目录
1.Spring简介
1.1Spring框架的核心特性
2.Spring IoC容器
2.1Spring IoC容器特点
2.2出现的背景
2.3关于IoC的理解
2.4案例演示
3.Spring注入方式
3.1set注入
3.2构造注入
3.3接口注入
4.Spring上下文与tomcat整合
4.1思考
4.2代码演示
4.3收获
1.Spring简介
Spring是一个开源的应用程序开发框架,它由Rod Johnson创建,主要用于构建企业级Java应用程序。它提供了一个全面的编程和配置模型,可以简化Java开发过程,提高开发效率和可维护性。即为了解决企业应用开发的复杂性而创建的。Spring使用基本的JavaBean来完成以前只可能由EJB完成的事情。
目的:解决企业应用开发的复杂性
功能:使用基本的JavaBean代替EJB,并提供了更多的企业应用功能
范围:任何Java应用
简单来说,Spring是一个轻量级的控制反转(IoC)和面向切面(AOP)的容器框架。
1.1Spring框架的核心特性
Spring框架的核心特性包括:
IoC容器:Spring的IoC(Inversi on of Control)容器管理对象的生命周期和依赖关系,通过依赖注入(DI)将对象的依赖关系外部化,降低了组件之间的耦合度,增强了代码的可测试性。
AOP支持:Spring提供了强大的面向切面编程(AOP)支持,可以实现横切关注点的模块化,例如日志记录、事务管理等功能,将它们与业务逻辑分离。
数据访问抽象层:Spring提供了包括JDBC、ORM(如Hibernate、MyBatis)等在内的数据访问抽象层,简化了数据库操作的编码工作,并提供了一致的异常处理机制。
MVC框架:Spring MVC是一个基于模型-视图-控制器模式的Web应用程序框架,用于构建灵活而功能强大的Web应用程序。它与Spring框架紧密集成,可以方便地进行请求处理、表单验证、视图渲染等等。
安全性:Spring提供了安全性模块,支持基于角色的访问控制和认证。
容器扩展:Spring框架可以通过扩展点和插件机制进行定制和扩展,以满足特定业务需求。
2.Spring IoC容器
2.1Spring IoC容器特点
实例化对象的权力由程序员转变为Spring IoC容器。
2.2出现的背景
IoC(Inversion of Control)出现的背景可以追溯到软件开发领域中的耦合和复杂性问题。
在传统的软件开发中,对象之间的依赖关系通常是硬编码在代码中的,对象之间直接进行创建和调用。这种紧耦合的设计导致了代码的复杂性和可维护性的下降。当需要修改某个对象的依赖关系时,必须修改代码并重新编译整个应用程序,这样显著增加了开发和维护的成本。
为了解决这些问题,IoC的概念逐渐被引入。
2.3关于IoC的理解
- 控制反转(IoC):将实例化对象的权力,由程序员控制转交给Spring容器来控制(权力的转交被称为反转)。
- 本质:IoC的本质是控制对象的创建和依赖关系的权力由调用者转移到了外部容器,也就是所谓的控制反转。它通过将对象的创建、初始化和依赖关系的管理交给容器来实现。
- 出现的原因:IoC的出现主要是为了解决传统软件开发中的耦合和复杂性问题,通过将对象的创建和依赖管理交给容器来实现控制反转,从而提高代码的模块化、可维护性和可测试性。
它通过将对象的创建、初始化和依赖关系的管理交给容器来实现。调用者只需要声明需要哪些对象和依赖,而无需关心对象的创建过程和依赖关系的维护。这种松散的耦合使得代码更加模块化、可扩展和易于测试。
2.4案例演示
在进行案例演示前我们需要进行项目对象模型的配置,如下,
pom.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>testspring</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>testspring Maven Webapp</name>
<!-- FIXME change it to the project's website -->
<url>http://www.example.com</url>
<properties>
<spring.version>5.0.1.RELEASE</spring.version>
<javax.servlet.version>4.0.0</javax.servlet.version>
<junit.version>4.12</junit.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- 2、导入spring依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 5.1、junit -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>${junit.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- 5.2、servlet -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>${javax.servlet.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>testspring</finalName>
<pluginManagement><!-- lock down plugins versions to avoid using Maven defaults (may be moved to parent pom) -->
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-clean-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</plugin>
<!-- see http://maven.apache.org/ref/current/maven-core/default-bindings.html#Plugin_bindings_for_war_packaging -->
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.0</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.22.1</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-install-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.5.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-deploy-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.8.2</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build>
</project>
然后就按照以下目录列表创建项目,如下:
UserService接口:
package com.kissship.ioc.service;
/**
* @author Kissship
* @site www.Kissship.com
* @company xxx公司
* @create 2023-08-15-14:50
*
* 用户更改个人信息的接口
*/
public interface UserService {
public void update();
}
UserServiceImpl1:
package com.kissship.ioc.service.impl;
import com.kissship.ioc.service.UserService;
/**
* @author Kissship
* @site www.Kissship.com
* @company xxx公司
* @create 2023-08-15-14:52
*
* 客户的需求
* 需求:客户在登录后需要具备更改个人信息的功能
*
* 场景1:
* 客户要求,在新增的需求上做迭代版本,如上传头像
*
* 场景2:
* ...
