前言
项目中经常会遇到一些非分布式的调度任务,需要在未来的某个时刻周期性执行。实现这样的功能,我们有多种方式可以选择:
-
Timer类, jdk1.3 引入,不推荐
它所有任务都是串行执行的,同一时间只能有一个任务在执行,而且前一个任务的延迟或异常都将会影响到之后的任务。
-
Spring 的
@Scheduled注解,不是很推荐
这种方式底层虽然是用线程池实现,但是有个最大的问题,所有的任务都使用的同一个线程池,可能会导致长周期的任务运行影响短周期任务运行,造成线程池"饥饿",更加推荐的做法是同种类型的任务使用同一个线程池。
-
自定义
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor实现调度任务
这也是本文重点讲解的方式,通过自定义ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor调度线程池,提交调度任务才是最优解。
创建方式
创建ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor方式一共有两种,第一种是通过自定义参数,第二种通过Executors工厂方法创建。 根据阿里巴巴代码规范中的建议,更加推荐我们使用第一种方式创建。
-
自定义参数创建
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,ThreadFactory threadFactory,RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
-
corePoolSize:核心工作的线程数量 -
threadFactory:线程工厂,用来创建线程 -
handler: 拒绝策略,饱和策略
-
Executors工厂方法创建
-
static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize)
根据核心线程数创建调度线程池。
-
static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory)
根据核心线程数和线程工厂创建调度线程池。
核心 API
-
schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit)
创建并执行在给定延迟后启用的一次性操作
-
command: 执行的任务 -
delay:延迟的时间 -
unit: 单位
-
scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long delay, TimeUnit unit)
定时执行周期任务,任务执行完成后,延迟 delay 时间执行
-
command: 执行的任务 -
initialDelay: 初始延迟的时间 -
delay: 上次执行结束,延迟多久执行 -
unit:单位
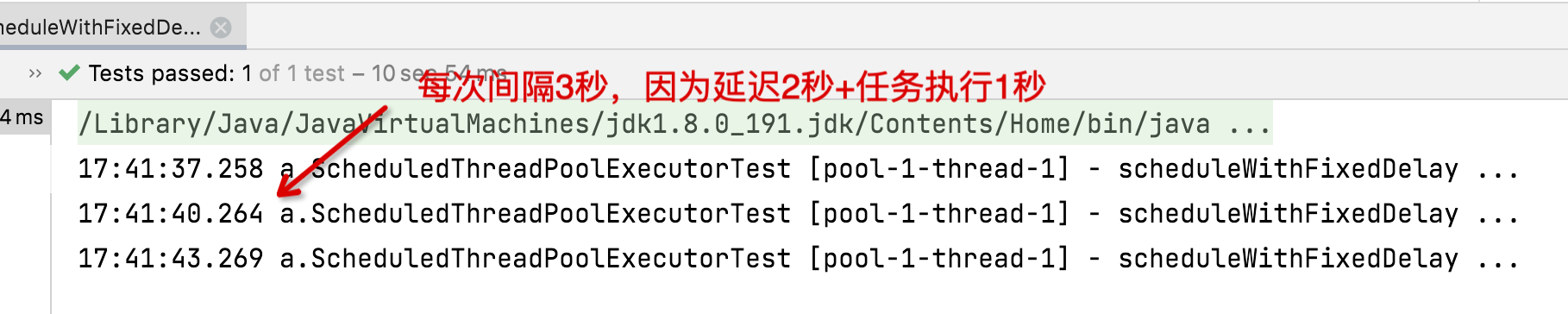
@Testpublic void testScheduleWithFixedDelay() throws InterruptedException {// 创建调度任务线程池ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1);// 按照上次执行完成后固定延迟时间调度scheduledExecutorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(() -> {try {log.info("scheduleWithFixedDelay ...");Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}, 1, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);Thread.sleep(10000);}
-
scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit)
按照固定的评率定时执行周期任务,不受任务运行时间影响。
-
command: 执行的任务 -
initialDelay: 初始延迟的时间 -
period: 周期 -
unit:单位
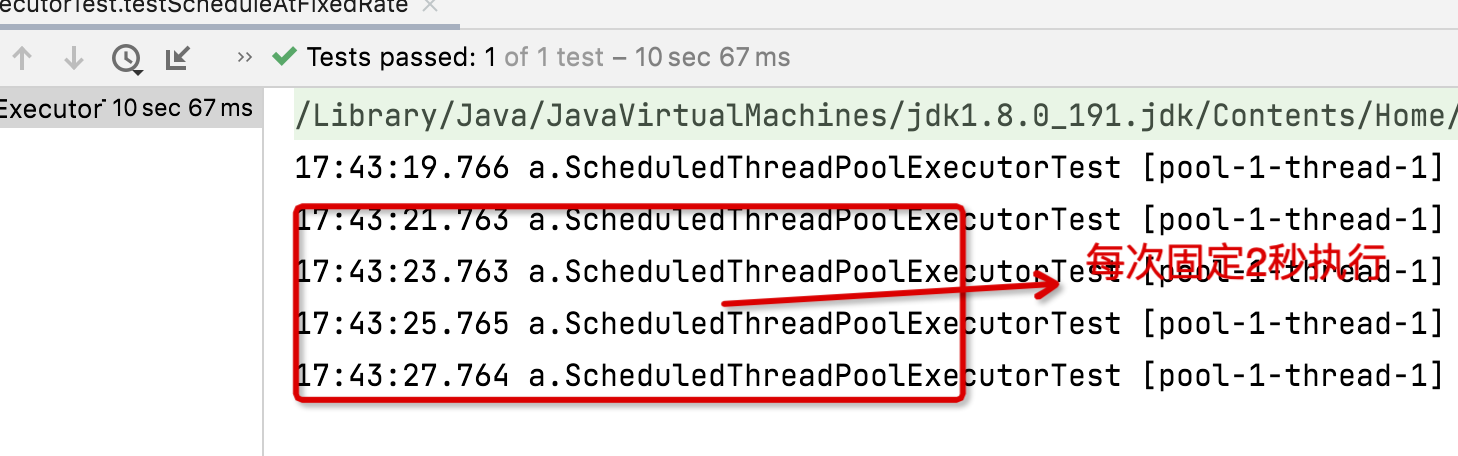
