Grpc简介:
gRPC是一个高性能、通用的开源RPC框架,其由Google主要面向移动应用开发并基于HTTP/2协议标准而设计,基于ProtoBuf(Protocol Buffers)序列化协议开发,且支持众多开发语言,能够基于语言自动生成客户端和服务端功能库。且支持java、C++、C#等众多开发语言。
特点:
- 通信协议基于标准的 HTTP/2 设计,支持双向流、消息头压缩、单 TCP 的多路复用、服务端推送等特性,这些特性使得 gRPC 在移动端设备上更加省电和节省网络流量;
- 语言中立,支持多种语言。
编译Grpc:
使用grpc
.proto
.proto 文件用来定义客户端和服务端的服务接口和消息字段格式。
如
syntax = "proto3"; //定义了使用 proto3 的语法
option java_package = "ex.grpc";
package mathtest; //表示定义消息的包名,对于 C++ 程序,消息类将会被包装在对应的命名空间中
// Defines the service 定义在 RPC 调用中的服务接口,sendRequest 为服务接口,MathRequest为输入参数,MathReply为返回值,MathTest 为服务类,服务端必须继承于它。
service MathTest {
// Function invoked to send the request
rpc sendRequest (MathRequest) returns (MathReply) {}
}
// The request message containing requested numbers,字段后面的数字并不表示该字段的值,只是 proto 程序用来生成相关源代码使用
message MathRequest {
int32 a = 1;
int32 b = 2;
}
// The response message containing response
message MathReply {
int32 result = 1;
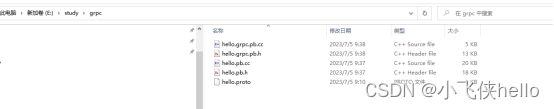
}hello.proto文件通过执行命令会生成hello.grpc.pb.cc、hello.grpc.pb.h、hello.pb.cc和hello.pb.h。服务端和客户端就是通过引用这些文件编写代码
配置环境变量
把protoc.exe所在的路径添加到环境变量。打开cmd,输入protoc,回车,可看到是否配置成功。
执行cmd命令
打开cmd, 使用cd命令进入到hello.proto文件所在的目录。
执行protoc.exe ./helloworld.proto --cpp_out=./
会生成hello.pb.h和hello.pb.cc文件
protoc.exe ./hello.proto--plugin=protoc-gen-grpc=E:/work/code/vate_fs/GrpcDemo/grpc/bin/grpc_cpp_plugin.exe --grpc_out=./
会生成hello.grpc.pb.h和hello.grpc.pb.cc文件
需要找到grpc_cpp_plugin.exe 所在的目录

延伸:关键字
Repeated
Repeated是protobuf中的一种限定修饰符,从字面意思看有“重复”的意思,实际上它就是用来指定某一个字段可以存放同一个类型的多个数据,相当于C++中的vector或者Java中的List
message Person {
required int32 age = 1;
required string name = 2;
}
message Family {
repeated Person person = 1;
}
Family family;
Person* person;
// 添加一个家庭成员,John
person = family.add_person();
person->set_age(25);
person->set_name("John");
// 添加一个家庭成员,Lucy
person = family.add_person();
person->set_age(23);
person->set_name("Lucy");
// 添加一个家庭成员,Tony
person = family.add_person();
person->set_age(2);
person->set_name("Tony");
// 显示所有家庭成员
int size = family.person_size();
cout << "这个家庭有 " << size << " 个成员,如下:" << endl;
for( int i=0; i<size; i++)
{
Person psn = family.person(i);
cout << i+1 << ". " << psn.name() << ", 年龄 " << psn.age() << endl;
}
required
required是必须的意思,数据发送方和接收方都必须处理这个字段
optional
字面意思是可选的意思,具体protobuf里面怎么处理这个字段呢,就是protobuf处理的时候另外加了一个bool的变量,用来标记这个optional字段是否有值,发送方在发送的时候,如果这个字段有值,那么就给bool变量标记为true,否则就标记为false,接收方在收到这个字段的同时,也会收到发送方同时发送的bool变量,拿着bool变量就知道这个字段是否有值了,这就是option的意思。
服务端
配置grpc的头文件和依赖库
在vs中,你可以用链接器选择 *.lib来选择目录下所有的静态库.
