文章目录
- 单例模式
- 饿汉式单例模式
- 懒汉式单例模式
- 懒汉式单例模式2
- 工厂模式(创建型模式)
- 简单工厂
- 工厂方法
- 抽象工厂
- 总结
单例模式
一个类不管创建多少次多线,永远只能得到该类型一个对象的实例。
A* p1 = new A();
A *p2 = new A();
A *p3 = new A();
常用的为日志模块,数据库模块。
方法:
1、构造函数私有化,拷贝构造,赋值重载去除;
2、定义一个唯一的类的实例对象;
3、获取类唯一实例对象的静态方法(因为没有对象,必须通过静态方法获取)
class Singleton
{
public:
static Singleton* getInstance()
{
return &instance;
}
private:
static Singleton instance;
Singleton(){};
Singleton(const Singleton&) = delete;
Singleton& operator=(const Singleton&) = delete;
}
Singleton Singleton::instance;
int main()
{
Singleton* p1 = Singleton::getInstance();
Singleton* p2 = Singleton::getInstance();
Singleton* p3 = Singleton::getInstance();
// p1 p2 p3地址相同
Singleton t = *p1; // 错误
return 0;
}
饿汉式单例模式
如上。
因为在程序启动时,实例对象就已经初始化好了,所以饿汉式一定线程安全。
但是对象类的构造函数可能很复杂,于是有懒汉单例模式。
懒汉式单例模式
class Singleton
{
public:
static Singleton* getInstance()
{
if(instance == nullptr)
{
instance = new Singleton();
}
return &instance;
}
private:
static Singleton *instance;
Singleton(){};
Singleton(const Singleton&) = delete;
Singleton& operator=(const Singleton&) = delete;
}
Singleton Singleton::instance = nullptr;
int main()
{
Singleton* p1 = Singleton::getInstance();
Singleton* p2 = Singleton::getInstance();
Singleton* p3 = Singleton::getInstance();
// p1 p2 p3地址相同
Singleton t = *p1; // 错误
return 0;
}
懒汉式单例模式不是线程安全,getInstance方法不是可重入函数。
解决方案:锁+双重判断,实现线程间的互斥。
static Singleton* getInstance()
