文章目录
- 作业内容
- Step 1. 创建三角形的2维bounding box
- Step 2. 判断bBox中的像素中心点是否在三角形内
- Step 3. 比较插值深度和Depth Buffer
- MSAA
作业内容
在屏幕上画出一个实心三角形,
换言之,栅格化一个三角形。上一次作业中,在视口变化之后,我们调用了函数
rasterize_wireframe(const Triangle& t)。但这一次,你需要自己填写并调用
函数 rasterize_triangle(const Triangle& t)。
该函数的内部工作流程如下:
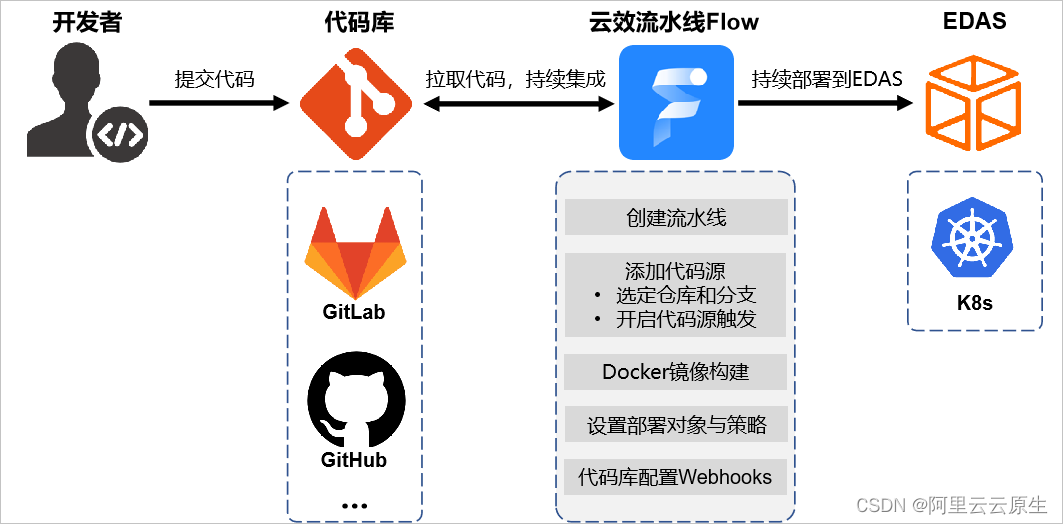
- 创建三角形的 2 维 bounding box。
- 遍历此 bounding box 内的所有像素(使用其整数索引)。然后,使用像素中
心的屏幕空间坐标来检查中心点是否在三角形内。 - 如果在内部,则将其位置处的插值深度值 (interpolated depth value) 与深度
缓冲区 (depth buffer) 中的相应值进行比较。 - 如果当前点更靠近相机,请设置像素颜色并更新深度缓冲区 (depth buffer)。
Step 1. 创建三角形的2维bounding box
GAMES101_Lecture_05.pdf 43页
- Checking All Pixels on the Screen?
已知三角形的三个顶点,如何得出蓝色矩形的width 和 height。 或者说左下角点和右上角的坐标
假设三角形的三个顶点经过t.toVector4( )输出的坐标如下:
===== P0 ======
108.579
350
-0.714285
1
===== p1 ======
350
108.579
-0.714285
1
===== p2 ======
591.421
350
-0.714285
1
那么bounding box 左下角和右上角的坐标为
B_1_x = min(P0_x, P1_x, P2_x)
B_1_y = min(P0_y, P1_y, P2_y)
B_2_x = max(P0_x, P1_x, P2_x)
B_2_y = max(P0_y, P1_y, P2_y)
bounding_box_width = B_2_x - B_1_x;
bounding_box_height = B_2_y - B_1_y;
unsigned int bBox_leftbottom_x;
unsigned int bBox_leftbottom_y;
unsigned int bBox_topright_x;
unsigned int bBox_topright_y;
unsigned int width, height;
bBox_leftbottom_x = floor(MIN(MIN(v[0].x(), v[1].x()), v[2].x())); //向下取整
bBox_leftbottom_y = floor(MIN(MIN(v[0].y(), v[1].y()), v[2].y()));
bBox_topright_x = ceil(MAX(MAX(v[0].x(), v[1].x()), v[2].x())); //向上取整
bBox_topright_y = ceil(MAX(MAX(v[0].y(), v[1].y()), v[2].y()));
std::cout << "bBox :leftbottom:(" << bBox_leftbottom_x <<
","<<bBox_leftbottom_y <<") "<<
"topright:("<<bBox_topright_x <<
","<< bBox_topright_y <<")" << std::endl;
width = bBox_topright_x - bBox_leftbottom_x;
height = bBox_topright_y - bBox_topright_y;
x: 108.579 y: 350 z: -0.714285
x: 350 y: 108.579 z: -0.714285
x: 591.421 y: 350 z: -0.714285
bBox :leftbottom:(108,108) topright:(592,350)
bBox_width:484
bBox_height:242
Step 2. 判断bBox中的像素中心点是否在三角形内
遍历此 bounding box 内的所有像素(使用其整数索引)。然后,使用像素中心的屏幕空间坐标来检查中心点是否在三角形内。
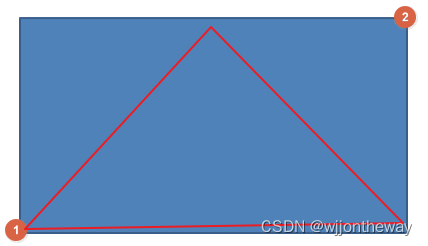
在Lecture 2中,判断一个点是否在三角形内,可以通过某个顶点到该点的向量与边的叉乘是否都满足z坐标的一致性,比如上图中判断(按逆时针方向)
- P 0 P 1 → \overrightarrow {P_0P_1} P0P1 x P 0 P Q → \overrightarrow {P_0P_Q} P0PQ
