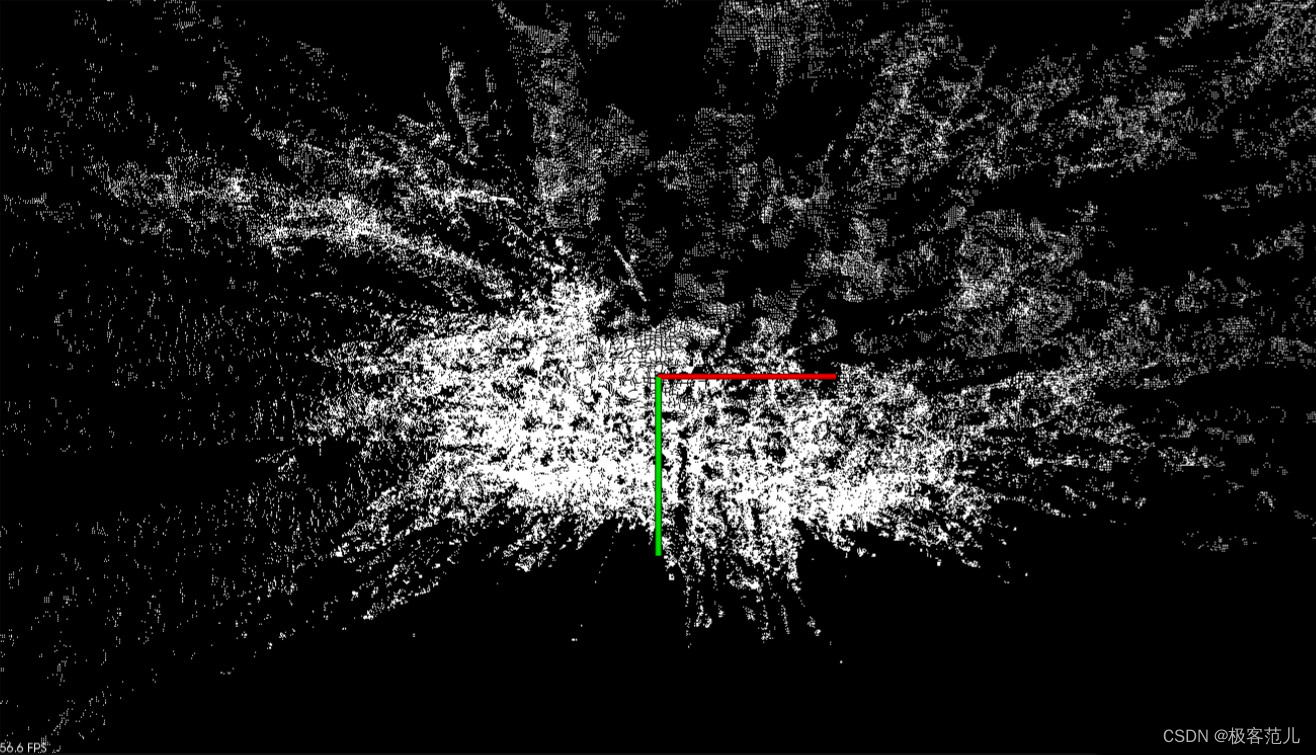
双目惯性相机最开始是从VINS中了解到的,2018年VINS中推荐过Loitor视觉惯性相机,但是后来看到GitHub Issue中有人反映Loitor丢帧、无技术支持等问题,加之购入渠道非官方故未入手Loitor,浏览知乎时关注到Indemind的该款产品,发现技术贴较多、SDK支持及销售渠道较为官方,故今年入手了一个,打算用于VI-SLAM用于视觉定位导航及双目三维重建等方面进行感知定位。
目前最近的SDK版本是1.4.2,这个相机成本便宜,有硬同步的IMU,频率也够高,自带标定,对于目前我只做视觉SLAM定位足够用了。然而封库,其他各种依赖库要跟着SDK的库,OpenCV不使用ROS自带的版本,使用单独版本3.4.3等等。这个SDK组织得真的是一言难尽,所以分析SDK中实时显示点云图代码并加以改进,记录下学习的过程。
文章目录
- 一、获取点云图
- 1、分析`get_points.cpp`源码
- (1)包含头文件和命名空间:
- (2)定义了一个名为clear的模板函数,用于清空队列。
- (3)main函数开始:
- 2、分析`util_pcl.h`源码
- (1)包含头文件和命名空间
- (2)定义了一个名为PCViewer的类
- (3)头文件保护
- 3、分析`util_pcl.h`源码
- (1)CustomColorVis函数:这是一个辅助函数,用于创建具有自定义颜色的点云可视化对象。它创建一个PCLVisualizer对象,并将点云数据添加到视图中,设置背景颜色、点云渲染属性以及相机位置。
- (2)PCViewer类的构造函数和析构函数:构造函数初始化viewer_成员变量为nullptr,析构函数在析构对象时关闭PCLVisualizer并释放相关资源。
- (3)Update(const cv::Mat &xyz)函数:根据输入的3D坐标矩阵,创建一个pcl::PointCloudpcl::PointXYZ对象,并调用另一个重载的Update函数。
- (4)Update(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::ConstPtr pc)函数:如果viewer_为空,创建一个PCLVisualizer对象并将其赋值给viewer_。然后更新视图中的点云数据,并调用spinOnce以刷新可视化。
- (5)WasVisual()函数:检查viewer_是否存在(非空),以确定是否成功创建了PCLVisualizer对象。
- (6)WasStopped()函数:检查viewer_是否存在且视图是否已停止(用户关闭了可视化窗口)。
- (7)ConvertMatToPointCloud(const cv::Mat &xyz, pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr pc)函数:根据输入的3D坐标矩阵,将有效的点转换为pcl::PointXYZ对象,并添加到点云对象中。最终,设置点云对象的宽度和高度。
- 二、保存点云图至本地
- 1、在get_points.cpp文件中添加对ConvertMatToPointCloud和SavePointCloudToFile函数的声明,以便在使用时正确识别它们
- 2、SavePointCloudToFile函数是私有成员函数,无法在main函数中直接访问。我们需要将其更改为公有成员函数,以便在main函数中调用。将util_pcl.h文件中的PCViewer类进行如下修改
- 3、在util_pcl.cpp中实现PCViewer类的SavePointCloudToFile函数,以便成功编译和链接。请按照之前提供的代码示例,在util_pcl.cpp中添加以下函数实现
- 三、改进后的代码
- 1、改进后的util_pcl.h
- 2、改进后的util_pcl.cpp
- 3、改进后的get_points.cpp
一、获取点云图
IMSEEE-SDK中的功能,可以初始化相机并获取实时的点云数据,然后使用PCL库进行可视化展示,首先我们分析get_points.cpp代码
1、分析get_points.cpp源码
// Copyright 2020 Indemind Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