{
if(instance == nullptr)
{
lock_guard<std::mutex> guard(mtx);
if(instance == nullptr)
instance = new Singleton();
}
return &instance;
}
static Singleton *volatile instance;
类外初始化:
Singleton *volatile Singleton::instance = nullptr;
使用volatile有一个线程给instance new时,其他线程立马就能知晓。
懒汉式单例模式2
保障线程安全。
class Singleton
{
public:
static Singleton* getInstance()
{
static Singleton instance; // 互斥动作,线程安全
return &instance;
}
private:
Singleton()
{
很多初始化的代码
}
Singleton(const Singleton&) = delete;
Singleton& operator=(const Singleton&) = delete;
}
int main()
{
return 0;
}
在getInstance方法中,静态对象的初始化本身就是一个线程互斥的动作,所以线程安全。
工厂模式(创建型模式)
作用:主要是封装对象的创建。
简单工厂
不属于正规的设计模式
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class product {
public:
virtual void show() = 0;
};
class productA : public product{
public:
void show() {
cout << "productA" << endl;
}
};
class productB : public product{
public:
void show() {
cout << "productB" << endl;
}
};
enum Type {
type1,
type2
};
class Factory {
public:
product *Create(enum Type type) {
switch(type) {
case type1:
return new productA();
case type2:
return new productB();
default:
break;
}
}
};
int main() {
Factory factory;
factory.Create(type1)->show();
factory.Create(type2)->show();
return 0;
}
不满足开闭原则,而且一个工厂干的事情太多。
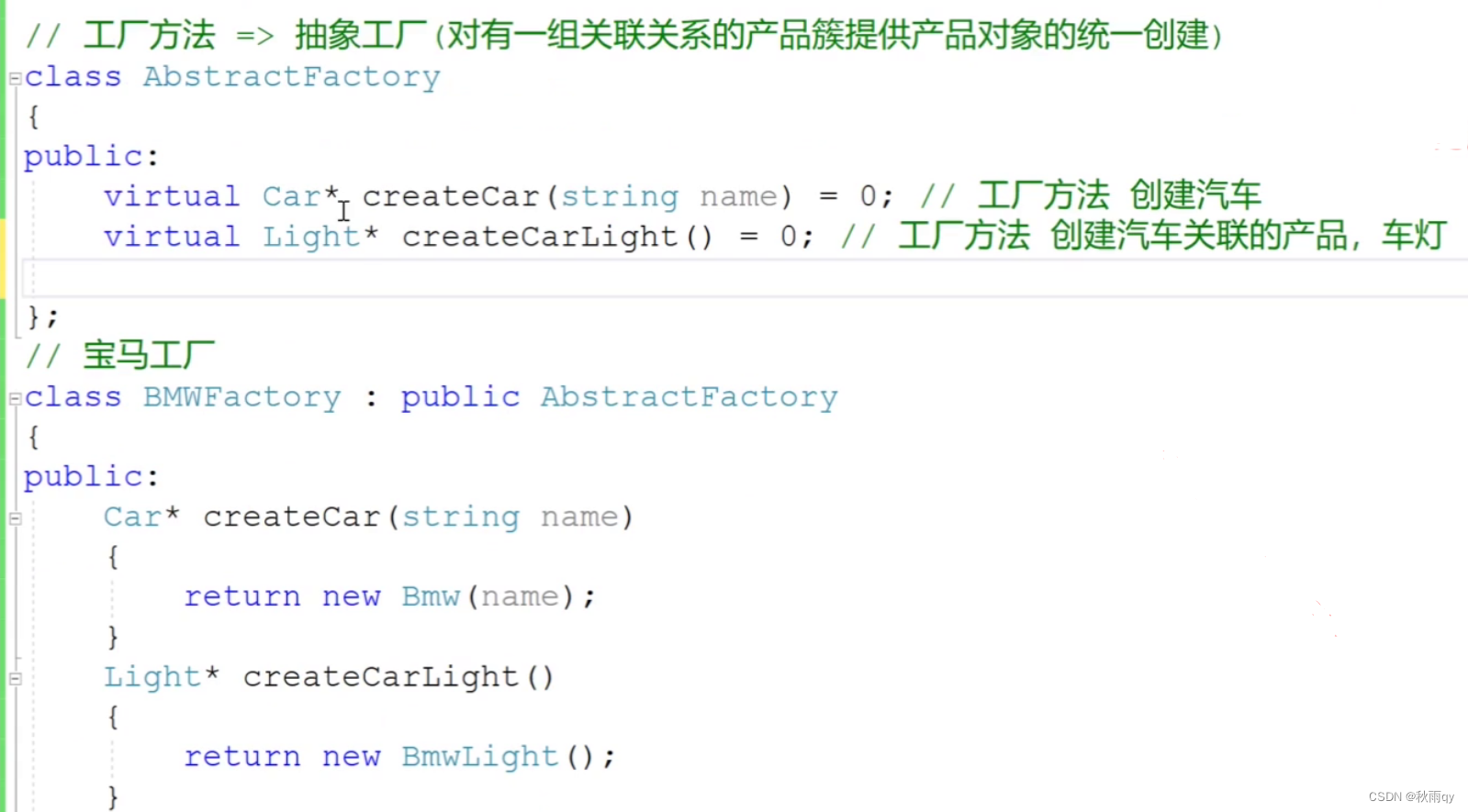
工厂方法
汽车类


工厂类:


调用:

抽象工厂
1是实际上很多产品是有关联的,不应该放在不同的工厂创建,2是工厂的子类型太多,写不完。
需要将工厂方法转换为抽象工厂。
总结