* 客户要求,在新增的需求上做优化,提升性能,如使用多线程
*/
public class UserServiceImpl1 implements UserService {
public void update() {
System.out.println("更改个人用户信息(普通用户功能)");
//添加上传头像功能的代码
// System.out.println("上传头像的功能");
}
}
UserServiceImpl2:
package com.kissship.ioc.service.impl;
import com.kissship.ioc.service.UserService;
/**
* @author Kissship
* @site www.Kissship.com
* @company xxx公司
* @create 2023-08-15-14:52
*
* 客户的需求
* 需求:客户在登录后需要具备更改个人信息的功能
*
* 场景1:
* 客户要求,在新增的需求上做迭代版本,如上传头像
*
* 场景2:
* ...
* 客户要求,在新增的需求上做优化,提升性能,如使用多线程
*/
public class UserServiceImpl2 implements UserService {
public void update() {
System.out.println("更改个人用户信息(普通用户功能)");
//添加上传头像功能的代码
System.out.println("上传头像的功能(会员用户功能)");
}
}
UserAction:
package com.kissship.ioc.web;
import com.kissship.ioc.service.UserService;
/**
* @author Kissship
* @site www.Kissship.com
* @company xxx公司
* @create 2023-08-15-15:04
*
* 程序员手动实例化对象的弊端:
* 1.一旦依赖的接口的实现需要大批量改动,迭代,维护的成本极高
* 2.当接口的实现类不同时,维护的成本高
*/
public class UserAction {
private UserService userService;
public UserService getUserService() {
return userService;
}
public void setUserService(UserService userService) {
this.userService = userService;
}
public String updata(){
userService.update();
return "list";
}
}
GoodsAction:
package com.kissship.ioc.web;
import com.kissship.ioc.service.UserService;
/**
* @author Kissship
* @site www.Kissship.com
* @company xxx公司
* @create 2023-08-15-15:09
*/
public class GoodsAction {
private UserService userService;
public UserService getUserService() {
return userService;
}
public void setUserService(UserService userService) {
this.userService = userService;
}
public String updata(){
userService.update();
return "list";
}
}
spring-context.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 凡是在Spring配置文件spring-context.xml中配置,那么该类javabean就交给了Spring容器管理-->
<bean class="com.kissship.ioc.web.UserAction" id="userAction">
<property name="userService" ref="userService"></property>
</bean>
<bean class="com.kissship.ioc.web.GoodsAction" id="goodsAction">
<property name="userService" ref="userServiceImpl1"></property>
</bean>
<bean class="com.kissship.ioc.service.impl.UserServiceImpl2" id="userService"></bean>
<bean class="com.kissship.ioc.service.impl.UserServiceImpl1" id="userServiceImpl1"></bean>
</beans>Demo1测试类:
package com.kissship.ioc.demo;
import com.kissship.ioc.web.GoodsAction;
import com.kissship.ioc.web.UserAction;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* @author Kissship