// limitations under the License.
#include "imrdata.h"//INDEMIND相机数据处理的头文件
#include "imrsdk.h"// INDEMIND相机SDK的头文件
#include "logging.h"//日志记录的头文件
#include "times.h"//时间处理的头文件
#include "types.h"//类型定义的头文件
#include "util_pcl.h"//PCL(点云库)的实用函数的头文件
#include <queue>//队列容器的头文件
#include <mutex>// 互斥锁的头文件
using namespace indem;//使用indem命名空间
template <typename T> void clear(std::queue<T> &q) {//定义了一个名为clear的模板函数,用于清空队列
std::queue<T> empty;
swap(empty, q);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
auto m_pSDK = new CIMRSDK();//创建一个CIMRSDK类的实例m_pSDK,该类是IMSEEE-SDK的主要接口
MRCONFIG config = {0};//定义并初始化一个MRCONFIG结构体变量config,用于配置相机的参数,包括是否启用SLAM、图像分辨率、图像帧率和IMU频率等
config.bSlam = false;
config.imgResolution = IMG_640;
config.imgFrequency = 50;
config.imuFrequency = 1000;
m_pSDK->Init(config);//调用m_pSDK->Init(config)初始化相机
std::queue<cv::Mat> points_queue;//创建一个用于存储点云数据的std::queue<cv::Mat>类型的队列points_queue
std::mutex mutex_points;//用于保护队列操作的互斥锁mutex_points
int points_count = 0;//定义并初始化一个整型变量points_count,用于记录接收到的点云数量
if (m_pSDK->EnablePointProcessor()) {//如果成功启用了点云处理功能
// m_pSDK->EnableLRConsistencyCheck();
// m_pSDK->SetDepthCalMode(DepthCalMode::HIGH_ACCURACY);
m_pSDK->RegistPointCloudCallback(//注册一个回调函数,当收到新的点云数据时,将其加入队列,并增加points_count的计数
[&points_count, &points_queue, &mutex_points](double time, cv::Mat points) {
if (!points.empty()) {
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex_points);
points_queue.push(points);
}
++points_count;
}
});
}
PCViewer pcviewer;//创建一个PCViewer类的实例pcviewer,用于实时显示点云
auto &&time_beg = times::now();//获取当前时间time_beg
while (true) {//进入主循环
if (!points_queue.empty()) {//不断检查点云队列是否非空
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex_points);//如果队列非空,使用互斥锁锁定队列
pcviewer.Update(points_queue.front());//调用pcviewer.Update()方法更新显示的点云,并清空队列
clear(points_queue);
}
char key = static_cast<char>(cv::waitKey(1));
