目录
1 主要内容
2 部分代码
3 程序结果
4 下载链接
1 主要内容
该程序复现《IHAOAVOA: An improved hybrid aquila optimizer and African vultures optimization algorithm for global optimization problems》,天鹰优化算法(AO)和非洲秃鹫算法(AVOA)各有优势:AO具有强大的全局勘探能力,但其局部开发阶段还不够稳定。另一方面,AVOA具有良好的开发能力,但勘探机制不足。基于这两种算法的特点,提出了一种改进的AO和AVOA混合优化算法,以克服单一算法的不足,为解决全局优化问题提供了更高质量的解决方案。
大家在学习和建立模型过程中,很难原创性的找到智能优化算法,一开始简单的算法改进,如粒子群中的权重非线性化或者种群精英化等均可以提升算法创新性,但是随着各种组合创新的出现,智能算法创新需要结合的方法越来越多,也需要越来越新颖,因此各种文献都祭出多种算法结合的“混合”优化算法,本次分享的两种算法结合的优化代码很具有参考意义,程序采用matlab编程,提供了23个测试函数,通过修改主函数的Function_name即可分别检查该算法对不同测试函数的性能。

- IHAOAVOA流程图
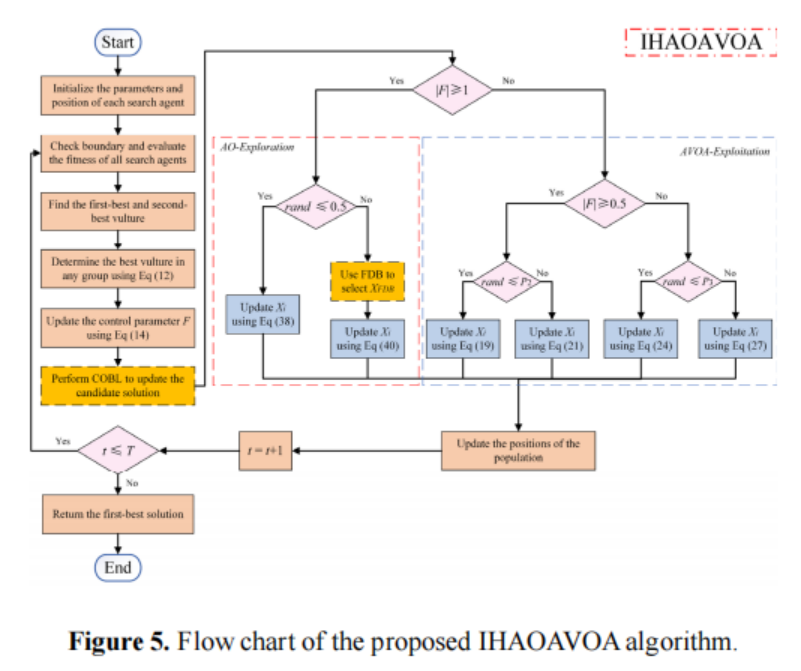
- 主要创新点
- 增加复合学习算法(COBL)
COBL是智能算法中一个强大的优化工具,已成功用于改进不同的原生元启发式算,主要思想是同时评价当前解的适应度值及其反向解,然后保留更适合的适应度值参与后续的迭代计算。因此,OBL可以有效地增加找到更好的候选解的可能性。
2.结合AO的勘探阶段和AVOA的开发阶段
综合两个算法的优势,实现更加快速找到最优值的作用。
2 部分代码
% The IHAOAVOA Optimization Algorithm
function [ihaoavoa_score,ihaoavoa_pos,ihaoavoa_curve]=IHAOAVOA(N,max_iter,lb,ub,dim,fobj)
tic
% initialize Best_vulture1, Best_vulture2
ihaoavoa_pos=zeros(1,dim);
ihaoavoa_score=inf;
Best_vulture2_X=zeros(1,dim);
Best_vulture2_F=inf;
%Initialize the first random population of vultures
