目录
一、Seata源码分析
1、Seata源码入口
1.1、2.0.0.RELEASE
1.2、2.2.6.RELEASE
2、Seata源码分析-2PC核心源码
3、Seata源码分析-数据源代理
3.1、数据源代理DataSourceProxy
4、Seata源码分析- Seata服务端(TC)源码
一、Seata源码分析
Seata源码下载地址官网
1、Seata源码入口
在微服务的使用Seata实际工作场景中,我们只需要引入对应依赖:spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-seata,就会进行自动装配,所以我们之间看META-INF/spring.factories,然后我们这里从GlobalTransactionAutoConfiguration开始看起。
1.1、2.0.0.RELEASE

全局事务扫描类源码:这个类型的核心点,就是加载配置,注入相关的Bean
/**
* seata自动配置类
*/
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(SeataProperties.class)
public class GlobalTransactionAutoConfiguration {
private final ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private final SeataProperties seataProperties;
public GlobalTransactionAutoConfiguration(ApplicationContext applicationContext,
SeataProperties seataProperties) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
this.seataProperties = seataProperties;
}
// 注入全局事务扫描器
@Bean
public GlobalTransactionScanner globalTransactionScanner() {
String applicationName = applicationContext.getEnvironment()
.getProperty("spring.application.name");
String txServiceGroup = seataProperties.getTxServiceGroup();
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(txServiceGroup)) {
txServiceGroup = applicationName + "-fescar-service-group";
seataProperties.setTxServiceGroup(txServiceGroup);
}
// 构建全局扫描器,传入参数:应用名、事务分组名,失败处理器
return new GlobalTransactionScanner(applicationName, txServiceGroup);
}
}GlobalTransactionScanner全局事务扫描器
在这其中我们要关心的是GlobalTransactionScanner这个类型,这个类型扫描@GlobalTransactional注解,并对代理方法进行拦截增强事务的功能。
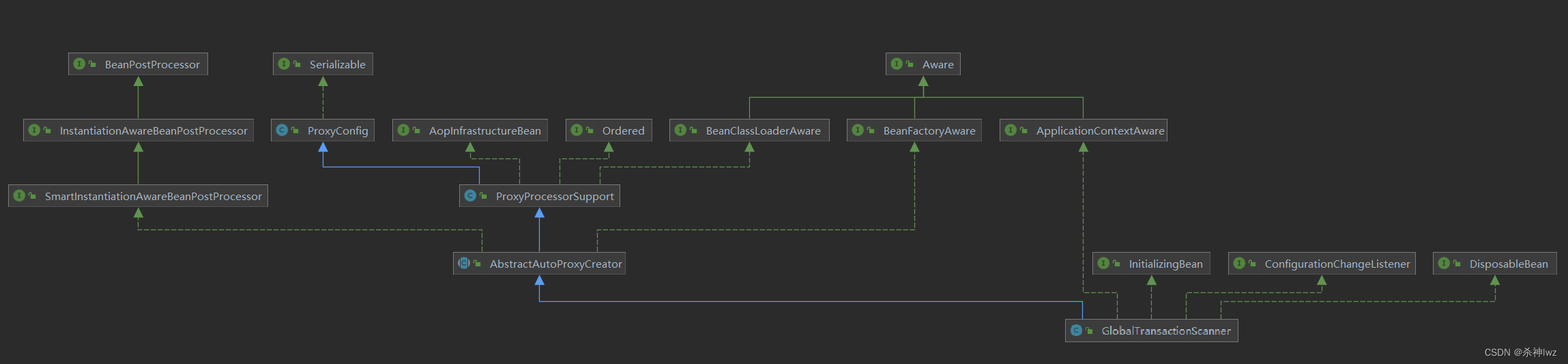
GlobalTransactionScanner的类关系图,其中我们现在继承了Aop的AbstractAutoProxyCreator类型,在这其中有一个重点方法,其实这个方法就是判断Bean对象是否需要代理,是否需要增强
源码:spring
public abstract class AbstractAutoProxyCreator extends ProxyProcessorSupport implements SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor, BeanFactoryAware {
...
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (beanName != null && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// Create proxy if we have advice.
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}这是父类提供的方法,那子类继承之后重写此方法,完成了定制化的效果,定义不同的代理对象
@Override
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
