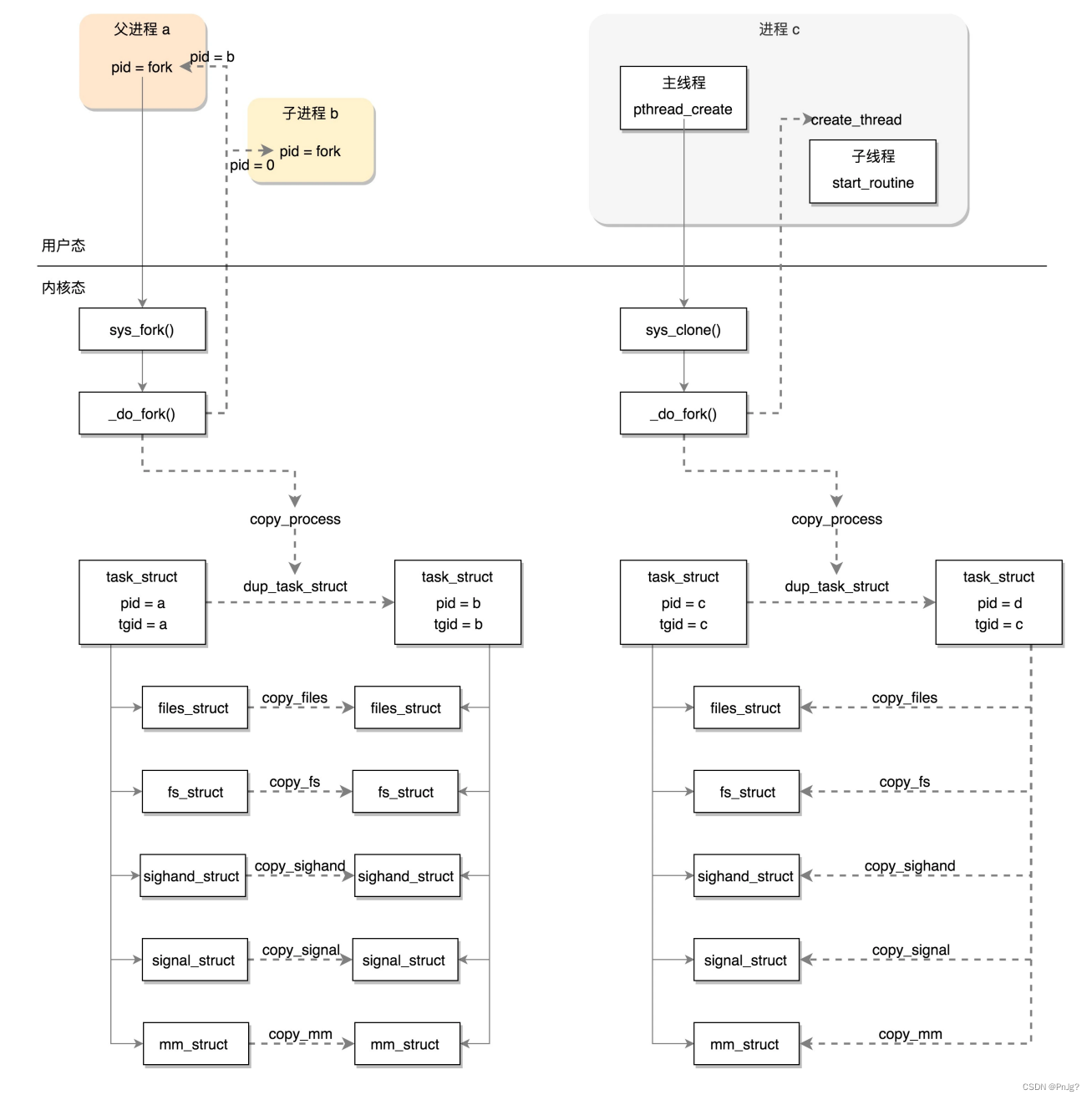
用户态创建线程:
线程不是一个完全由内核实现的机制,它是由内核态和用户态合作完成的。pthread_create不是一个系统调用,是Glibc库的一个函数。
在nptl/pthread_creat.c里面找到了这个函数:
int __pthread_create_2_1 (pthread_t *newthread, const pthread_attr_t *attr, void *(*start_routine) (void
{
......