X=initialization(N,dim,ub,lb);
%% Controlling parameter
%/********AVOA**********/
p2=0.4;
p3=0.6;
alpha=0.8;
betha=0.2;
gamma=2.5;
%/********AO**********/
avto = 1:dim;
u = .0265;
r0 = 10;
rao = r0 +u*avto;
omega = .005;
phi0 = 3*pi/2;
phi = -omega*avto+phi0;
x = rao .* sin(phi);
y = rao .* cos(phi);
%/********LOBL**********/
k=12000; % Scale Coefficient
t=1; % Loop counter
%%Main loop
while t <= max_iter
%% Evaluate the fitness
for i=1:size(X,1)
% Calculate the fitness of the population
current_vulture_X = X(i,:);
current_vulture_F=fobj(current_vulture_X);
% Update the first best two vultures if needed
if current_vulture_Fif current_vulture_F>ihaoavoa_score && current_vulture_F2,2,1,1)*((sin((pi/2)*(t/max_iter))^gamma)+cos((pi/2)*(t/max_iter))-1);
P1=(2*rand+1)*(1-(t/max_iter))+a;
%% FDB
index = fitnessDistanceBalance(X,ihaoavoa_score);
%% Update the location
for i=1:size(X,1)
current_vulture_X = X(i,:); % pick the current vulture back to the population
F=P1*(2*rand()-1);
random_vulture_X=random_select(ihaoavoa_pos,Best_vulture2_X,alpha,betha);
%% Composite opposition-based learning strategy (COBL)
if rand<0.5
opposite_X=lb+ub-rand*current_vulture_X;
else
opposite_X=(ub + lb)/2 + (ub + lb)/(2*k) - current_vulture_X/k;
end
Flag_UB=opposite_X>ub; % check if they exceed (up) the boundaries
Flag_LB=opposite_Xif they exceed (down) the boundaries
opposite_X=(opposite_X.*(~(Flag_UB+Flag_LB)))+ub.*Flag_UB+lb.*Flag_LB;
Fnew=fobj(opposite_X);
if Fnewif Fnewif abs(F) >= 1
if rand <0.5
current_vulture_X=ihaoavoa_pos*(1-t/max_iter)+(mean(X(i,:))-ihaoavoa_pos)*rand();
else
current_vulture_X=ihaoavoa_pos.*Levy(dim)+X(index,:)+(y-x)*rand;
end
%% Exploitation stage:AVOA
elseif abs(F) < 1
current_vulture_X = exploitation(current_vulture_X, ihaoavoa_pos, Best_vulture2_X, random_vulture_X, F, p2, p3, dim, ub, lb); % Modified the position-weighted equation
end
X(i,:) = current_vulture_X; % place the current vulture back into the population
end
3 程序结果
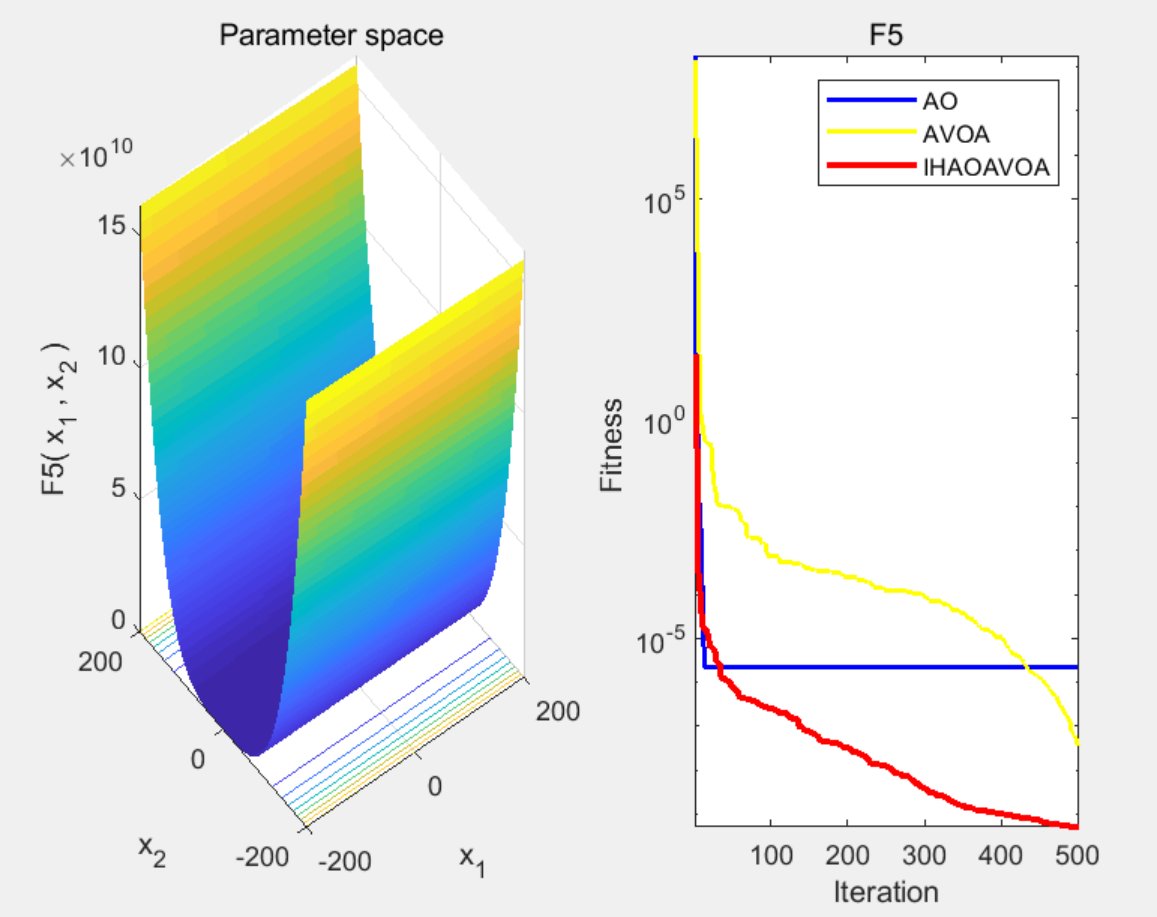

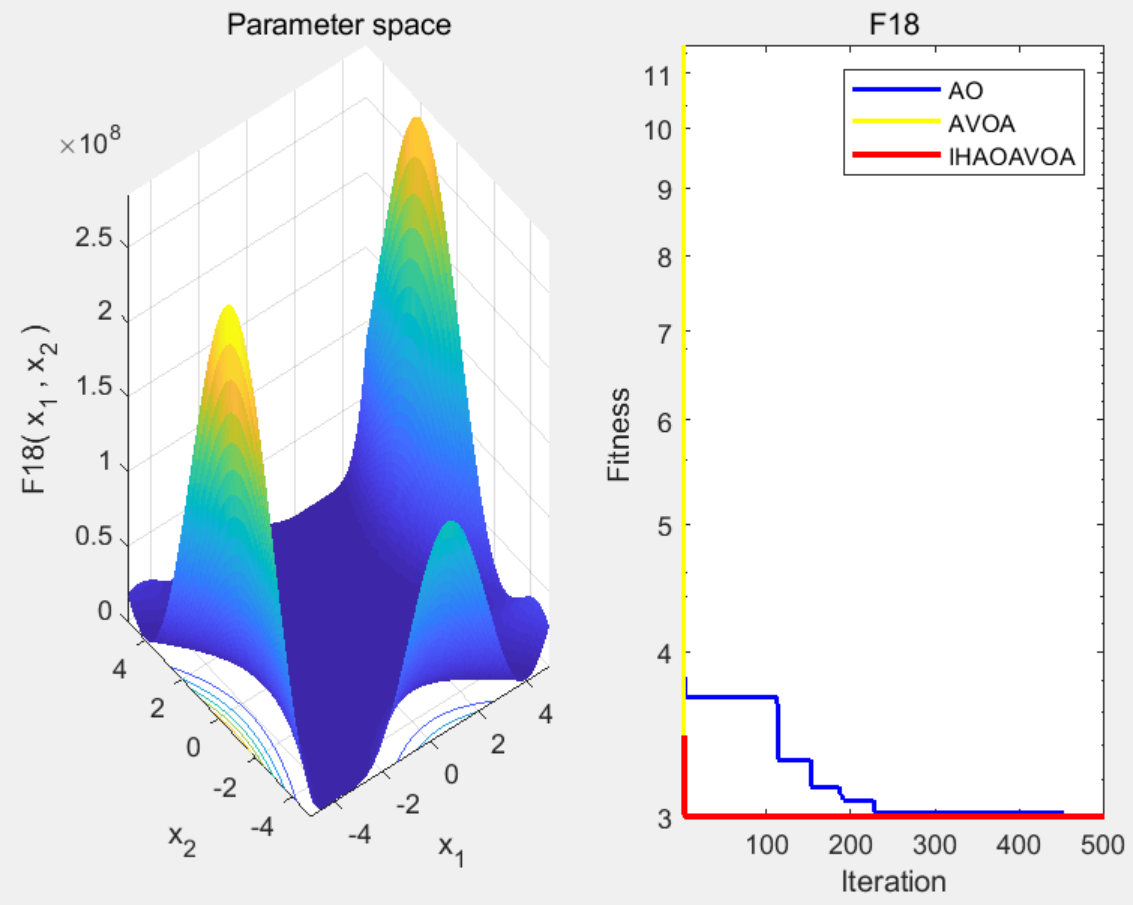
4 下载链接
见下方联系方式->程序目录






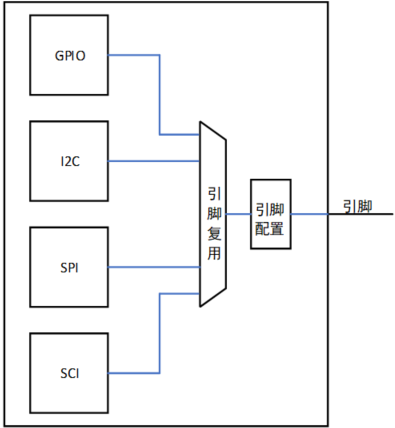

![[XSCTF]easyxor](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5ae276a2b4f741629aa1354e7cf4a914.png)