if (key == 27 || key == 'q' || key == 'Q') { // ESC/Q//检查是否按下了ESC键或者'q'键,如果是则退出循环
break;
}
if (pcviewer.WasStopped()) {
break;//检查pcviewer是否已停止,如果是则退出循环
}
}
delete m_pSDK;//释放相机资源,删除m_pSDK实例
auto &&time_end = times::now();//获取循环结束后的时间time_end
float elapsed_ms =
times::count<times::microseconds>(time_end - time_beg) * 0.001f;//计算从开始到结束的时间间隔,并转换为毫秒
#ifdef __linux//输出日志信息,包括开始时间、结束时间、运行时间和接收到的点云数量
LOG(INFO) << "Time beg: " << times::to_local_string(time_beg)
<< ", end: " << times::to_local_string(time_end)
<< ", cost: " << elapsed_ms << "ms";
LOG(INFO) << "depth count: " << points_count
<< ", fps: " << (1000.f * points_count / elapsed_ms);
#endif
return 0;//返回0,表示程序正常结束
}
这是一个使用INDEMIND相机的IMSEEE-SDK来获取点云数据并实时显示的示例代码。下面是对代码的分析:
(1)包含头文件和命名空间:
- imrdata.h: INDEMIND相机数据处理的头文件。
- imrsdk.h: INDEMIND相机SDK的头文件。
- logging.h: 日志记录的头文件。
- times.h: 时间处理的头文件。
- types.h: 类型定义的头文件。
- util_pcl.h: PCL(点云库)的实用函数的头文件。
- queue: 队列容器的头文件。
- mutex: 互斥锁的头文件。
- cv::Mat: OpenCV库中的矩阵类。
- using namespace indem;: 使用indem命名空间。
(2)定义了一个名为clear的模板函数,用于清空队列。
(3)main函数开始:
- 创建一个CIMRSDK类的实例m_pSDK,该类是IMSEEE-SDK的主要接口。
- 定义并初始化一个MRCONFIG结构体变量config,用于配置相机的参数,包括是否启用SLAM、图像分辨率、图像帧率和IMU频率等。
- 调用m_pSDK->Init(config)初始化相机。
创建一个用于存储点云数据的std::queuecv::Mat类型的队列points_queue,以及一个用于保护队列操作的互斥锁mutex_points。 - 定义并初始化一个整型变量points_count,用于记录接收到的点云数量。
- 如果成功启用了点云处理功能(通过调用m_pSDK->EnablePointProcessor()):
①注册一个回调函数,当收到新的点云数据时,将其加入队列,并增加points_count的计数。 - 创建一个PCViewer类的实例pcviewer,用于实时显示点云。
- 获取当前时间time_beg。
- 进入主循环,不断检查点云队列是否非空:
①如果队列非空,使用互斥锁锁定队列,然后调用pcviewer.Update()方法更新显示的点云,并清空队列。
②检查是否按下了ESC键或者’q’键,如果是则退出循环。
③检查pcviewer是否已停止,如果是则退出循环。 - 释放相机资源,删除m_pSDK实例。
- 获取循环结束后的时间time_end。
- 计算从开始到结束的时间间隔,并转换为毫秒。
- 输出日志信息,包括开始时间、结束时间、运行时间和接收到的点云数量。
- 返回0,表示程序正常结束。
get_points.cpp引入的头文件util_pcl.h,分析util_pcl.h的代码
2、分析util_pcl.h源码
// Copyright 2020 Indemind Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
// limitations under the License.
// limitations under the License.
