目录
1--虚拟头节点的使用
2--设计链表
3--反转链表
4--两两交换链表中的节点
5--快慢指针
5-1--删除链表倒数第N个节点
5-2--环形链表
5-3--环形链表II
1--虚拟头节点的使用
在链表相关题目中,常新定义一个虚拟头结点 dummynode 来指向原链表的头结点,当需要返回链表时,只需返回 dummynode->next;

#include <iostream>
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
if(head==nullptr) return head;
ListNode* dummynode = new ListNode(); // 新建虚拟头结点
dummynode->next = head;
ListNode* cur = dummynode;
while(cur->next != nullptr){
if(cur->next->val == val){
ListNode* tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
delete tmp;
tmp = nullptr;
}
else{
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return dummynode->next;
}
};
int main(int arc, char *argv[]){
ListNode* Node1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode* Node2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode* Node3 = new ListNode(6);
ListNode* Node4 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode* Node5 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode* Node6 = new ListNode(5);
ListNode* Node7 = new ListNode(6);
Node1->next = Node2;
Node2->next = Node3;
Node3->next = Node4;
Node4->next = Node5;
Node5->next = Node6;
Node6->next = Node7;
Solution S1;
int val = 6;
ListNode* res = S1.removeElements(Node1, val);
ListNode* cur = res;
while(cur != NULL){
std::cout << cur->val << " ";
cur = cur->next;
}
return 0;
}2--设计链表

#include <iostream>
class MyLinkedList {
public:
// 定义链表节点结构体
struct LinkedNode {
int val;
LinkedNode* next;
LinkedNode(int val):val(val), next(nullptr){}
};
// 初始化链表
MyLinkedList() {
_dummyHead = new LinkedNode(0); // 虚拟头结点
_size = 0;
}
int get(int index) {
if (index > (_size - 1) || index < 0) { // 不合法index
return -1;
}
LinkedNode* cur = _dummyHead->next;
while(index--){
cur = cur->next;
}
return cur->val;
}
void addAtHead(int val) {
LinkedNode* newNode = new LinkedNode(val);
newNode->next = _dummyHead->next;
_dummyHead->next = newNode;
_size++;
}
void addAtTail(int val) {
LinkedNode* newNode = new LinkedNode(val);
LinkedNode* cur = _dummyHead;
while(cur->next != nullptr){
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = newNode;
_size++;
}
void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if(index > _size) return;
if(index < 0) index = 0;
LinkedNode* newNode = new LinkedNode(val);
LinkedNode* cur = _dummyHead;
while(index--) {
cur = cur->next;
}
newNode->next = cur->next;
cur->next = newNode;
_size++;
}
void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if (index >= _size || index < 0) {
return;
}
LinkedNode* cur = _dummyHead;
while(index--) {
cur = cur ->next;
}
LinkedNode* tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
delete tmp;
tmp=nullptr;
_size--;
}
// 打印链表
void printLinkedList() {
LinkedNode* cur = _dummyHead;
while (cur->next != nullptr) {
std::cout << cur->next->val << " ";
cur = cur->next;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
private:
int _size;
LinkedNode* _dummyHead;
};
int main(int arc, char *argv[]){
MyLinkedList myLinkedList;
myLinkedList.addAtHead(1);
myLinkedList.addAtTail(3);
myLinkedList.addAtIndex(1, 2); // 链表变为 1->2->3
std::cout << myLinkedList.get(1) << std::endl; // 返回 2
myLinkedList.deleteAtIndex(1); // 现在,链表变为 1->3
std::cout << myLinkedList.get(1) << std::endl; // 返回 3
return 0;
}3--反转链表

双指针解法:
#include <iostream>
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head){
if(head == nullptr) return head;
ListNode *pre = nullptr;
ListNode *cur = head;
while(cur != NULL){
ListNode *tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
return pre;
}
};
int main(int arc, char *argv[]){
ListNode *Node1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode *Node2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode *Node3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode *Node4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode *Node5 = new ListNode(5);
Node1->next = Node2;
Node2->next = Node3;
Node3->next = Node4;
Node4->next = Node5;
Solution S1;
ListNode *res = S1.reverseList(Node1);
ListNode *cur = res;
while(cur != NULL){
std::cout << cur->val << " ";
cur = cur->next;
}
return 0;
}递归写法:
#include <iostream>
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head){
if(head == nullptr) return head;
return reverse(head, nullptr);
}
ListNode* reverse(ListNode* cur, ListNode* pre){
if(cur == nullptr) return pre;
ListNode *tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
return reverse(tmp, cur);
}
};
int main(int arc, char *argv[]){
ListNode *Node1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode *Node2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode *Node3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode *Node4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode *Node5 = new ListNode(5);
Node1->next = Node2;
Node2->next = Node3;
Node3->next = Node4;
Node4->next = Node5;
Solution S1;
ListNode *res = S1.reverseList(Node1);
ListNode *cur = res;
while(cur != NULL){
std::cout << cur->val << " ";
cur = cur->next;
}
return 0;
}4--两两交换链表中的节点

