPointerLast];
float accY = imuAccY[imuPointerLast];
float accZ = imuAccZ[imuPointerLast];
float x1 = cos(roll) * accX - sin(roll) * accY;
float y1 = sin(roll) * accX + cos(roll) * accY;
float z1 = accZ;
float x2 = x1;
float y2 = cos(pitch) * y1 - sin(pitch) * z1;
float z2 = sin(pitch) * y1 + cos(pitch) * z1;
accX = cos(yaw) * x2 + sin(yaw) * z2;
accY = y2;
accZ = -sin(yaw) * x2 + cos(yaw) * z2;
int imuPointerBack = (imuPointerLast + imuQueLength - 1) % imuQueLength;
double timeDiff = imuTime[imuPointerLast] - imuTime[imuPointerBack];
if (timeDiff < scanPeriod) {
// 1. 位置积分
imuShiftX[imuPointerLast] = imuShiftX[imuPointerBack] + imuVeloX[imuPointerBack] * timeDiff + accX * timeDiff * timeDiff / 2;
imuShiftY[imuPointerLast] = imuShiftY[imuPointerBack] + imuVeloY[imuPointerBack] * timeDiff + accY * timeDiff * timeDiff / 2;
imuShiftZ[imuPointerLast] = imuShiftZ[imuPointerBack] + imuVeloZ[imuPointerBack] * timeDiff + accZ * timeDiff * timeDiff / 2;
// 2. 速度积分
imuVeloX[imuPointerLast] = imuVeloX[imuPointerBack] + accX * timeDiff;
imuVeloY[imuPointerLast] = imuVeloY[imuPointerBack] + accY * timeDiff;
imuVeloZ[imuPointerLast] = imuVeloZ[imuPointerBack] + accZ * timeDiff;
// 3. 角度积分
imuAngularRotationX[imuPointerLast] = imuAngularRotationX[imuPointerBack] + imuAngularVeloX[imuPointerBack] * timeDiff;
imuAngularRotationY[imuPointerLast] = imuAngularRotationY[imuPointerBack] + imuAngularVeloY[imuPointerBack] * timeDiff;
imuAngularRotationZ[imuPointerLast] = imuAngularRotationZ[imuPointerBack] + imuAngularVeloZ[imuPointerBack] * timeDiff;
}
}
以上就是消息接收过程,接下来我们看主流程runFeatureAssociation。
1. runFeatureAssociation()
主函数的流程非常清晰,总共分为2个大的步骤
- 特征提取,提取线特征和面特征
- 特征匹配,利用最小二乘法,获取当前最优的位姿
void runFeatureAssociation()
{
if (newSegmentedCloud && newSegmentedCloudInfo && newOutlierCloud &&
std::abs(timeNewSegmentedCloudInfo - timeNewSegmentedCloud) < 0.05 &&
std::abs(timeNewOutlierCloud - timeNewSegmentedCloud) < 0.05){
newSegmentedCloud = false;
newSegmentedCloudInfo = false;
newOutlierCloud = false;
}else{
return;
}
/**
1. Feature Extraction
*/
// 1-1去除运动畸变
adjustDistortion();
// 1-2 计算曲率
calculateSmoothness();
// 1-3 标记出远点和离散点
markOccludedPoints();
// 1-4 特征提取
extractFeatures();
// 1-5 发布提取的特征点云消息
publishCloud(); // cloud for visualization
/**
2. Feature Association
*/
if (!systemInitedLM) {
checkSystemInitialization();
return;
}
//2-1 更新初始位姿
updateInitialGuess();
//2-2 特征点匹配
updateTransformation();
// 2-3坐标变换
integrateTransformation();
// 2-4发布雷达里程计消息
publishOdometry();
// 2-5发布用于图优化的点云
publishCloudsLast(); // cloud to mapOptimization
}
特征提取的过程:先对点云进行畸变校正(运动补偿),接着计算点的平滑程度,然后按照平滑度排序,如果是不平滑的点,则选为线特征(柱子或者墙壁的棱角),如果是平滑的点,则选为面特征(地面,墙面等平面)。同时为了避免选择的特征过于集中在同一个地方,会把360°方向切分为6个区域,每个区域平均选择2个线特征和4个面特征。
2. adjustDistortion()
使用IMU数据插值,去除运动畸变
// 1-1去除运动畸变
void adjustDistortion()
{
bool halfPassed = false;
int cloudSize = segmentedCloud->points.size();
PointType point;
for (int i = 0; i < cloudSize; i++) {
point.x = segmentedCloud->points[i].y;
point.y = segmentedCloud->points[i].z;
point.z = segmentedCloud->points[i].x;
//调整点所在的位置
float ori = -atan2(point.x, point.z);
if (!halfPassed) {
if (ori < segInfo.startOrientation - M_PI / 2)
ori += 2 * M_PI;
else if (ori > segInfo.startOrientation + M_PI * 3 / 2)
ori -= 2 * M_PI;
if (ori - segInfo.startOrientation > M_PI)
halfPassed = true;
} else {
ori += 2 * M_PI;
if (ori < segInfo.endOrientation - M_PI * 3 / 2)
ori += 2 * M_PI;
else if (ori > segInfo.endOrientation + M_PI / 2)
ori -= 2 * M_PI;
}
//保存各点的相对时间
float relTime = (ori - segInfo.startOrientation) / segInfo.orientationDiff;
point.intensity = int(segmentedCloud->points[i].intensity) + scanPeriod * relTime;
if (imuPointerLast >= 0) {
float pointTime = relTime * scanPeriod;
imuPointerFront = imuPointerLastIteration;
//与IMU时间戳对齐
while (imuPointerFront != imuPointerLast) {
if (timeScanCur + pointTime < imuTime[imuPointerFront]) {
break;
}
imuPointerFront = (imuPointerFront + 1) % imuQueLength;
}
//imuPointerFront == imuPointerLast,IMU数据比激光早且无后边数据,无法插值
if (timeScanCur + pointTime > imuTime[imuPointerFront]) {
imuRollCur = imuRoll[imuPointerFront];
imuPitchCur = imuPitch[imuPointerFront];
imuYawCur = imuYaw[imuPointerFront];
imuVeloXCur = imuVeloX[imuPointerFront];
imuVeloYCur = imuVeloY[imuPointerFront];
imuVeloZCur = imuVeloZ[imuPointerFront];
imuShiftXCur = imuShiftX[imuPointerFront];
imuShiftYCur = imuShiftY[imuPointerFront];
imuShiftZCur = imuShiftZ[imuPointerFront];
} else { //IMU插值,角度、速度、位移
int imuPointerBack = (imuPointerFront + imuQueLength - 1) % imuQueLength;
float ratioFront = (timeScanCur + pointTime - imuTime[imuPointerBack])
/ (imuTime[imuPointerFront] - imuTime[imuPointerBack]);
float ratioBack = (imuTime[imuPointerFront] - timeScanCur - pointTime)
/ (imuTime[imuPointerFront] - imuTime[imuPointerBack]);
imuRollCur = imuRoll[imuPointerFront] * ratioFront + imuRoll[imuPointerBack] * ratioBack;
imuPitchCur = imuPitch[imuPointerFront] * ratioFront + imuPitch[imuPointerBack] * ratioBack;
if (imuYaw[imuPointerFront] - imuYaw[imuPointerBack] > M_PI) {
imuYawCur = imuYaw[imuPointerFront] * ratioFront + (imuYaw[imuPointerBack] + 2 * M_PI) * ratioBack;
} else if (imuYaw[imuPointerFront] - imuYaw[imuPointerBack] < -M_PI) {
imuYawCur = imuYaw[imuPointerFront] * ratioFront + (imuYaw[imuPointerBack] - 2 * M_PI) * ratioBack;
} else {
imuYawCur = imuYaw[imuPointerFront] * ratioFront + imuYaw[imuPointerBack] * ratioBack;
}
imuVeloXCur = imuVeloX[imuPointerFront] * ratioFront + imuVeloX[imuPointerBack] * ratioBack;
imuVeloYCur = imuVeloY[imuPointerFront] * ratioFront + imuVeloY[imuPointerBack] * ratioBack;
imuVeloZCur = imuVeloZ[imuPointerFront] * ratioFront + imuVeloZ[imuPointerBack] * ratioBack;
imuShiftXCur = imuShiftX[imuPointerFront] * ratioFront + imuShiftX[imuPointerBack] * ratioBack;
imuShiftYCur = imuShiftY[imuPointerFront] * ratioFront + imuShiftY[imuPointerBack] * ratioBack;
imuShiftZCur = imuShiftZ[imuPointerFront] * ratioFront + imuShiftZ[imuPointerBack] * ratioBack;
}
//此处的更新数据用于updateImuRollPitchYawStartSinCos()
if (i == 0) {
imuRollStart = imuRollCur;
imuPitchStart = imuPitchCur;
imuYawStart = imuYawCur;
imuVeloXStart = imuVeloXCur;
imuVeloYStart = imuVeloYCur;
imuVeloZStart = imuVeloZCur;
imuShiftXStart = imuShiftXCur;
imuShiftYStart = imuShiftYCur;
imuShiftZStart = imuShiftZCur;
if (timeScanCur + pointTime > imuTime[imuPointerFront]) {
imuAngularRotationXCur = imuAngularRotationX[imuPointerFront];
imuAngularRotationYCur = imuAngularRotationY[imuPointerFront];
imuAngularRotationZCur = imuAngularRotationZ[imuPointerFront];
}else{
int imuPointerBack = (imuPointerFront + imuQueLength - 1) % imuQueLength;
float ratioFront = (timeScanCur + pointTime - imuTime[imuPointerBack])
/ (imuTime[imuPointerFront] - imuTime[imuPointerBack]);
float ratioBack = (imuTime[imuPointerFront] - timeScanCur - pointTime)
/ (imuTime[imuPointerFront] - imuTime[imuPointerBack]);
imuAngularRotationXCur = imuAngularRotationX[imuPointerFront] * ratioFront + imuAngularRotationX[imuPointerBack] * ratioBack;
imuAngularRotationYCur = imuAngularRotationY[imuPointerFront] * ratioFront + imuAngularRotationY[imuPointerBack] * ratioBack;
imuAngularRotationZCur = imuAngularRotationZ[imuPointerFront] * ratioFront + imuAngularRotationZ[imuPointerBack] * ratioBack;
}
imuAngularFromStartX = imuAngularRotationXCur - imuAngularRotationXLast;
imuAngularFromStartY = imuAngularRotationYCur - imuAngularRotationYLast;
imuAngularFromStartZ = imuAngularRotationZCur - imuAngularRotationZLast;
imuAngularRotationXLast = imuAngularRotationXCur;
imuAngularRotationYLast = imuAngularRotationYCur;
imuAngularRotationZLast = imuAngularRotationZCur;
updateImuRollPitchYawStartSinCos();
} else {
VeloToStartIMU(); //速度投影到初始时刻