* @site www.Kissship.com
* @company xxx公司
* @create 2023-08-15-15:42
*/
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//加载Spring核心配置文件(建模),获取Spring的上下文对象,上下文对象中可以获取任何javabean对象
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("/spring-context.xml");
UserAction userAction = (UserAction) context.getBean("userAction");
userAction.updata();
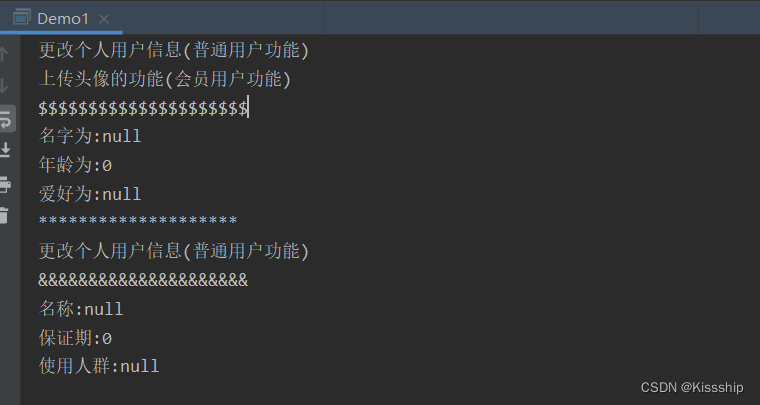
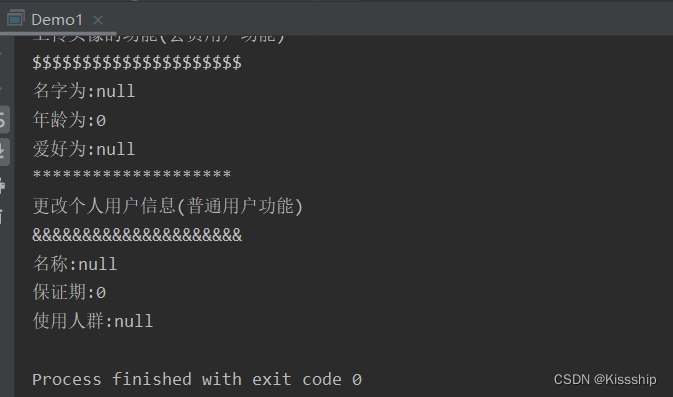
System.out.println("********************");
GoodsAction goodsAction = (GoodsAction) context.getBean("goodsAction");
goodsAction.updata();
}
}
演示效果:

3.Spring注入方式
3.1set注入
将GoodsAction中的所有代码修改为以下代码:
package com.kissship.ioc.web;
import com.kissship.ioc.service.UserService;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author Kissship
* @site www.Kissship.com
* @company xxx公司
* @create 2023-08-15-15:09
*/
public class GoodsAction {
/**
* 例如:在不同的控制器中进行方法调用
*/
private UserService userService;
private String gname;//名称
private int age;//保质期
private List<String> peoples;//使用人群
public String getGname() {
return gname;
}
public void setGname(String gname) {
this.gname = gname;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public List<String> getPeoples() {
return peoples;
}
public void setPeoples(List<String> peoples) {
this.peoples = peoples;
}
public UserService getUserService() {
return userService;
}
public void setUserService(UserService userService) {
this.userService = userService;
}
public void pop(){
System.out.println("名称:"+this.gname);
System.out.println("保证期:"+this.age);
System.out.println("使用人群:"+this.peoples);
}
public String update(){
userService.update();
return "list";
}
}
再修改spring-context.xml配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 凡是在Spring配置文件spring-context.xml中配置,那么该类javabean就交给了Spring容器管理-->
<bean class="com.kissship.ioc.web.UserAction" id="userAction">
<property name="userService" ref="userService"></property>
</bean>
<bean class="com.kissship.ioc.web.GoodsAction" id="goodsAction">
<property name="userService" ref="userServiceImpl1"></property>
<property name="gname" value="小文"></property>
<property name="age" value="19"></property>
<property name="peoples">
<list>
<value>印度飞饼</value>
<value>意大利炮</value>
<value>北京烤鸭</value>
<value>墨西哥卷</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean class="com.kissship.ioc.service.impl.UserServiceImpl2" id="userService"></bean>