#ifndef UTIL_PCL_H_//头文件的保护宏,防止头文件的重复包含
#define UTIL_PCL_H_//头文件的保护宏,防止头文件的重复包含
#pragma once//另一种头文件保护的方法,确保头文件只被编译一次
#include <memory>//标准库头文件,用于使用智能指针
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>//OpenCV库的核心头文件
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>//PCL(点云库)的可视化模块头文件
class PCViewer {//定义了一个名为PCViewer的类
public:
PCViewer();//构造函数,用于初始化点云可视化器
~PCViewer();//析构函数,用于释放点云可视化器资源
void Update(const cv::Mat &xyz);//更新点云数据,并将其转换为PCL的点云格式进行显示
void Update(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::ConstPtr pc);//更新点云数据,并直接显示PCL的点云格式
bool WasVisual() const;//检查点云可视化器是否已创建成功
bool WasStopped() const;//检查点云可视化是否已停止
private:
void ConvertMatToPointCloud(const cv::Mat &xyz,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr pc);//将OpenCV的矩阵格式的点云数据转换为PCL的点云格式。
std::shared_ptr<pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer> viewer_;//PCL可视化器的智能指针
};
#endif//结束头文件的保护
(1)包含头文件和命名空间
- : 标准库头文件,用于使用智能指针。
- <opencv2/core/core.hpp>: OpenCV库的核心头文件。
- <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>: PCL(点云库)的可视化模块头文件。
(2)定义了一个名为PCViewer的类
- 公共成员函数:
①PCViewer():构造函数,用于初始化点云可视化器。
②~PCViewer():析构函数,用于释放点云可视化器资源。
③Update(const cv::Mat &xyz):更新点云数据,并将其转换为PCL的点云格式进行显示。
④Update(pcl::PointCloudpcl::PointXYZ::ConstPtr pc):更新点云数据,并直接显示PCL的点云格式。
⑤WasVisual() const:检查点云可视化器是否已创建成功。
⑥WasStopped() const:检查点云可视化是否已停止。 - 私有成员函数:
ConvertMatToPointCloud(const cv::Mat &xyz, pcl::PointCloudpcl::PointXYZ::Ptr pc):将OpenCV的矩阵格式的点云数据转换为PCL的点云格式。 - 私有成员变量:
std::shared_ptrpcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer_:PCL可视化器的智能指针。
(3)头文件保护
#ifndef UTIL_PCL_H_和#define UTIL_PCL_H_:头文件的保护宏,防止头文件的重复包含。#pragma once:另一种头文件保护的方法,确保头文件只被编译一次。#endif:结束头文件的保护。
该头文件定义了一个简单的点云可视化类PCViewer,其中包含了点云数据的更新和显示函数,以及相应的辅助函数
3、分析util_pcl.h源码
// Copyright 2020 Indemind Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
// limitations under the License.
#include "util_pcl.h"
// #include <pcl/common/common_headers.h>
#include <cmath>
std::shared_ptr<pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer>
CustomColorVis(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::ConstPtr pc) {
// --------------------------------------------
// -----Open 3D viewer and add point cloud-----
// --------------------------------------------
//这是一个辅助函数,用于创建具有自定义颜色的点云可视化对象。它创建一个PCLVisualizer对象,并将点云数据添加到视图中,设置背景颜色、点云渲染属性以及相机位置。
std::shared_ptr<pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer> viewer(
new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("PointCloud Viewer"));
viewer->setBackgroundColor(0, 0, 0);
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> single_color(
pc, 255, 255, 255);
viewer->addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>(pc, single_color, "point cloud");
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(
pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 1, "point cloud");
// viewer->addCoordinateSystem(1.0);
viewer->addCoordinateSystem(1000.0);
viewer->initCameraParameters();
viewer->setCameraPosition(0, 0, -150, 0, -1, 0);
return (viewer);
}
//构造函数初始化viewer_成员变量为nullptr
PCViewer::PCViewer() : viewer_(nullptr) {}
//析构函数在析构对象时关闭PCLVisualizer并释放相关资源
PCViewer::~PCViewer() {
// VLOG(2) << __func__;
if (viewer_) {
// viewer_->saveCameraParameters("pcl_camera_params.txt");
viewer_->close();
viewer_ == nullptr;
}
}
//根据输入的3D坐标矩阵,创建一个pcl::PointCloudpcl::PointXYZ对象,并调用另一个重载的Update函数
void PCViewer::Update(const cv::Mat &xyz) {
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr pc(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
ConvertMatToPointCloud(xyz, pc);
Update(pc);
}
//如果viewer_为空,创建一个PCLVisualizer对象并将其赋值给viewer_。然后更新视图中的点云数据,并调用spinOnce以刷新可视化