TransformToStartIMU(&point); //点的坐标变换到初始时刻
}
}
segmentedCloud->points[i] = point;
}
imuPointerLastIteration = imuPointerLast;
}
3. calculateSmoothness()
计算平滑度
平滑度的计算是取当前点的左边5个点和右边5个点和当前点的深度差值,然后求平方。而论文中的计算方法和代码中的不一样,论文中是取深度差的平均值,然后除以自身的模,也就是说论文中的曲率和尺度无关,不管当前点离lidar近还是远,只要曲率超过一定的值就可以,同时在仿真环境也可以解决尺度的问题,而代码中直接取得是绝对大小。

// 1-2 计算曲率,以相邻左右各五个点计算
void calculateSmoothness()
{
int cloudSize = segmentedCloud->points.size();
for (int i = 5; i < cloudSize - 5; i++) {
// 1. 计算相邻10个点深度差的和
float diffRange = segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i-5] + segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i-4]
+ segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i-3] + segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i-2]
+ segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i-1] - segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i] * 10
+ segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i+1] + segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i+2]
+ segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i+3] + segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i+4]
+ segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i+5];
// 2. 取平方
cloudCurvature[i] = diffRange*diffRange;
cloudNeighborPicked[i] = 0;
cloudLabel[i] = 0;
// 3. 保存曲率,保存索引
cloudSmoothness[i].value = cloudCurvature[i];
cloudSmoothness[i].ind = i;
}
}
为什么cloudSmoothness也要保存索引,是因为后面会对cloudSmoothness数组排序,排序之后数组原来的索引就乱了,保存索引之后就知道点在原始点云中的索引(index)是多少。
4. markOccludedPoints()
计算完平滑度之后,我们首先标记一下效果不是非常理想的点,方便后续处理。那么什么是效果不好的点呢?在LOAM论文中有以下2种情况。
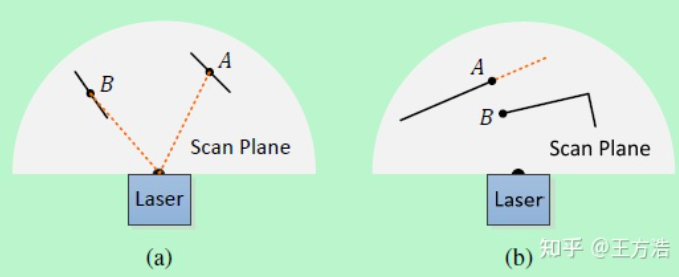
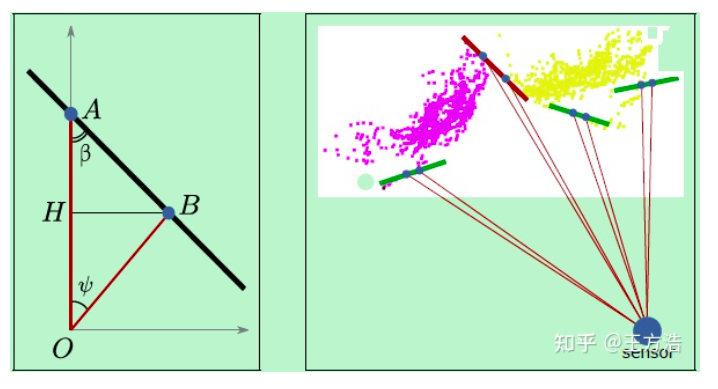
- 图(a) 中有2个特征点A和B,但B的方向和激光雷达的光束几乎平行,因此移动的过程中很可能丢失,所以尽量不要选择B。
- 图(b)中有2个特征点A和B,但A后续可能会被B遮挡了,橙色线标识的部分。所以A也尽量要排除。
实际上图(a)中所说的情况在LOAM中存在,而在LeGO-LOAM中可能不存在,因为LOAM没有做分割,而LeGO-LOAM做过分割,已经去除掉斜率比较大的点了,所以代码中我没有找到图(a)的情况。
// 1-3 标记出远点和离散点
//标记瑕点,相邻但距离较远的点(平行点被误判为平面点的情况),以及邻域距离变化较大的点(遮挡点被误判为边点的情况)
void markOccludedPoints()
{
int cloudSize = segmentedCloud->points.size();
for (int i = 5; i < cloudSize - 6; ++i){
float depth1 = segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i];
float depth2 = segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i+1];
int columnDiff = std::abs(int(segInfo.segmentedCloudColInd[i+1] - segInfo.segmentedCloudColInd[i]));
if (columnDiff < 10){
// 如果当前点和周围点的距离过大 就标记为 1
// 标记有遮挡的点
if (depth1 - depth2 > 0.3){
cloudNeighborPicked[i - 5] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i - 4] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i - 3] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i - 2] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i - 1] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i] = 1;
}else if (depth2 - depth1 > 0.3){
cloudNeighborPicked[i + 1] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i + 2] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i + 3] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i + 4] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i + 5] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i + 6] = 1;
}
}
float diff1 = std::abs(float(segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i-1] - segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i]));
float diff2 = std::abs(float(segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i+1] - segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i]));
// 如果一个点突变很远,则也被标记成 1
if (diff1 > 0.02 * segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i] && diff2 > 0.02 * segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i])
cloudNeighborPicked[i] = 1;
}
}
从代码中分析,在激光点云图像中(原始点云图像化处理之后)如果一个点和左右相邻的两个点之间的距离比较大,那么就认为这个很有可能是一个噪声点,然后提取特征时候尽量避免这个点。
5. extractFeatures()
接下来就进行提取特征的操作了,提取的特征分为2类,一类是曲率比较大的线特征,一类是曲率比较小的面特征。
提取的方法是把平面划分为6等分,也就是6个方向(LOAM中为前、后、左、右4个方向),根据上述计算好的曲率进行排序,然后每个方向最多选择2个线特征和4个面特征,如果超过则跳过,在下一个方向上继续选择。如果一个点已经被选择为特征点,那么它的相邻点会被标记,不允许被选为特征了。如果在某处点云过于密集,则会降采样处理,这样就保证了选取的特征点不在过于密集的地方。
// 1-4 特征提取
void extractFeatures()
{
// 初始化对应的指针
cornerPointsSharp->clear();
cornerPointsLessSharp->clear();
surfPointsFlat->clear();
surfPointsLessFlat->clear();
for (int i = 0; i < N_SCAN; i++) {
surfPointsLessFlatScan->clear();
// 1. 将一帧激光图像分成 6个子图,每个方向分别选择线特征和面特征,提取的特征点相对均匀
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
int sp = (segInfo.startRingIndex[i] * (6 - j) + segInfo.endRingIndex[i] * j) / 6;
int ep = (segInfo.startRingIndex[i] * (5 - j) + segInfo.endRingIndex[i] * (j + 1)) / 6 - 1;
if (sp >= ep)
continue;
// 2. 根据曲率排序
std::sort(cloudSmoothness.begin()+sp, cloudSmoothness.begin()+ep, by_value());
int largestPickedNum = 0;
// 线特征点的选择
for (int k = ep; k >= sp; k--) {
// 3. 选择线特征,不为地面,segInfo.segmentedCloudGroundFlag[ind] == false
int ind = cloudSmoothness[k].ind;
if (cloudNeighborPicked[ind] == 0 &&
cloudCurvature[ind] > edgeThreshold &&
segInfo.segmentedCloudGroundFlag[ind] == false) {
largestPickedNum++;
// 3.1 挑选出曲率最大的2个点
if (largestPickedNum <= 2) {
cloudLabel[ind] = 2;
cornerPointsSharp->push_back(segmentedCloud->points[ind]);
cornerPointsLessSharp->push_back(segmentedCloud->points[ind]);
// 3.2 平滑一些的线特征20个,用于mapping
} else if (largestPickedNum <= 20) {
cloudLabel[ind] = 1;
cornerPointsLessSharp->push_back(segmentedCloud->points[ind]);
} else {
// 3.3 超过则退出
break;
}
// 3.4 标记相邻点,防止特征点过于集中
cloudNeighborPicked[ind] = 1;
for (int l = 1; l <= 5; l++) {
int columnDiff = std::abs(int(segInfo.segmentedCloudColInd[ind + l] - segInfo.segmentedCloudColInd[ind + l - 1]));
if (columnDiff > 10)
break;
cloudNeighborPicked[ind + l] = 1;
}
for (int l = -1; l >= -5; l--) {
int columnDiff = std::abs(int(segInfo.segmentedCloudColInd[ind + l] - segInfo.segmentedCloudColInd[ind + l + 1]));
if (columnDiff > 10)
break;
cloudNeighborPicked[ind + l] = 1;
}
}
}
int smallestPickedNum = 0;
// 面特征点的选取 在已经标记过的地面点中选取
// 4. 选择面特征,为地面,segInfo.segmentedCloudGroundFlag[ind] == true
for (int k = sp; k <= ep; k++) {
int ind = cloudSmoothness[k].ind;
if (cloudNeighborPicked[ind] == 0 &&
cloudCurvature[ind] < surfThreshold &&
segInfo.segmentedCloudGroundFlag[ind] == true) {
cloudLabel[ind] = -1;
surfPointsFlat->push_back(segmentedCloud->points[ind]);
smallestPickedNum++;
// 4.1 选择最多4个面特征
if (smallestPickedNum >= 4) {
break;
}
// 4.2 标记相邻点
cloudNeighborPicked[ind] = 1;
for (int l = 1; l <= 5; l++) {
int columnDiff = std::abs(int(segInfo.segmentedCloudColInd[ind + l] - segInfo.segmentedCloudColInd[ind + l - 1]));
if (columnDiff > 10)
break;
cloudNeighborPicked[ind + l] = 1;
}
for (int l = -1; l >= -5; l--) {
int columnDiff = std::abs(int(segInfo.segmentedCloudColInd[ind + l] - segInfo.segmentedCloudColInd[ind + l + 1]));
if (columnDiff > 10)
break;
cloudNeighborPicked[ind + l] = 1;
}
}
}
// 5. 选择是地面的面特征,和其它没被选择的点(除了地面的点,并且不是线特征)
for (int k = sp; k <= ep; k++) {
if (cloudLabel[k] <= 0) {
surfPointsLessFlatScan->push_back(segmentedCloud->points[k]);
}
}
}
// 降低采样频率 防止选取过于密集
// 5.1 下采样平滑一些的面特征
surfPointsLessFlatScanDS->clear();
downSizeFilter.setInputCloud(surfPointsLessFlatScan);
downSizeFilter.filter(*surfPointsLessFlatScanDS);
*surfPointsLessFlat += *surfPointsLessFlatScanDS;
}
}
最后总结一下,特征点的选择满足以下3个条件:
- 选择的边缘点或平面点的数量不能超过每个方向上的最大值,一共有6个方向,每个方向上最多2个线特征,4个面特征。
- 线特征和面特征周围相邻的点不能被选中。
- 不能是平行于激光雷达光束的点或者被遮挡的点。
然后接着总结下代码中的输出:
- cornerPointsSharp 线特征(不为地面),每个方向上最多2个
- cornerPointsLessSharp 比cornerPointsSharp平滑的线特征(不为地面),每个方向上20个
- surfPointsFlat 面特征(为地面),每个方向上最多4个
- surfPointsLessFlat 面特征(地面或者分割点云中不为线特征的点)
至此,特征提取就介绍完毕了,接着介绍特征匹配。
特征匹配主要是根据上述提取出的面特征和线特征进行匹配,然后根据最小二乘法,得出前后2帧的坐标转换。LeGO-LOAM相对LOAM的不同之处在于,LeGO-LOAM分别对线和面进行匹配,根据线特征匹配得到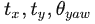 ,根据面特征匹配得到
,根据面特征匹配得到 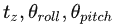 。而LOAM是合并了2个匹配,一次得出
。而LOAM是合并了2个匹配,一次得出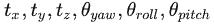 。