<bean class="com.kissship.ioc.service.impl.UserServiceImpl1" id="userServiceImpl1"></bean>
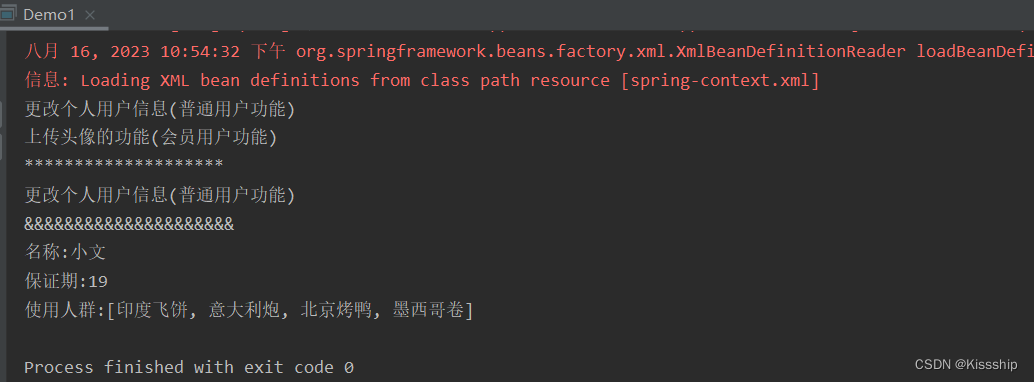
</beans>最后返回demo测试类执行结果,如下:
3.2构造注入
将User Action中的代码修改成以下代码:
package com.kissship.ioc.web;
import com.kissship.ioc.service.UserService;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author Kissship
* @site www.Kissship.com
* @company xxx公司
* @create 2023-08-15-15:04
*
* 程序员手动实例化对象的弊端:
* 1.一旦依赖的接口的实现需要大批量改动,迭代,维护的成本极高
* 2.当接口的实现类不同时,维护的成本高
*/
public class UserAction {
private UserService userService ;
private String uname;//姓名
private int age;//年龄
private List<String> hobby;//爱好
public UserAction() {
}
public UserAction(String uname, int age, List<String> hobby) {
this.uname = uname;
this.age = age;
this.hobby = hobby;
}
public UserService getUserService() {
return userService;
}
public void setUserService(UserService userService) {
this.userService = userService;
}
public void pop(){
System.out.println("名字为:"+this.uname);
System.out.println("年龄为:"+this.age);
System.out.println("爱好为:"+this.hobby);
}
public String updata(){
userService.update();
return "list";
}
}
再修改spring-context.xml 配置文件,如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 凡是在Spring配置文件spring-context.xml中配置,那么该类javabean就交给了Spring容器管理-->
<bean class="com.kissship.ioc.web.UserAction" id="userAction">
<property name="userService" ref="userService"></property>
<constructor-arg name="uname" value="扎克" ></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="18" ></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="hobby">
<list>
<value>唱,跳</value>
<value>Rap</value>
<value>篮球</value>
</list>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean class="com.kissship.ioc.web.GoodsAction" id="goodsAction">
<property name="userService" ref="userServiceImpl1"></property>
<property name="gname" value="小文"></property>
<property name="age" value="19"></property>
<property name="peoples">
<list>
<value>印度飞饼</value>
<value>意大利炮</value>
<value>北京烤鸭</value>
<value>墨西哥卷</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean class="com.kissship.ioc.service.impl.UserServiceImpl2" id="userService"></bean>
<bean class="com.kissship.ioc.service.impl.UserServiceImpl1" id="userServiceImpl1"></bean>
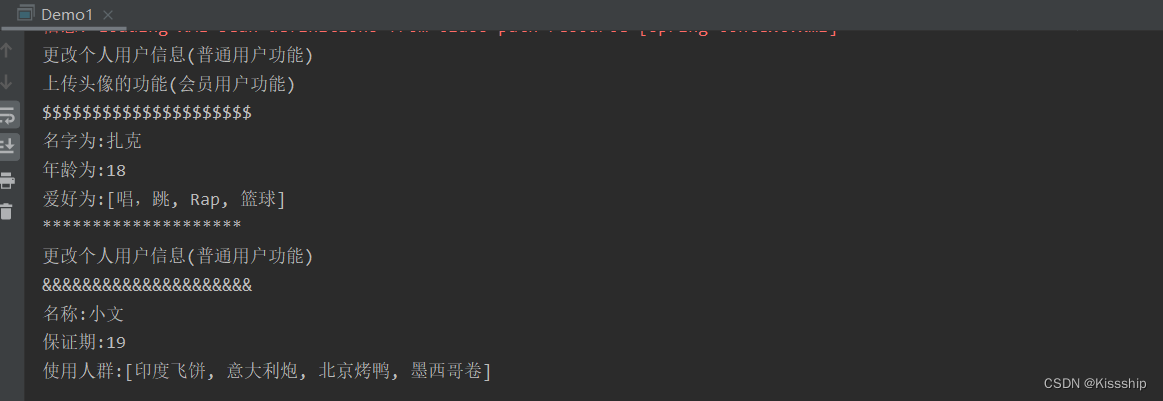
</beans>最后返回demo测试类执行结果,结果如下:
3.3接口注入
自动装配:byName byType
byName:javaBean会根据属性名在spring的上下文中的bean的id进行查找,只要有就会自动装配