具体为:在VS项目工程的“属性>配置属性>链接器>命令行>其他选项”中,设置"[lib目录]\*.lib "即可在工程中一次性引入全部lib。
在qt无法批量导入,一定要把grpc依赖包里的近50个静态库一个一个添加进来。
注意事项:把zlibd.dll放到输出可执行程序路径下。
创建继承于服务类的子类
重写虚函数的方式,实现服务接口。
注册服务、创建开始服务。
#include <string>
#include <grpcpp/grpcpp.h>
#include "mathtest.grpc.pb.h"
using grpc::Server;
using grpc::ServerBuilder;
using grpc::ServerContext;
using grpc::Status;
using mathtest::MathTest;
using mathtest::MathRequest;
using mathtest::MathReply;
class MathServiceImplementation final : public MathTest::Service {
Status sendRequest(
ServerContext* context,
const MathRequest* request,
MathReply* reply
) override {
int a = request->a();
int b = request->b();
reply->set_result(a * b);
return Status::OK;
}
};
void Run() {
std::string address("0.0.0.0:5000");
MathServiceImplementation service;
ServerBuilder builder;
builder.AddListeningPort(address, grpc::InsecureServerCredentials());
builder.RegisterService(&service);
std::unique_ptr<Server> server(builder.BuildAndStart());
std::cout << "Server listening on port: " << address << std::endl;
server->Wait();
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
Run();
return 0;
}客户端
配置grpc的头文件和依赖库,和服务端一样
客户端封装成一个自定义类,定义一个独占智能指针std::unique_ptr<MathTest::Stub> stub_;
通过私有成员变量 stub_ 向服务端发送请求消息并接收返回结果。
初始化自定义类对象,通过地址创建实例化stub_对象。
#include <string>
#include <grpcpp/grpcpp.h>
#include "mathtest.grpc.pb.h"
using grpc::Channel;
using grpc::ClientContext;
using grpc::Status;
using mathtest::MathTest;
using mathtest::MathRequest;
using mathtest::MathReply;
class MathTestClient {
public:
MathTestClient(std::shared_ptr<Channel> channel) : stub_(MathTest::NewStub(channel)) {}
int sendRequest(int a, int b) {
MathRequest request;
request.set_a(a);
request.set_b(b);
MathReply reply;
ClientContext context;
Status status = stub_->sendRequest(&context, request, &reply);
if(status.ok()){
return reply.result();
} else {
std::cout << status.error_code() << ": " << status.error_message() << std::endl;
return -1;
}
}
private:
std::unique_ptr<MathTest::Stub> stub_;
};
void Run() {
std::string address("0.0.0.0:5000");
MathTestClient client(
grpc::CreateChannel(
address,
grpc::InsecureChannelCredentials()
)
);
int response;
int a = 5;
int b = 10;
response = client.sendRequest(a, b);
std::cout << "Answer received: " << a << " * " << b << " = " << response << std::endl;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
Run();
return 0;
}
protobuf对简单数据的赋值,简单数据直接采用set_xx()即可,该xx为proto文件的定义消息上的变量
//在proto定义的消息
message Project{
uint32 Type=1;//类型
string Path=2;//路径
}
Project request;
request.set_type(Type);
request.set_path(Path.toStdString());
对应获取变量为直接是变量作为函数
string path = request->path();
Uint32 type = request->type();
protobuf 中的嵌套消息的使用主要对set_allocated_和mutable_的使用
1 使用set_allocated_,赋值的对象需要new出来,不能用局部的,这里保存的是对象的指针。
2 使用mutable_,赋值时候,可以使用局部变量,因为在调用的时,内部做了new操作。
message ErrorCode {
string message = 1; //错误信息
string note = 2; //注释
uint32 code = 3; //错误码
}
message ProjectRet{
ErrorCode errorCode=1;//错误码
string Value=2;//值
}
test_lib::ProjectRet *response;
std::string hashvalue = “asa”;
response->set_hashvalue(hashvalue);
test_lib::ErrorCode* errorcode = new test_lib::ErrorCode;
errorcode->set_note("Project");
errorcode->set_code(0);
errorcode->set_message("OK");
response->set_allocated_errorcode(errorcode);
grpc有四种交互模式
https://blog.csdn.net/Fallinlove520/article/details/121989585?spm=1001.2014.3001.5506