。
为什么LeGO-LOAM这么做呢,我们先看面特征匹配。
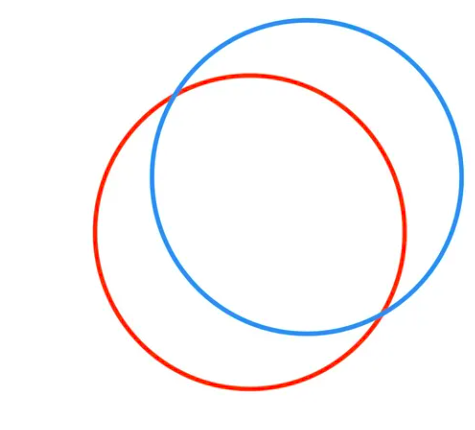
由于LeGO-LOAM做了地面分割,而且面特征是地面上的点,因此2个地面的点进行匹配之后,我们实际上只能保证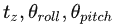 是准确的。因为2个平面重叠时候
是准确的。因为2个平面重叠时候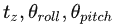 必定是确定的。
必定是确定的。
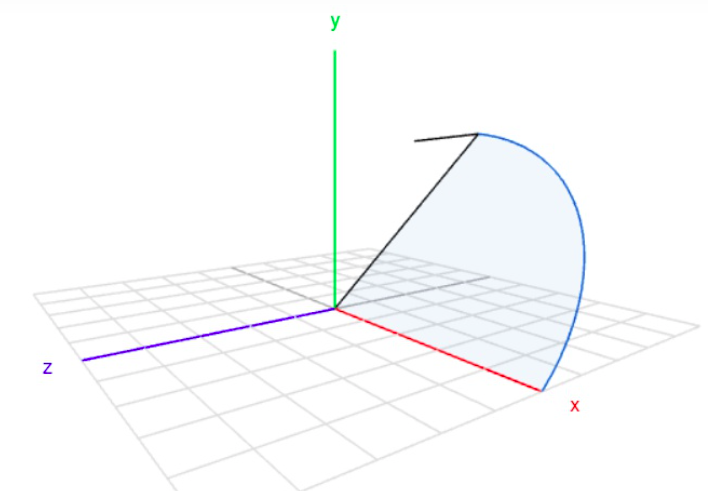
如下图所示,虽然2个平面重叠了,它还可以在水平面上移动和旋转(yaw),也就是说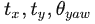 还可以变换,这是建立在只有水平地面的情况下,如果有多个平面,那么
还可以变换,这是建立在只有水平地面的情况下,如果有多个平面,那么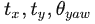 也可以是确定的。
也可以是确定的。
在通过面特征确定好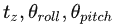 之后,接着再根据线特征确认
之后,接着再根据线特征确认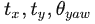 。线特征的匹配也是通过计算点到线的距离最短,通过线特征主要是确定
。线特征的匹配也是通过计算点到线的距离最短,通过线特征主要是确定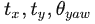 。至此整个匹配的过程就完成了。通过上述方法LeGO-LOAM达到同样的精度,比LOAM节省了35%的时间。
。至此整个匹配的过程就完成了。通过上述方法LeGO-LOAM达到同样的精度,比LOAM节省了35%的时间。
下面我们详细介绍下特征匹配的过程,首先是线特征匹配。
线特征匹配
空间中一个点的坐标可以通过旋转和平移来转换到另一个坐标。
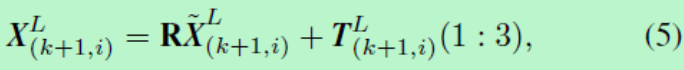
那么前1帧中的点通过公式(5)可以转换到当前帧,假设我们以空间中点的欧式距离来表示匹配的好坏,那么我们可以把问题转换为以下公式。
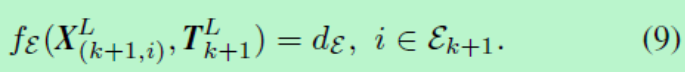
找到 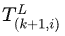 (可以理解为公式5中的R和T)使得前一帧中所有的点通过
(可以理解为公式5中的R和T)使得前一帧中所有的点通过 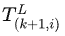 转换后,和当前帧的点的欧式距离最小,这样的R和T就是前一帧和当前帧的最优坐标转换。
转换后,和当前帧的点的欧式距离最小,这样的R和T就是前一帧和当前帧的最优坐标转换。
最小二乘法
上述的问题是不是有点类似以下经典的最小二乘法的问题。
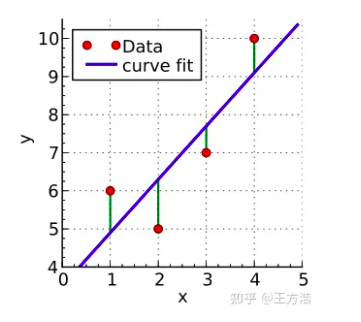
我们希望找到一条直线 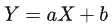 ,并且使得它和这4个点最匹配。回到坐标转换的例子,X代表前一帧的点,Y代表当前帧的点,而a代表旋转矩阵R,b代表平移矩阵b。通过计算每个点的平方差最小,来求解a和b的最优值。
,并且使得它和这4个点最匹配。回到坐标转换的例子,X代表前一帧的点,Y代表当前帧的点,而a代表旋转矩阵R,b代表平移矩阵b。通过计算每个点的平方差最小,来求解a和b的最优值。
代价函数
实际上LeGO-LOAM中线特征匹配不是计算2个点之间的平方差最小,而是先根据当前点i,查找它在前一帧的最小近邻点j,并且找到离j最近的l,j和l不是同一个扫描线但都属于前一帧的点云。然后再求点i到线 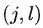 的距离,实际上就是求点到线的距离。然后遍历当前帧所有的线特征,重复执行上述过程直到收敛。
的距离,实际上就是求点到线的距离。然后遍历当前帧所有的线特征,重复执行上述过程直到收敛。
可以看到上述最小二乘法中的代价函数没有采用点和点的匹配,而是采用线和线的匹配,而求解线和线的距离用到的是点到线的距离。也就说最小二乘法的代价函数可以定义任意的类型,而不仅仅限定于欧氏距离,你定义了什么样的代价函数,就会得到什么样的拟合结果。

面特征匹配
面特征的匹配也是类似线特征匹配,不过是计算点到面的距离,因此根据当前帧的点i,查找上一帧中最小近邻点j,然后在当前扫描线中找到l,在相邻的扫描线中找到m,构成一个平面,然后计算点i到平面 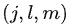 的距离。
的距离。
点到面的距离计算公式。
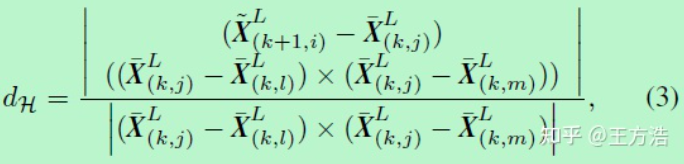
面特征的匹配就是找到一个转换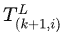 ,使得当前帧所有点到前一帧面的距离平方差最小。
,使得当前帧所有点到前一帧面的距离平方差最小。
6. updateInitialGuess()
更新初始位姿。
这个函数主要功能是对激光里程计初始化,在loam 代码中,激光里程计是将第一帧作为参考帧。如果系统没有初始化,则一直将当前帧作为参考帧。函数根据 IMU积分的结果,计算出一个初始位姿transformCur,这个位姿指的是雷达旋转一圈后发生的相对位姿变换。
7. updateTransformation()
边特征点和面特征点之间的匹配,这个过程和 LOAM 一致。
//2-2 特征点匹配
void updateTransformation(){
// 如果角特征点数量 和 面特征点数量较少 返回不执行匹配过程
if (laserCloudCornerLastNum < 10 || laserCloudSurfLastNum < 100)
return;
// 1. 面特征匹配
for (int iterCount1 = 0; iterCount1 < 25; iterCount1++) {
laserCloudOri->clear();
coeffSel->clear();
// 1.1 查找匹配的特征,计算协方差矩阵
findCorrespondingSurfFeatures(iterCount1);
if (laserCloudOri->points.size() < 10)
continue;
// 1.2 计算Transformation 面特征匹配计算变换矩阵(z,roll,pitch)
if (calculateTransformationSurf(iterCount1) == false)
break;
}
// 2. 线特征匹配
for (int iterCount2 = 0; iterCount2 < 25; iterCount2++) {
laserCloudOri->clear();
coeffSel->clear();
// 2.1 查找匹配的特征,计算协方差矩阵
findCorrespondingCornerFeatures(iterCount2);
if (laserCloudOri->points.size() < 10)
continue;
// 2.2 计算Transformation 边特征匹配计算变换矩阵(x,y,yaw)
if (calculateTransformationCorner(iterCount2) == false)
break;
}
}
8. findCorrespondingSurfFeatures()
查找面特征和计算回归系数,点离线越远回归系数越低,离线越近的点系数越高。
void findCorrespondingSurfFeatures(int iterCount){
int surfPointsFlatNum = surfPointsFlat->points.size();
for (int i = 0; i < surfPointsFlatNum; i++) {
// 1. 转换到起始点
TransformToStart(&surfPointsFlat->points[i], &pointSel);
if (iterCount % 5 == 0) {
// 2.1 通过i查找j
kdtreeSurfLast->nearestKSearch(pointSel, 1, pointSearchInd, pointSearchSqDis);
int closestPointInd = -1, minPointInd2 = -1, minPointInd3 = -1;
if (pointSearchSqDis[0] < nearestFeatureSearchSqDist) {
closestPointInd = pointSearchInd[0];
int closestPointScan = int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[closestPointInd].intensity);
float pointSqDis, minPointSqDis2 = nearestFeatureSearchSqDist, minPointSqDis3 = nearestFeatureSearchSqDist;
for (int j = closestPointInd + 1; j < surfPointsFlatNum; j++) {
if (int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].intensity) > closestPointScan + 2.5) {
break;
}
pointSqDis = (laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) *
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) +
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) *
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) +
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z) *
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z);
if (int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].intensity) <= closestPointScan) {
if (pointSqDis < minPointSqDis2) {
minPointSqDis2 = pointSqDis;
minPointInd2 = j;
}
} else {
if (pointSqDis < minPointSqDis3) {
minPointSqDis3 = pointSqDis;
minPointInd3 = j;
}
}
}
for (int j = closestPointInd - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].intensity) < closestPointScan - 2.5) {
break;
}
pointSqDis = (laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) *
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) +
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) *
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) +
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z) *
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z);
if (int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].intensity) >= closestPointScan) {
if (pointSqDis < minPointSqDis2) {
minPointSqDis2 = pointSqDis;
minPointInd2 = j;
}
} else {
if (pointSqDis < minPointSqDis3) {
minPointSqDis3 = pointSqDis;
minPointInd3 = j;
}
}
}
}
// 2.2 查找l和m
pointSearchSurfInd1[i] = closestPointInd;
pointSearchSurfInd2[i] = minPointInd2;
pointSearchSurfInd3[i] = minPointInd3;
}
if (pointSearchSurfInd2[i] >= 0 && pointSearchSurfInd3[i] >= 0) {
tripod1 = laserCloudSurfLast->points[pointSearchSurfInd1[i]];
tripod2 = laserCloudSurfLast->points[pointSearchSurfInd2[i]];
tripod3 = laserCloudSurfLast->points[pointSearchSurfInd3[i]];
float pa = (tripod2.y - tripod1.y) * (tripod3.z - tripod1.z)
- (tripod3.y - tripod1.y) * (tripod2.z - tripod1.z);
float pb = (tripod2.z - tripod1.z) * (tripod3.x - tripod1.x)
- (tripod3.z - tripod1.z) * (tripod2.x - tripod1.x);
float pc = (tripod2.x - tripod1.x) * (tripod3.y - tripod1.y)
- (tripod3.x - tripod1.x) * (tripod2.y - tripod1.y);
float pd = -(pa * tripod1.x + pb * tripod1.y + pc * tripod1.z);
float ps = sqrt(pa * pa + pb * pb + pc * pc);
pa /= ps;
pb /= ps;
pc /= ps;
pd /= ps;
float pd2 = pa * pointSel.x + pb * pointSel.y + pc * pointSel.z + pd;
float s = 1;
if (iterCount >= 5) {
s = 1 - 1.8 * fabs(pd2) / sqrt(sqrt(pointSel.x * pointSel.x
+ pointSel.y * pointSel.y + pointSel.z * pointSel.z));
}
// 3. 计算回归系数
if (s > 0.1 && pd2 != 0) {
coeff.x = s * pa;
coeff.y = s * pb;
coeff.z = s * pc;
coeff.intensity = s * pd2;
laserCloudOri->push_back(surfPointsFlat->points[i]);
coeffSel->push_back(coeff);
}
}
}
}
9. calculateTransformationSurf()
通过回归系数求解坐标转换Transformation。
bool calculateTransformationSurf(int iterCount){
int pointSelNum = laserCloudOri->points.size();
cv::Mat matA(pointSelNum, 3, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matAt(3, pointSelNum, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matAtA(3, 3, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matB(pointSelNum, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matAtB(3, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matX(3, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
float srx = sin(transformCur[0]);
float crx = cos(transformCur[0]);
float sry = sin(transformCur[1]);
float cry = cos(transformCur[1]);
