Java - 通过反射进行赋值以及函数调用
- 前言
- 一. 通过反射进行赋值
- 1.1 测试
- 1.2 总结
- 二. 通过反射进行函数调用
前言
说来惭愧,虽然反射在Java中是非常重要和常见的一种机制。但是,每当自己去写这方面的代码的时候,总是容易愣住。还得想一想代码怎么写。因此写下这篇文章做个笔记。
可以先看下这篇文章 Java-通过反射来打印类
一. 通过反射进行赋值
1.我们准备一个Teacher类,并把相关的属性都设置为private私有。准备他的get函数,set就不必啦。
public class Teacher {
private int userId;
private String userName;
public int getUserId() {
return userId;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
private void hello(String name, Integer userId) {
System.out.println("Hello World," + name + ", " + userId);
}
}
那么我们如何通过反射来进行赋值呢?关键代码:拿到这个类中的字段。
Field fieldName= xxx.class.getDeclaredField("fieldName");
1.1 测试
测试1:
@org.junit.Test
public void test3() throws Exception {
Teacher teacher = new Teacher();
Field userName = Teacher.class.getDeclaredField("userName");
// 授权访问私有成员变量
userName.setAccessible(true);
userName.set(teacher, "ljj");
System.out.println(teacher.getUserName());:
System.out.println(teacher.getUserId());
}
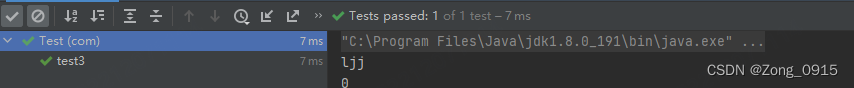
结果如下:可见userId输出为0。因为我们没有对它进行赋值。所以初始值为0,而userName则赋值成功。
测试2:setAccessible我们设置为false(默认)
@org.junit.Test
public void test3() throws Exception {
Teacher teacher = new Teacher();
System.out.println(teacher.getUserId());
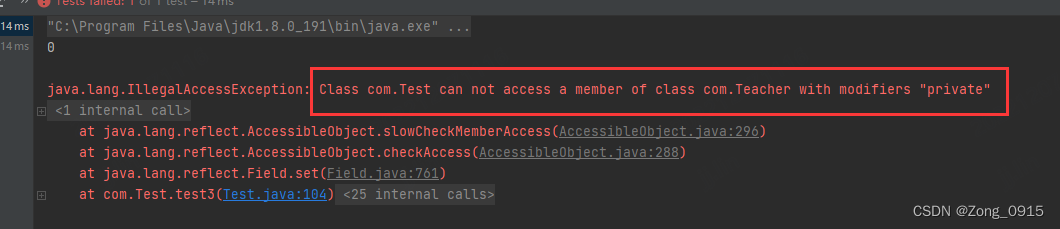
Field userId = Teacher.class.getDeclaredField("userId");
userId.setAccessible(false);
userId.set(teacher, 10);
System.out.println(teacher.getUserId());
}
结果如下:
测试3:setAccessible设置为true,然后再次赋值userId。
@org.junit.Test
public void test3() throws Exception {
Teacher teacher = new Teacher();
System.out.println(teacher.getUserId());
Field userId = Teacher.class.getDeclaredField("userId");
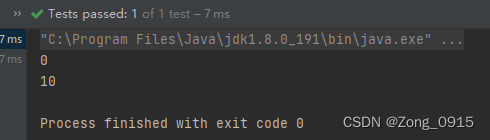
userId.setAccessible(true);
userId.set(teacher, 10);
System.out.println(teacher.getUserId());
}
结果如下:
测试4:给Teacher加一个public类型的属性address:
public String address;
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
测试如下:
@org.junit.Test
public void test3() throws Exception {
Teacher teacher = new Teacher();
Field address = Teacher.class.getDeclaredField("address");
address.set(teacher, "abcd");
System.out.println(teacher.getAddress());
}
结果:
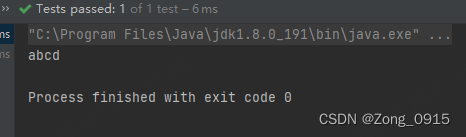
1.2 总结
- 可以通过
Field name= Object.class.getDeclaredField("name");的方式拿到类的字段。 - 通过
name.set(Target, value);进行属性的赋值。 - 如果字段是私有的,还需要设置
setAccessible(true);其他不需要。
二. 通过反射进行函数调用
关键代码:
Method method = Teacher.class.getDeclaredMethod(方法名称, 参数类型1.class, 参数类型2.class,...);
以本文案例为例:
private void hello(String name, Integer userId) {
System.out.println("Hello World," + name + ", " + userId);
}
那么不难写出代码如下:
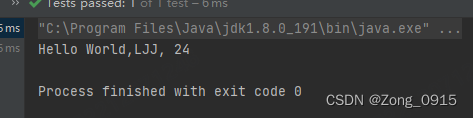
@org.junit.Test
public void test3() throws Exception {
Teacher teacher = new Teacher();
// 写对方法名称、参数类型
Method hello = Teacher.class.getDeclaredMethod("hello", String.class, Integer.class);
// 因为是私有的,所以要想访问,需要设置Accessible
hello.setAccessible(true);
// 对应的参数
Object[] objects = {"LJJ", 24};
// 调用函数
hello.invoke(teacher, objects);
}
结果如下: