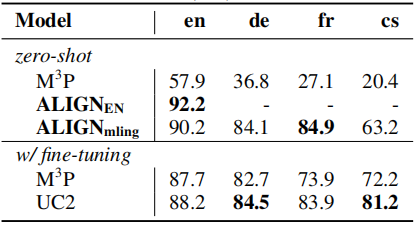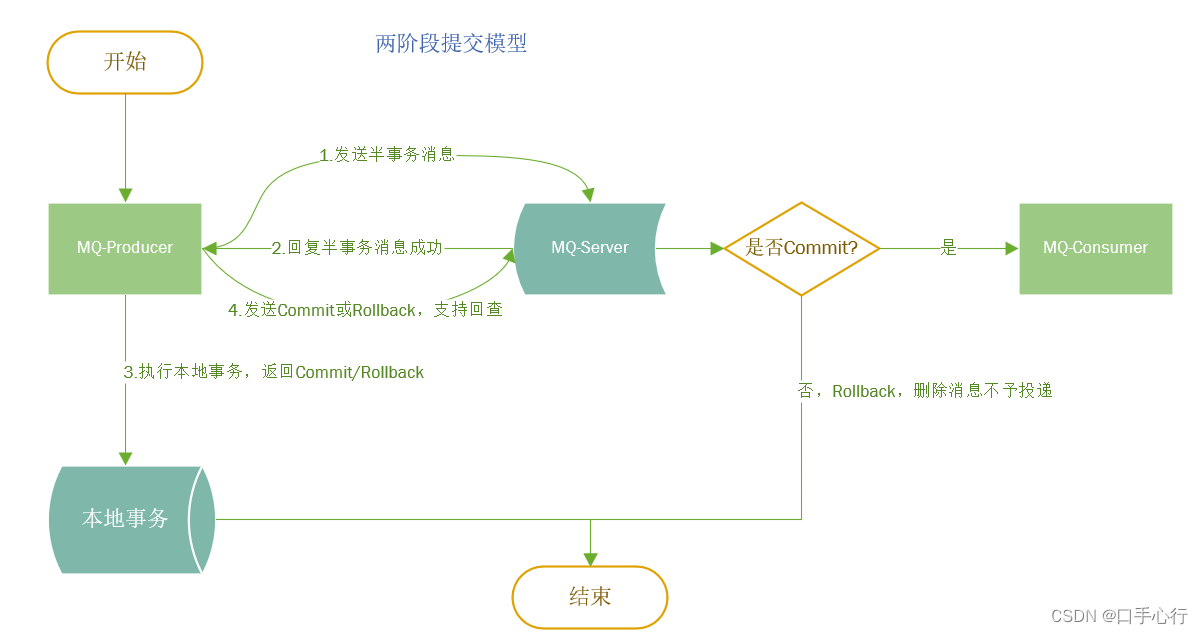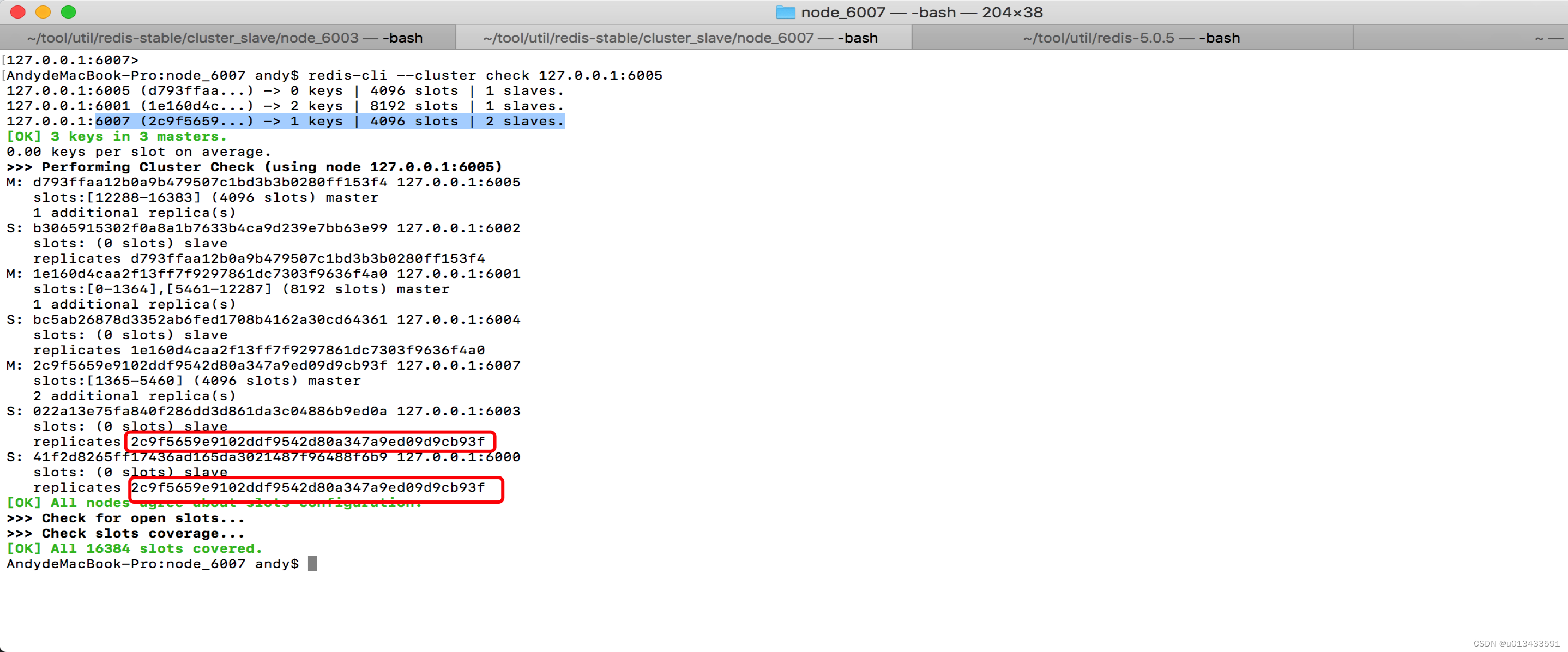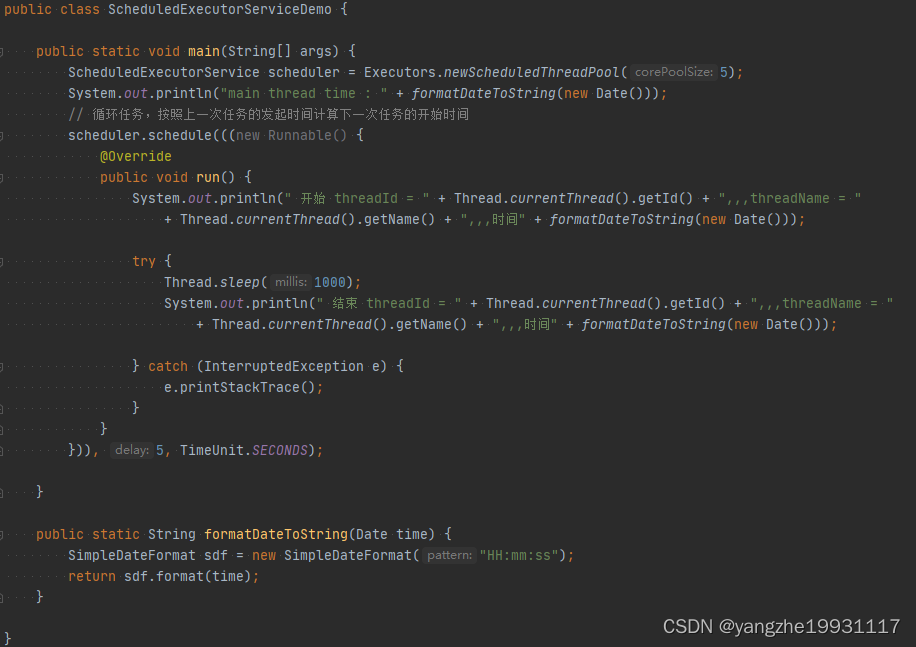
只运行一次