float srz = sin(transformCur[2]);
float crz = cos(transformCur[2]);
float tx = transformCur[3];
float ty = transformCur[4];
float tz = transformCur[5];
float a1 = crx*sry*srz; float a2 = crx*crz*sry; float a3 = srx*sry; float a4 = tx*a1 - ty*a2 - tz*a3;
float a5 = srx*srz; float a6 = crz*srx; float a7 = ty*a6 - tz*crx - tx*a5;
float a8 = crx*cry*srz; float a9 = crx*cry*crz; float a10 = cry*srx; float a11 = tz*a10 + ty*a9 - tx*a8;
float b1 = -crz*sry - cry*srx*srz; float b2 = cry*crz*srx - sry*srz;
float b5 = cry*crz - srx*sry*srz; float b6 = cry*srz + crz*srx*sry;
float c1 = -b6; float c2 = b5; float c3 = tx*b6 - ty*b5; float c4 = -crx*crz; float c5 = crx*srz; float c6 = ty*c5 + tx*-c4;
float c7 = b2; float c8 = -b1; float c9 = tx*-b2 - ty*-b1;
for (int i = 0; i < pointSelNum; i++) {
pointOri = laserCloudOri->points[i];
coeff = coeffSel->points[i];
float arx = (-a1*pointOri.x + a2*pointOri.y + a3*pointOri.z + a4) * coeff.x
+ (a5*pointOri.x - a6*pointOri.y + crx*pointOri.z + a7) * coeff.y
+ (a8*pointOri.x - a9*pointOri.y - a10*pointOri.z + a11) * coeff.z;
float arz = (c1*pointOri.x + c2*pointOri.y + c3) * coeff.x
+ (c4*pointOri.x - c5*pointOri.y + c6) * coeff.y
+ (c7*pointOri.x + c8*pointOri.y + c9) * coeff.z;
float aty = -b6 * coeff.x + c4 * coeff.y + b2 * coeff.z;
float d2 = coeff.intensity;
matA.at<float>(i, 0) = arx;
matA.at<float>(i, 1) = arz;
matA.at<float>(i, 2) = aty;
matB.at<float>(i, 0) = -0.05 * d2;
}
cv::transpose(matA, matAt);
matAtA = matAt * matA;
matAtB = matAt * matB;
// 1. 最小二乘法求解
cv::solve(matAtA, matAtB, matX, cv::DECOMP_QR);
if (iterCount == 0) {
cv::Mat matE(1, 3, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matV(3, 3, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matV2(3, 3, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::eigen(matAtA, matE, matV);
matV.copyTo(matV2);
isDegenerate = false;
float eignThre[3] = {10, 10, 10};
for (int i = 2; i >= 0; i--) {
if (matE.at<float>(0, i) < eignThre[i]) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
matV2.at<float>(i, j) = 0;
}
isDegenerate = true;
} else {
break;
}
}
matP = matV.inv() * matV2;
}
if (isDegenerate) {
cv::Mat matX2(3, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
matX.copyTo(matX2);
matX = matP * matX2;
}
transformCur[0] += matX.at<float>(0, 0);
transformCur[2] += matX.at<float>(1, 0);
transformCur[4] += matX.at<float>(2, 0);
for(int i=0; i<6; i++){
if(isnan(transformCur[i]))
transformCur[i]=0;
}
float deltaR = sqrt(
pow(rad2deg(matX.at<float>(0, 0)), 2) +
pow(rad2deg(matX.at<float>(1, 0)), 2));
float deltaT = sqrt(
pow(matX.at<float>(2, 0) * 100, 2));
// 2. 结果收敛则返回
if (deltaR < 0.1 && deltaT < 0.1) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
10. integrateTransformation()
将前后两帧位姿累加,获得对第一帧的位姿,同时从局部坐标系转换到全局坐标系,加入IMU数据更新出位姿。
// 2-3坐标变换
void integrateTransformation(){
float rx, ry, rz, tx, ty, tz;
// transformSum 是 IMU累计的变化量 ,0,1,2 分别代表的是 pitch yaw roll 的内容,
// transformCur 是当前的分量,函数的作用是局部坐标转换成全局坐标
//将两帧之间的位姿累加,获得相对于第一帧的旋转矩阵,局部坐标系转化为全局坐标系
AccumulateRotation(transformSum[0], transformSum[1], transformSum[2],
-transformCur[0], -transformCur[1], -transformCur[2], rx, ry, rz);
//更新平移量
float x1 = cos(rz) * (transformCur[3] - imuShiftFromStartX)
- sin(rz) * (transformCur[4] - imuShiftFromStartY);
float y1 = sin(rz) * (transformCur[3] - imuShiftFromStartX)
+ cos(rz) * (transformCur[4] - imuShiftFromStartY);
float z1 = transformCur[5] - imuShiftFromStartZ;
float x2 = x1;
float y2 = cos(rx) * y1 - sin(rx) * z1;
float z2 = sin(rx) * y1 + cos(rx) * z1;
tx = transformSum[3] - (cos(ry) * x2 + sin(ry) * z2);
ty = transformSum[4] - y2;
tz = transformSum[5] - (-sin(ry) * x2 + cos(ry) * z2);
// 加入 imu 当前数据 更新位姿
PluginIMURotation(rx, ry, rz, imuPitchStart, imuYawStart, imuRollStart,
imuPitchLast, imuYawLast, imuRollLast, rx, ry, rz);
transformSum[0] = rx;
transformSum[1] = ry;
transformSum[2] = rz;
transformSum[3] = tx;
transformSum[4] = ty;
transformSum[5] = tz;
}
11. publishOdometry()
发布激光里程计位姿和 TF 变换。这里的坐标变换实际上是odom 相对于地图原点的,所以会有累计误差出现。
12. publishCloudsLast()
发布用于图优化的点云
由于上一帧的点云已经被统一到了当前帧的起始时刻,匹配的是当前帧的终止位姿相对于起始位姿的转换,此处的内容是按照优化后的结果,那当前帧的点云统一到终止时刻,然后将特征点云发布出去。
特征提取和特征匹配2步完成了lidar里程计的输出。接着看建图过程的分析。
3、mapOptimization —— 图的优化
整体功能分为回环检测、可视化以及位姿全局优化,核心是位姿优化。
主体流程:订阅特征提取后的点云、里程计数据 -> 计算当前姿态优化的初始值 -> 提取局部关键帧 -> 降采样 -> scan-to-map地图优化(线特征、面特征、L-M)-> 保存关键帧与因子图优化 -> 闭环检测 -> 发布TF变换、点云
0. main()
主函数分为2个主要的功能,一是启动单独的线程进行回环检测,二是在循环中执行主流程。
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "lego_loam");
ROS_INFO("\033[1;32m---->\033[0m Map Optimization Started.");
mapOptimization MO;
// 1. 回环检测
std::thread loopthread(&mapOptimization::loopClosureThread, &MO);
// 2. 可视化线程
std::thread visualizeMapThread(&mapOptimization::visualizeGlobalMapThread, &MO);
ros::Rate rate(200);
while (ros::ok())
{
ros::spinOnce();
// 3. 主流程
MO.run();
rate.sleep();
}
loopthread.join();
visualizeMapThread.join();
return 0;
}
lidar制图在构造函数中订阅消息,订阅的消息主要是以下5个。主要是接收特征提取之后的点云,lidar里程计和IMU消息。
subLaserCloudCornerLast = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/laser_cloud_corner_last", 2, &mapOptimization::laserCloudCornerLastHandler, this);
subLaserCloudSurfLast = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/laser_cloud_surf_last", 2, &mapOptimization::laserCloudSurfLastHandler, this);
subOutlierCloudLast = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/outlier_cloud_last", 2, &mapOptimization::laserCloudOutlierLastHandler, this);
subLaserOdometry = nh.subscribe<nav_msgs::Odometry>("/laser_odom_to_init", 5, &mapOptimization::laserOdometryHandler, this);
subImu = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::Imu> (imuTopic, 50, &mapOptimization::imuHandler, this);
1. run()
void run(){
// 是否是最新的消息
if (newLaserCloudCornerLast && std::abs(timeLaserCloudCornerLast - timeLaserOdometry) < 0.005 &&
newLaserCloudSurfLast && std::abs(timeLaserCloudSurfLast - timeLaserOdometry) < 0.005 &&
newLaserCloudOutlierLast && std::abs(timeLaserCloudOutlierLast - timeLaserOdometry) < 0.005 &&
newLaserOdometry)
{
newLaserCloudCornerLast = false; newLaserCloudSurfLast = false; newLaserCloudOutlierLast = false; newLaserOdometry = false;
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mtx);
// 设置lidar mapping时间间隔,以相对较慢的速度建图
//设置优化的间隔为0.3秒
if (timeLaserOdometry - timeLastProcessing >= mappingProcessInterval) {
timeLastProcessing = timeLaserOdometry;
// 1. 转换到map坐标系
transformAssociateToMap();
// 2. 提取周围关键帧
extractSurroundingKeyFrames();
// 3. 下采样当前帧
downsampleCurrentScan();
// 4. scan到map优化
scan2MapOptimization();
// 5. 保存关键帧和因子
saveKeyFramesAndFactor();
// 6. 校正位姿
correctPoses();
// 7. 发布坐标转换
publishTF();
// 8. 发布关键帧和姿态
publishKeyPosesAndFrames();
// 9. 清除点云
clearCloud();
}
}
}
2. transformAssociateToMap()
转换到map坐标系
3. extractSurroundingKeyFrames()
如果使用了回环检测,则添加过去50个关键帧,如果没有使用回环检测,则添加离当前欧式距离最近的50个关键帧,然后拼接成点云。
// 2. 提取周围关键帧
void extractSurroundingKeyFrames(){
if (cloudKeyPoses3D->points.empty() == true)
return;
// 如果使能回环检测
if (loopClosureEnableFlag == true){
// only use recent key poses for graph building 只使用最近的关键姿态进行图的构建
// 1. 添加最近的关键位姿到图
if (recentCornerCloudKeyFrames.size() < surroundingKeyframeSearchNum){ // queue is not full (the beginning of mapping or a loop is just closed)
// clear recent key frames queue 清除关键帧序列
recentCornerCloudKeyFrames. clear();
recentSurfCloudKeyFrames. clear();
recentOutlierCloudKeyFrames.clear();
int numPoses = cloudKeyPoses3D->points.size();
for (int i = numPoses-1; i >= 0; --i){
int thisKeyInd = (int)cloudKeyPoses3D->points[i].intensity;
PointTypePose thisTransformation = cloudKeyPoses6D->points[thisKeyInd];
updateTransformPointCloudSinCos(&thisTransformation);
// extract surrounding map
// 提取过去50个关键帧
recentCornerCloudKeyFrames. push_front(transformPointCloud(cornerCloudKeyFrames[thisKeyInd]));
recentSurfCloudKeyFrames. push_front(transformPointCloud(surfCloudKeyFrames[thisKeyInd]));
recentOutlierCloudKeyFrames.push_front(transformPointCloud(outlierCloudKeyFrames[thisKeyInd]));
if (recentCornerCloudKeyFrames.size() >= surroundingKeyframeSearchNum)
break;
}
}else{ // queue is full, pop the oldest key frame and push the latest key frame
if (latestFrameID != cloudKeyPoses3D->points.size() - 1){ // if the robot is not moving, no need to update recent frames
recentCornerCloudKeyFrames. pop_front();
recentSurfCloudKeyFrames. pop_front();
recentOutlierCloudKeyFrames.pop_front();
// push latest scan to the end of queue
// 2. 弹出队列中时间最久的帧,添加最新的帧到队列
latestFrameID = cloudKeyPoses3D->points.size() - 1;
PointTypePose thisTransformation = cloudKeyPoses6D->points[latestFrameID];
updateTransformPointCloudSinCos(&thisTransformation);
recentCornerCloudKeyFrames. push_back(transformPointCloud(cornerCloudKeyFrames[latestFrameID]));
recentSurfCloudKeyFrames.push_back(transformPointCloud(surfCloudKeyFrames[latestFrameID]));
recentOutlierCloudKeyFrames.push_back(transformPointCloud(outlierCloudKeyFrames[latestFrameID]));
}
}
// 3. 拼接为点云
for (int i = 0; i < recentCornerCloudKeyFrames.size(); ++i){
*laserCloudCornerFromMap += *recentCornerCloudKeyFrames[i];
*laserCloudSurfFromMap += *recentSurfCloudKeyFrames[i];
*laserCloudSurfFromMap += *recentOutlierCloudKeyFrames[i];
}
}else{ // 如果没有使能回环检测
surroundingKeyPoses->clear();
surroundingKeyPosesDS->clear();
// extract all the nearby key poses and downsample them
// 1. 查找当前pose 50米内的姿态
kdtreeSurroundingKeyPoses->setInputCloud(cloudKeyPoses3D);
kdtreeSurroundingKeyPoses->radiusSearch(currentRobotPosPoint, (double)surroundingKeyframeSearchRadius, pointSearchInd, pointSearchSqDis, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < pointSearchInd.size(); ++i)
surroundingKeyPoses->points.push_back(cloudKeyPoses3D->points[pointSearchInd[i]]);
downSizeFilterSurroundingKeyPoses.setInputCloud(surroundingKeyPoses);
downSizeFilterSurroundingKeyPoses.filter(*surroundingKeyPosesDS);
// delete key frames that are not in surrounding region
// 2. 删除不在周围区域的关键帧
int numSurroundingPosesDS = surroundingKeyPosesDS->points.size();
for (int i = 0; i < surroundingExistingKeyPosesID.size(); ++i){
bool existingFlag = false;
for (int j = 0; j < numSurroundingPosesDS; ++j){
if (surroundingExistingKeyPosesID[i] == (int)surroundingKeyPosesDS->points[j].intensity){
existingFlag = true;
break;
}
}
if (existingFlag == false){
surroundingExistingKeyPosesID. erase(surroundingExistingKeyPosesID. begin() + i);
surroundingCornerCloudKeyFrames. erase(surroundingCornerCloudKeyFrames. begin() + i);
surroundingSurfCloudKeyFrames. erase(surroundingSurfCloudKeyFrames. begin() + i);
surroundingOutlierCloudKeyFrames.erase(surroundingOutlierCloudKeyFrames.begin() + i);
--i;
}
}
// add new key frames that are not in calculated existing key frames
// 3. 添加新关键帧
for (int i = 0; i < numSurroundingPosesDS; ++i) {
bool existingFlag = false;
for (auto iter = surroundingExistingKeyPosesID.begin(); iter != surroundingExistingKeyPosesID.end(); ++iter){
if ((*iter) == (int)surroundingKeyPosesDS->points[i].intensity){
existingFlag = true;
break;
}
}
if (existingFlag == true){
continue;
}else{
int thisKeyInd = (int)surroundingKeyPosesDS->points[i].intensity;
PointTypePose thisTransformation = cloudKeyPoses6D->points[thisKeyInd];
updateTransformPointCloudSinCos(&thisTransformation);
surroundingExistingKeyPosesID. push_back(thisKeyInd);
surroundingCornerCloudKeyFrames. push_back(transformPointCloud(cornerCloudKeyFrames[thisKeyInd]));
surroundingSurfCloudKeyFrames. push_back(transformPointCloud(surfCloudKeyFrames[thisKeyInd]));
surroundingOutlierCloudKeyFrames.push_back(transformPointCloud(outlierCloudKeyFrames[thisKeyInd]));
}
}
// 4. 拼接点云
for (int i = 0; i < surroundingExistingKeyPosesID.size(); ++i) {
*laserCloudCornerFromMap += *surroundingCornerCloudKeyFrames[i];
*laserCloudSurfFromMap += *surroundingSurfCloudKeyFrames[i];
*laserCloudSurfFromMap += *surroundingOutlierCloudKeyFrames[i];
}
}
// 下采样角特征和面特征
// Downsample the surrounding corner key frames (or map)
downSizeFilterCorner.setInputCloud(laserCloudCornerFromMap);
downSizeFilterCorner.filter(*laserCloudCornerFromMapDS);
laserCloudCornerFromMapDSNum = laserCloudCornerFromMapDS->points.size();
// Downsample the surrounding surf key frames (or map)
downSizeFilterSurf.setInputCloud(laserCloudSurfFromMap);
downSizeFilterSurf.filter(*laserCloudSurfFromMapDS);
laserCloudSurfFromMapDSNum = laserCloudSurfFromMapDS->points.size();
}
4. downsampleCurrentScan()
// 3. 下采样当前帧
void downsampleCurrentScan(){
laserCloudCornerLastDS->clear();
downSizeFilterCorner.setInputCloud(laserCloudCornerLast);
downSizeFilterCorner.filter(*laserCloudCornerLastDS);
laserCloudCornerLastDSNum = laserCloudCornerLastDS->points.size();
laserCloudSurfLastDS->clear();
downSizeFilterSurf.setInputCloud(laserCloudSurfLast);
downSizeFilterSurf.filter(*laserCloudSurfLastDS);
laserCloudSurfLastDSNum = laserCloudSurfLastDS->points.size();
laserCloudOutlierLastDS->clear();
downSizeFilterOutlier.setInputCloud(laserCloudOutlierLast);
downSizeFilterOutlier.filter(*laserCloudOutlierLastDS);
laserCloudOutlierLastDSNum = laserCloudOutlierLastDS->points.size();
laserCloudSurfTotalLast->clear();
laserCloudSurfTotalLastDS->clear();
*laserCloudSurfTotalLast += *laserCloudSurfLastDS;
*laserCloudSurfTotalLast += *laserCloudOutlierLastDS;
downSizeFilterSurf.setInputCloud(laserCloudSurfTotalLast);
downSizeFilterSurf.filter(*laserCloudSurfTotalLastDS);
laserCloudSurfTotalLastDSNum = laserCloudSurfTotalLastDS->points.size();
}
前面的几个函数,转换到map 坐标系,提取关键帧,降采样等 主要的作用就是方便后续的图优化过程,提高图优化的速度。
5. scan2MapOptimization()
通过最小二乘法,添加当前的扫描帧(scan)到map
这个函数的作用主要是 使用 scan -> map 的位姿匹配过程,机器人当前的位姿 transformTobeMapped 与之前的激光里程计构建的地图匹配,最后通过非线性优化,使得两者之间的误差最小,多次迭代之后,误差变得更小。
在优化的同时,插入 IMU 信息然后对 roll 和 pitch 修正,对transformTobeMapped 进行中值滤波,最后获取最终的机器人位姿。
虽然,在 scan -> scan 的匹配之后,又进行了 scan -> map 的匹配,但是只是在局部的实验中完成了回环检测的过程,所以实际意义上,这依旧是没有修正累计误差。
// 4. scan到map优化
void scan2MapOptimization(){
// laserCloudCornerFromMapDSNum是extractSurroundingKeyFrames()函数最后降采样得到的coner点云数
// laserCloudSurfFromMapDSNum是extractSurroundingKeyFrames()函数降采样得到的surface点云数
if (laserCloudCornerFromMapDSNum > 10 && laserCloudSurfFromMapDSNum > 100) {
// laserCloudCornerFromMapDS 与 laserCloudSurfFromMapDS 来源有两种情况
// 第一种:来自 recentCornerCloudKeyFrames 此时有回环检测
// 第二种:来自 surroundingCornerCloudKeyFrames 此时没有使用回环检测
// 1. 根据周围关键帧点云创建kdtree(角特征点云、面特征点云)
kdtreeCornerFromMap->setInputCloud(laserCloudCornerFromMapDS);
kdtreeSurfFromMap->setInputCloud(laserCloudSurfFromMapDS);
for (int iterCount = 0; iterCount < 10; iterCount++) {
laserCloudOri->clear();
coeffSel->clear();
// 2.角和面特征计算距离
cornerOptimization(iterCount);
surfOptimization(iterCount);
// 3. LM优化
if (LMOptimization(iterCount) == true)
break;
}
// 此时迭代结束,更新转移矩阵
transformUpdate();
}
}
cornerOptimization()
void cornerOptimization(int iterCount){
updatePointAssociateToMapSinCos();
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudCornerLastDSNum; i++) {
pointOri = laserCloudCornerLastDS->points[i];
pointAssociateToMap(&pointOri, &pointSel);
// 1. 查找最近的5个点
kdtreeCornerFromMap->nearestKSearch(pointSel, 5, pointSearchInd, pointSearchSqDis);
// 2. 上述点距离小于1m
if (pointSearchSqDis[4] < 1.0) {
float cx = 0, cy = 0, cz = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
cx += laserCloudCornerFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].x;
cy += laserCloudCornerFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].y;
cz += laserCloudCornerFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].z;