}
versioned_symbol (libpthread, __pthread_create_2_1, pthread_create, GLIBC_2_1);下面依次来看这个函数做了些啥:
首先处理的是线程的属性参数。例如前面写程序的时候,我们设置的线程栈大小。如果没有传入 线程属性,就取默认值:
const struct pthread_attr *iattr = (struct pthread_attr *) attr;
struct pthread_attr default_attr;
if (iattr == NULL)
{
......
iattr = &default_attr;
}
接下来,就像在内核里一样,每一个进程或者线程都有一个task_struct结构,在用户态也有一个用于维护线程的结构,就是这个pthread结构(也就是pthread相当于内核态里面的task_struct)。
struct pthread *pd = NULL;凡是涉及函数的调用,都要使用到栈。每个线程也有自己的栈。那接下来就是创建线程栈了:
int err = ALLOCATE_STACK (iattr, &pd);
这里的ALLOCATE_STACK是一个宏,我们找到它的定义之后,发现它其实就是一个函数,他的主要代码如下:
# define ALLOCATE_STACK(attr, pd) allocate_stack (attr, pd, &stackaddr)
static int
allocate_stack (const struct pthread_attr *attr, struct pthread **pdp,
ALLOCATE_STACK_PARMS)
{
struct pthread *pd;
size_t size;
size_t pagesize_m1 = __getpagesize () - 1;
......
size = attr->stacksize;
......
/* Allocate some anonymous memory. If possible use the cache. */
size_t guardsize;
void *mem;
const int prot = (PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE
| ((GL(dl_stack_flags) & PF_X) ? PROT_EXEC : 0));
/* Adjust the stack size for alignment. */
size &= ~__static_tls_align_m1;
/* Make sure the size of the stack is enough for the guard and
eventually the thread descriptor. */
guardsize = (attr->guardsize + pagesize_m1) & ~pagesize_m1;
size += guardsize;
pd = get_cached_stack (&size, &mem);
if (pd == NULL)
{
/* If a guard page is required, avoid committing memory by first
allocate with PROT_NONE and then reserve with required permission
excluding the guard page. */
mem = __mmap (NULL, size, (guardsize == 0) ? prot : PROT_NONE,
MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_ANONYMOUS | MAP_STACK, -1, 0);
/* Place the thread descriptor at the end of the stack. */
#if TLS_TCB_AT_TP
pd = (struct pthread *) ((char *) mem + size) - 1;
#elif TLS_DTV_AT_TP
pd = (struct pthread *) ((((uintptr_t) mem + size - __static_tls_size) & ~__static_tls_align_m1) - T
#endif
/* Now mprotect the required region excluding the guard area. */
char *guard = guard_position (mem, size, guardsize, pd, pagesize_m1);
setup_stack_prot (mem, size, guard, guardsize, prot);
pd->stackblock = mem;
pd->stackblock_size = size;
pd->guardsize = guardsize;
pd->specific[0] = pd->specific_1stblock;
/* And add to the list of stacks in use. */
stack_list_add (&pd->list, &stack_used);
}
*pdp = pd;
void *stacktop;
# if TLS_TCB_AT_TP
/* The stack begins before the TCB and the static TLS block. */
stacktop = ((char *) (pd + 1) - __static_tls_size);
# elif TLS_DTV_AT_TP
stacktop = (char *) (pd - 1);
# endif
*stack = stacktop;
......
