认识阻塞队列
- 一、相关概念
- 1.1 阻塞队列是什么
- 1.2 生产者消费者模型
- 二、标准库中的阻塞队列
- 2.1 使用
- 2.2 生产者消费者模型实现
- 三、实现阻塞队列
- 3.1 循环队列
- 3.2 实现的细节
- 3.3 代码
一、相关概念
1.1 阻塞队列是什么
阻塞队列是一种特殊的队列,也遵守 “先进先出” 的原则。
1)是一种线程安全的数据结构;
2)带有阻塞功能:
- 当队列满的时候, 继续入队列就会阻塞,直到有其他线程从队列中取走元素;
- 当队列空的时候, 继续出队列也会阻塞,直到有其他线程往队列中插入元素。
阻塞队列的一个典型应用场景就是 “生产者消费者模型”,这是一种非常典型的开发模型!
1.2 生产者消费者模型
生产者消费者模式就是通过一个容器来解决生产者和消费者的强耦合问题。
生产者和消费者彼此之间不直接通讯,而通过阻塞队列来进行通讯,所以生产者生产完数据之后不用等待消费者处理,直接扔给阻塞队列,消费者不找生产者要数据,而是直接从阻塞队列里取。
1)阻塞队列能使生产者和消费者之间解耦合!
比如过年一家人一起包饺子,一般都是有明确分工,比如一个人负责擀饺子皮,其他人负责包,擀饺子皮的人就是 “生产者”,包饺子的人就是 “消费者”。
擀饺子皮的人不关心包饺子的人是谁 (能包就行,无论是手工包,借助工具,还是机器包),包饺子的人也不关心擀饺子皮的人是谁 (有饺子皮就行,无论是用擀面杖擀的,还是拿罐头瓶擀,还是直接从超市买的)。
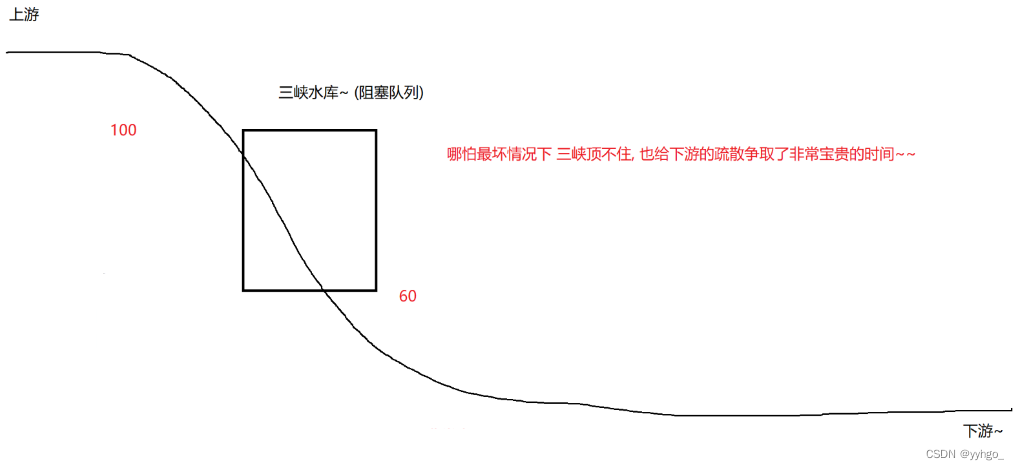
2)阻塞队列就相当于一个缓冲区,平衡了生产者和消费者的处理能力!削峰填谷!
比如在 “秒杀” 场景下,服务器同一时刻可能会收到大量的支付请求。如果直接处理这些支付请求,服务器可能扛不住 (每个支付请求的处理都需要比较复杂的流程)。这个时候就可以把这些请求都放到一个阻塞队列中,然后再由消费者线程慢慢的来处理每个支付请求。这样做可以有效进行 “削峰”,防止服务器被突然到来的一波请求直接冲垮。
比如三峡大坝:
二、标准库中的阻塞队列
2.1 使用
在 Java 标准库中内置了阻塞队列。如果我们需要在一些程序中使用阻塞队列,直接使用标准库中的即可:
- BlockingQueue 是一个接口,真正实现的类是 LinkedBlockingQueue、ArrayBlockingQueue等…
- put 方法用于阻塞式的入队列,take 用于阻塞式的出队列
- BlockingQueue 也有 offer、poll、peek 等方法,但是这些方法不带有阻塞特性
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BlockingQueue<Integer> blockingQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(100);
// 带有阻塞功能的入队列
blockingQueue.put(1);
blockingQueue.put(2);
blockingQueue.put(3);
Integer ret = blockingQueue.take();
System.out.println(ret);
ret = blockingQueue.take();
System.out.println(ret);
ret = blockingQueue.take();
System.out.println(ret);
ret = blockingQueue.take();
System.out.println(ret);
}
}
注意: 阻塞队列没有提供"带有阻塞的"取队首元素的功能,所以需要先take取出判断,不符合再重新put进队列!