}
// 3. 5个点的质心
cx /= 5; cy /= 5; cz /= 5;
float a11 = 0, a12 = 0, a13 = 0, a22 = 0, a23 = 0, a33 = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
float ax = laserCloudCornerFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].x - cx;
float ay = laserCloudCornerFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].y - cy;
float az = laserCloudCornerFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].z - cz;
a11 += ax * ax; a12 += ax * ay; a13 += ax * az;
a22 += ay * ay; a23 += ay * az;
a33 += az * az;
}
// 4. 协方差
a11 /= 5; a12 /= 5; a13 /= 5; a22 /= 5; a23 /= 5; a33 /= 5;
matA1.at<float>(0, 0) = a11; matA1.at<float>(0, 1) = a12; matA1.at<float>(0, 2) = a13;
matA1.at<float>(1, 0) = a12; matA1.at<float>(1, 1) = a22; matA1.at<float>(1, 2) = a23;
matA1.at<float>(2, 0) = a13; matA1.at<float>(2, 1) = a23; matA1.at<float>(2, 2) = a33;
cv::eigen(matA1, matD1, matV1);
if (matD1.at<float>(0, 0) > 3 * matD1.at<float>(0, 1)) {
float x0 = pointSel.x;
float y0 = pointSel.y;
float z0 = pointSel.z;
float x1 = cx + 0.1 * matV1.at<float>(0, 0);
float y1 = cy + 0.1 * matV1.at<float>(0, 1);
float z1 = cz + 0.1 * matV1.at<float>(0, 2);
float x2 = cx - 0.1 * matV1.at<float>(0, 0);
float y2 = cy - 0.1 * matV1.at<float>(0, 1);
float z2 = cz - 0.1 * matV1.at<float>(0, 2);
float a012 = sqrt(((x0 - x1)*(y0 - y2) - (x0 - x2)*(y0 - y1))
* ((x0 - x1)*(y0 - y2) - (x0 - x2)*(y0 - y1))
+ ((x0 - x1)*(z0 - z2) - (x0 - x2)*(z0 - z1))
* ((x0 - x1)*(z0 - z2) - (x0 - x2)*(z0 - z1))
+ ((y0 - y1)*(z0 - z2) - (y0 - y2)*(z0 - z1))
* ((y0 - y1)*(z0 - z2) - (y0 - y2)*(z0 - z1)));
float l12 = sqrt((x1 - x2)*(x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2)*(y1 - y2) + (z1 - z2)*(z1 - z2));
float la = ((y1 - y2)*((x0 - x1)*(y0 - y2) - (x0 - x2)*(y0 - y1))
+ (z1 - z2)*((x0 - x1)*(z0 - z2) - (x0 - x2)*(z0 - z1))) / a012 / l12;
float lb = -((x1 - x2)*((x0 - x1)*(y0 - y2) - (x0 - x2)*(y0 - y1))
- (z1 - z2)*((y0 - y1)*(z0 - z2) - (y0 - y2)*(z0 - z1))) / a012 / l12;
float lc = -((x1 - x2)*((x0 - x1)*(z0 - z2) - (x0 - x2)*(z0 - z1))
+ (y1 - y2)*((y0 - y1)*(z0 - z2) - (y0 - y2)*(z0 - z1))) / a012 / l12;
float ld2 = a012 / l12;
float s = 1 - 0.9 * fabs(ld2);
// 5. 计算coeff
coeff.x = s * la;
coeff.y = s * lb;
coeff.z = s * lc;
coeff.intensity = s * ld2;
if (s > 0.1) {
laserCloudOri->push_back(pointOri);
coeffSel->push_back(coeff);
}
}
}
}
}
surfOptimization()
void surfOptimization(int iterCount){
updatePointAssociateToMapSinCos();
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudSurfTotalLastDSNum; i++) {
pointOri = laserCloudSurfTotalLastDS->points[i];
pointAssociateToMap(&pointOri, &pointSel);
kdtreeSurfFromMap->nearestKSearch(pointSel, 5, pointSearchInd, pointSearchSqDis);
if (pointSearchSqDis[4] < 1.0) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
matA0.at<float>(j, 0) = laserCloudSurfFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].x;
matA0.at<float>(j, 1) = laserCloudSurfFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].y;
matA0.at<float>(j, 2) = laserCloudSurfFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].z;
}
cv::solve(matA0, matB0, matX0, cv::DECOMP_QR);
float pa = matX0.at<float>(0, 0);
float pb = matX0.at<float>(1, 0);
float pc = matX0.at<float>(2, 0);
float pd = 1;
float ps = sqrt(pa * pa + pb * pb + pc * pc);
pa /= ps; pb /= ps; pc /= ps; pd /= ps;
bool planeValid = true;
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
if (fabs(pa * laserCloudSurfFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].x +
pb * laserCloudSurfFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].y +
pc * laserCloudSurfFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].z + pd) > 0.2) {
planeValid = false;
break;
}
}
if (planeValid) {
float pd2 = pa * pointSel.x + pb * pointSel.y + pc * pointSel.z + pd;
float s = 1 - 0.9 * fabs(pd2) / sqrt(sqrt(pointSel.x * pointSel.x
+ pointSel.y * pointSel.y + pointSel.z * pointSel.z));
coeff.x = s * pa;
coeff.y = s * pb;
coeff.z = s * pc;
coeff.intensity = s * pd2;
if (s > 0.1) {
laserCloudOri->push_back(pointOri);
coeffSel->push_back(coeff);
}
}
}
}
}
LMOptimization()
bool LMOptimization(int iterCount){
float srx = sin(transformTobeMapped[0]);
float crx = cos(transformTobeMapped[0]);
float sry = sin(transformTobeMapped[1]);
float cry = cos(transformTobeMapped[1]);
float srz = sin(transformTobeMapped[2]);
float crz = cos(transformTobeMapped[2]);
int laserCloudSelNum = laserCloudOri->points.size();
if (laserCloudSelNum < 50) {
return false;
}
cv::Mat matA(laserCloudSelNum, 6, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matAt(6, laserCloudSelNum, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matAtA(6, 6, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matB(laserCloudSelNum, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matAtB(6, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matX(6, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
// 1. 遍历laserCloudSel
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudSelNum; i++) {
pointOri = laserCloudOri->points[i];
coeff = coeffSel->points[i];
float arx = (crx*sry*srz*pointOri.x + crx*crz*sry*pointOri.y - srx*sry*pointOri.z) * coeff.x
+ (-srx*srz*pointOri.x - crz*srx*pointOri.y - crx*pointOri.z) * coeff.y
+ (crx*cry*srz*pointOri.x + crx*cry*crz*pointOri.y - cry*srx*pointOri.z) * coeff.z;
float ary = ((cry*srx*srz - crz*sry)*pointOri.x
+ (sry*srz + cry*crz*srx)*pointOri.y + crx*cry*pointOri.z) * coeff.x
+ ((-cry*crz - srx*sry*srz)*pointOri.x
+ (cry*srz - crz*srx*sry)*pointOri.y - crx*sry*pointOri.z) * coeff.z;
float arz = ((crz*srx*sry - cry*srz)*pointOri.x + (-cry*crz-srx*sry*srz)*pointOri.y)*coeff.x
+ (crx*crz*pointOri.x - crx*srz*pointOri.y) * coeff.y
+ ((sry*srz + cry*crz*srx)*pointOri.x + (crz*sry-cry*srx*srz)*pointOri.y)*coeff.z;
matA.at<float>(i, 0) = arx;
matA.at<float>(i, 1) = ary;
matA.at<float>(i, 2) = arz;
matA.at<float>(i, 3) = coeff.x;
matA.at<float>(i, 4) = coeff.y;
matA.at<float>(i, 5) = coeff.z;
matB.at<float>(i, 0) = -coeff.intensity;
}
// 2. 最小二乘法
cv::transpose(matA, matAt);
matAtA = matAt * matA;
matAtB = matAt * matB;
cv::solve(matAtA, matAtB, matX, cv::DECOMP_QR);
if (iterCount == 0) {
cv::Mat matE(1, 6, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matV(6, 6, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matV2(6, 6, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::eigen(matAtA, matE, matV);
matV.copyTo(matV2);
isDegenerate = false;
float eignThre[6] = {100, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100};
for (int i = 5; i >= 0; i--) {
if (matE.at<float>(0, i) < eignThre[i]) {
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
matV2.at<float>(i, j) = 0;
}
isDegenerate = true;
} else {
break;
}
}
matP = matV.inv() * matV2;
}
if (isDegenerate) {
cv::Mat matX2(6, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
matX.copyTo(matX2);
matX = matP * matX2;
}
// 3. 获取transform
transformTobeMapped[0] += matX.at<float>(0, 0);
transformTobeMapped[1] += matX.at<float>(1, 0);
transformTobeMapped[2] += matX.at<float>(2, 0);
transformTobeMapped[3] += matX.at<float>(3, 0);
transformTobeMapped[4] += matX.at<float>(4, 0);
transformTobeMapped[5] += matX.at<float>(5, 0);
float deltaR = sqrt(
pow(pcl::rad2deg(matX.at<float>(0, 0)), 2) +
pow(pcl::rad2deg(matX.at<float>(1, 0)), 2) +
pow(pcl::rad2deg(matX.at<float>(2, 0)), 2));
float deltaT = sqrt(
pow(matX.at<float>(3, 0) * 100, 2) +
pow(matX.at<float>(4, 0) * 100, 2) +
pow(matX.at<float>(5, 0) * 100, 2));
if (deltaR < 0.05 && deltaT < 0.05) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
6. saveKeyFramesAndFactor()
通过前后2帧进行优化,保存优化后的位姿
saveKeyFramesAndFactor() 这个函数的主要作用就是选取关键帧。如果当前帧与上一帧之间的欧氏距离 大于 0.3 米 则认为是一个新的关键帧。此时需要计算出当前帧与与上一帧之间的约束情况。 这种约束可以认为是小回环,加入到后端中去优化。将优化后的结果作为关键帧的位姿与点云,然后同步到 scan -> map 过程中。