}allocate_stack主要做了以下这些事情:
1、如果你在线程属性里面设置过栈的大小,需要你把设置的值拿出来;
2、为了防止栈的访问越界,在栈的末尾会有一块空间guardsize,一旦访问到这里就错误了;
3、其实线程栈是在进程的堆里面创建的。如果一个进程不断地创建和删除线程,我们不可能不断 地去申请和清除线程栈使用的内存块,这样就需要有一个缓存。get_cached_stack就是根据计算出来的size大小,看一看已经有的缓存中,有没有已经能够满足条件的;
如果缓存里面没有,就需要调用__mmap创建一块新的,系统调用那一节我们讲过,如果要在 堆里面malloc一块内存,比较大的话,用__mmap;
4、线程栈也是自顶向下生长的,还记得每个线程要有一个pthread结构,这个结构也是放在栈的 空间里面的。在栈底的位置,其实是地址最高位;
5、计算出guard内存的位置,调用setup_stack_prot设置这块内存的是受保护的;
6、接下来,开始填充pthread这个结构里面的成员变量stackblock、stackblock_size、 guardsize、specific。这里的specific是用于存放Thread Specific Data的,也即属于线程的全局变量;
7、将这个线程栈放到stack_used链表中,其实管理线程栈总共有两个链表,一个是 stack_used,也就是这个栈正被使用;另一个是stack_cache,就是上面说的,一旦线程结束,先缓存起来,不释放,等有其他的线程创建的时候,给其他的线程用。
搞定了用户态栈的问题,其实用户态的事情基本搞定了一半,总结一下,在用户态中调用了glibc里面的pthread_create函数,在这里面做了一下几件事:
1、设置线程的属性,如果没有就用默认值
2、维护一个pthread结构,这个结构就相当于内核态里面的task_struct
3、因为凡是涉及函数的调用都要用到栈,每个线程都有一个自己的栈,所以要给线程分配一个栈,在这里面设置了防止越界的空间、栈大小、栈缓存(一个线程结束后可以供给其他线程用)
4、把pthread放入栈
5、填充pthread的成员变量
5、把这个线程栈放入stack_used链表中表示这个线程栈正在被使用。
内核态创建任务
接着pthread_create看,其实有了用户态的栈,接着需要解决的就是用户态的程序从哪里开始运行的问题。
pd->start_routine = start_routine;
pd->arg = arg;
pd->schedpolicy = self->schedpolicy;
pd->schedparam = self->schedparam;
/* Pass the descriptor to the caller. */
*newthread = (pthread_t) pd;
atomic_increment (&__nptl_nthreads);
retval = create_thread (pd, iattr, &stopped_start, STACK_VARIABLES_ARGS, &thread_ran);
start_routine就是咱们给线程的函数,start_routine,start_routine的参数arg,以及调度策略都要赋值给pthread。接下来__nptl_nthreads加一,说明有多了一个线程。真正创建线程的是调用create_thread函数,这个函数定义如下:
static int
create_thread (struct pthread *pd, const struct pthread_attr *attr,
bool *stopped_start, STACK_VARIABLES_PARMS, bool *thread_ran)
{
const int clone_flags = (CLONE_VM | CLONE_FS | CLONE_FILES | CLONE_SYSVSEM | CLONE_SIGHAND | CLONE_THR
ARCH_CLONE (&start_thread, STACK_VARIABLES_ARGS, clone_flags, pd, &pd->tid, tp, &pd->tid);
/* It's started now, so if we fail below, we'll have to cancel it
and let it clean itself up. */
*thread_ran = true;
}这里面有很长的clone_flags。
然后就是ARCH_CLONE,其实调用的是__clone:
# define ARCH_CLONE __clone
/* The userland implementation is:
int clone (int (*fn)(void *arg), void *child_stack, int flags, void *arg),
the kernel entry is:
int clone (long flags, void *child_stack).
The parameters are passed in register and on the stack from userland:
rdi: fn
rsi: child_stack
rdx: flags
rcx: arg
r8d: TID field in parent
r9d: thread pointer
%esp+8: TID field in child
The kernel expects:
rax: system call number
rdi: flags
rsi: child_stack
rdx: TID field in parent
r10: TID field in child
r8: thread pointer */
.text
ENTRY (__clone)
movq $-EINVAL,%rax
......
/* Insert the argument onto the new stack. */
subq $16,%rsi
movq %rcx,8(%rsi)
/* Save the function pointer. It will be popped off in the
child in the ebx frobbing below. */
movq %rdi,0(%rsi)
/* Do the system call. */
movq %rdx, %rdi
movq %r8, %rdx
movq %r9, %r8
mov 8(%rsp), %R10_LP
movl $SYS_ify(clone),%eax
......
syscall
......