@Testpublic void testScheduleAtFixedRate() throws InterruptedException {// 创建调度任务线程池ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1);// 按照固定2秒时间执行scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {try {log.info("scheduleWithFixedDelay ...");Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}, 1, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);Thread.sleep(10000);}
tips: 以上 API 全部返回ScheduledExecutorService类,调用调用getDelay()可以获取任务下次的执行时间点,非常好用的。
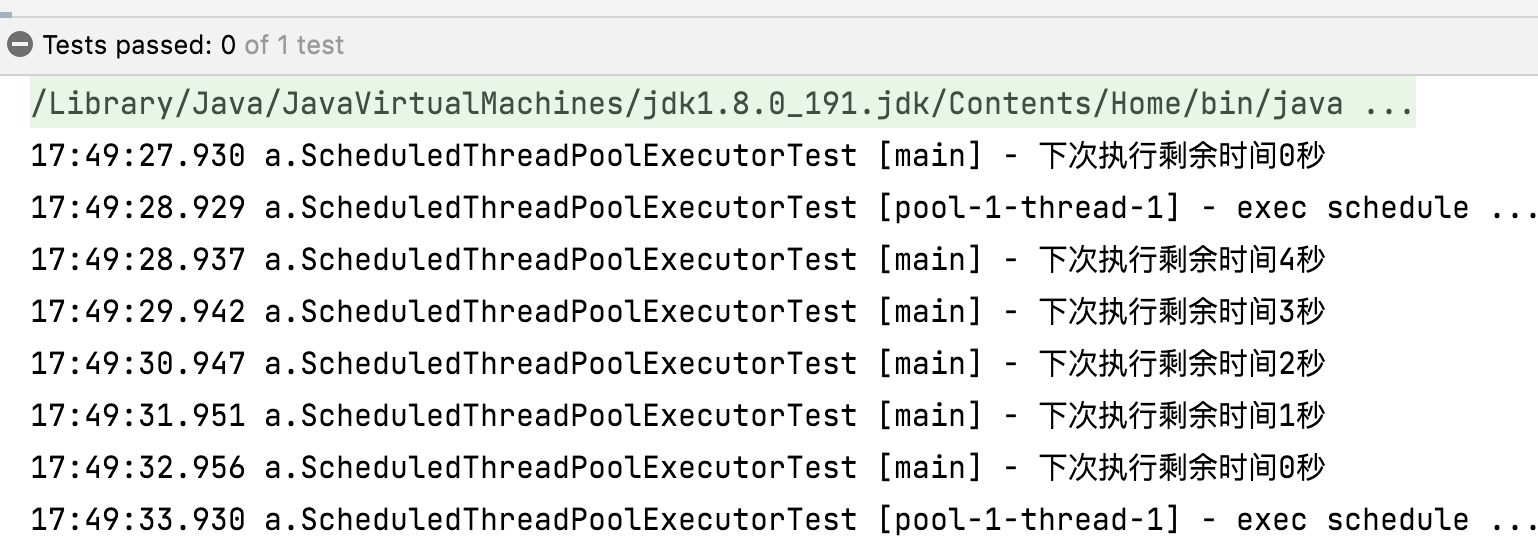
@Testpublic void testResp() throws InterruptedException {// 创建调度任务线程池ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1);// 按照上次执行完成后固定延迟5秒时间调度ScheduledFuture<?> scheduledFuture = scheduledExecutorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(() -> {log.info("exec schedule ...");}, 1, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);while (true) {// 获取剩余时间long delay = scheduledFuture.getDelay(TimeUnit.SECONDS);log.info("下次执行剩余时间{}秒", delay);Thread.sleep(1000);}}
综合例子
下面我们演示个例子,通过ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor实现每周四 18:00:00 定时执行任务。
// 通过ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor实现每周四 18:00:00 定时执行任务@Testpublic void test() {// 获取当前时间LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();System.out.println(now);// 获取周四时间LocalDateTime time = now.withHour(18).withMinute(0).withSecond(0).withNano(0).with(DayOfWeek.THURSDAY);// 如果 当前时间 > 本周周四,必须找到下周周四if(now.compareTo(time) > 0) {time = time.plusWeeks(1);}System.out.println(time);// initailDelay 代表当前时间和周四的时间差// period 一周的间隔时间long initailDelay = Duration.between(now, time).toMillis();long period = 1000 * 60 * 60 * 24 * 7;ScheduledExecutorService pool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);pool.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {System.out.println("running...");}, initailDelay, period, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);}
使用注意事项
使用 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 时一定要注意异常处理, 如果使用不当,会导致定时任务不再执行,记住要 try catch 捕获异常,具体参考这篇文章:ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor踩过最痛的坑。
总结
本文主要讲解了ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor这个线程池类的使用,可以用来实现我们的调度任务,那么它是怎么实现的,我们也可以思考下。
![【C语言】移位操作符 位操作符 - 对二进制位进行精准操作【+面试题目】_[初阶篇]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2df7227933834ee6b0c82ef0fb0be6e7.png)