void PCViewer::Update(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::ConstPtr pc) {
if (viewer_ == nullptr) {
viewer_ = CustomColorVis(pc);
}
viewer_->updatePointCloud(pc, "point cloud");
viewer_->spinOnce();
}
//检查viewer_是否存在(非空),以确定是否成功创建了PCLVisualizer对象
bool PCViewer::WasVisual() const { return viewer_ != nullptr; }
//检查viewer_是否存在且视图是否已停止(用户关闭了可视化窗口)
bool PCViewer::WasStopped() const {
return viewer_ != nullptr && viewer_->wasStopped();
}
//根据输入的3D坐标矩阵,将有效的点转换为pcl::PointXYZ对象,并添加到点云对象中。最终,设置点云对象的宽度和高度
void PCViewer::ConvertMatToPointCloud(const cv::Mat &xyz,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr pc) {
// cv::Mat channels[3];
// cv::split(xyz, channels);
// double min, max;
// cv::minMaxLoc(channels[2], &min, &max);
for (int i = 0; i < xyz.rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < xyz.cols; j++) {
auto &&p = xyz.at<cv::Point3f>(i, j);
if (std::isfinite(p.x) && std::isfinite(p.y) && std::isfinite(p.z)) {
// LOG(INFO) << "[" << i << "," << j << "] x: " << p.x << ", y: " << p.y
// << ", z: " << p.z;
pcl::PointXYZ point;
point.x = p.x * 1000.0;
point.y = p.y * 1000.0;
point.z = p.z * 1000.0;
// point.z = p.z - min;
pc->points.push_back(point);
}
}
}
pc->width = static_cast<int>(pc->points.size());
pc->height = 1;
}
(1)CustomColorVis函数:这是一个辅助函数,用于创建具有自定义颜色的点云可视化对象。它创建一个PCLVisualizer对象,并将点云数据添加到视图中,设置背景颜色、点云渲染属性以及相机位置。
(2)PCViewer类的构造函数和析构函数:构造函数初始化viewer_成员变量为nullptr,析构函数在析构对象时关闭PCLVisualizer并释放相关资源。
(3)Update(const cv::Mat &xyz)函数:根据输入的3D坐标矩阵,创建一个pcl::PointCloudpcl::PointXYZ对象,并调用另一个重载的Update函数。
(4)Update(pcl::PointCloudpcl::PointXYZ::ConstPtr pc)函数:如果viewer_为空,创建一个PCLVisualizer对象并将其赋值给viewer_。然后更新视图中的点云数据,并调用spinOnce以刷新可视化。
(5)WasVisual()函数:检查viewer_是否存在(非空),以确定是否成功创建了PCLVisualizer对象。
(6)WasStopped()函数:检查viewer_是否存在且视图是否已停止(用户关闭了可视化窗口)。
(7)ConvertMatToPointCloud(const cv::Mat &xyz, pcl::PointCloudpcl::PointXYZ::Ptr pc)函数:根据输入的3D坐标矩阵,将有效的点转换为pcl::PointXYZ对象,并添加到点云对象中。最终,设置点云对象的宽度和高度。
二、保存点云图至本地
想将保存在队列中的点云数据保存为点云图形文件(如PCD、PLY等格式),可以在合适的时机将队列中的点云数据取出,并使用PCL库将其保存到本地
1、在get_points.cpp文件中添加对ConvertMatToPointCloud和SavePointCloudToFile函数的声明,以便在使用时正确识别它们
// 保存点云图到本地
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr pointcloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcviewer.ConvertMatToPointCloud(points_queue.front(), pointcloud);
std::string filename = "point_cloud.pcd";
pcviewer.SavePointCloudToFile(filename, pointcloud);
2、SavePointCloudToFile函数是私有成员函数,无法在main函数中直接访问。我们需要将其更改为公有成员函数,以便在main函数中调用。将util_pcl.h文件中的PCViewer类进行如下修改
void SavePointCloudToFile(const std::string& filename,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr pc); // 添加这一行
3、在util_pcl.cpp中实现PCViewer类的SavePointCloudToFile函数,以便成功编译和链接。请按照之前提供的代码示例,在util_pcl.cpp中添加以下函数实现
void PCViewer::SavePointCloudToFile(const std::string& filename,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr pc) {
pcl::PCDWriter writer;
writer.write(filename, *pc);
}
三、改进后的代码
1、改进后的util_pcl.h
#ifndef UTIL_PCL_H_
#define UTIL_PCL_H_
#pragma once
#include <memory>
#include <string> // 添加这一行
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
class PCViewer {
public:
PCViewer();
~PCViewer();
void Update(const cv::Mat &xyz);
void Update(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::ConstPtr pc);
bool WasVisual() const;
bool WasStopped() const;
void ConvertMatToPointCloud(const cv::Mat &xyz,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr pc);
void SavePointCloudToFile(const std::string& filename,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr pc); // 添加这一行
private:
std::shared_ptr<pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer> viewer_;
};
#endif
#ifndef UTIL_PCL_H_
#define UTIL_PCL_H_
#pragma once
#include <memory>
