DeadObjectException解题
RemoteException occurs on reporting focusChanged, w=Window{2470935 u0 bundle_id/bundle_id.MainActivity}
android.os.DeadObjectException
at android.os.BinderProxy.transactNative(Native Method)
at android.os.BinderProxy.transact(Binder.java:1143)
at android.view.IWindow$Stub$Proxy.windowFocusChanged(IWindow.java:500)
at com.android.server.wm.WindowState.reportFocusChangedSerialized(WindowState.java:3879)
at com.android.server.wm.WindowManagerService$H.handleMessage(WindowManagerService.java:5426)
at android.os.Handler.dispatchMessage(Handler.java:106)
at android.os.Looper.loop(Looper.java:214)
at android.os.HandlerThread.run(HandlerThread.java:65)
at com.android.server.ServiceThread.run(ServiceThread.java:44)
Question 1: 能否try-catch住?
想要搞清楚这个问题,我们需要对try-catch有个基础的了解。用法上面的东西,不在这里的讨论范围之内。
我们经常面临一个面试的问题。 OutOfMemoryError 可以被 try catch 吗? 对了,我不反感面试,因为面试会暴露我们知识点上的很多问题。所以,我们由这个问题来展开。
想要搞清楚这个问题。我们就要知道一些基础理论
- 什么可以被
try-catch?
针对上面的面试题,我们就有了一下的问题。
OutOfMemoryError可以被try-catch吗?- 捕获
OutOfMemoryError有什么意义? JVM中哪一块内存不会发生OOM?
回归到主题,针对DeadObjectException,我们就有了这个问题。
- 当前这个
Exception,可以被catch住么?有用么?
Question 1.1: 什么可以被try-catch
我们可以知道,Android的可抛出类(即Throwable),可以有两个子类, 异常Exception和错误Error。而所有的Thrwoable都可以被捕捉。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-tUzs8BWS-1670401244216)(https://picx.zhimg.com/80/v2-712ccd82f388ea55eba4e8958984f479_1440w.webp)]
Exception
**异常Exception:一般指可以或应该捕获和处理的异常。**它的两个直接子类IOException和RuntimeException及其子类都是我们在代码中经常遇到的一些错误。AWTException表示,抽象的窗口工具发生了异常,该Exception,在java.awt中抛出。java.awt为JAVA提供的用于创建界面以及图形绘制的软件包。而在Android开发中,我们基本不会遇到该Exception。
RuntimeException是在程序运行中可能发生的异常,我们可以不捕获它,但可能带来Crash的代价,但是过多的捕获异常又不利于暴露和调试异常情况。在开发过程中,我们更多的应该及时暴露问题。
运行时异常和受检异常
运行时异常:都是RuntimeException类及其子类异常,如NullPointerException(空指针异常)、IndexOutOfBoundsException(下标越界异常)等,这些异常是不检查异常,程序中可以选择捕获处理,也可以不处理。这些异常一般是由程序逻辑错误引起的,程序应该从逻辑角度尽可能避免这类异常的发生。运行时异常的特点是Java编译器不会检查它,也就是说,当程序中可能出现这类异常,即使没有用try-catch语句捕获它,也没有用throws子句声明抛出它,也会编译通过。
非运行时异常 (编译异常):是RuntimeException以外的异常,类型上都属于Exception类及其子类。从程序语法角度讲是必须进行处理的异常,如果不处理,程序就不能编译通过。如IOException、SQLException等以及用户自定义的Exception异常,一般情况下不自定义检查异常。
常见异常中英对照
| 异常类型 | 具体显示 |
|---|---|
| 算数异常类 | ArithmeticExecption |
| 空指针异常类型 | NullPointerException |
| 类型强制转换类型 | ClassCastException |
| 数组负下标异常 | NegativeArrayException |
| 数组下标越界异常 | ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException |
| 文件已结束异常 | EOFException |
| 文件未找到异常 | FileNotFoundException |
| 字符串转换为数字异常 | NumberFormatException |
| 操作数据库异常 | SQLException |
| 输入输出异常 | IOException |
| 方法未找到异常 | NoSuchMethodException |
| 下标越界异常 | IndexOutOfBoundsExecption |
| 系统异常 | SystemException |
| 创建一个大小为负数的数组错误异常 | NegativeArraySizeException |
| 数据格式异常 | NumberFormatException |
| 安全异常 | SecurityException |
| 不支持的操作异常 | UnsupportedOperationException |
Error
错误 Error :一般指非正常状态的,比较严重的,不应该被捕获的系统错误。 我们常见的Error就是OOM和StackOverflowError了
Question 1.2: OutOfMemoryError 可以被 try catch 吗?
根据上面所得到的信息。OOM其实是可以被捕捉的。
Question 1.3: 捕获 OutOfMemoryError 有什么意义?
一般情况下,捕获OutOfMemoryError并没有什么太大意义,在开发中也几乎没有写过这种代码。
如果把捕获OOM当做处理OOM的一种手段,无疑是不合适的。因为无法保证catch的代码就是导致OOM的原因,可能它只是压死骆驼的最后一根稻草,甚至也无法保证catch代码块中不会再次触发OOM 。
Android源码中有这样的操作。在View.java的buildDrawingCacheImpl()方法中有这么一段代码.
try {
bitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(mResources.getDisplayMetrics(),
width, height, quality);
bitmap.setDensity(getResources().getDisplayMetrics().densityDpi);
if (autoScale) {
mDrawingCache = bitmap;
} else {
mUnscaledDrawingCache = bitmap;
}
if (opaque && use32BitCache) bitmap.setHasAlpha(false);
} catch (OutOfMemoryError e) {
// If there is not enough memory to create the bitmap cache, just
// ignore the issue as bitmap caches are not required to draw the
// view hierarchy
if (autoScale) {
mDrawingCache = null;
} else {
mUnscaledDrawingCache = null;
}
mCachingFailed = true;
buildDrawingCacheImpl()方法的大致作用是为当前View生成一个Bitmap缓存。在构建Bitmap对象的时候,如果捕捉到了OOM ,就放弃生成Bitmap缓存,因为在View的绘制过程中Bitmap Cache并不是必须存在的。所以在这里没有必要抛出OOM,而是自己捕获就可以了。
在你自己明确知道可能发生OOM的情况下设置一个兜底策略,这可能是捕获OOM的唯一意义了.
Question 1.4: JVM中哪一块内存不会发生OOM?
要了解这个问题。需要先了解JVM模型是什么样的。
简单版本如下图:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-qRnVfXG7-1670401244217)(https://picx.zhimg.com/80/v2-279cac84feaaca095a49f75f19f76a47_1440w.webp)]
还有一个终极版本:
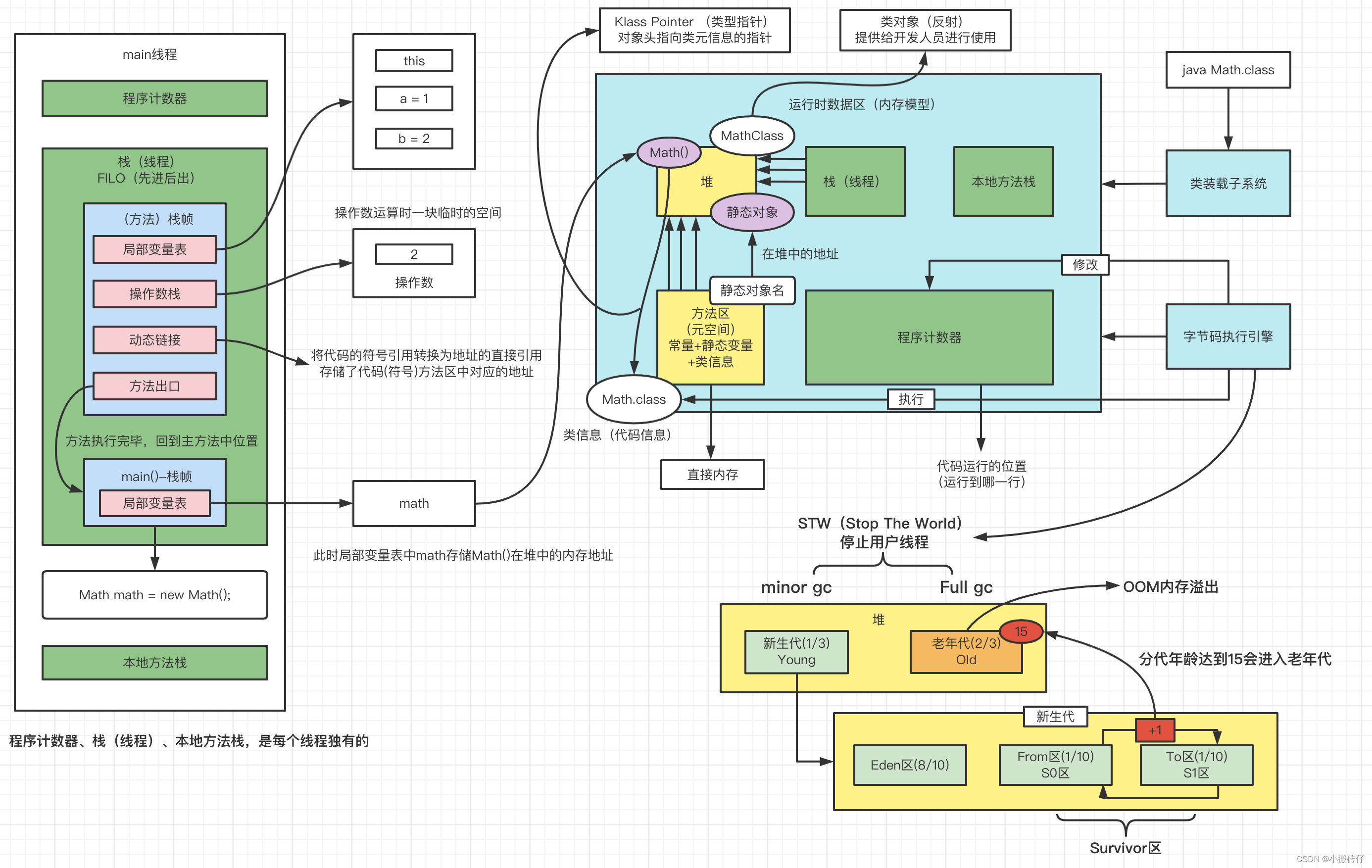
Java虚拟机栈
每个方法被执行的时候,Java虚拟机栈都会同步创建一个栈帧用于存储局部变量表、操作数栈、动态连接、方法出口等信息。每个方法被调用直到执行完毕的过程,就对应着一个栈帧在虚拟机栈中从入栈到出栈的过程。
如果线程请求的栈深度大于虚拟机所允许的深度,将抛出StackOverflowError异常。如果 Java 虚拟机栈支持动态扩展,当栈扩展时无法申请到足够的内存会排抛出OutOfMemoryError异常。
本地方法栈
本地方法栈为虚拟机使用到的Native方法服务。《Java 虚拟机规范》对本地方法栈中方法使用的语言、使用方式和数据结构并没有任何强制规定,因此具体的虚拟机可以根据需要自由实现它。
Hotspot将本地方法栈和虚拟机栈合二为一。本地方法栈也会在栈深度溢出和栈扩展失败时分别抛出 StackOverflowError和OutOfMemoryError。
Java 堆
所有线程共享的一块内存区域,在虚拟机启动时创建。此内存区域的唯一目的就是存放对象实例,Java世界里 “几乎” 所有的对象实例都在这里分配内存。
在 《Java 虚拟机规范》中对Java堆的描述是:“所有的对象实例以及数组都应当在堆上分配”。Java 堆以处于物理上不连续的内存空间,但在逻辑上它应该被视为连续的。但对于大对象(典型的如数组对象),多数虚拟机实现出于实现简单、存储高效的考虑,很可能会要求连续的内存空间。
Java 堆既可以被实现成固定大小,也可以是扩展的。如果在Java堆中没有内存完成实例分配,并且堆无法再扩展时Java虚拟机将会抛出OutOfMemoryError。
方法区
方法区是各个线程共享的内存区域,它用于存储已被虚拟机加载的类型信息、常量、静态变量、即时编译器编译后的代码缓存等数据。Hotspot设计之初选择把垃圾收集器的分代设计扩展至方法区,或者说使用永久代来实现方法区而已,使得HotSpot的 GC 能够像管理 Java 堆一样管理这部分内存,但导致 Java 应用更容易遇到内存溢出的问题。
在 JDK 8 中,彻底废弃了永久代的概念。如果方法区无法满足新的内存分配的需求时,将抛出 OutOfMemoryError 。
运行时常量池。
方法区的一部分。Class 文件的常量池表,用于存放编译期生成的各种字面量与符号引用,这部分内容将在类加载后方法方法去的运行时常量池。运行时常量池具有动态性,运行期间也可以将新的常量放入池中,如 String.intern() 。常量池受到方法区的限制,当无法再申请到内存时,会抛出 OutOfMemoryError 。
Question 1.5: 当前这个Exception,可以被catch住么?有用么?
我们从上面的只是可以知道,DeadObjectException 可以被catch住。但是有用么?也是要具体问题具体分析的。如果报在我们自己的代码里,try-catch是有用的。
结论
首先我们要来看,在哪里报错的错
ServiceThread
我在Android的frameworks里面,一个不知名的版本中,找到了这样的一个注释。
/**
* Special handler thread that we create for system services that require their own loopers.
*/
public class ServiceThread extends HandlerThread
其实这玩意就是,一个给需要有一个Lopper的系统服务用的HandlerThread 。
所以
这玩意是个系统服务。要通过Binder来给我们的App分发windowFocusChanged的时候报错了。首先,我们肯定无法去底层做try-catch的。而且,我也相信,这一定是做了try-catch的。
下面,我们就要讨论,如果在引发点,来做try-catch有没有用。其实是没用的。因为,对于我们的程序来说,接收到用户的操作,给系统发送请求。引发了页面变化。对我们的程序来说,try-catch只到通过Binder调用远端的接口。这个错误报在里远端的Looper里,对我们来说,已经圆满完成任务了。
所以,try-catch对于这个报错来说,在我们自己代码里是无用的。
Question 2: 这个BUG是怎么引起的?
我们就要看懂这个报错,就要知道,这个BUG是怎么引起的。什么时候会爆这个错。这个BUG是报在了windowFocusChanged过程中。所以,我们要了解Activity.onWindowFocusChanged()的调用流程是怎样的。并且,用法是什么样的。
Activity.onWindowFocusChanged 用法
方法原型如下:
public void onWindowFocusChanged (boolean hasFocus)
触发onWindowFocusChanged的情况有多种,比如应用前后台来回切换、软键盘弹出或者隐藏、首次进入一个Activity后会在onResume方法之后调用等。
那么,这个方法有什么用处呢?
Activity生命周期中,onStart, onResume, onCreate都不是真正visible的时间点, 真正的visible时间点是onWindowFocusChanged()函数被执行时。从onWindowFocusChanged被执行起,用户可以与应用进行交互了, 而这之前,对用户的操作需要做一点限制,常见的就是测量控件,获取控件的宽高。
如果我们不用
onWindowFocusChanged怎么获取View宽高?延后调用?监听Layout?
Activity.onWindowFocusChanged 调用过程
我们以ActivityThread.handleResumeActivity()方法作为切入点开始分析。
public final class ActivityThread extends ClientTransactionHandler
//省略其他方法
...
@Override
public void handleResumeActivity(IBinder token, boolean finalStateRequest, boolean isForward,
String reason) {
//省略部分代码
...
final ActivityClientRecord r = performResumeActivity(token, finalStateRequest, reason);
final Activity a = r.activity;
//省略部分代码
...
r.window = r.activity.getWindow();
View decor = r.window.getDecorView();
decor.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager();
WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes();
a.mDecor = decor;
l.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_BASE_APPLICATION;
l.softInputMode |= forwardBit;
wm.addView(decor, l);
//省略部分代码
...
}
}
我们知道这个方法是控制Acitvity.onResume执行的,也就是说在onResume之后,才会将DecorView的对象decor(activity显示内容的最外层容器)对象添加到ViewManager的对象wm中。那么wm对象是在什么时候初始化的呢?他是在Activity中初始化的,我们看一下是哪个方法里初始化的。
public class Activity extends ContextThemeWrapper
implements LayoutInflater.Factory2,
Window.Callback, KeyEvent.Callback,
OnCreateContextMenuListener, ComponentCallbacks2,
Window.OnWindowDismissedCallback, WindowControllerCallback,
AutofillManager.AutofillClient {
//省略其他方法
...
final void attach(Context context, ActivityThread aThread,
Instrumentation instr, IBinder token, int ident,
Application application, Intent intent, ActivityInfo info,
CharSequence title, Activity parent, String id,
NonConfigurationInstances lastNonConfigurationInstances,
Configuration config, String referrer, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
Window window, ActivityConfigCallback activityConfigCallback) {
//省略部分代码
...
mWindow = new PhoneWindow(this, window, activityConfigCallback);
mWindow.setWindowControllerCallback(this);
mWindow.setCallback(this);
mWindow.setOnWindowDismissedCallback(this);
mWindow.getLayoutInflater().setPrivateFactory(this);
//省略部分代码
...
mWindow.setWindowManager(
(WindowManager)context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE),
mToken, mComponent.flattenToString(),
(info.flags & ActivityInfo.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED) != 0);
if (mParent != null) {
mWindow.setContainer(mParent.getWindow());
}
mWindowManager = mWindow.getWindowManager();
//省略部分代码
...
}
/** Retrieve the window manager for showing custom windows. */
public WindowManager getWindowManager() {
return mWindowManager;
}
//省略其他方法
...
}
我们看到Activity.attach方法中创建了Window唯一实现类PhoneWindow类型的mWindow对象,mWindowManager对象也是从PhoneWindow获取的。那么他是在哪里初始化的呢?
public abstract class Window {
//省略其他方法
...
/**
* Set the window manager for use by this Window to, for example,
* display panels. This is <em>not</em> used for displaying the
* Window itself -- that must be done by the client.
*
* @param wm The window manager for adding new windows.
*/
public void setWindowManager(WindowManager wm, IBinder appToken, String appName,
boolean hardwareAccelerated) {
mAppToken = appToken;
mAppName = appName;
mHardwareAccelerated = hardwareAccelerated
|| SystemProperties.getBoolean(PROPERTY_HARDWARE_UI, false);
if (wm == null) {
wm = (WindowManager)mContext.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
}
mWindowManager = ((WindowManagerImpl)wm).createLocalWindowManager(this);
}
//省略其他方法
...
}
Window是PhoneWindow的基类,在setWindowManager方法中初始化了mWindowManager对象。(WindowManagerImpl类是WindowManager的实现类,WindowManager接口继承了ViewManager接口)。
我们回到最初wm.addView(decor,l)方法,实际上是调用了WindowManagerImpl.addView方法,我们看一下该方法的实现。
public final class WindowManagerImpl implements WindowManager {
private final WindowManagerGlobal mGlobal = WindowManagerGlobal.getInstance();
//省略部分代码
...
@Override
public void addView(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
applyDefaultToken(params);
mGlobal.addView(view, params, mContext.getDisplay(), mParentWindow);
}
}
我们看到addView方法调用了WindowManagerGlobal.addView方法,我们看一下该方法的实现。
public final class WindowManagerGlobal {
//省略部分方法
...
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params,
Display display, Window parentWindow) {
//省略部分代码
...
ViewRootImpl root;
View panelParentView = null;
//省略部分代码
...
root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);
view.setLayoutParams(wparams);
mViews.add(view);
mRoots.add(root);
mParams.add(wparams);
// do this last because it fires off messages to start doing things
try {
root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
// BadTokenException or InvalidDisplayException, clean up.
if (index >= 0) {
removeViewLocked(index, true);
}
throw e;
}
}
}
在addView中方法调用了ViewRootImpl.setView方法,我们看一下该方法的实现。
public final class ViewRootImpl implements ViewParent,
View.AttachInfo.Callbacks, ThreadedRenderer.DrawCallbacks {
final IWindowSession mWindowSession;
final W mWindow;
public ViewRootImpl(Context context, Display display) {
mWindowSession = WindowManagerGlobal.getWindowSession();
mWindow = new W(this);
//省略部分代码
...
}
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView) {
//省略部分代码
...
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplay(mWindow, mSeq, mWindowAttributes,
getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(), mWinFrame,
mAttachInfo.mContentInsets, mAttachInfo.mStableInsets,
mAttachInfo.mOutsets, mAttachInfo.mDisplayCutout, mInputChannel);
//省略部分代码
...
}
static class W extends IWindow.Stub {
private final WeakReference<ViewRootImpl> mViewAncestor;
private final IWindowSession mWindowSession;
W(ViewRootImpl viewAncestor) {
mViewAncestor = new WeakReference<ViewRootImpl>(viewAncestor);
mWindowSession = viewAncestor.mWindowSession;
}
@Override
public void windowFocusChanged(boolean hasFocus, boolean inTouchMode) {
final ViewRootImpl viewAncestor = mViewAncestor.get();
if (viewAncestor != null) {
viewAncestor.windowFocusChanged(hasFocus, inTouchMode);
}
}
//省略其他代码
...
}
}
setView方法调用了IWindowSession.addToDisplay方法(注意:mWindow对象是W类型的,后面会用到这个对象)。我们看一下该方法的实现。
public final class WindowManagerGlobal {
//省略部分方法
...
public static IWindowSession getWindowSession() {
synchronized (WindowManagerGlobal.class) {
if (sWindowSession == null) {
try {
InputMethodManager imm = InputMethodManager.getInstance();
IWindowManager windowManager = getWindowManagerService();
sWindowSession = windowManager.openSession(
new IWindowSessionCallback.Stub() {
@Override
public void onAnimatorScaleChanged(float scale) {
ValueAnimator.setDurationScale(scale);
}
},
imm.getClient(), imm.getInputContext());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
return sWindowSession;
}
}
}
通过以上代码,我们看到IWindowSession对象,是通过WindowMangerService创建的,WindowManagerService实现了IWindowManager。我们看一下WindowMangerService.openSession方法。
public class WindowManagerService extends IWindowManager.Stub
implements Watchdog.Monitor, WindowManagerPolicy.WindowManagerFuncs {
//省略其他代码
...
// -------------------------------------------------------------
// IWindowManager API
// -------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public IWindowSession openSession(IWindowSessionCallback callback, IInputMethodClient client,
IInputContext inputContext) {
if (client == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("null client");
if (inputContext == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("null inputContext");
Session session = new Session(this, callback, client, inputContext);
return session;
}
}
我们看到openSession方法中创建了Session对象返回,也就是说ViewRootImpl.setView方法中调用的是Session.addToDisplay方法,我们看一下该方法的实现。
class Session extends IWindowSession.Stub implements IBinder.DeathRecipient {
final WindowManagerService mService;
public Session(WindowManagerService service, IWindowSessionCallback callback,
IInputMethodClient client, IInputContext inputContext) {
mService = service;
}
//省略部分代码
...
@Override
public int addToDisplay(IWindow window, int seq, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs,
int viewVisibility, int displayId, Rect outFrame, Rect outContentInsets,
Rect outStableInsets, Rect outOutsets,
DisplayCutout.ParcelableWrapper outDisplayCutout, InputChannel outInputChannel) {
return mService.addWindow(this, window, seq, attrs, viewVisibility, displayId, outFrame,
outContentInsets, outStableInsets, outOutsets, outDisplayCutout, outInputChannel);
}
}
addToDisplay方法中调用了WindowManagerService.addWindow方法。我们看一下addWindow方法的实现.
public class WindowManagerService extends IWindowManager.Stub
implements Watchdog.Monitor, WindowManagerPolicy.WindowManagerFuncs {
//省略其他代码
...
public int addWindow(Session session, IWindow client, int seq,
LayoutParams attrs, int viewVisibility, int displayId, Rect outFrame,
Rect outContentInsets, Rect outStableInsets, Rect outOutsets,
DisplayCutout.ParcelableWrapper outDisplayCutout, InputChannel outInputChannel) {
final WindowState win = new WindowState(this, session, client, token, parentWindow,
appOp[0], seq, attrs, viewVisibility, session.mUid,
session.mCanAddInternalSystemWindow);
//省略部分代码
...
focusChanged = updateFocusedWindowLocked(UPDATE_FOCUS_WILL_ASSIGN_LAYERS,
false /*updateInputWindows*/);
//省略部分代码
...
}
// TODO: Move to DisplayContent
boolean updateFocusedWindowLocked(int mode, boolean updateInputWindows) {
mH.sendEmptyMessage(H.REPORT_FOCUS_CHANGE);
}
final class H extends android.os.Handler {
public static final int REPORT_FOCUS_CHANGE = 2;
//省略部分代码
...
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (DEBUG_WINDOW_TRACE) {
Slog.v(TAG_WM, "handleMessage: entry what=" + msg.what);
}
switch (msg.what) {
case REPORT_FOCUS_CHANGE: {
WindowState newFocus;
newFocus.reportFocusChangedSerialized(true, mInTouchMode);
} break;
//省略部分代码
...
}
}
}
在WindowManagerService.addWindow方法中调用了updateFocusedWindowLocked方法,然后通过Handler调用了WindowState.reportFocusChangedSerialized方法。我们看一下该方法的实现.
class WindowState extends WindowContainer<WindowState> implements WindowManagerPolicy.WindowState {
final IWindow mClient;
//省略其他代码
...
WindowState(WindowManagerService service, Session s, IWindow c, WindowToken token,
WindowState parentWindow, int appOp, int seq, WindowManager.LayoutParams a,
int viewVisibility, int ownerId, boolean ownerCanAddInternalSystemWindow,
PowerManagerWrapper powerManagerWrapper) {
super(service);
mClient = c;
}
/**
* Report a focus change. Must be called with no locks held, and consistently
* from the same serialized thread (such as dispatched from a handler).
*/
void reportFocusChangedSerialized(boolean focused, boolean inTouchMode) {
try {
mClient.windowFocusChanged(focused, inTouchMode);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
if (mFocusCallbacks != null) {
final int N = mFocusCallbacks.beginBroadcast();
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
IWindowFocusObserver obs = mFocusCallbacks.getBroadcastItem(i);
try {
if (focused) {
obs.focusGained(mWindowId.asBinder());
} else {
obs.focusLost(mWindowId.asBinder());
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
}
mFocusCallbacks.finishBroadcast();
}
}
}
WindowState.reportFocusChangedSerialized方法中调用了mClient.windowFocusChanged方法,mClient是IWindow的对象,也就是我们构建的调用WindowMangerService.addWindow方法时传入的W类的对象,因此会调用W.windowFocusChanged方法。
public final class ViewRootImpl implements ViewParent,
View.AttachInfo.Callbacks, ThreadedRenderer.DrawCallbacks {
final IWindowSession mWindowSession;
final W mWindow;
public ViewRootImpl(Context context, Display display) {
mWindowSession = WindowManagerGlobal.getWindowSession();
mWindow = new W(this);
//省略部分代码
...
}
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView) {
//省略部分代码
...
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplay(mWindow, mSeq, mWindowAttributes,
getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(), mWinFrame,
mAttachInfo.mContentInsets, mAttachInfo.mStableInsets,
mAttachInfo.mOutsets, mAttachInfo.mDisplayCutout, mInputChannel);
//省略部分代码
...
}
static class W extends IWindow.Stub {
private final WeakReference<ViewRootImpl> mViewAncestor;
private final IWindowSession mWindowSession;
W(ViewRootImpl viewAncestor) {
mViewAncestor = new WeakReference<ViewRootImpl>(viewAncestor);
mWindowSession = viewAncestor.mWindowSession;
}
@Override
public void windowFocusChanged(boolean hasFocus, boolean inTouchMode) {
final ViewRootImpl viewAncestor = mViewAncestor.get();
if (viewAncestor != null) {
viewAncestor.windowFocusChanged(hasFocus, inTouchMode);
}
}
//省略其他代码
...
}
public void windowFocusChanged(boolean hasFocus, boolean inTouchMode) {
synchronized (this) {
mWindowFocusChanged = true;
mUpcomingWindowFocus = hasFocus;
mUpcomingInTouchMode = inTouchMode;
}
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = MSG_WINDOW_FOCUS_CHANGED;
mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
private final static int MSG_WINDOW_FOCUS_CHANGED = 6;
final class ViewRootHandler extends Handler {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case MSG_WINDOW_FOCUS_CHANGED: {
handleWindowFocusChanged();
} break;
}
}
private void handleWindowFocusChanged() {
mView.dispatchWindowFocusChanged(hasWindowFocus);
}
}
W.windowFocusChanged方法会调用ViewRootImpl.windowFocusChange方法,该方法通过Handler执行handleWindowFocusChanged方法,该方法调用View.dispatchWindowFocusChanged方法,我们知道,mView是DecorView的实例,所以最终调用DecorView.onWindowChangeFocused方法。
public class DecorView extends FrameLayout implements RootViewSurfaceTaker, WindowCallbacks {
//省略其他代码
...
@Override
public void onWindowFocusChanged(boolean hasWindowFocus) {
super.onWindowFocusChanged(hasWindowFocus);
// If the user is chording a menu shortcut, release the chord since
// this window lost focus
if (mWindow.hasFeature(Window.FEATURE_OPTIONS_PANEL) && !hasWindowFocus
&& mWindow.mPanelChordingKey != 0) {
mWindow.closePanel(Window.FEATURE_OPTIONS_PANEL);
}
final Window.Callback cb = mWindow.getCallback();
if (cb != null && !mWindow.isDestroyed() && mFeatureId < 0) {
cb.onWindowFocusChanged(hasWindowFocus);
}
if (mPrimaryActionMode != null) {
mPrimaryActionMode.onWindowFocusChanged(hasWindowFocus);
}
if (mFloatingActionMode != null) {
mFloatingActionMode.onWindowFocusChanged(hasWindowFocus);
}
updateElevation();
}
}
DecorView.onWindowFocusChanged方法中调用了cb.onWindowFocusChanged方法,我们发现Activity实现了Window.CallBack并在创建PhoneWindow时,实例传给了PhoneWindow,因此这个方法调用的就是Acitivity中的onWindowFocusChanged。这就是onWindowFocusChanged首次执行过程。
分析Exception引发的原因
这个BUG是报在了WindowState.reportFocusChangedSerialized里。根据上面的信息。这个过程是WindowManagerService已经将视图展示,WindowState通知我们自己的ViewRootImpl 分发onWindowFocusChanged 事件。而这个时候,我们的ViewRootImpl 没了。
这个就是这个报错的原因,也是这个Exception能给我们提供的唯一信息。所以,我们能够推断出:
- 这个信息不完整,肯定在前面有一个崩溃的BUG,让我们的页面死亡。或者由于某些逻辑,自己没了。
- 锁定的范围应该在
onResume或前序生命周期的某些异步逻辑。
版权与说明
此篇文章,为本地文件远端副本。并用做分享使用。里面引用或摘抄了很多其他人的文章。如有侵权,联系必删。并感谢引用人的辛勤努力。