2.2 生产者消费者模型实现
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BlockingQueue<Integer> blockingQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Integer>();
Thread customer = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
try {
int value = blockingQueue.take();
System.out.println("消费元素: " + value);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "消费者");
customer.start();
Thread producer = new Thread(() -> {
Random random = new Random();
while (true) {
try {
int num = random.nextInt(1000);
System.out.println("生产元素: " + num);
blockingQueue.put(num);
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "生产者");
producer.start();
customer.join();
producer.join();
}
三、实现阻塞队列
3.1 循环队列
我们来基于数据实现:循环队列!

怎样区别"空"还是"满"?
1)浪费一个数组空间;2)添加计数器
循环队列更多内容~~请点击
3.2 实现的细节
保证线程安全,关键就是加锁!
实现阻塞:
1.如果队列为空,出队列就阻塞;
2.如果队列为满,入队列就阻塞。


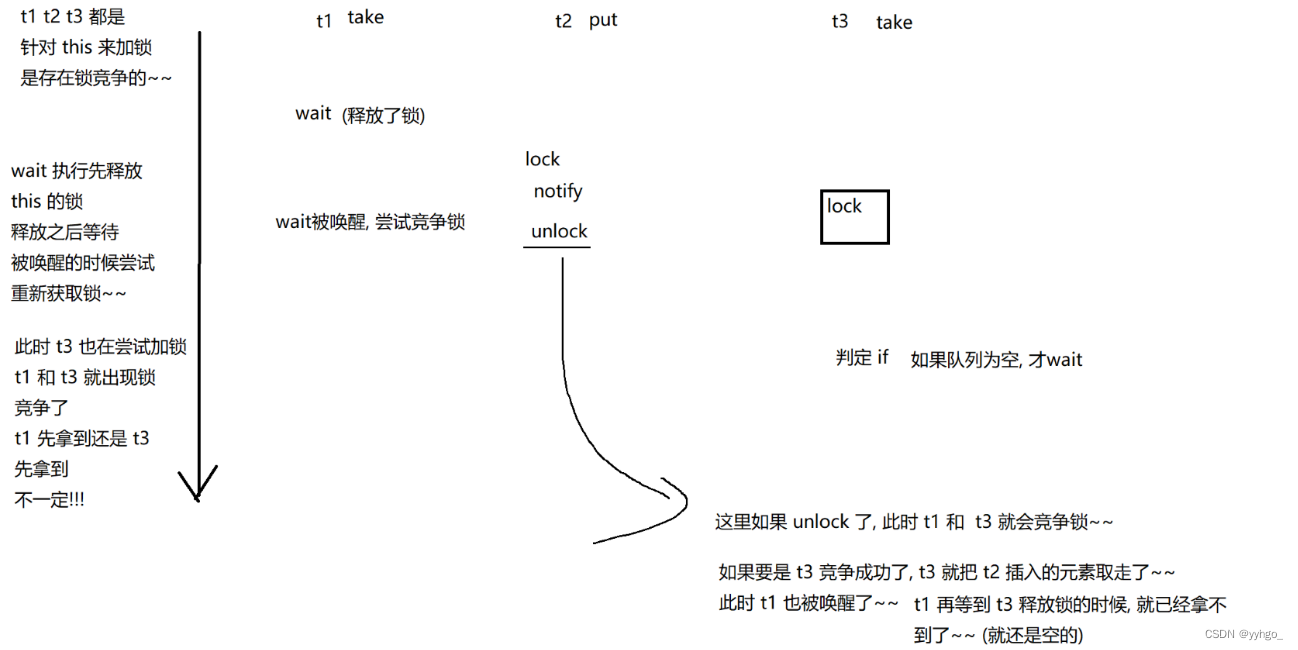
即使没有t3这一手,还有interrupt,也是有影响~~
所以,使用while是稳妥的写法!!!