// 5. 保存关键帧和因子
void saveKeyFramesAndFactor(){
currentRobotPosPoint.x = transformAftMapped[3];
currentRobotPosPoint.y = transformAftMapped[4];
currentRobotPosPoint.z = transformAftMapped[5];
// 当前帧和之前帧的距离小于0.3米
bool saveThisKeyFrame = true;
if (sqrt((previousRobotPosPoint.x-currentRobotPosPoint.x)*(previousRobotPosPoint.x-currentRobotPosPoint.x)
+(previousRobotPosPoint.y-currentRobotPosPoint.y)*(previousRobotPosPoint.y-currentRobotPosPoint.y)
+(previousRobotPosPoint.z-currentRobotPosPoint.z)*(previousRobotPosPoint.z-currentRobotPosPoint.z)) < 0.3){
saveThisKeyFrame = false;
}
// saveThisKeyFrame为false,并且cloudKeyPoses3D不为空
if (saveThisKeyFrame == false && !cloudKeyPoses3D->points.empty())
return;
previousRobotPosPoint = currentRobotPosPoint;
/**
* update grsam graph 把当前pose加入grsam graph
*/
if (cloudKeyPoses3D->points.empty()){
//刚刚初始化,增加PriorFactor因子
gtSAMgraph.add(PriorFactor<Pose3>(0, Pose3(Rot3::RzRyRx(transformTobeMapped[2], transformTobeMapped[0], transformTobeMapped[1]),
Point3(transformTobeMapped[5], transformTobeMapped[3], transformTobeMapped[4])), priorNoise));
initialEstimate.insert(0, Pose3(Rot3::RzRyRx(transformTobeMapped[2], transformTobeMapped[0], transformTobeMapped[1]),
Point3(transformTobeMapped[5], transformTobeMapped[3], transformTobeMapped[4])));
for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i)
transformLast[i] = transformTobeMapped[i];
}
//非刚刚初始化,从transformLast获得上一次位姿
else{
gtsam::Pose3 poseFrom = Pose3(Rot3::RzRyRx(transformLast[2], transformLast[0], transformLast[1]),
Point3(transformLast[5], transformLast[3], transformLast[4]));
gtsam::Pose3 poseTo = Pose3(Rot3::RzRyRx(transformAftMapped[2], transformAftMapped[0], transformAftMapped[1]),
Point3(transformAftMapped[5], transformAftMapped[3], transformAftMapped[4]));
gtSAMgraph.add(BetweenFactor<Pose3>(cloudKeyPoses3D->points.size()-1, cloudKeyPoses3D->points.size(), poseFrom.between(poseTo), odometryNoise));
initialEstimate.insert(cloudKeyPoses3D->points.size(), Pose3(Rot3::RzRyRx(transformAftMapped[2], transformAftMapped[0], transformAftMapped[1]),
Point3(transformAftMapped[5], transformAftMapped[3], transformAftMapped[4])));
}
/**
* update iSAM 更新 iSAM
*/
isam->update(gtSAMgraph, initialEstimate); //第一个参数是新加到系统中的因子,第二个参数是新变量的初始点
isam->update();
gtSAMgraph.resize(0);
initialEstimate.clear();
/**
* save key poses 保存关键poses
*/
PointType thisPose3D;
PointTypePose thisPose6D;
Pose3 latestEstimate;
isamCurrentEstimate = isam->calculateEstimate();
latestEstimate = isamCurrentEstimate.at<Pose3>(isamCurrentEstimate.size()-1);
thisPose3D.x = latestEstimate.translation().y();
thisPose3D.y = latestEstimate.translation().z();
thisPose3D.z = latestEstimate.translation().x();
thisPose3D.intensity = cloudKeyPoses3D->points.size(); // this can be used as index
cloudKeyPoses3D->push_back(thisPose3D);
thisPose6D.x = thisPose3D.x;
thisPose6D.y = thisPose3D.y;
thisPose6D.z = thisPose3D.z;
thisPose6D.intensity = thisPose3D.intensity; // this can be used as index
thisPose6D.roll = latestEstimate.rotation().pitch();
thisPose6D.pitch = latestEstimate.rotation().yaw();
thisPose6D.yaw = latestEstimate.rotation().roll(); // in camera frame
thisPose6D.time = timeLaserOdometry;
cloudKeyPoses6D->push_back(thisPose6D);
/**
* save updated transform
*/
if (cloudKeyPoses3D->points.size() > 1){
transformAftMapped[0] = latestEstimate.rotation().pitch();
transformAftMapped[1] = latestEstimate.rotation().yaw();
transformAftMapped[2] = latestEstimate.rotation().roll();
transformAftMapped[3] = latestEstimate.translation().y();
transformAftMapped[4] = latestEstimate.translation().z();
transformAftMapped[5] = latestEstimate.translation().x();
for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i){
transformLast[i] = transformAftMapped[i];
transformTobeMapped[i] = transformAftMapped[i];
}
}
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr thisCornerKeyFrame(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr thisSurfKeyFrame(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr thisOutlierKeyFrame(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
pcl::copyPointCloud(*laserCloudCornerLastDS, *thisCornerKeyFrame);
pcl::copyPointCloud(*laserCloudSurfLastDS, *thisSurfKeyFrame);
pcl::copyPointCloud(*laserCloudOutlierLastDS, *thisOutlierKeyFrame);
// 保存点云
cornerCloudKeyFrames.push_back(thisCornerKeyFrame);
surfCloudKeyFrames.push_back(thisSurfKeyFrame);
outlierCloudKeyFrames.push_back(thisOutlierKeyFrame);
}
7. correctPoses()
回环检测如果成功,会设置 aLoopIsClosed 为 true,才会进行这一步。将 isam 优化后的位姿替换之前的位姿。
// 6. 校正位姿
void correctPoses(){
if (aLoopIsClosed == true){
recentCornerCloudKeyFrames. clear();
recentSurfCloudKeyFrames. clear();
recentOutlierCloudKeyFrames.clear();
// update key poses
// 1. 将isam优化后的位姿替换之前的位姿
int numPoses = isamCurrentEstimate.size();
for (int i = 0; i < numPoses; ++i){
cloudKeyPoses3D->points[i].x = isamCurrentEstimate.at<Pose3>(i).translation().y();
cloudKeyPoses3D->points[i].y = isamCurrentEstimate.at<Pose3>(i).translation().z();
cloudKeyPoses3D->points[i].z = isamCurrentEstimate.at<Pose3>(i).translation().x();
cloudKeyPoses6D->points[i].x = cloudKeyPoses3D->points[i].x;
cloudKeyPoses6D->points[i].y = cloudKeyPoses3D->points[i].y;
cloudKeyPoses6D->points[i].z = cloudKeyPoses3D->points[i].z;
cloudKeyPoses6D->points[i].roll = isamCurrentEstimate.at<Pose3>(i).rotation().pitch();
cloudKeyPoses6D->points[i].pitch = isamCurrentEstimate.at<Pose3>(i).rotation().yaw();
cloudKeyPoses6D->points[i].yaw = isamCurrentEstimate.at<Pose3>(i).rotation().roll();
}
aLoopIsClosed = false;
}
}
8. loopClosureThread() —— 回环检测
回环检测可以消除漂移(drift),通过ICP算法对比当前帧和之前帧是否匹配,如果匹配则进行图优化。
// 回环检测
void loopClosureThread(){
if (loopClosureEnableFlag == false)
return;
ros::Rate rate(1);
while (ros::ok()){
rate.sleep();
// 进行回环检测
performLoopClosure();
}
}
下面再看回环检测的过程。
判断是否进入回环在 detectLoopClosure 中进行,判断条件是首尾之间的距离小于7米,并且时间相差30s以上。
detectLoopClosure()
bool detectLoopClosure(){
latestSurfKeyFrameCloud->clear();
nearHistorySurfKeyFrameCloud->clear();
nearHistorySurfKeyFrameCloudDS->clear();
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mtx);
// find the closest history key frame
std::vector<int> pointSearchIndLoop;
std::vector<float> pointSearchSqDisLoop;
// 1. 查找当前点7米范围内是否有之前已经采样的点
kdtreeHistoryKeyPoses->setInputCloud(cloudKeyPoses3D);
kdtreeHistoryKeyPoses->radiusSearch(currentRobotPosPoint, historyKeyframeSearchRadius, pointSearchIndLoop, pointSearchSqDisLoop, 0);
closestHistoryFrameID = -1;
// 2. 时间相差30s以上
for (int i = 0; i < pointSearchIndLoop.size(); ++i){
int id = pointSearchIndLoop[i];
if (abs(cloudKeyPoses6D->points[id].time - timeLaserOdometry) > 30.0){
closestHistoryFrameID = id;
break;
}
}
if (closestHistoryFrameID == -1){
return false;
}
// save latest key frames 保存最新的关键帧
latestFrameIDLoopCloure = cloudKeyPoses3D->points.size() - 1;
*latestSurfKeyFrameCloud += *transformPointCloud(cornerCloudKeyFrames[latestFrameIDLoopCloure], &cloudKeyPoses6D->points[latestFrameIDLoopCloure]);
*latestSurfKeyFrameCloud += *transformPointCloud(surfCloudKeyFrames[latestFrameIDLoopCloure], &cloudKeyPoses6D->points[latestFrameIDLoopCloure]);
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr hahaCloud(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
int cloudSize = latestSurfKeyFrameCloud->points.size();
for (int i = 0; i < cloudSize; ++i){
if ((int)latestSurfKeyFrameCloud->points[i].intensity >= 0){
hahaCloud->push_back(latestSurfKeyFrameCloud->points[i]);
}
}
latestSurfKeyFrameCloud->clear();
*latestSurfKeyFrameCloud = *hahaCloud;
// save history near key frames
for (int j = -historyKeyframeSearchNum; j <= historyKeyframeSearchNum; ++j){
