数据结构.数组
- 1.数组的概念和特点
- 2.数组的定义和初始化
- 3.数组的遍历
- 4.数组的基本操作(不多说 注解很详细)
- 5.操作的时间复杂度
1.数组的概念和特点
数组就是一种容器(装数据的),用来存储相同类型的数据值。
数组的特点:
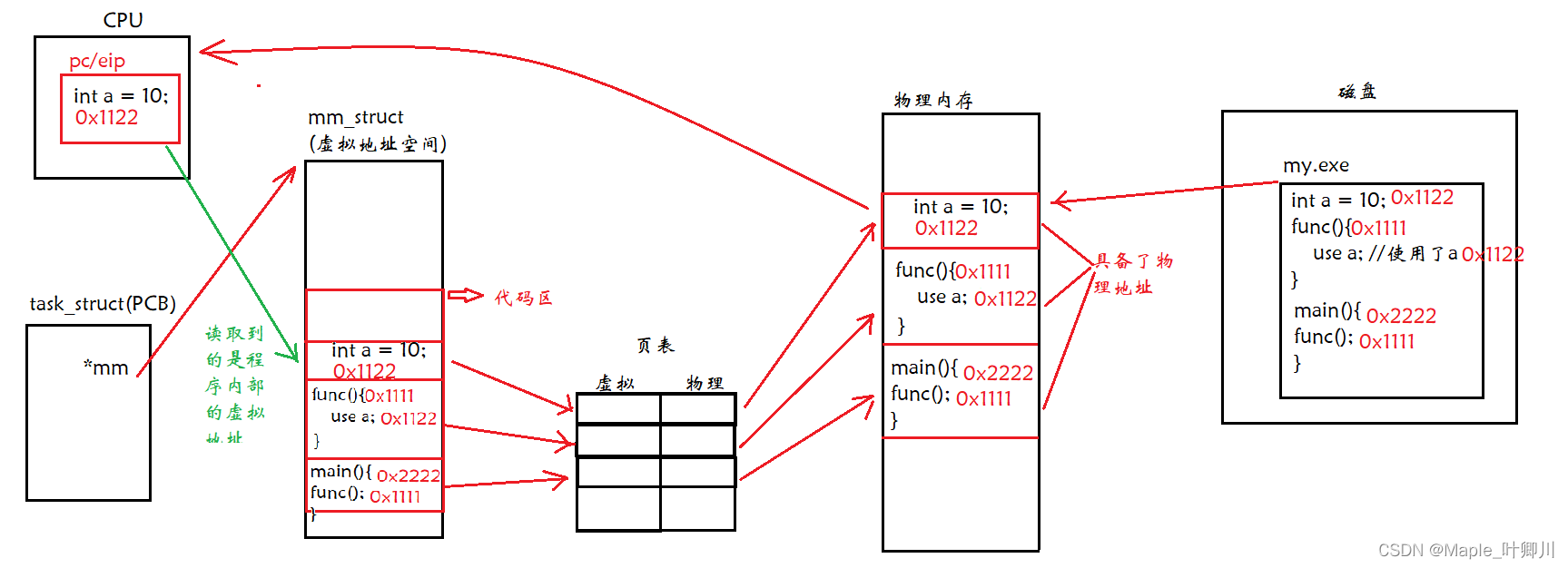
1.引用类型(或者可以认为数组即对象)
2.可以存同一个类型很多个数据
3.长度不可变(短板 需要用到扩容—这就用到后面说的链表的好处了,数组是静态的,链表才是真正意义上的动态数据结构)
2.数组的定义和初始化
1.数组的定义:
数据类型[] 数组名;//int[] a;
数据类型 数组名[]; //int a[];
2.数组的创建:三种方式
int[] a=new int[10];
int[] a={a,b,c,d};
int[] a=new int[]{a,b,c,d};
3.数组的索引(index):
[0,数组名.length)
第一个位置索引是0
最后一个位置索引是length-1
3.数组的遍历
1.for循环
int[] a={1,2,3,4};
for (int i=0;i<a.length;i++){
System.out.print(a[i]+"------");
}
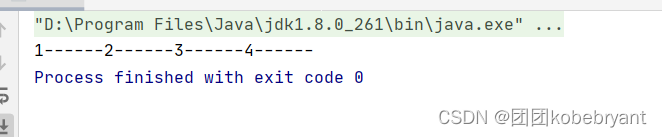
2.增强for循环
int[] a={1,2,3,4};
for (int arr:a){//arr是给要遍历的a数组临时取的名字
System.out.print(arr+"-----");
}
小总结:for循环知道索引,可以拿到想要的值,增强for循环没有索引,全部遍历出来
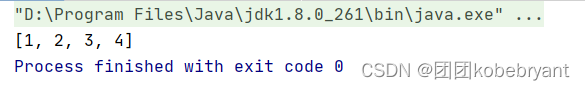
3.最简单的直接用人家提供的Arrays.toString(数组名)
int[] a={1,2,3,4};
System.out.print(Arrays.toString(a));
4.数组的基本操作(不多说 注解很详细)
package com.ffyc.datastructure;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Random;
//数组
public class MyArray<T> {//写成泛型 就可以存多种数据类型
/*创建自己的数组 基于java中的数组 进行二次封装 制作属于我们自己的可变数组 操作增删改查*/
/*泛型 然后增加是扩容(创建新数组)、删除缩容 */
//1.创建数组 初始化
private T[] data;//数组的数据容器 用来保存自己数组的
private int size;//实际保存数据的个数 永远指向待插入位置的索引
/*get/set方法 可获得数组和数组长度*/
//构造方法 有参无参
MyArray() {//无参
this(20);//默认创建容量为20的数组
}
MyArray(int capacity) {//有参 创建一个数组 当然要指定容量了
this.size=0;
data= (T[]) new Object[capacity];//T是不可以直接new的 可以先newObjects 再强制类型转换创建成T
}
//2.数组的方法
//2.1判断数组是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return this.size==0;
}
//2.2获取数组中实际保存元素的个数
/* public int getSize(){
return this.size;
}*/
//这个方法已经有了 直接用就可以
//2.3 增 向数组末尾添加元素
public void addTail(T ele){
//直接调add 索引为size
add(this.size,ele);
}
//2.3 增 向数组头部添加元素
public void addHead(T ele){
//直接调add 索引为0即可
add(0,ele);
}
//2.3 增 向指定位置(任意位置)添加元素 牵扯元素后移 循环 从后面开始移
/*添加操作:插前判断 插后加加 */
public void add(int index,T ele){
if (index<0||index>size){//判断数组索引位置是否有效
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is error");
}
//位置有范围 还有满了不能插入 都需要判断
if (this.size==data.length){//判断数组是否已满