private static ScheduledExecutorService scheduler;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
// 循环任务,按照上一次任务的发起时间计算下一次任务的开始时间
scheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(((
new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(
" 开始 threadId = "
+ Thread.currentThread().getId()
+ ",,,threadName = " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ ",,,时间" + formatDateToString(new Date())
);
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(
" 结束 threadId = "
+ Thread.currentThread().getId()
+ ",,,threadName = " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ ",,,时间" + formatDateToString(new Date())
);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//模拟抛出异常
if (1 == 1) {
throw new RuntimeException("异常");
}
}
})),
0, 1,
TimeUnit.SECONDS);
Thread.sleep(20000);
System.out.println(
" 主线程 threadId = "
+ Thread.currentThread().getId()
+ ",,,threadName = " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ ",,,时间" + formatDateToString(new Date())
);
}
public static String formatDateToString(Date time) {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss");
return sdf.format(time);
}
![]()
private static ScheduledExecutorService scheduler;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
// 循环任务,按照上一次任务的发起时间计算下一次任务的开始时间
scheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(((
new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(
" 开始 threadId = "
+ Thread.currentThread().getId()
+ ",,,threadName = " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ ",,,时间" + formatDateToString(new Date())
);
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(
" 结束 threadId = "
+ Thread.currentThread().getId()
+ ",,,threadName = " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ ",,,时间" + formatDateToString(new Date())
);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
})),
0, 1,
TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
public static String formatDateToString(Date time) {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss");
return sdf.format(time);
}
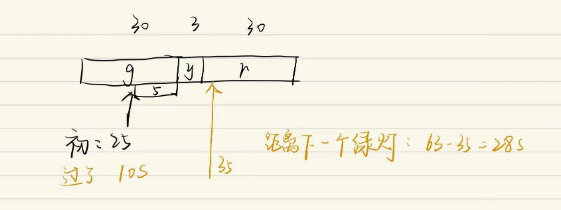
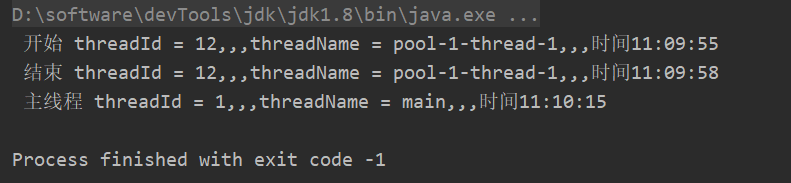
可以看到其实间隔时间已经变成了 任务执行时间来控制,但是一般来说,很少有任务执行时间超过间隔时间,但是这个知识点还是要知道。