if (closestHistoryFrameID + j < 0 || closestHistoryFrameID + j > latestFrameIDLoopCloure)
continue;
*nearHistorySurfKeyFrameCloud += *transformPointCloud(cornerCloudKeyFrames[closestHistoryFrameID+j], &cloudKeyPoses6D->points[closestHistoryFrameID+j]);
*nearHistorySurfKeyFrameCloud += *transformPointCloud(surfCloudKeyFrames[closestHistoryFrameID+j], &cloudKeyPoses6D->points[closestHistoryFrameID+j]);
}
downSizeFilterHistoryKeyFrames.setInputCloud(nearHistorySurfKeyFrameCloud);
downSizeFilterHistoryKeyFrames.filter(*nearHistorySurfKeyFrameCloudDS);
// publish history near key frames
if (pubHistoryKeyFrames.getNumSubscribers() != 0){
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 cloudMsgTemp;
pcl::toROSMsg(*nearHistorySurfKeyFrameCloudDS, cloudMsgTemp);
cloudMsgTemp.header.stamp = ros::Time().fromSec(timeLaserOdometry);
cloudMsgTemp.header.frame_id = "/camera_init";
pubHistoryKeyFrames.publish(cloudMsgTemp);
}
return true;
}
如果检测到回环之后,接着进行ICP匹配,然后进行图优化。作者同时提醒回环检测的ICP算法当里程计漂移太大时经常失败。对于更高级的闭环方法,建议采样 SC-LeGO-LOAM ,它的特征采用的是点云描述符。
performLoopClosure()
void performLoopClosure(){
if (cloudKeyPoses3D->points.empty() == true)
return;
// try to find close key frame if there are any 尝试去寻找回环点
if (potentialLoopFlag == false){
if (detectLoopClosure() == true){
potentialLoopFlag = true; // find some key frames that is old enough or close enough for loop closure
timeSaveFirstCurrentScanForLoopClosure = timeLaserOdometry;
}
if (potentialLoopFlag == false)
return;
}
// reset the flag first no matter icp successes or not
potentialLoopFlag = false;
// ICP Settings
pcl::IterativeClosestPoint<PointType, PointType> icp;
icp.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance(100);
icp.setMaximumIterations(100);
icp.setTransformationEpsilon(1e-6);
icp.setEuclideanFitnessEpsilon(1e-6);
icp.setRANSACIterations(0);
// Align clouds
// 匹配当前帧点云和之前的历史点云
icp.setInputSource(latestSurfKeyFrameCloud);
icp.setInputTarget(nearHistorySurfKeyFrameCloudDS);
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr unused_result(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
icp.align(*unused_result);
if (icp.hasConverged() == false || icp.getFitnessScore() > historyKeyframeFitnessScore)
return;
// publish corrected cloud
// 发布校正之后的点云
if (pubIcpKeyFrames.getNumSubscribers() != 0){
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr closed_cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
pcl::transformPointCloud (*latestSurfKeyFrameCloud, *closed_cloud, icp.getFinalTransformation());
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 cloudMsgTemp;
pcl::toROSMsg(*closed_cloud, cloudMsgTemp);
cloudMsgTemp.header.stamp = ros::Time().fromSec(timeLaserOdometry);
cloudMsgTemp.header.frame_id = "/camera_init";
pubIcpKeyFrames.publish(cloudMsgTemp);
}
/*
get pose constraint
*/
float x, y, z, roll, pitch, yaw;
Eigen::Affine3f correctionCameraFrame;
correctionCameraFrame = icp.getFinalTransformation(); // get transformation in camera frame (because points are in camera frame)
pcl::getTranslationAndEulerAngles(correctionCameraFrame, x, y, z, roll, pitch, yaw);
Eigen::Affine3f correctionLidarFrame = pcl::getTransformation(z, x, y, yaw, roll, pitch);
// transform from world origin to wrong pose
Eigen::Affine3f tWrong = pclPointToAffine3fCameraToLidar(cloudKeyPoses6D->points[latestFrameIDLoopCloure]);
// transform from world origin to corrected pose
Eigen::Affine3f tCorrect = correctionLidarFrame * tWrong; // pre-multiplying -> successive rotation about a fixed frame
pcl::getTranslationAndEulerAngles (tCorrect, x, y, z, roll, pitch, yaw);
gtsam::Pose3 poseFrom = Pose3(Rot3::RzRyRx(roll, pitch, yaw), Point3(x, y, z));
gtsam::Pose3 poseTo = pclPointTogtsamPose3(cloudKeyPoses6D->points[closestHistoryFrameID]);
gtsam::Vector Vector6(6);
float noiseScore = icp.getFitnessScore();
Vector6 << noiseScore, noiseScore, noiseScore, noiseScore, noiseScore, noiseScore;
constraintNoise = noiseModel::Diagonal::Variances(Vector6);
/*
add constraints
添加约束
*/
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mtx);
gtSAMgraph.add(BetweenFactor<Pose3>(latestFrameIDLoopCloure, closestHistoryFrameID, poseFrom.between(poseTo), constraintNoise));
isam->update(gtSAMgraph);
isam->update();
gtSAMgraph.resize(0);
aLoopIsClosed = true;
}
4、transformFusion —— 融合粗、精配准的里程计信息
0. main()
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "lego_loam");
TransformFusion TFusion; //构造函数,重要的两个回调函数
ROS_INFO("\033[1;32m---->\033[0m Transform Fusion Started.");
ros::spin();
return 0;
}
1. laserOdometryHandler()
laserOdometryHandler 是将粗配准的里程计信息与精配准的里程计信息融合计算,并在回调函数中便发送了最终外发的里程计话题。在该回调函数中的TF与里程计话题才是最终决定的。
void laserOdometryHandler(const nav_msgs::Odometry::ConstPtr& laserOdometry)
{
currentHeader = laserOdometry->header;
double roll, pitch, yaw;
geometry_msgs::Quaternion geoQuat = laserOdometry->pose.pose.orientation;
tf::Matrix3x3(tf::Quaternion(geoQuat.z, -geoQuat.x, -geoQuat.y, geoQuat.w)).getRPY(roll, pitch, yaw);
transformSum[0] = -pitch;
transformSum[1] = -yaw;
transformSum[2] = roll;
transformSum[3] = laserOdometry->pose.pose.position.x;
transformSum[4] = laserOdometry->pose.pose.position.y;
transformSum[5] = laserOdometry->pose.pose.position.z;
//点云坐标转化到世界坐标
//位姿与速度的融合计算
transformAssociateToMap();
geoQuat = tf::createQuaternionMsgFromRollPitchYaw
(transformMapped[2], -transformMapped[0], -transformMapped[1]);
laserOdometry2.header.stamp = laserOdometry->header.stamp;
laserOdometry2.pose.pose.orientation.x = -geoQuat.y;
laserOdometry2.pose.pose.orientation.y = -geoQuat.z;
laserOdometry2.pose.pose.orientation.z = geoQuat.x;
laserOdometry2.pose.pose.orientation.w = geoQuat.w;
laserOdometry2.pose.pose.position.x = transformMapped[3];
laserOdometry2.pose.pose.position.y = transformMapped[4];
laserOdometry2.pose.pose.position.z = transformMapped[5];
pubLaserOdometry2.publish(laserOdometry2);
laserOdometryTrans2.stamp_ = laserOdometry->header.stamp;
laserOdometryTrans2.setRotation(tf::Quaternion(-geoQuat.y, -geoQuat.z, geoQuat.x, geoQuat.w));
laserOdometryTrans2.setOrigin(tf::Vector3(transformMapped[3], transformMapped[4], transformMapped[5]));
tfBroadcaster2.sendTransform(laserOdometryTrans2);
}
2. odomAftMappedHandler()
通过 odomAftMappedHandler 函数获取精配准后的位姿作为 transformAftMapped,而获取配准后的速度信息作为 transformBefMapped 准备下一次计算。
void odomAftMappedHandler(const nav_msgs::Odometry::ConstPtr& odomAftMapped)
{
double roll, pitch, yaw;
geometry_msgs::Quaternion geoQuat = odomAftMapped->pose.pose.orientation;
tf::Matrix3x3(tf::Quaternion(geoQuat.z, -geoQuat.x, -geoQuat.y, geoQuat.w)).getRPY(roll, pitch, yaw);
//位姿作为计算的基础
transformAftMapped[0] = -pitch;
transformAftMapped[1] = -yaw;
transformAftMapped[2] = roll;
transformAftMapped[3] = odomAftMapped->pose.pose.position.x;
transformAftMapped[4] = odomAftMapped->pose.pose.position.y;
transformAftMapped[5] = odomAftMapped->pose.pose.position.z;
//速度作为下一次计算的先验
transformBefMapped[0] = odomAftMapped->twist.twist.angular.x;
transformBefMapped[1] = odomAftMapped->twist.twist.angular.y;
transformBefMapped[2] = odomAftMapped->twist.twist.angular.z;
transformBefMapped[3] = odomAftMapped->twist.twist.linear.x;
transformBefMapped[4] = odomAftMapped->twist.twist.linear.y;
transformBefMapped[5] = odomAftMapped->twist.twist.linear.z;
}
粗配准的里程计信息是FeatureAssociation发出的,精配准的信息是mapOptimization发出的,均以200Hz的频率,当odomAftMappedHandler收到精配准信息后更新位姿,这个位姿将在laserOdometryHandler收到下一条粗配准信息后综合计算再发出。
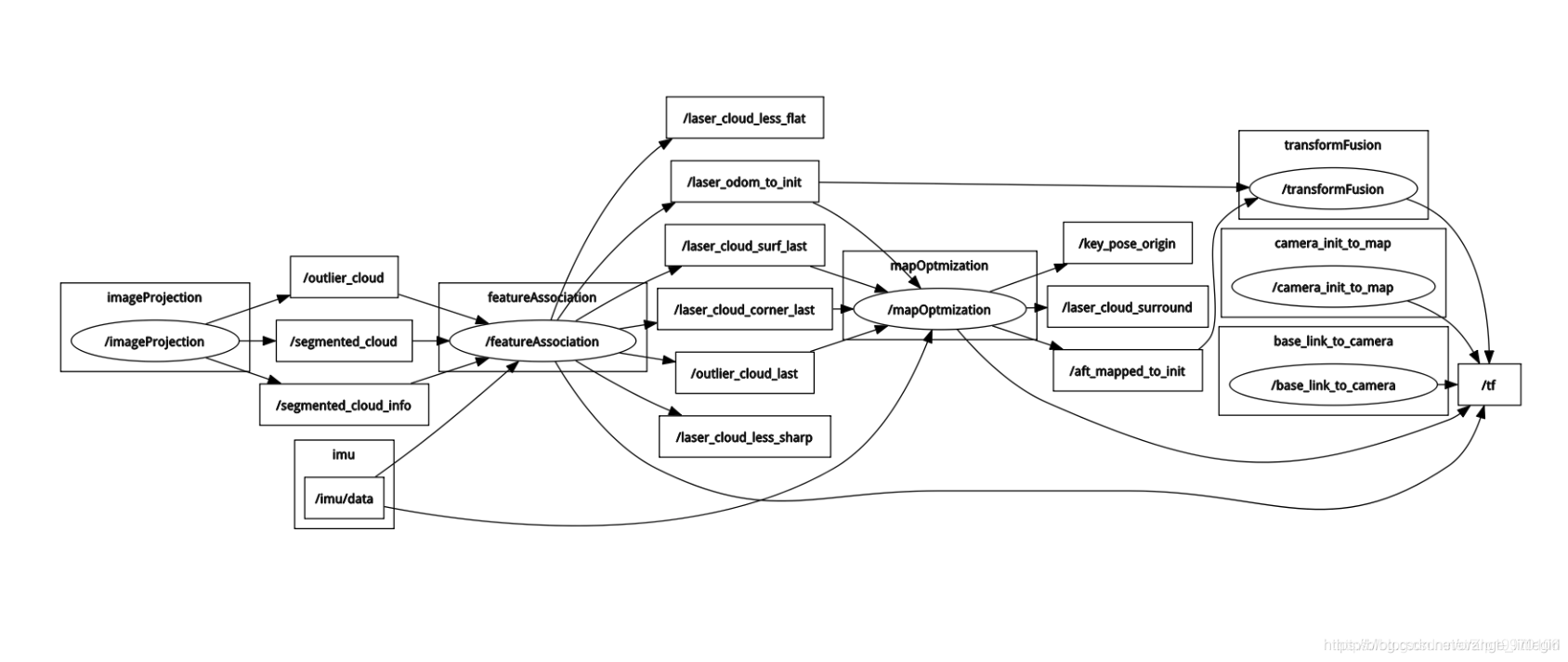
参考:
- LeGO-LOAM分析之特征提取(一)【王方浩】
- LeGO-LOAM分析之特征提取(二)【王方浩】
- LeGO-LOAM分析之建图(三)【王方浩】
- LeGo-LOAM源码篇:源码分析(1)
- LeGo-LOAM源码篇:源码分析(2)
- LeGo-LOAM源码篇:源码分析(3)
- Lego_Loam–源码分析
- LeGo-LOAM源码阅读笔记(五)—transformFusion.cpp
- gtsam_tutorial
另:(有时间再看)
- LeGo-LOAM源码阅读笔记