- P 1 P 2 → \overrightarrow {P_1P_2} P1P2 x P 1 P Q → \overrightarrow {P_1P_Q} P1PQ
- P 2 P 0 → \overrightarrow {P_2P_0} P2P0 x P 2 P Q → \overrightarrow {P_2P_Q} P2PQ
借助Egien提供的向量叉乘的接口
v1_tmp = vector_3f_p0p1.cross(vector_3f_p0pq);
v2_tmp = vector_3f_p1p2.cross(vector_3f_p1pq);
v3_tmp = vector_3f_p2p1.cross(vector_3f_p2pq);
static bool insideTriangle(int x, int y, const Vector3f* _v)
{
// TODO : Implement this function to check if the point (x, y) is inside the triangle represented by _v[0], _v[1], _v[2]
Vector3f q = Vector3f(x, y, 1.0); // Homogeneous
Vector3f p0_pq = q - _v[0];
Vector3f p1_pq = q - _v[1];
Vector3f p2_pq = q - _v[2];
Vector3f v1_tmp = (_v[1] - _v[0]).cross(p0_pq); //p0_p1 x p0_pq
Vector3f v2_tmp = (_v[2] - _v[1]).cross(p1_pq); //p1_p2 x p1_pq
Vector3f v3_tmp = (_v[0] - _v[2]).cross(p2_pq); //p2_p0 x p2_pq
if ((v1_tmp.z() > 0 && v2_tmp.z() > 0 && v3_tmp.z() > 0) ||
(v1_tmp.z() < 0 && v2_tmp.z() < 0 && v3_tmp.z() < 0) ||
(v1_tmp.z() < 1e-6 && v2_tmp.z() < 1e-6 && v3_tmp.z() < 1e-6))
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
Step 3. 比较插值深度和Depth Buffer
- 如果在内部,则将其位置处的插值深度值 (interpolated depth value) 与深度
缓冲区 (depth buffer) 中的相应值进行比较。 - 如果当前点更靠近相机,请设置像素颜色并更新深度缓冲区 (depth buffer)。
注意,需要将工程的属性修改成兼容C++17, 否则下面语句报错
auto [alpha, beta, gamma] = computeBarycentric2D(x, y, t.v);
for (int x = (int)bBox_leftbottom_x; x <= bBox_topright_x; x++)
{
for (int y = (int)bBox_leftbottom_y; y <= bBox_topright_y; y++)
{
if (insideTriangle(x, y, t.v))
{
// If so, use the following code to get the interpolated z value.
auto [alpha, beta, gamma] = computeBarycentric2D(x, y, t.v);
float w_reciprocal = 1.0 / (alpha / v[0].w() + beta / v[1].w() + gamma / v[2].w());
float z_interpolated = alpha * v[0].z() / v[0].w() + beta * v[1].z() / v[1].w() + gamma * v[2].z() / v[2].w();
z_interpolated *= w_reciprocal;
// compare the interpolated depth value with depth buffer value
if (depth_buf[get_index(x, y)] > z_interpolated)
{
depth_buf[get_index(x, y)] = z_interpolated;
// TODO : set the current pixel (use the set_pixel function) to the color of the triangle (use getColor function) if it should be painted.