/* throw new IllegalArgumentException("this array is full");*/
//如果数组满 就扩容
resize(2*data.length);//更改数组容器
}
//在index位置插 要将index及以后的都后移 从最后面开始移
for (int i=size-1;i>=index;i--){
data[i+1]=data[i];//后移操作 把把前一个位置上的数赋值给后面 空出一个位置(即就是待插入元素的位置)
}
data[index]=ele;
this.size++;//记得长度++
}
//改变数组容器 可扩容也可缩容
public void resize(int newCapacity){
T[] newData= (T[]) new Object[newCapacity];//new一个新数组 然后复制进去(循环)
for (int i=0;i<this.size;i++){
newData[i]=data[i];
}
this.data=newData;//把新数组替换调原来的数组
}
//2.6 查 获取指定位置的元素
public T getEleByIndex(int index){
//判断数组越界
if (index<0||index>=size){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is error");
}
return data[index];
}
//2.5 改 修改指定位置的元素
public void updataByIndex(int index,T ele){
//判断数组越界
if (index<0||index>=size){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is error");
}
data[index]=ele;
}
//2.7 包含(搜索)操作 判断数组中是否包含指定元素 循环就可以
public int isContains(T ele){
for (int i=0;i<this.size;i++){
if (this.data[i].equals(ele)){
return i;//找到返回索引
}
}
return -1;//遍历完还没找到 就是不包含 返回-1
}
/*这里的删除只能删除第一次出现的*/
//2.4 删 删除指定位置的元素 元素前移 长度-1
public T remove(int index){
//判断位置是否有效
if (index<0||index>=size){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is invalid");//无效索引
}
//位置有效就开始操作 前移
T result=data[index];//一定要放在删除之前先保存
for (int i=index+1;i<size;i++){//从待删元素的后一个元素开始前移
data[index]=data[index+1];//前移
}
this.size--;
data[size]=null;//前移占了删除位置 后面就空一个位置
//返回删除元素的位置
//删除之后进行缩容操作
if (this.size==data.length/4&&data.length/2>0){//加条件data.length/2>0 因为缩容1/2是0 不能缩容到0 1/4 真正不需要那么多的时候才缩容 解决复杂度震荡(删一个增一个 又扩又缩)
resize(data.length/2);
}
return result;
}
//2.4 头删
public T removeHead() {
if (isEmpty()){
return null;
}
T result=this.data[0];//记录第一个元素队首元素
//删除后 把后面的元素前移
for (int i=1;i<this.size;i++){
this.data[i-1]=this.data[i];
}
this.size-=1;
//缩容
if (this.size==data.length/4&&data.length/2>0){//加条件data.length/2>0 因为缩容1/2是0 不能缩容到0 1/4 真正不需要那么多的时候才缩容 解决复杂度震荡(删一个增一个 又扩又缩)
resize(data.length/2);
}
return result;
}
//2.4 尾删
public T removeTail(){
if (isEmpty()){
return null;//判断数组是否为空 为空就没得删了
}