3.3 代码
// 名字还是不要和标准库的混淆
class MyBlockingQueue {
private int[] items = new int[1000];
private volatile int head = 0;
private volatile int tail = 0;
private volatile int size = 0;
// 入队列
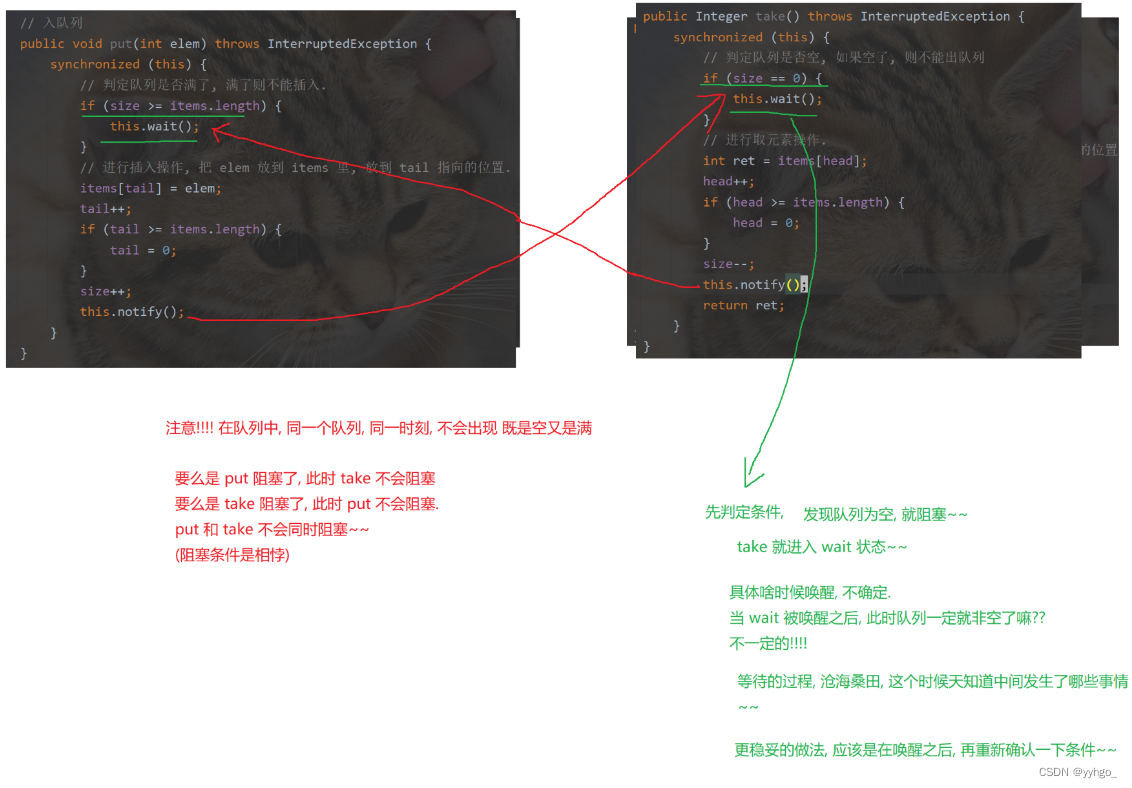
public void put(int elem) throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (this) {
// 判定队列是否满了, 满了则不能插入.
while (size >= items.length) {
this.wait();
}
// 进行插入操作, 把 elem 放到 items 里, 放到 tail 指向的位置.
items[tail] = elem;
tail++;
if (tail >= items.length) {
tail = 0;
}
size++;
this.notify();
}
}
// 出队列, 返回删除的元素内容
public Integer take() throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (this) {
// 判定队列是否空, 如果空了, 则不能出队列
while (size == 0) {
this.wait();
}
// 进行取元素操作.
int ret = items[head];
head++;
if (head >= items.length) {
head = 0;
}
size--;
this.notify();
return ret;
}
}
}
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyBlockingQueue queue = new MyBlockingQueue();
Thread producer = new Thread(() -> {
int n = 1;
while (true) {
try {
queue.put(n);
System.out.println("生产元素 " + n);
n++;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
Thread customer = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
try {
int n = queue.take();
System.out.println("消费元素 " + n);
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
producer.start();
customer.start();
}
}
](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/32e4e5eb993fe0514c9785a254e84e88.jpeg)







![[附源码]JAVA毕业设计医药垃圾分类管理系统(系统+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/dc5b7a96bada4377aa20de907e280e61.png)