set_pixel(Vector3f(x, y, z_interpolated), t.getColor());
}
}
}
}
MSAA
用 super-sampling 处理 Anti-aliasing : 你可能会注意到,当我们放大图像时,图像边缘会有锯齿感。我们可以用 super-sampling来解决这个问题,即对每个像素进行 2 * 2 采样,并比较前后的结果 (这里并不需要考虑像素与像素间的样本复用)。需要注意的点有,对于像素内的每一个样本都需要维护它自己的深度值,即每一个像素都需要维护一个 samplelist。最后,如果你实现正确的话,你得到的三角形不应该有不正常的黑边
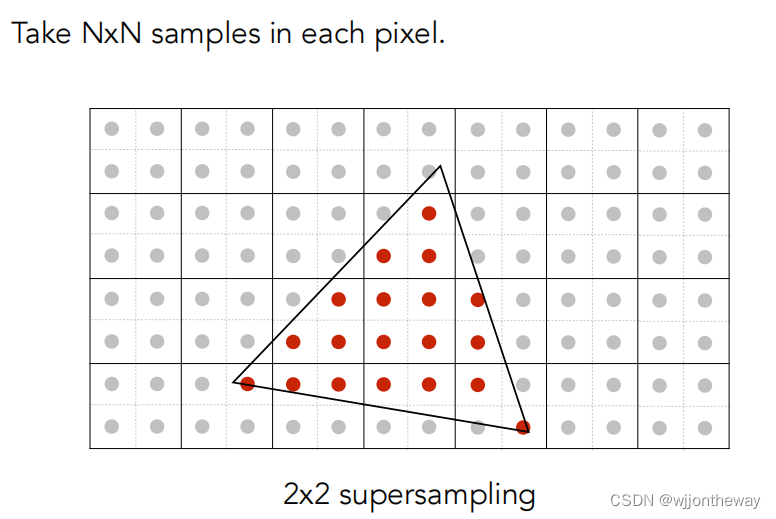
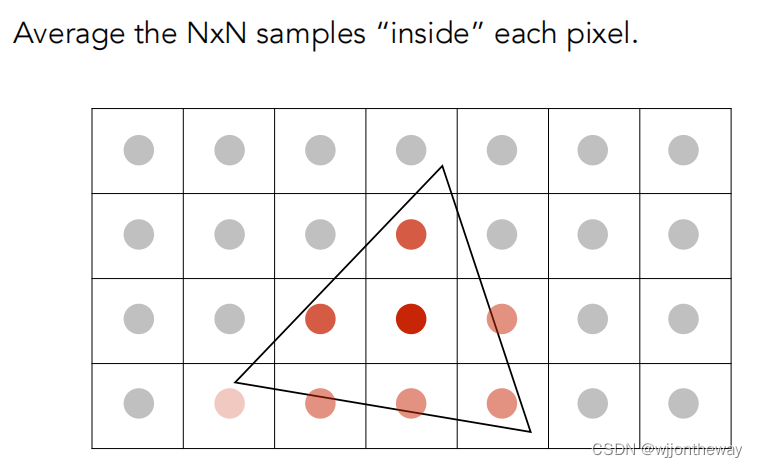
for (int x = (int)bBox_leftbottom_x; x <= bBox_topright_x; x++)
{
for (int y = (int)bBox_leftbottom_y; y <= bBox_topright_y; y++)
{
float depth_tmp = 0.0; // max value for float in system
int count = 0;
Vector2f sample_point[4] = { Vector2f(0.25, 0.25),Vector2f(0.75, 0.25), Vector2f(0.75,0.75), Vector2f(0.75, 0.25) };
for (int i=0; i<4; i++)
{
if (insideTriangle(x+ sample_point[i].x(), y+sample_point[i].y(), t.v))
{
// If so, use the following code to get the interpolated z value.
auto [alpha, beta, gamma] = computeBarycentric2D(x, y, t.v);
float w_reciprocal = 1.0 / (alpha / v[0].w() + beta / v[1].w() + gamma / v[2].w());
float z_interpolated = alpha * v[0].z() / v[0].w() + beta * v[1].z() / v[1].w() + gamma * v[2].z() / v[2].w();
z_interpolated *= w_reciprocal;
depth_tmp += z_interpolated;
count +=1;
}
}
float depth_average = depth_tmp / 4;
if (count>0&&depth_buf[get_index(x,y)]> depth_average)
{
depth_buf[get_index(x, y)] = depth_average;
set_pixel(Vector3f(x, y, depth_average), t.getColor() * count / 4.0 + frame_buf[get_index(x, y)] * (4 - count) / 4.0);
}
}
}