PSEUDO_END (__clone)
如果在进程的主线程里面调用其他系统调用,当前用户态的栈是指向整个进程的栈,栈顶指针也 是指向进程的栈,指令指针也是指向进程的主线程的代码。此时此刻执行到这里,调用clone的时候,用户态的栈、栈顶指针、指令指针和其他系统调用一样,都是指向主线程的。
但是对于线程来说,这些都要变。当clone这个系统调用成功的时候,除了内核里面有这个线程对应的task_struct,当系统调用返回到用户态的时候,用户态的栈应该是线程的栈,栈顶指针应该指向线程的栈,指令指针应该指向线程将要执行的那个函数。
所以这些都需要我们自己做,将线程要执行的函数的参数和指令的位置都压到栈里面,当从内核 返回,从栈里弹出来的时候,就从这个函数开始,带着这些参数执行下去。
接下来我们就要进入内核了。内核里面对于clone系统调用的定义是这样的:
SYSCALL_DEFINE5(clone, unsigned long, clone_flags, unsigned long, newsp,
int __user *, parent_tidptr,
int __user *, child_tidptr,
unsigned long, tls)
{
return _do_fork(clone_flags, newsp, 0, parent_tidptr, child_tidptr, tls);
}
在clone中系统调用里面执行了_do_fork,这里的_do_fork跟进程创建中的逻辑类似,主要有以下的区别:
第一个是上面复杂的标志位设定:
对于copy_files,原来是调用dup_fd复制一个files_struct的,现在因为CLONE_FILES标识位变成将原来的files_struct引用计数加一:
static int copy_files(unsigned long clone_flags, struct task_struct *tsk)
{
struct files_struct *oldf, *newf;
oldf = current->files;
if (clone_flags & CLONE_FILES) {
atomic_inc(&oldf->count);
goto out;
}
newf = dup_fd(oldf, &error);
tsk->files = newf;
out:
return error;
}对于copy_fs,原来是调用copy_fs_struct复制一个fs_struct,现在因为CLONE_FS标识位变成将 原来的fs_struct的用户数加一:
static int copy_fs(unsigned long clone_flags, struct task_struct *tsk)
{
struct fs_struct *fs = current->fs;
if (clone_flags & CLONE_FS) {
fs->users++;
return 0;
}
tsk->fs = copy_fs_struct(fs);
return 0;
}对于copy_sighand,原来是创建一个新的sighand_struct,现在因为CLONE_SIGHAND标识位变成将原来的sighand_struct引用计数加一:
static int copy_sighand(unsigned long clone_flags, struct task_struct *tsk)
{
struct sighand_struct *sig;
if (clone_flags & CLONE_SIGHAND) {
atomic_inc(¤t->sighand->count);
return 0;
}
sig = kmem_cache_alloc(sighand_cachep, GFP_KERNEL);
atomic_set(&sig->count, 1);
memcpy(sig->action, current->sighand->action, sizeof(sig->action));
return 0;
}
对于copy_signal,原来是创建一个新的signal_struct,现在因为CLONE_THREAD直接返回了。
static int copy_signal(unsigned long clone_flags, struct task_struct *tsk)
{
struct signal_struct *sig;
if (clone_flags & CLONE_THREAD)
return 0;
sig = kmem_cache_zalloc(signal_cachep, GFP_KERNEL);
tsk->signal = sig;
init_sigpending(&sig->shared_pending);
......