try {
// 加锁防止并发
synchronized (PROXYED_SET) {
if (PROXYED_SET.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
interceptor = null;
//check TCC proxy
// 检查是否是TCC模式
if (TCCBeanParserUtils.isTccAutoProxy(bean, beanName, applicationContext)) {
//TCC interceptor, proxy bean of sofa:reference/dubbo:reference, and LocalTCC
// 如果是:添加TCC拦截器
interceptor = new TccActionInterceptor(TCCBeanParserUtils.getRemotingDesc(beanName));
ConfigurationCache.addConfigListener(ConfigurationKeys.DISABLE_GLOBAL_TRANSACTION,
(ConfigurationChangeListener)interceptor);
} else {
// 不是TCC模式
Class<?> serviceInterface = SpringProxyUtils.findTargetClass(bean);
Class<?>[] interfacesIfJdk = SpringProxyUtils.findInterfaces(bean);
// 判断是否有相关事务注解,如果没有就不代理
if (!existsAnnotation(new Class[]{serviceInterface})
&& !existsAnnotation(interfacesIfJdk)) {
return bean;
}
// 当发现存在全局事务注解标注的Bean,添加拦截器
if (globalTransactionalInterceptor == null) {
// 添加拦截器
globalTransactionalInterceptor = new GlobalTransactionalInterceptor(failureHandlerHook);
ConfigurationCache.addConfigListener(
ConfigurationKeys.DISABLE_GLOBAL_TRANSACTION,
(ConfigurationChangeListener)globalTransactionalInterceptor);
}
interceptor = globalTransactionalInterceptor;
}
LOGGER.info("Bean[{}] with name [{}] would use interceptor [{}]", bean.getClass().getName(), beanName, interceptor.getClass().getName());
// 检查是否是代理对象
if (!AopUtils.isAopProxy(bean)) {
// 不是调用Spring代理(父级)
bean = super.wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
} else {
// 已经是代理对象,反射获取代理类中的已经存在的拦截器组合,然后添加到该集合当中
AdvisedSupport advised = SpringProxyUtils.getAdvisedSupport(bean);
Advisor[] advisor = buildAdvisors(beanName, getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(null, null, null));
for (Advisor avr : advisor) {
advised.addAdvisor(0, avr);
}
}
// 将Bean添加到Set中
PROXYED_SET.add(beanName);
return bean;
}
} catch (Exception exx) {
throw new RuntimeException(exx);
}
}1.2、2.2.6.RELEASE
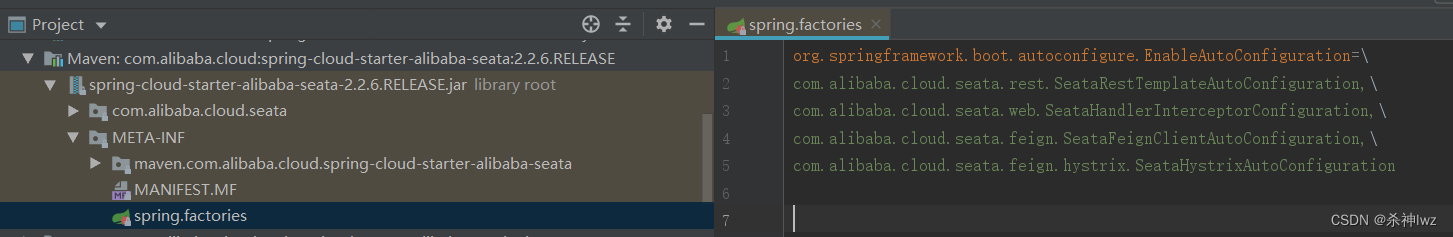
上图没有GlobalTransactionAutoConfiguration,pom中有seata-spring-boot-starter
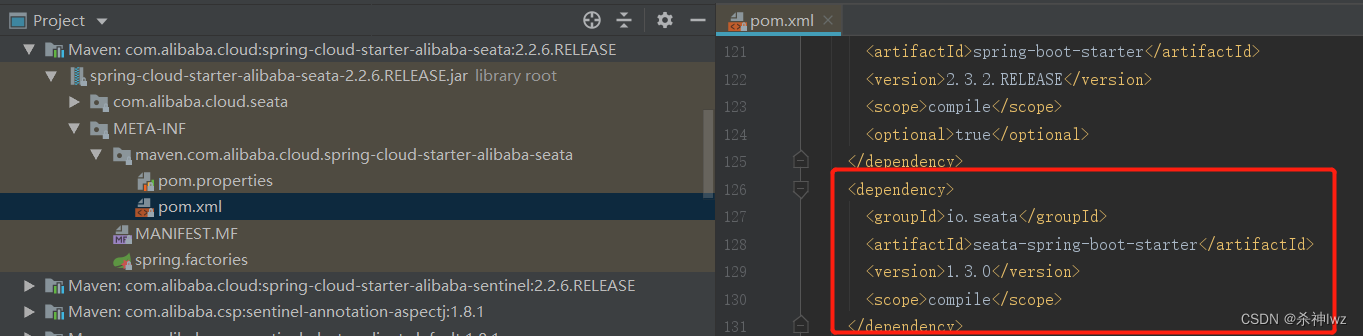
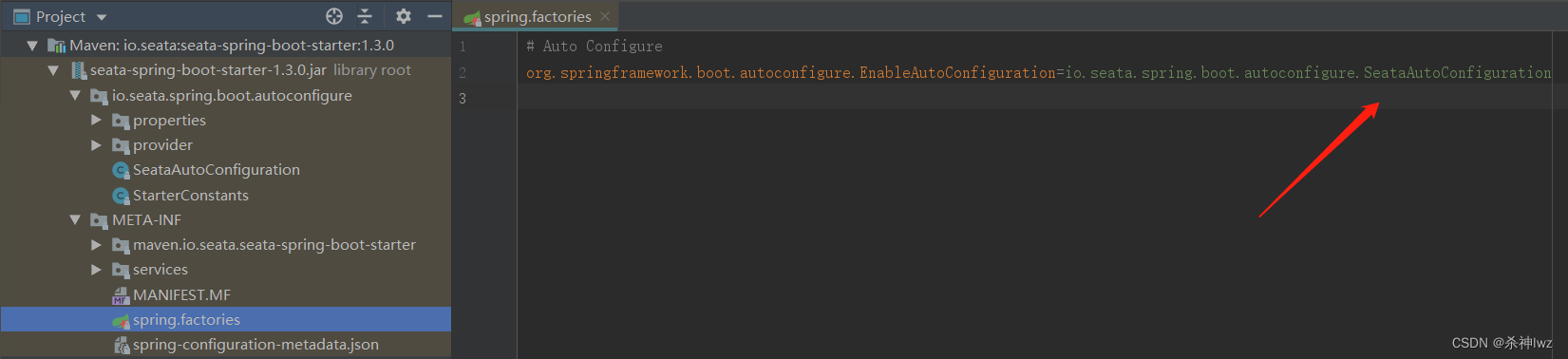
源码:seata-spring-boot-starter工程下
package io.seata.spring.boot.autoconfigure;
...
@ComponentScan(
basePackages = {"io.seata.spring.boot.autoconfigure.properties"}
)
@ConditionalOnProperty(
prefix = "seata",
name = {"enabled"},
havingValue = "true",
matchIfMissing = true
)
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties({SeataProperties.class})
public class SeataAutoConfiguration {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SeataAutoConfiguration.class);
public SeataAutoConfiguration() {
}
@Bean({"springApplicationContextProvider"})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(
name = {"springApplicationContextProvider"}
)
public SpringApplicationContextProvider springApplicationContextProvider() {
return new SpringApplicationContextProvider();
}
@Bean({"failureHandler"})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({FailureHandler.class})
public FailureHandler failureHandler() {
return new DefaultFailureHandlerImpl();
}
@Bean
@DependsOn({"springApplicationContextProvider", "failureHandler"})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({GlobalTransactionScanner.class})
public GlobalTransactionScanner globalTransactionScanner(SeataProperties seataProperties, FailureHandler failureHandler) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Automatically configure Seata");
}
return new GlobalTransactionScanner(seataProperties.getApplicationId(), seataProperties.getTxServiceGroup(), failureHandler);
}
@Bean({"seataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator"})
@ConditionalOnProperty(
prefix = "seata",
name = {"enableAutoDataSourceProxy", "enable-auto-data-source-proxy"},
havingValue = "true",
matchIfMissing = true
)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator.class})
public SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator seataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator(SeataProperties seataProperties) {
return new SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator(seataProperties.isUseJdkProxy(), seataProperties.getExcludesForAutoProxying());
}
}
源码
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = SEATA_PREFIX, name = "enabled", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
@AutoConfigureAfter({SeataCoreAutoConfiguration.class})
public class SeataAutoConfiguration {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SeataAutoConfiguration.class);
@Bean(BEAN_NAME_FAILURE_HANDLER)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(FailureHandler.class)
public FailureHandler failureHandler() {
return new DefaultFailureHandlerImpl();
}
@Bean
@DependsOn({BEAN_NAME_SPRING_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_PROVIDER, BEAN_NAME_FAILURE_HANDLER})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(GlobalTransactionScanner.class)
public static GlobalTransactionScanner globalTransactionScanner(SeataProperties seataProperties, FailureHandler failureHandler,
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory,
@Autowired(required = false) List<ScannerChecker> scannerCheckers) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Automatically configure Seata");
}
// set bean factory
GlobalTransactionScanner.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// add checkers
// '/META-INF/services/io.seata.spring.annotation.ScannerChecker'
GlobalTransactionScanner.addScannerCheckers(EnhancedServiceLoader.loadAll(ScannerChecker.class));
// spring beans
GlobalTransactionScanner.addScannerCheckers(scannerCheckers);
// add scannable packages
GlobalTransactionScanner.addScannablePackages(seataProperties.getScanPackages());
// add excludeBeanNames
GlobalTransactionScanner.addScannerExcludeBeanNames(seataProperties.getExcludesForScanning());
//set accessKey and secretKey
GlobalTransactionScanner.setAccessKey(seataProperties.getAccessKey());
GlobalTransactionScanner.setSecretKey(seataProperties.getSecretKey());
// create global transaction scanner
return new GlobalTransactionScanner(seataProperties.getApplicationId(), seataProperties.getTxServiceGroup(), failureHandler);
}
}新版拆分细化自动配置装配
2、Seata源码分析-2PC核心源码
GlobalTransactionalInterceptor全局事务拦截器,一旦执行拦截器,就会进入到其中的invoke方法,在这其中会做一些@GlobalTransactional注解的判断,如果有注解以后,会执行全局事务和全局锁,那么在执行全局事务的时候会调用handleGlobalTransaction全局事务处理器,这里主要是获取事务信息
Object handleGlobalTransaction(final MethodInvocation methodInvocation,
final GlobalTransactional globalTrxAnno) throws Throwable {
boolean succeed = true;
try {
return transactionalTemplate.execute(new TransactionalExecutor() {
@Override
public Object execute() throws Throwable {
return methodInvocation.proceed();
}
// 获取事务名称,默认获取方法名
public String name() {
String name = globalTrxAnno.name();
if (!StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(name)) {
return name;
}
return formatMethod(methodInvocation.getMethod());
}
/**
* 解析GlobalTransactional注解属性,封装为对象
* @return
*/
@Override
public TransactionInfo getTransactionInfo() {
// reset the value of timeout
// 获取超时时间,默认60秒
int timeout = globalTrxAnno.timeoutMills();
if (timeout <= 0 || timeout == DEFAULT_GLOBAL_TRANSACTION_TIMEOUT) {
timeout = defaultGlobalTransactionTimeout;
}
// 构建事务信息对象
TransactionInfo transactionInfo = new TransactionInfo();
transactionInfo.setTimeOut(timeout);// 超时时间
transactionInfo.setName(name()); // 事务名称
transactionInfo.setPropagation(globalTrxAnno.propagation());// 事务传播
transactionInfo.setLockRetryInternal(globalTrxAnno.lockRetryInternal());// 校验或占用全局锁重试间隔
transactionInfo.setLockRetryTimes(globalTrxAnno.lockRetryTimes());// 校验或占用全局锁重试次数
Set<RollbackRule> rollbackRules = new LinkedHashSet<>();
// 其他构建信息
for (Class<?> rbRule : globalTrxAnno.rollbackFor()) {
rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRule(rbRule));
}
for (String rbRule : globalTrxAnno.rollbackForClassName()) {
rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRule(rbRule));
}
for (Class<?> rbRule : globalTrxAnno.noRollbackFor()) {
rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRule(rbRule));
}
for (String rbRule : globalTrxAnno.noRollbackForClassName()) {
rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRule(rbRule));
}
transactionInfo.setRollbackRules(rollbackRules);
return transactionInfo;
}
});
} catch (TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException e) {
// 执行异常
TransactionalExecutor.Code code = e.getCode();
switch (code) {
case RollbackDone:
throw e.getOriginalException();
case BeginFailure:
succeed = false;
failureHandler.onBeginFailure(e.getTransaction(), e.getCause());
throw e.getCause();
case CommitFailure:
succeed = false;
failureHandler.onCommitFailure(e.getTransaction(), e.getCause());
throw e.getCause();
case RollbackFailure:
failureHandler.onRollbackFailure(e.getTransaction(), e.getOriginalException());
throw e.getOriginalException();
case RollbackRetrying:
failureHandler.onRollbackRetrying(e.getTransaction(), e.getOriginalException());
throw e.getOriginalException();
default:
throw new ShouldNeverHappenException(String.format("Unknown TransactionalExecutor.Code: %s", code));
}
} finally {
if (degradeCheck) {
EVENT_BUS.post(new DegradeCheckEvent(succeed));
}
}
}在这其中,我们要关注一个重点方法execute()
其实这个方法主要的作用就是,执行事务的流程,大概一下几点:
1. 获取事务信息
2. 开始执行全局事务
3. 发生异常全局回滚,各个数据通过undo_log表进行事务补偿
4. 全局事务提交
5. 清除所有资源
这个位置是非常核心的一个位置,因为我们所有的业务进来以后都会走这个位置。
这其中的第三步和第四步就是在想TC(Seata-Server)发起全局事务的提交/回滚
public Object execute(TransactionalExecutor business) throws Throwable {
// 1. Get transactionInfo
// 获取事务信息
TransactionInfo txInfo = business.getTransactionInfo();
if (txInfo == null) {
throw new ShouldNeverHappenException("transactionInfo does not exist");
}
// 1.1 Get current transaction, if not null, the tx role is 'GlobalTransactionRole.Participant'.
// 获取当前事务,主要获取Xid
GlobalTransaction tx = GlobalTransactionContext.getCurrent();
// 1.2 Handle the transaction propagation.
// 根据配置的不同事务传播行为,执行不同的逻辑
Propagation propagation = txInfo.getPropagation();
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResourcesHolder = null;
try {
switch (propagation) {
case NOT_SUPPORTED:
// If transaction is existing, suspend it.
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
suspendedResourcesHolder = tx.suspend();
}
// Execute without transaction and return.
return business.execute();
case REQUIRES_NEW:
// If transaction is existing, suspend it, and then begin new transaction.
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
suspendedResourcesHolder = tx.suspend();
tx = GlobalTransactionContext.createNew();
}
// Continue and execute with new transaction
break;
case SUPPORTS:
// If transaction is not existing, execute without transaction.
if (notExistingTransaction(tx)) {
return business.execute();
}
// Continue and execute with new transaction
break;
case REQUIRED:
// If current transaction is existing, execute with current transaction,
// else continue and execute with new transaction.
break;
case NEVER:
// If transaction is existing, throw exception.
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
throw new TransactionException(
String.format("Existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'never', xid = %s"
, tx.getXid()));
} else {
// Execute without transaction and return.
return business.execute();
}
case MANDATORY:
// If transaction is not existing, throw exception.
if (notExistingTransaction(tx)) {
throw new TransactionException("No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
}
// Continue and execute with current transaction.
break;
default:
throw new TransactionException("Not Supported Propagation:" + propagation);
}
// 1.3 If null, create new transaction with role 'GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher'.
// 当前没有事务,则创建一个新的事务
if (tx == null) {
tx = GlobalTransactionContext.createNew();
}
// set current tx config to holder
GlobalLockConfig previousConfig = replaceGlobalLockConfig(txInfo);
try {
// 2. If the tx role is 'GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher', send the request of beginTransaction to TC,
// else do nothing. Of course, the hooks will still be triggered.
// 开始执行全局事务
beginTransaction(txInfo, tx);
Object rs;
try {
// Do Your Business
// 执行当前业务逻辑:
// 1. 在TC注册当前分支事务,TC会在branch_table中插入一条分支事务数据
// 2. 执行本地update语句,并在执行前后查询数据状态,并把数据前后镜像存入到undo_log表中
// 3. 远程调用其他应用,远程应用接收到xid,也会注册分支事务,写入branch_table及本地undo_log表
// 4. 会在lock_table表中插入全局锁数据(一个分支一条)
rs = business.execute();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 3. The needed business exception to rollback.
// 发生异常全局回滚,各个数据通过undo_log表进行事务补偿
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, tx, ex);
throw ex;
}
// 4. everything is fine, commit.
// 全局提交事务
commitTransaction(tx);
return rs;
} finally {
//5. clear
// 清除所有资源
resumeGlobalLockConfig(previousConfig);
triggerAfterCompletion();
cleanUp();
}
} finally {
// If the transaction is suspended, resume it.
if (suspendedResourcesHolder != null) {
tx.resume(suspendedResourcesHolder);
}
}
}如何发起全局事务
这个位置我们就看当前这个代码中的 beginTransaction(txInfo, tx);方法
// 向TC发起请求,这里采用了模板模式
private void beginTransaction(TransactionInfo txInfo, GlobalTransaction tx) throws TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException {
try {
triggerBeforeBegin();
// 对TC发起请求
tx.begin(txInfo.getTimeOut(), txInfo.getName());
triggerAfterBegin();
} catch (TransactionException txe) {
throw new TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException(tx, txe,
TransactionalExecutor.Code.BeginFailure);
}
}那我们向下来看begin方法,那要注意,这里调用begin方法的是DefaultGlobalTransaction
@Override
public void begin(int timeout, String name) throws TransactionException {
//判断调用者是否是TM
if (role != GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher) {
assertXIDNotNull();
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Ignore Begin(): just involved in global transaction [{}]", xid);
}
return;
}
assertXIDNull();
String currentXid = RootContext.getXID();
if (currentXid != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Global transaction already exists," +
" can't begin a new global transaction, currentXid = " + currentXid);
}
// 获取Xid
xid = transactionManager.begin(null, null, name, timeout);
status = GlobalStatus.Begin;
RootContext.bind(xid);
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Begin new global transaction [{}]", xid);
}
}在向下来看begin方法,这时候使用的是(默认事务管理者)DefaultTransactionManager.begin,来真正的获取xid,其中就是传入事务的相关信息,最终TC端返回对应的全局事务Xid。
@Override
public String begin(String applicationId, String transactionServiceGroup, String name, int timeout)
throws TransactionException {
GlobalBeginRequest request = new GlobalBeginRequest();
request.setTransactionName(name);
request.setTimeout(timeout);
// 发送请求得到响应
GlobalBeginResponse response = (GlobalBeginResponse) syncCall(request);
if (response.getResultCode() == ResultCode.Failed) {
throw new TmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.BeginFailed, response.getMsg());
}
//返回Xid
return response.getXid();
}这里采用的是Netty的通讯方式
private AbstractTransactionResponse syncCall(AbstractTransactionRequest request) throws TransactionException {
try {
// 通过Netty发送请求
return (AbstractTransactionResponse) TmNettyRemotingClient.getInstance().sendSyncRequest(request);
} catch (TimeoutException toe) {
throw new TmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.IO, "RPC timeout", toe);
}
}3、Seata源码分析-数据源代理
AT模式的核心点:
1. 获取全局锁、开启全局事务
2. 解析SQL并写入undolog
AT模式如何解析SQL并写入undolog
首先要先明确实际上Seata其中采用了数据源代理的模式。
那么这个就需要我们在回顾一下GlobalTransactionScanner这个类型,在这个类型中继承了一些的接口和抽象类,比较关键的几个:
AbstractAutoProxyCreator Spring实现AOP的一种方式
ConfigurationChangeListener 监听器基准接口
InitializingBean Bean初始化
ApplicationContextAware Spring容器
DisposableBean Spring容器销毁
回顾一下:
1. 继承ApplicationContextAware类型以后,需要实现对应的方法:
void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException
当spring启动完成后,会自动调用这个类型,把ApplicationContext给bean。也就是说,GlobalTransactionScanner天然能拿到Spring的环境。
2. 继承了InitializingBean接口,需要实现一个方法:
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
凡是继承该接口的类,在初始化bean的时候,当所有properties都设置完成后,会执行该方法。
3. 继承DisposableBean,需要实现一个方法:
void destroy() throws Exception;
和InitializingBean接口相反,这个是在销毁的时候会调用这个方法。
4. AbstractAutoProxyCreator就比较复杂了,它Spring实现AOP的一种方式。本质上是一个BeanPostProcessor,他在bean初始化之前,调用内部的createProxy方法,创建一个bean的AOP代理bean并返回,对Bean的增强。
总结一下:总体的逻辑就是,GlobalTransactionScanner扫描有注解的bean,做AOP增强。数据源代理
关于数据源代理这里我们全局事务拦截成功后最终还是执行了业务方法的,但是由于Seata对数据源做了代理,所以sql解析与undolog入库操作是在数据源代理中执行的,箭头处的代理就是Seata对DataSource,Connection,Statement做的代理封装类
数据源代理是非常重要的一个环节。我们知道,在分布式事务运行过程中,undo log等的记录、资源的锁定等,都是用户无感知的,因为这些操作都在数据源的代理中完成了。
3.1、数据源代理DataSourceProxy
DataSourceProxy的主要功能为,它在构造方法中调用了一个自定义的init方法,主要做了以下能力的增强:
1. 为每个数据源标识了资源组ID
2. 如果配置打开,会有一个定时线程池定时更新表的元数据信息并缓存到本地
3. 生成代理连接ConnectionProxy
那我们先来看init方法
private void init(DataSource dataSource, String resourceGroupId) {
//资源组ID,默认是“default”这个默认值
this.resourceGroupId = resourceGroupId;
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection()) {
//根据原始数据源得到JDBC连接和数据库类型
jdbcUrl = connection.getMetaData().getURL();
dbType = JdbcUtils.getDbType(jdbcUrl);
if (JdbcConstants.ORACLE.equals(dbType)) {
userName = connection.getMetaData().getUserName();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("can not init dataSource", e);
}
DefaultResourceManager.get().registerResource(this);
if (ENABLE_TABLE_META_CHECKER_ENABLE) {
//如果配置开关打开,会定时线程池不断更新表的元数据信息
/**
*每分钟查询一次数据源的表结构信息并缓存,在需要查询数据库结构时会用到,不然每次去数据库查询结构效率会很低。
*/
tableMetaExcutor.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection()) {
TableMetaCacheFactory.getTableMetaCache(DataSourceProxy.this.getDbType())
.refresh(connection, DataSourceProxy.this.getResourceId());
} catch (Exception ignore) {
}
}, 0, TABLE_META_CHECKER_INTERVAL, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
//Set the default branch type to 'AT' in the RootContext.
RootContext.setDefaultBranchType(this.getBranchType());
}这3个增强里面,前两个都比较容易理解,第三是最重要的。我们知道在AT模式里面,会自动记录undo log、资源锁定等等,都是通过ConnectionProxy完成的。
另外,DataSourceProxy重写了几个方法。
重点是getConnection,此时会返回一个ConnectionProxy,而不是原生的Connection
@Override
public ConnectionProxy getConnection() throws SQLException {
Connection targetConnection = targetDataSource.getConnection();
return new ConnectionProxy(this, targetConnection);
}
@Override
public ConnectionProxy getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
Connection targetConnection = targetDataSource.getConnection(username, password);
return new ConnectionProxy(this, targetConnection);
}ConnectionProxy分析
ConnectionProxy继承了AbstractConnectionProxy。一看到Abstract,就知道它的父类封装了很多通用工作。它的父类里面还使用了PreparedStatementProxy、StatementProxy、DataSourceProxy。
AbstractConnectionProxy
在这个抽象连接对象中,定义了很多通用的逻辑,所以在这其中要关注的主要在于PreparedStatementProxy和StatementProxy,其实这里的通用逻辑就是数据源连接的步骤,获取连接,创建执行对象等等这些
@Override
public Statement createStatement() throws SQLException {
//调用真实连接对象获得Statement对象
Statement targetStatement = getTargetConnection().createStatement();
//创建Statement的代理
return new StatementProxy(this, targetStatement);
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql) throws SQLException {
//数据库类型,比如mysql、oracle等
String dbType = getDbType();
// support oracle 10.2+
PreparedStatement targetPreparedStatement = null;
//如果是AT模式且开启全局事务,那么就会进入if分支
if (BranchType.AT == RootContext.getBranchType()) {
List<SQLRecognizer> sqlRecognizers = SQLVisitorFactory.get(sql, dbType);
if (sqlRecognizers != null && sqlRecognizers.size() == 1) {
SQLRecognizer sqlRecognizer = sqlRecognizers.get(0);
if (sqlRecognizer != null && sqlRecognizer.getSQLType() == SQLType.INSERT) {
//得到表的元数据
TableMeta tableMeta = TableMetaCacheFactory.getTableMetaCache(dbType).getTableMeta(getTargetConnection(),
sqlRecognizer.getTableName(), getDataSourceProxy().getResourceId());
//得到表的主键列名
String[] pkNameArray = new String[tableMeta.getPrimaryKeyOnlyName().size()];
tableMeta.getPrimaryKeyOnlyName().toArray(pkNameArray);
targetPreparedStatement = getTargetConnection().prepareStatement(sql,pkNameArray);
}
}
}
if (targetPreparedStatement == null) {
targetPreparedStatement = getTargetConnection().prepareStatement(sql);
}
// 创建PreparedStatementProxy代理
return new PreparedStatementProxy(this, targetPreparedStatement, sql);
}分布式事务SQL执行
在这两个代理对象中,执行SQL语句的关键方法如下:
@Override
public ResultSet executeQuery(String sql) throws SQLException {
this.targetSQL = sql;
return ExecuteTemplate.execute(this, (statement, args) -> statement.executeQuery((String) args[0]), sql);
}
@Override
public int executeUpdate(String sql) throws SQLException {
this.targetSQL = sql;
return ExecuteTemplate.execute(this, (statement, args) -> statement.executeUpdate((String) args[0]), sql);
}
@Override
public boolean execute(String sql) throws SQLException {
this.targetSQL = sql;
return ExecuteTemplate.execute(this, (statement, args) -> statement.execute((String) args[0]), sql);
}其他执行SQL语句的方法与上面三个方法都是类似的,都是调用ExecuteTemplate.execute方法,下面来看一下ExecuteTemplate类:
public class ExecuteTemplate {
/**
* Execute t.
*
* @param <T> the type parameter
* @param <S> the type parameter
* @param statementProxy the statement proxy
* @param statementCallback the statement callback
* @param args the args
* @return the t
* @throws SQLException the sql exception
*/
public static <T, S extends Statement> T execute(StatementProxy<S> statementProxy,
StatementCallback<T, S> statementCallback,
Object... args) throws SQLException {
return execute(null, statementProxy, statementCallback, args);
}
/**
* Execute t.
*
* @param <T> the type parameter
* @param <S> the type parameter
* @param sqlRecognizers the sql recognizer list
* @param statementProxy the statement proxy
* @param statementCallback the statement callback
* @param args the args
* @return the t
* @throws SQLException the sql exception
*/
public static <T, S extends Statement> T execute(List<SQLRecognizer> sqlRecognizers,
StatementProxy<S> statementProxy,
StatementCallback<T, S> statementCallback,
Object... args) throws SQLException {
// 如果没有全局锁,并且不是AT模式,直接执行SQL
if (!RootContext.requireGlobalLock() && BranchType.AT != RootContext.getBranchType()) {
// Just work as original statement
return statementCallback.execute(statementProxy.getTargetStatement(), args);
}
// 得到数据库类型 ->MySQL
String dbType = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy().getDbType();
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(sqlRecognizers)) {
//sqlRecognizers为SQL语句的解析器,获取执行的SQL,通过它可以获得SQL语句表名、相关的列名、类型的等信息,最后解析出对应的SQL表达式
sqlRecognizers = SQLVisitorFactory.get(
statementProxy.getTargetSQL(),
dbType);
}
Executor<T> executor;
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(sqlRecognizers)) {
//如果seata没有找到合适的SQL语句解析器,那么便创建简单执行器PlainExecutor,
//PlainExecutor直接使用原生的Statement对象执行SQL
executor = new PlainExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback);
} else {
if (sqlRecognizers.size() == 1) {
SQLRecognizer sqlRecognizer = sqlRecognizers.get(0);
switch (sqlRecognizer.getSQLType()) {
//下面根据是增、删、改、加锁查询、普通查询分别创建对应的处理器
case INSERT:
executor = EnhancedServiceLoader.load(InsertExecutor.class, dbType,
new Class[]{StatementProxy.class, StatementCallback.class, SQLRecognizer.class},
new Object[]{statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer});
break;
case UPDATE:
executor = new UpdateExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
break;
case DELETE:
executor = new DeleteExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
break;
case SELECT_FOR_UPDATE:
executor = new SelectForUpdateExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
break;
default:
executor = new PlainExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback);
break;
}
} else {
// 此执行器可以处理一条SQL语句包含多个Delete、Update语句
executor = new MultiExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizers);
}
}
T rs;
try {
// 执行器执行
rs = executor.execute(args);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
if (!(ex instanceof SQLException)) {
// Turn other exception into SQLException
ex = new SQLException(ex);
}
throw (SQLException) ex;
}
return rs;
}
}
从ExecuteTemplate中可以看到,seata将SQL语句的执行委托给了不同的执行器。seata提供了6个执行器(模板模式),所有执行器的父类型为AbstractDMLBaseExecutor。
- UpdateExecutor 执行update语句
- InsertExecutor 执行insert语句
- DeleteExecutor 执行delete语句
- SelectForUpdateExecutor 执行select for update语句
- PlainExecutor 执行普通查询语句
- MultiExecutor 复合执行器,在一条SQL语句中执行多条语句
executor.execute(args);方法,自然这里调用的就是父类的方法
@Override
public T execute(Object... args) throws Throwable {
String xid = RootContext.getXID();
if (xid != null) {
// 获取xid
statementProxy.getConnectionProxy().bind(xid);
}
// 设置全局锁
statementProxy.getConnectionProxy().setGlobalLockRequire(RootContext.requireGlobalLock());
return doExecute(args);
}向下来看doExecute()方法,AbstractDMLBaseExecutor重写的方法
@Override
public T doExecute(Object... args) throws Throwable {
AbstractConnectionProxy connectionProxy = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy();
if (connectionProxy.getAutoCommit()) {
return executeAutoCommitTrue(args);
} else {
return executeAutoCommitFalse(args);
}
}首先我们都清楚,数据库本身都是自动提交
@Override
public T doExecute(Object... args) throws Throwable {
AbstractConnectionProxy connectionProxy = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy();
if (connectionProxy.getAutoCommit()) {
return executeAutoCommitTrue(args);
} else {
return executeAutoCommitFalse(args);
}
}进入executeAutoCommitTrue()方法中
protected T executeAutoCommitTrue(Object[] args) throws Throwable {
ConnectionProxy connectionProxy = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy();
try {
// 更改为手动提交
connectionProxy.changeAutoCommit();
return new LockRetryPolicy(connectionProxy).execute(() -> {
// 调用手动提交方法 得到分支业务最终结果
T result = executeAutoCommitFalse(args);
// 执行提交
connectionProxy.commit();
return result;
});
} catch (Exception e) {
// when exception occur in finally,this exception will lost, so just print it here
LOGGER.error("execute executeAutoCommitTrue error:{}", e.getMessage(), e);
if (!LockRetryPolicy.isLockRetryPolicyBranchRollbackOnConflict()) {
connectionProxy.getTargetConnection().rollback();
}
throw e;
} finally {
connectionProxy.getContext().reset();
connectionProxy.setAutoCommit(true);
}
}然后查看connectionProxy.changeAutoCommit();更改为手动提交
protected T executeAutoCommitFalse(Object[] args) throws Exception {
if (!JdbcConstants.MYSQL.equalsIgnoreCase(getDbType()) && isMultiPk()) {
throw new NotSupportYetException("multi pk only support mysql!");
}
// 前镜像
TableRecords beforeImage = beforeImage();
// 执行具体业余
T result = statementCallback.execute(statementProxy.getTargetStatement(), args);
// 后镜像
TableRecords afterImage = afterImage(beforeImage);
// 暂存UndoLog,为了在Commit的时候保存到数据库
prepareUndoLog(beforeImage, afterImage);
return result;
}然后再回到executeAutoCommitTrue这个方法中向下看connectionProxy.commit();
@Override
public void commit() throws SQLException {
try {
LOCK_RETRY_POLICY.execute(() -> {
// 具体执行
doCommit();
return null;
});
} catch (SQLException e) {
if (targetConnection != null && !getAutoCommit() && !getContext().isAutoCommitChanged()) {
rollback();
}
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new SQLException(e);
}
}进入到doCommit方法中
private void doCommit() throws SQLException {
//判断是否存在全局事务
if (context.inGlobalTransaction()) {
processGlobalTransactionCommit();
} else if (context.isGlobalLockRequire()) {
processLocalCommitWithGlobalLocks();
} else {
targetConnection.commit();
}
}此时很明显存在全局事务,所以进入到processGlobalTransactionCommit方法中
private void processGlobalTransactionCommit() throws SQLException {
try {
// 注册分支
register();
} catch (TransactionException e) {
recognizeLockKeyConflictException(e, context.buildLockKeys());
}
try {
//写入数据库undolog
UndoLogManagerFactory.getUndoLogManager(this.getDbType()).flushUndoLogs(this);
//执行原生提交
targetConnection.commit();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
LOGGER.error("process connectionProxy commit error: {}", ex.getMessage(), ex);
report(false);
throw new SQLException(ex);
}
if (IS_REPORT_SUCCESS_ENABLE) {
report(true);
}
context.reset();
}其中的register方法就是注册分支事务的方法,同时还有把undolog写入数据库和执行提交的操作
/ 注册分支事务,生成分支事务id
private void register() throws TransactionException {
if (!context.hasUndoLog() || !context.hasLockKey()) {
return;
}
// 注册分支事务
Long branchId = DefaultResourceManager.get().branchRegister(BranchType.AT, getDataSourceProxy().getResourceId(),
null, context.getXid(), null, context.buildLockKeys());
context.setBranchId(branchId);
}接下来就具体看看写入数据库的方法flushUndoLogs
@Override
public void flushUndoLogs(ConnectionProxy cp) throws SQLException {
ConnectionContext connectionContext = cp.getContext();
if (!connectionContext.hasUndoLog()) {
return;
}
String xid = connectionContext.getXid();
long branchId = connectionContext.getBranchId();
BranchUndoLog branchUndoLog = new BranchUndoLog();
branchUndoLog.setXid(xid);
branchUndoLog.setBranchId(branchId);
branchUndoLog.setSqlUndoLogs(connectionContext.getUndoItems());
UndoLogParser parser = UndoLogParserFactory.getInstance();
byte[] undoLogContent = parser.encode(branchUndoLog);
CompressorType compressorType = CompressorType.NONE;
if (needCompress(undoLogContent)) {
compressorType = ROLLBACK_INFO_COMPRESS_TYPE;
undoLogContent = CompressorFactory.getCompressor(compressorType.getCode()).compress(undoLogContent);
}
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Flushing UNDO LOG: {}", new String(undoLogContent, Constants.DEFAULT_CHARSET));
}
// 写入数据库具体位置
insertUndoLogWithNormal(xid, branchId, buildContext(parser.getName(), compressorType), undoLogContent, cp.getTargetConnection());
}具体写入方法,此时我们使用的是MySql,所以执行的是MySql实现类
@Override
protected void insertUndoLogWithNormal(String xid, long branchId, String rollbackCtx, byte[] undoLogContent,
Connection conn) throws SQLException {
insertUndoLog(xid, branchId, rollbackCtx, undoLogContent, State.Normal, conn);
}
@Override
protected void insertUndoLogWithGlobalFinished(String xid, long branchId, UndoLogParser parser, Connection conn) throws SQLException {
insertUndoLog(xid, branchId, buildContext(parser.getName(), CompressorType.NONE), parser.getDefaultContent(), State.GlobalFinished, conn);
}
// 具体写入
private void insertUndoLog(String xid, long branchId, String rollbackCtx, byte[] undoLogContent,
State state, Connection conn) throws SQLException {
try (PreparedStatement pst = conn.prepareStatement(INSERT_UNDO_LOG_SQL)) {
pst.setLong(1, branchId);
pst.setString(2, xid);
pst.setString(3, rollbackCtx);
pst.setBytes(4, undoLogContent);
pst.setInt(5, state.getValue());
pst.executeUpdate();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!(e instanceof SQLException)) {
e = new SQLException(e);
}
throw (SQLException) e;
}
}4、Seata源码分析- Seata服务端(TC)源码
服务端表解释
我们的Seata服务端在应用的时候需要准备三张表,那么这三张表分别代表的意思就是
1. branch_table 分支事务表
2. global_table 全局事务表
3. lock_table 全局锁表
客户端请求服务端以后,我们就需要把对应的全局事务包括分支事务和全局锁全部存放到这里。
TC服务端启动入口
那么任何的Java工程启动都需要主函数main,所以我们就从这里入手,首先在seata源码工程中搜索这个入口
这里看Server.java这里就是启动入口,在这个入口中找到协调者,因为TC整体的操作就是协调整体的全局事务
// 协调协调者
DefaultCoordinator coordinator = new DefaultCoordinator(nettyRemotingServer);// 处理全局事务开始
@Override
protected void doGlobalBegin(GlobalBeginRequest request, GlobalBeginResponse response, RpcContext rpcContext)
throws TransactionException {
// 响应客户端XID
response.setXid(core.begin(rpcContext.getApplicationId(), rpcContext.getTransactionServiceGroup(),
request.getTransactionName(), request.getTimeout()));
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Begin new global transaction applicationId: {},transactionServiceGroup: {}, transactionName: {},timeout:{},xid:{}",
rpcContext.getApplicationId(), rpcContext.getTransactionServiceGroup(), request.getTransactionName(), request.getTimeout(), response.getXid());
}
}
// 处理全局提交
@Override
protected void doGlobalCommit(GlobalCommitRequest request, GlobalCommitResponse response, RpcContext rpcContext)
throws TransactionException {
MDC.put(RootContext.MDC_KEY_XID, request.getXid());
response.setGlobalStatus(core.commit(request.getXid()));
}
// 处理全局回滚
@Override
protected void doGlobalRollback(GlobalRollbackRequest request, GlobalRollbackResponse response,
RpcContext rpcContext) throws TransactionException {
MDC.put(RootContext.MDC_KEY_XID, request.getXid());
response.setGlobalStatus(core.rollback(request.getXid()));
}首先关注doGlobalBegin方法中的core.begin()方法,来看一下具体操作
@Override
public String begin(String applicationId, String transactionServiceGroup, String name, int timeout)
throws TransactionException {
// 创建全局事务Session
GlobalSession session = GlobalSession.createGlobalSession(applicationId, transactionServiceGroup, name,
timeout);
MDC.put(RootContext.MDC_KEY_XID, session.getXid());
// 为Session中添加回调监听 SessionHolder.getRootSessionManager()去获取一个全局Session管理器DataBaseSessionManager
// 观察者设计模式
session.addSessionLifecycleListener(SessionHolder.getRootSessionManager());
// 全局事务开启
session.begin();
// transaction start event
eventBus.post(new GlobalTransactionEvent(session.getTransactionId(), GlobalTransactionEvent.ROLE_TC,
session.getTransactionName(), applicationId, transactionServiceGroup, session.getBeginTime(), null, session.getStatus()));
return session.getXid();
}在向下我们要关注一下全局Session管理器DataBaseSessionManager,进入到getRootSessionManager()方法中
/**
* Gets root session manager.
* 获取一个全局Session管理器
* @return the root session manager
*/
public static SessionManager getRootSessionManager() {
if (ROOT_SESSION_MANAGER == null) {
throw new ShouldNeverHappenException("SessionManager is NOT init!");
}
return ROOT_SESSION_MANAGER;
}这个管理器如何生成的呢,我们可以看一下init初始化方法
public static void init(String mode) {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(mode)) {
mode = CONFIG.getConfig(ConfigurationKeys.STORE_MODE);
}
// 判断Seata模式,当前为DB
StoreMode storeMode = StoreMode.get(mode);
if (StoreMode.DB.equals(storeMode)) {
// 通过SPI机制读取SessionManager接口实现类,读取的是META-INF.service目录,在通过反射机制创建对象DataBaseSessionManager
ROOT_SESSION_MANAGER = EnhancedServiceLoader.load(SessionManager.class, StoreMode.DB.getName());
ASYNC_COMMITTING_SESSION_MANAGER = EnhancedServiceLoader.load(SessionManager.class, StoreMode.DB.getName(),
....
}// 观察者设计模式,创建DataBaseSessionManager
session.addSessionLifecycleListener(SessionHolder.getRootSessionManager());但是此时有一个问题,就是我们的init方法在哪里调用的拿,其实我们回到Server中,我们发现在构建默认协调者之前就调用了init方法,说明在执行处理全局事务开始之前,就已经创建好了这个SessionManager了
SessionHolder.init(parameterParser.getStoreMode());
// 默认协调者
DefaultCoordinator coordinator = new DefaultCoordinator(nettyRemotingServer);好了此时分析清楚如何得到这个SessionManager以后,我们在回过头来看代码session.begin()位置
@Override
public String begin(String applicationId, String transactionServiceGroup, String name, int timeout)
throws TransactionException {
// 创建全局事务Session
GlobalSession session = GlobalSession.createGlobalSession(applicationId, transactionServiceGroup, name,
timeout);
MDC.put(RootContext.MDC_KEY_XID, session.getXid());
// 为Session中添加回调监听 SessionHolder.getRootSessionManager()去获取一个全局Session管理器DataBaseSessionManager
// 观察者设计模式,创建DataBaseSessionManager
session.addSessionLifecycleListener(SessionHolder.getRootSessionManager());
// 全局事务开始
session.begin();
// transaction start event
eventBus.post(new GlobalTransactionEvent(session.getTransactionId(), GlobalTransactionEvent.ROLE_TC,
session.getTransactionName(), applicationId, transactionServiceGroup, session.getBeginTime(), null, session.getStatus()));
return session.getXid();
}session.begin()
@Override
public void begin() throws TransactionException {
// 声明全局事务开始
this.status = GlobalStatus.Begin;
// 开始时间
this.beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 激活全局事务
this.active = true;
// 将SessionManager放入到集合中,调用onBegin方法
for (SessionLifecycleListener lifecycleListener : lifecycleListeners) {
lifecycleListener.onBegin(this);
}
}这里来看一下 onBegin方法,调用的是父级的方法,在这其中我们要关注addGlobalSession方法,但是要注意,这里我们用的是db模式所以调用的是db模式的DateBaseSessionManager
@Override
public void onBegin(GlobalSession globalSession) throws TransactionException {
addGlobalSession(globalSession);
}@Override
public void addGlobalSession(GlobalSession session) throws TransactionException {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(taskName)) {
// 写入session
boolean ret = transactionStoreManager.writeSession(LogOperation.GLOBAL_ADD, session);
if (!ret) {
throw new StoreException("addGlobalSession failed.");
}
} else {
boolean ret = transactionStoreManager.writeSession(LogOperation.GLOBAL_UPDATE, session);
if (!ret) {
throw new StoreException("addGlobalSession failed.");
}
}
}然后我们来看写入这里
@Override
public boolean writeSession(LogOperation logOperation, SessionStorable session) {
// 第一次进入一定是写入
if (LogOperation.GLOBAL_ADD.equals(logOperation)) {
return logStore.insertGlobalTransactionDO(SessionConverter.convertGlobalTransactionDO(session));
} else if (LogOperation.GLOBAL_UPDATE.equals(logOperation)) {
return logStore.updateGlobalTransactionDO(SessionConverter.convertGlobalTransactionDO(session));
} else if (LogOperation.GLOBAL_REMOVE.equals(logOperation)) {
return logStore.deleteGlobalTransactionDO(SessionConverter.convertGlobalTransactionDO(session));
} else if (LogOperation.BRANCH_ADD.equals(logOperation)) {
return logStore.insertBranchTransactionDO(SessionConverter.convertBranchTransactionDO(session));
} else if (LogOperation.BRANCH_UPDATE.equals(logOperation)) {
return logStore.updateBranchTransactionDO(SessionConverter.convertBranchTransactionDO(session));
} else if (LogOperation.BRANCH_REMOVE.equals(logOperation)) {
return logStore.deleteBranchTransactionDO(SessionConverter.convertBranchTransactionDO(session));
} else {
throw new StoreException("Unknown LogOperation:" + logOperation.name());
}
}因为我们第一次调用一定是写入,所以此时我们应该查看insertGlobalTransactionDO,此方法的作用就是写入全局事务表中global_table
@Override
public boolean insertGlobalTransactionDO(GlobalTransactionDO globalTransactionDO) {
String sql = LogStoreSqlsFactory.getLogStoreSqls(dbType).getInsertGlobalTransactionSQL(globalTable);
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
conn = logStoreDataSource.getConnection();
conn.setAutoCommit(true);
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, globalTransactionDO.getXid());
ps.setLong(2, globalTransactionDO.getTransactionId());
ps.setInt(3, globalTransactionDO.getStatus());
ps.setString(4, globalTransactionDO.getApplicationId());
ps.setString(5, globalTransactionDO.getTransactionServiceGroup());
String transactionName = globalTransactionDO.getTransactionName();
transactionName = transactionName.length() > transactionNameColumnSize ? transactionName.substring(0,
transactionNameColumnSize) : transactionName;
ps.setString(6, transactionName);
ps.setInt(7, globalTransactionDO.getTimeout());
ps.setLong(8, globalTransactionDO.getBeginTime());
ps.setString(9, globalTransactionDO.getApplicationData());
return ps.executeUpdate() > 0;
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new StoreException(e);
} finally {
IOUtil.close(ps, conn);
}
}我们可以查看GlobalTransactionDO实体类的属性,和global_table 的字段进行比对,就能看出其中道理。
Spring Cloud Alibaba Seata(二)
何弱者?何为强者?谁能保证强者恒强不被超越,谁又敢说弱者恒弱,就不能逆天改命?