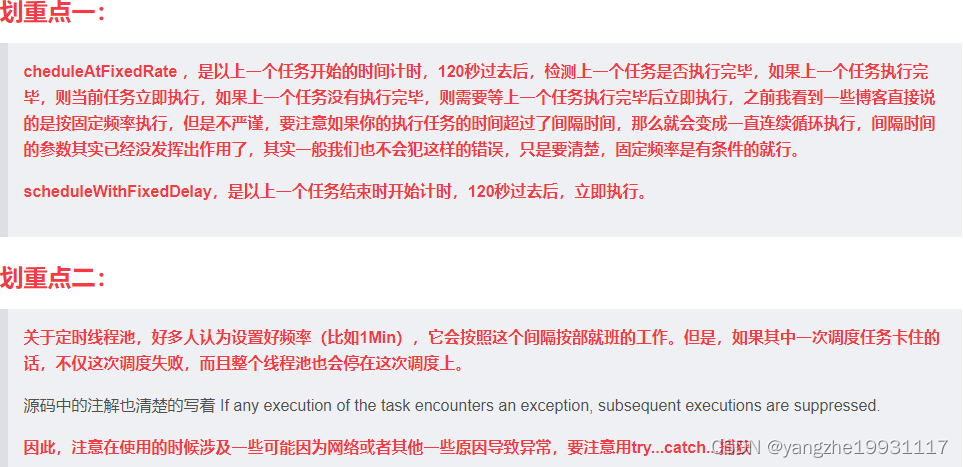
scheduleAtFixedRate 正常使用 延迟时间1S,执行任务时间 1S,间隔时间3S
private static ScheduledExecutorService scheduler;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
// 循环任务,按照上一次任务的发起时间计算下一次任务的开始时间
scheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(((
new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(
" 开始 threadId = "
+ Thread.currentThread().getId()
+ ",,,threadName = " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ ",,,时间" + formatDateToString(new Date())
);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(
" 结束 threadId = "
+ Thread.currentThread().getId()
+ ",,,threadName = " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ ",,,时间" + formatDateToString(new Date())
);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
})),
0, 3,
TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
public static String formatDateToString(Date time) {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss");
return sdf.format(time);
}

scheduleWithFixedDelay 正常使用
private static ScheduledExecutorService scheduler;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
// 循环任务,按照上一次任务的发起时间计算下一次任务的开始时间
scheduler.scheduleWithFixedDelay(((
new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(
" 开始 threadId = "
+ Thread.currentThread().getId()
+ ",,,threadName = " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ ",,,时间" + formatDateToString(new Date())
);
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(
" 结束 threadId = "
+ Thread.currentThread().getId()
+ ",,,threadName = " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ ",,,时间" + formatDateToString(new Date())
);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
})),
0, 1,
TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
public static String formatDateToString(Date time) {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss");
return sdf.format(time);
}
scheduleWithFixedDelay以上一次任务的结束时间 + 延迟时间 = 下一次任务的开始时间。

以上就是两个循环任务的使用

private static ScheduledExecutorService scheduler;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5, new ThreadFactory() {
private AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger(0);
//可以在这里对线程做一些操作
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
int count = counter.incrementAndGet();
System.out.println("线程创建counter = " + count);
Thread thread = new Thread(r);
thread.setName("测试线程"+count);
return thread;
}
});
System.out.println("main thread time : " + formatDateToString(new Date()));
// 循环任务,按照上一次任务的发起时间计算下一次任务的开始时间
scheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(((
new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(
" 开始 threadId = "
+ Thread.currentThread().getId()
+ ",,,threadName = " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ ",,,时间" + formatDateToString(new Date())
);
}
})),
1,5,
TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
public static String formatDateToString(Date time) {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss");
return sdf.format(time);
}
其实就是提供了一个扩展点,允许你在创建线程的时候,做一些管理或者说一些其他的操作

也可以使用 ThreadFactoryBuilder 构建类 来构建FactoryBuilder
scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5,new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("测试线程-%d")
// .setDaemon(true) //这个参数是设置为守护线程 也叫 服务线程
.build());

![[毕业设计]2022-2023年最新最全计算机专业毕设选题推荐汇总](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/887a898b20664b399694dcf15cedcd68.png)