}对于copy_mm,原来是调用dup_mm复制一个mm_struct,现在因为CLONE_VM标识位而直接指向了原来的mm_struct
static int copy_mm(unsigned long clone_flags, struct task_struct *tsk)
{
struct mm_struct *mm, *oldmm;
oldmm = current->mm;
if (clone_flags & CLONE_VM) {
mmget(oldmm);
mm = oldmm;
goto good_mm;
}
mm = dup_mm(tsk);
good_mm:
tsk->mm = mm;
tsk->active_mm = mm;
return 0;
}第二个就是对于亲缘关系的影响
毕竟我们要识别多个线程是不是属于一个进程。
p->pid = pid_nr(pid);
if (clone_flags & CLONE_THREAD) {
p->exit_signal = -1;
p->group_leader = current->group_leader;
p->tgid = current->tgid;
} else {
if (clone_flags & CLONE_PARENT)
p->exit_signal = current->group_leader->exit_signal;
else
p->exit_signal = (clone_flags & CSIGNAL);
p->group_leader = p;
p->tgid = p->pid;
}
/* CLONE_PARENT re-uses the old parent */
if (clone_flags & (CLONE_PARENT|CLONE_THREAD)) {
p->real_parent = current->real_parent;
p->parent_exec_id = current->parent_exec_id;
} else {
p->real_parent = current;
p->parent_exec_id = current->self_exec_id;
}
如果是新进程,那这个进程的group_leader就是他自己,tgid是它自己的pid,这就完全重打 锣鼓另开张了,自己是线程组的头。如果是新线程,group_leader是当前进程的, group_leader,tgid是当前进程的tgid,也就是当前进程的pid,这个时候还是拜原来进程为 老大。
如果是新进程,新进程的real_parent是当前的进程,在进程树里面又见一辈人;如果是新线 程,线程的real_parent是当前的进程的real_parent,其实是平辈的。
第三,对于信号的处理
如何保证发给进程的信号虽然可以被一个线程处理,但是影响范围应该是整个进程的。例如,kill一个进程,则所有线程都要被干掉。如果一个信号是发给一个线程的 pthread_kill,则应该只有线程能够收到。
在copy_process的主流程里面,无论是创建进程还是线程,都会初始化struct sigpending pending,也就是每个task_struct,都会有这样一个成员变量。这就是一个信号列表。如果这个 task_struct是一个线程,这里面的信号就是发给这个线程的;如果这个task_struct是一个进程,这里面的信号是发给主线程的。
init_sigpending(&p->pending);另外,上面copy_signal的时候,我们可以看到,在创建进程的过程中,会初始化signal_struct里面的struct sigpending shared_pending。但是,在创建线程的过程中,连signal_struct都共享了。也就是说,整个进程里的所有线程共享一个shared_pending,这也是一个信号列表,是发给整个进程的,哪个线程处理都一样。
init_sigpending(&sig->shared_pending);至此,clone在内核的调用完毕,要返回系统调用,回到用户态。
用户态执行线程
根据__clone的第一个参数,回到用户态也不是直接运行我们指定的那个函数,而是一个通用的 start_thread,这是所有线程在用户态的统一入口。
#define START_THREAD_DEFN \
static int __attribute__ ((noreturn)) start_thread (void *arg)
START_THREAD_DEFN
{
struct pthread *pd = START_THREAD_SELF;
/* Run the code the user provided. */
THREAD_SETMEM (pd, result, pd->start_routine (pd->arg));
/* Call destructors for the thread_local TLS variables. */
/* Run the destructor for the thread-local data. */
__nptl_deallocate_tsd ();
if (__glibc_unlikely (atomic_decrement_and_test (&__nptl_nthreads)))
/* This was the last thread. */
exit (0);
__free_tcb (pd);
__exit_thread ();
}
在start_thread入口函数中,才真正的调用用户提供的函数,在用户的函数执行完毕之后,会释 放这个线程相关的数据。例如,线程本地数据thread_local variables,线程数目也减一。如果 这是最后一个线程了,就直接退出进程,另外__free_tcb用于释放pthread。
void
internal_function
__free_tcb (struct pthread *pd)
{
......
__deallocate_stack (pd);
}
void
internal_function
__deallocate_stack (struct pthread *pd)
{
/* Remove the thread from the list of threads with user defined
stacks. */
stack_list_del (&pd->list);
/* Not much to do. Just free the mmap()ed memory. Note that we do
not reset the 'used' flag in the 'tid' field. This is done by
the kernel. If no thread has been created yet this field is
still zero. */
if (__glibc_likely (! pd->user_stack))
(void) queue_stack (pd);
}
__free_tcb会调用__deallocate_stack来释放整个线程栈,这个线程栈要从当前使用线程栈的列表stack_used中拿下来,放到缓存的线程栈列表stack_cache中。
总结
创建进程的话,调用的系统调用是fork,在copy_process函数里面,会将五大结构 files_struct、fs_struct、sighand_struct、signal_struct、mm_struct都复制一遍,从此父进程 和子进程各用各的数据结构。而创建线程的话,调用的是系统调用clone,在copy_process函数 里面, 五大结构仅仅是引用计数加一,也即线程共享进程的数据结构。