#include <iostream>
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
if(head == nullptr) return head;
ListNode *dummyNode = new ListNode();
dummyNode->next = head;
ListNode *cur = dummyNode;
while(cur->next != nullptr && cur->next->next != nullptr){
ListNode *tmp1 = cur->next;
ListNode *tmp2 = cur->next->next->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
cur->next->next = tmp1;
tmp1->next = tmp2;
cur = cur->next->next;
}
return dummyNode->next;
}
};
int main(int arc, char *argv[]){
ListNode *Node1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode *Node2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode *Node3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode *Node4 = new ListNode(4);
Node1->next = Node2;
Node2->next = Node3;
Node3->next = Node4;
Solution S1;
ListNode *res = S1.swapPairs(Node1);
ListNode *cur = res;
while(cur != NULL){
std::cout << cur->val << " ";
cur = cur->next;
}
return 0;
}5--快慢指针
5-1--删除链表倒数第N个节点
快慢指针

#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode *dummyNode = new ListNode();
dummyNode->next = head;
ListNode* slow = dummyNode;
ListNode* fast = dummyNode;
while(n-- && fast != NULL){
fast = fast->next;
}
while(fast->next != NULL){
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
ListNode *target = slow->next;
slow->next = target->next;
delete target;
target = nullptr;
return dummyNode->next;
}
};
int main(int argc, char argv[]){
ListNode *Node1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode *Node2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode *Node3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode *Node4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode *Node5 = new ListNode(5);
Node1->next = Node2;
Node2->next = Node3;
Node3->next = Node4;
Node4->next = Node5;
int n = 2;
Solution S1;
ListNode *res = S1.removeNthFromEnd(Node1, n);
ListNode *cur = res;
while(cur != NULL){
std::cout << cur->val << " ";
cur = cur->next;
}
return 0;
}5-2--环形链表

快慢指针,当链表有环时,快慢指针必定相遇;
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
if(head == nullptr) return false;
ListNode *slow = head;
ListNode *fast = head;
while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if(slow == fast) break;
}
if(fast == NULL || fast->next == NULL) return false;
else return true;
}
};
int main(int argc, char argv[]){
ListNode *Node1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode *Node2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode *Node3 = new ListNode(0);
ListNode *Node4 = new ListNode(-4);
Node1->next = Node2;
Node2->next = Node3;
Node3->next = Node4;
Node4->next = Node2;
Solution S1;
bool res = S1.hasCycle(Node1);
if(res) std::cout << "true" << std::endl;
else std::cout << "false" << std::endl;
return 0;
}5-3--环形链表II
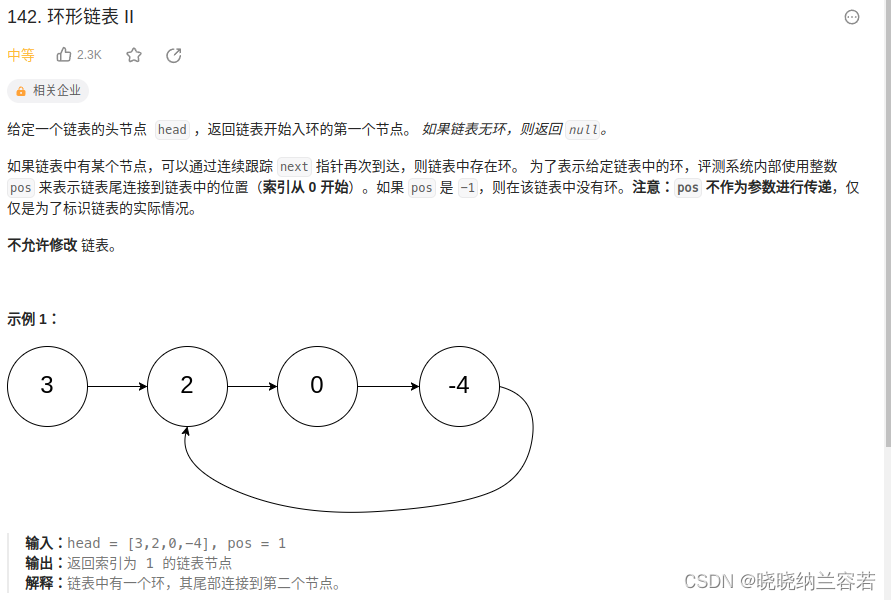
快慢指针,快指针每次走两步,慢指针每次走一步,根据快慢指针是否相遇判断是否有环;
当快慢指针第一次相遇后,慢指针从头出发,快指针从第一次相遇的节点出发,快慢指针均每次走一步,当下一次相遇时就处于环的入口节点,返回即可;
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
if(head == nullptr) return head;
ListNode *slow = head;
ListNode *fast = head;
while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if(fast == slow) break; // 第一次相遇
}
if(fast == NULL || fast->next == NULL) return NULL; // 没有环
// 从头开始走
slow = head;
while(slow != fast){
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
// 第二次相遇就是环的入口
return slow;
}
};
int main(int argc, char argv[]){
ListNode *Node1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode *Node2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode *Node3 = new ListNode(0);
ListNode *Node4 = new ListNode(-4);
Node1->next = Node2;
Node2->next = Node3;
Node3->next = Node4;
Node4->next = Node2;
Solution S1;
ListNode * res = S1.detectCycle(Node1);
std::cout << res->val << std::endl;
return 0;
}