修改spring-context..xml配置文件,如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" default-autowire="byName" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 凡是在Spring配置文件spring-context.xml中配置,那么该类javabean就交给了Spring容器管理--> <bean class="com.kissship.ioc.web.UserAction" id="userAction"> <property name="userService" ref="userService"></property> <!-- <constructor-arg name="uname" value="扎克" ></constructor-arg>--> <!-- <constructor-arg name="age" value="18" ></constructor-arg>--> <!-- <constructor-arg name="hobby">--> <!-- <list>--> <!-- <value>唱,跳</value>--> <!-- <value>Rap</value>--> <!-- <value>篮球</value>--> <!-- </list>--> <!-- </constructor-arg>--> </bean> <bean class="com.kissship.ioc.web.GoodsAction" id="goodsAction"> <property name="userService" ref="userServiceImpl1"></property> <!-- <property name="gname" value="小文"></property>--> <!-- <property name="age" value="19"></property>--> <!-- <property name="peoples">--> <!-- <list>--> <!-- <value>印度飞饼</value>--> <!-- <value>意大利炮</value>--> <!-- <value>北京烤鸭</value>--> <!-- <value>墨西哥卷</value>--> <!-- </list>--> <!-- </property>--> </bean> <bean class="com.kissship.ioc.service.impl.UserServiceImpl2" id="userService"></bean> <bean class="com.kissship.ioc.service.impl.UserServiceImpl1" id="userServiceImpl1"></bean> </beans>测试结果:
注:如果名称不同或者没有改名称将会有空指针报错(null值报错)
byType:JavaBean会议根据属性名对应的接口,在spring上下文中进行查找
查找方式:是根据spring上下文中是否有接口实现类进行匹配,只要有就自动配置。
修改spring-context.xml 配置文件,如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" default-autowire="byType" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 凡是在Spring配置文件spring-context.xml中配置,那么该类javabean就交给了Spring容器管理--> <bean class="com.kissship.ioc.web.UserAction" id="userAction"> <property name="userService" ref="userService"></property> <!-- <constructor-arg name="uname" value="扎克" ></constructor-arg>--> <!-- <constructor-arg name="age" value="18" ></constructor-arg>--> <!-- <constructor-arg name="hobby">--> <!-- <list>--> <!-- <value>唱,跳</value>--> <!-- <value>Rap</value>--> <!-- <value>篮球</value>--> <!-- </list>--> <!-- </constructor-arg>--> </bean> <bean class="com.kissship.ioc.web.GoodsAction" id="goodsAction"> <property name="userService" ref="userServiceImpl1"></property> <!-- <property name="gname" value="小文"></property>--> <!-- <property name="age" value="19"></property>--> <!-- <property name="peoples">--> <!-- <list>--> <!-- <value>印度飞饼</value>--> <!-- <value>意大利炮</value>--> <!-- <value>北京烤鸭</value>--> <!-- <value>墨西哥卷</value>--> <!-- </list>--> <!-- </property>--> </bean> <bean class="com.kissship.ioc.service.impl.UserServiceImpl2" id="userService"></bean> <bean class="com.kissship.ioc.service.impl.UserServiceImpl1" id="userServiceImpl1"></bean> </beans>测试结果:
注:如果没有或者有两个以上的接口实现类将会报错,因为是自动查询如有多个将不知道是哪个。
4.Spring上下文与tomcat整合
4.1思考
- 现在是每一个请求都建模一次,非常消耗性能。
- 希望只进行一次建模,然后每个请求都要可以获取到spring上下文。
- 那就是 监听器 ,将spring上下文放入tomcat上下文中
4.2代码演示
创建一个监听器SpringLoadListener,如下:
package com.kissship.ioc.listener;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextAttributeListener;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener;
/**
* @author Kissship
* @site www.Kissship.com
* @company xxx公司
* @create 2023-08-16-23:54
*/
@WebListener
public class SpringLoadListener implements ServletContextAttributeListener {
//将spring上下文放入tomcat上下文中。
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
//加载spring核心配置文件(建模),获取spring上下文对象及上下文对象中可以获取任何javabean的对象
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("/spring-context.xml");
//获取tomcat上下文
ServletContext servletContext = sce.getServletContext();
servletContext.setAttribute("springContext", context);
}
}
然后我们需要在测试前创建一个UserServlet进行访问,如下:
package com.kissship.ioc.web;
import com.kissship.ioc.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author Kissship
* @site www.Kissship.com
* @company xxx公司
* @create 2023-08-16-23:59
*/
@WebServlet("/userList")
public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = (ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) req.getServletContext().getAttribute("springContext");
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
System.out.println(userService);
userService.update();
}
}然后进行重启tomcat进行请求测试就行了。
4.3收获
学习Spring框架后,你将获得以下几方面的收获:
1. 简化开发流程:Spring框架提供了丰富的开发工具和模块,帮助你简化企业级应用程序的开发过程。通过使用Spring的IoC容器和注解,你可以将应用程序的对象的创建和配置工作交给框架处理,从而简化了开发过程,减少了冗余的代码。
2. 提高开发效率:Spring框架提供了很多现成的功能模块,如数据访问、事务管理、安全性支持等,可以减少开发人员手动编写这些功能模块的工作量。你可以通过配置或注解的方式快速集成这些功能,从而提高了开发效率。
3. 松耦合的设计:通过IoC容器和依赖注入,Spring框架实现了对象之间的松耦合。你可以更加专注于业务逻辑的实现,而不用过多关注对象之间的依赖关系。这种松耦合的设计使得应用程序更加灵活、可扩展和易于维护。
4. 更好的可测试性:Spring框架的设计理念使得应用程序的各个组件可以更容易地进行单元测试和集成测试。通过依赖注入,你可以轻松地模拟各个组件的依赖关系,从而更方便地编写测试代码,并保证应用程序的质量。
5. AOP的应用:Spring框架提供了全面的AOP支持,使你能够将与核心业务逻辑无关的功能模块(如事务管理、日志记录、缓存等)以切面的方式进行统一管理。这种模块化的设计能够提高代码的重用性和可维护性。
6. 更好的代码组织和可维护性:通过使用Spring框架,你可以将应用程序的不同层次的代码(如控制层、业务逻辑层、数据访问层)更好地组织起来,实现代码的分层和模块化。这种组织方式使得代码更具可读性、可维护性,方便团队协作开发。
最后ISpring之IoC容器篇就到这里,祝大家在敲代码的路上一路通畅!