先在 LinkedList.js 给链表添加一个移除方法
class Node {
constructor(element, next) {
this.element = element;
this.next = next;
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null; // 链表的头
this.size = 0; // 链表长度
}
// 可以直接在尾部添加内容,或者根据索引添加
add(index, element) {
// 传入一个参数是需要设置一下 index, element
if (arguments.length === 1) {
// 在尾部添加,传入的 index 就当做是 element
element = index;
// 然后把 this.size 当做索引
index = this.size;
}
// 处理越界可能
if (index < 0 || index > this.size) throw new Error("越界");
// 判断 index 是否为 0
if (index === 0) {
// 老的头
let head = this.head;
// 设置新头,将老的头变为当前节点的下一个
this.head = new Node(element, head);
} else {
// 先找到当前索引的上一个
let prevNode = this.getNode(index - 1);
// 将当前上一个节点的 next 指向新的节点,新的节点的下一个指向上一个节点的 next
prevNode.next = new Node(element, prevNode.next);
}
// 累加 size
this.size++;
}
getNode(index) {
// 从头开始找
let current = this.head;
// 不能向后找,找到索引的位置
for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
current = current.next;
}
return current;
}
remove(index) {
if (index === 0) {
let node = this.head;
if (!node) return null;
this.head = node.next;
this.size--;
return node.element;
}
}
}
let ll = new LinkedList();
ll.add(0, 1);
ll.add(0, 2);
ll.add(3);
ll.add(1, 4);
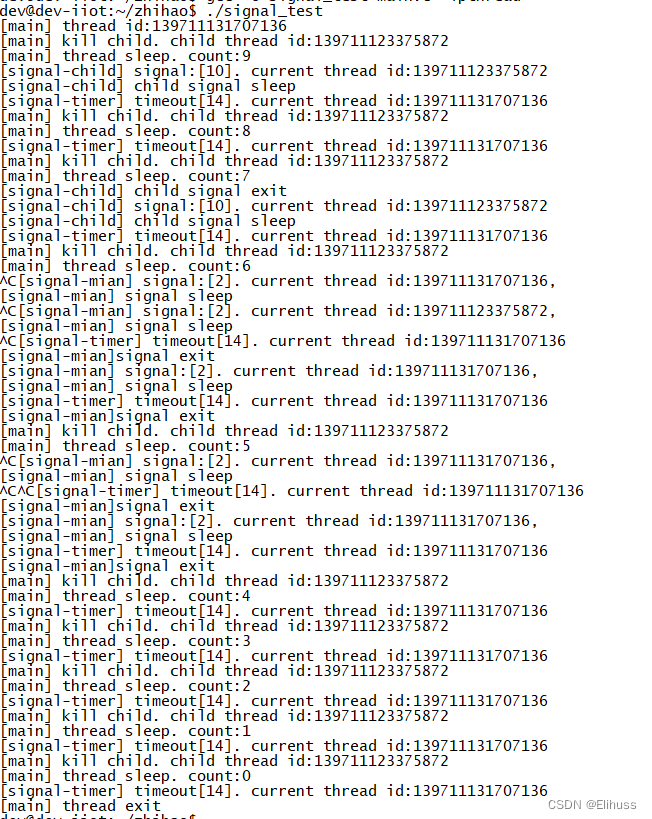
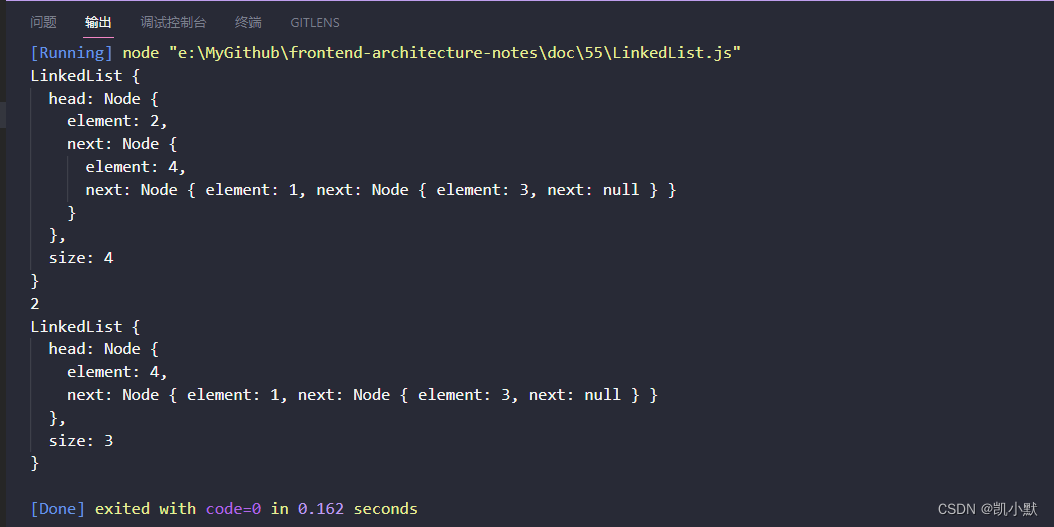
console.dir(ll, { depth: 100 });
console.dir(ll.remove(0));
console.dir(ll, { depth: 100 });
module.exports = LinkedList;
下面实现可写流:
- 先创建一个队列的类,利用上面 LinkedList 维护一个链表
- 然后创建自己的可写流 KaimoWriteStream 类继承 EventEmitter
- 再区分是否是在写入状态,根据写入状态确定存缓存还是真正的写入
- 最后写入完一个之后,判断是否需要清空缓存,需要的话就继续将 poll 返回的数据继续写入
const EventEmitter = require("events");
const fs = require("fs");
let LinkedList = require("./LinkedList");
class Queue {
constructor() {
this.LinkedList = new LinkedList();
}
offer(element) {
this.LinkedList.add(element);
}
poll() {
return this.LinkedList.remove(0);
}
}
class KaimoWriteStream extends EventEmitter {
constructor(path, opts = {}) {
super();
this.path = path;
this.flags = opts.flags || "w";
this.autoClose = opts.autoClose || true;
this.encoding = opts.encoding || "utf8";
this.start = opts.start || 0;
this.mode = opts.mode || 0o666;
this.highWaterMark = opts.highWaterMark || 16 * 1024;
// 维护当前存入的数据个数
// 每次调用 write 方法,会根据写入的内容的个数累加给 len 属性(缓存的长度)
this.len = 0;
// 是否正在写入
this.writing = false;
// 是否需要触发 drain 事件
this.needDrain = false;
// 写入的偏移量
this.offset = this.start;
// 用来缓存的队列
this.cache = new Queue();
// 默认先打开文件
this.open();
}
// open 方法是异步的
open() {
fs.open(this.path, this.flags, this.mode, (err, fd) => {
if (err) {
return this.emit("error", err);
}
// 将 fd 保存到实例上,用于稍后的读取操作
this.fd = fd;
this.emit("open", fd);
});
}
write(chunk, encoding = "utf8", cb = () => {}) {
// 统一转为 buffer
chunk = Buffer.isBuffer(chunk) ? chunk : Buffer.from(chunk);
this.len += chunk.length;
// write 方法的返回值
let flag = this.len < this.highWaterMark;
// drain 事件的触发:1.必须写入的个数达到预期或者超过预期
this.needDrain = !flag;
if (this.writing) {
// 正在写入
this.cache.offer({
chunk,
encoding,
cb
});
} else {
// 没有正在写入
this.writing = true; // 标识正在写入了
// 真正写入的逻辑
this._write(chunk, encoding, () => {
// 原来用户传入的 callback
cb();
// 当前内容写入完毕后清空缓存区中的内容
this.clearBuffer();
});
}
return flag;
}
_write(chunk, encoding, cb) {
// 写入必须要等待文件打开完毕,如果打开了会触发 open 事件
if (typeof this.fd !== "number") {
// 如果没有 fd 就返回一个 open 的一次性事件,再去回调 _write 方法
return this.once("open", () => this._write(chunk, encoding, cb));
}
// 将用户数据写入到文件中
fs.write(this.fd, chunk, 0, chunk.length, this.offset, (err, written) => {
if (err) {
return this.emit("error", err);
}
this.len -= written; // 缓存中的数量要减少
this.offset += written;
console.log("chunk--->", chunk.toString());
cb(); // 当前文件内容写入完毕后,再去清空缓存中的
});
}
clearBuffer() {
let data = this.cache.poll();
if (data) {
// 需要清空缓存
let { chunk, encoding, cb } = data;
this._write(chunk, encoding, () => {
cb();
// 当前缓存的第一个执行后,再去清空第二个
this.clearBuffer();
});
} else {
this.writing = false;
if (this.needDrain) {
// 当前触发后下次就不需要再次触发了
this.needDrain = false;
this.emit("drain");
}
}
}
}
module.exports = KaimoWriteStream;
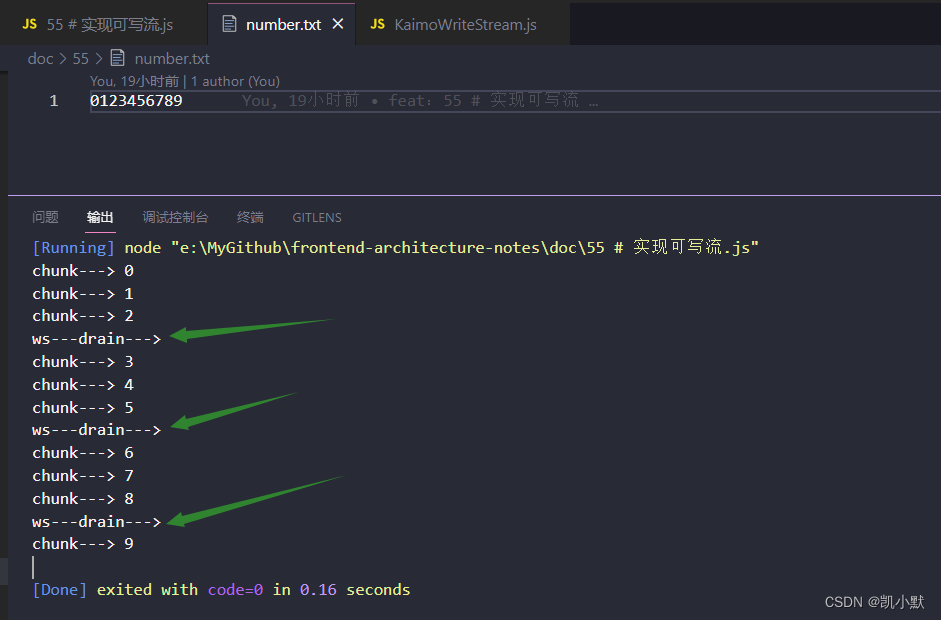
下面用实现的可写流测试一下上一节的例子:写入10个数,只占用一个字节的内存
const path = require("path");
const KaimoWriteStream = require("./55/KaimoWriteStream");
let ws = new KaimoWriteStream(path.resolve(__dirname, "./55/number.txt"), {
highWaterMark: 3 // 利用 highWaterMark 来控制写入的速率
});
let numberIndex = 0;
function write() {
let flag = true; // 是否可以写入
while (flag && numberIndex < 10) {
flag = ws.write(numberIndex + "");
numberIndex++;
}
}
write();
ws.on("drain", () => {
console.log("ws---drain--->");
write();
});