T result=this.data[--this.size];//记录尾部的元素 size永远指向待插入元素的位置先-- 先--才是最后一个元素
//缩容
if (this.size==data.length/4&&data.length/2>0){//加条件data.length/2>0 因为缩容1/2是0 不能缩容到0 1/4 真正不需要那么多的时候才缩容 解决复杂度震荡(删一个增一个 又扩又缩)
resize(data.length/2);
}
return result;
}
//2.4 删 删除指定元素 返回删除元素的位置
public int removeEle(T ele){
//判断待删除元素是否存在
int index= isContains(ele);//判断元素是否存在 返回一个索引 存在就用这个索引直接删
if (index==-1){
return -1;
}else {
remove(index);
}
return index;//返回删除元素的位置
}
//2.8 遍历操作 把数组中每个元素进行输出 写到toString方法中
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
sb.append("[");//开始的时候放左括号
//遍历
for (int i=0;i<this.size;i++){
sb.append(data[i].toString());
//逗号隔开
if(i!=this.size-1){
sb.append(",");
}
}
sb.append("]");//结束的时候追加右括号 就都在括号里了
return sb.toString();
}
//下面get、set方法
public T[] getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(T[] data) {
this.data = data;
}
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
public void setSize(int size) {
this.size = size;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArray<Integer> myArray=new MyArray<Integer>(10);
int count=20;//嘿嘿 多少个都可以添加进去
//添加操作 随机数添加
Random random=new Random();
for (int i=0;i<count;i++){
myArray.addTail(random.nextInt(10));//加Integer.MAX_VALUE就都是整数
}
System.out.println("数组:"+myArray);
//判断10是否在数组中
System.out.println("2是否存在:"+(myArray.isContains(2)==-1?false:true));
MyArray<String> strArray=new MyArray<>();
strArray.addTail("qw");
strArray.addTail("er");
strArray.addTail("r");
strArray.addTail("q");
strArray.addTail("k");
System.out.println("字符串:"+strArray);//默认调toString方法
System.out.println("c是否存在:"+(strArray.isContains("c")==-1?false:true));
strArray.add(2,"123");
System.out.println("字符串:"+strArray);//默认调toString方法
}
}
测试结果:

5.操作的时间复杂度
O(1)<O(n)<O(lgn)<Onlogn<O(n^2)
增加和删除:遍历一遍数组 时间复杂度O(n)
查找和修改:已知索引O(1),位置索引O(n) 因为未知索引需要遍历一遍
增加的时候resize扩容:均摊复杂度 O(1)
均摊思想:
不同情况下时间复杂度出现级别差别,就比如未满是插入是O(1),满了插入要扩容O(n),基本是低级,偶尔高级,将高的均摊到低的 下来整体就是O(1)
n次O(1)的操作=1次O(n)的操作 平均就是1次O(1)
复杂度的震荡:
数组满了的时候新增就会扩容,扩容后又删除,用不到那么多空间就会缩容,频繁这样操作就会又扩又缩,太急着缩容了太勤快
解决办法:Lazy
让size==capacity/4时,才会缩容 即减半