#include <string> // 添加这一行
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
class PCViewer {
public:
PCViewer();
~PCViewer();
void Update(const cv::Mat &xyz);
void Update(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::ConstPtr pc);
bool WasVisual() const;
bool WasStopped() const;
void ConvertMatToPointCloud(const cv::Mat &xyz,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr pc);
void SavePointCloudToFile(const std::string& filename,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr pc); // 添加这一行
private:
std::shared_ptr<pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer> viewer_;
};
#endif
2、改进后的util_pcl.cpp
// Copyright 2020 Indemind Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
// limitations under the License.
#include "util_pcl.h"
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
// #include <pcl/common/common_headers.h>
#include <cmath>
std::shared_ptr<pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer>
CustomColorVis(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::ConstPtr pc) {
// --------------------------------------------
// -----Open 3D viewer and add point cloud-----
// --------------------------------------------
std::shared_ptr<pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer> viewer(
new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("PointCloud Viewer"));
viewer->setBackgroundColor(0, 0, 0);
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> single_color(
pc, 255, 255, 255);
viewer->addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>(pc, single_color, "point cloud");
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(
pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 1, "point cloud");
// viewer->addCoordinateSystem(1.0);
viewer->addCoordinateSystem(1000.0);
viewer->initCameraParameters();
viewer->setCameraPosition(0, 0, -150, 0, -1, 0);
return (viewer);
}
PCViewer::PCViewer() : viewer_(nullptr) {}
PCViewer::~PCViewer() {
// VLOG(2) << __func__;
if (viewer_) {
// viewer_->saveCameraParameters("pcl_camera_params.txt");
viewer_->close();
viewer_ == nullptr;
}
}
void PCViewer::Update(const cv::Mat &xyz) {
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr pc(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
ConvertMatToPointCloud(xyz, pc);
Update(pc);
}
void PCViewer::Update(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::ConstPtr pc) {
if (viewer_ == nullptr) {
viewer_ = CustomColorVis(pc);
}
viewer_->updatePointCloud(pc, "point cloud");
viewer_->spinOnce();
}
bool PCViewer::WasVisual() const { return viewer_ != nullptr; }
bool PCViewer::WasStopped() const {
return viewer_ != nullptr && viewer_->wasStopped();
}
void PCViewer::SavePointCloudToFile(const std::string& filename,pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr pc) {
pcl::PCDWriter writer;
writer.write(filename, *pc);
}
void PCViewer::ConvertMatToPointCloud(const cv::Mat &xyz,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr pc) {
// cv::Mat channels[3];
// cv::split(xyz, channels);
// double min, max;
// cv::minMaxLoc(channels[2], &min, &max);
for (int i = 0; i < xyz.rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < xyz.cols; j++) {
auto &&p = xyz.at<cv::Point3f>(i, j);
if (std::isfinite(p.x) && std::isfinite(p.y) && std::isfinite(p.z)) {
// LOG(INFO) << "[" << i << "," << j << "] x: " << p.x << ", y: " << p.y
// << ", z: " << p.z;
pcl::PointXYZ point;
point.x = p.x * 1000.0;
point.y = p.y * 1000.0;
point.z = p.z * 1000.0;
// point.z = p.z - min;
pc->points.push_back(point);
}
}
}
pc->width = static_cast<int>(pc->points.size());
pc->height = 1;
}
3、改进后的get_points.cpp
#include "imrdata.h"
#include "imrsdk.h"
#include "logging.h"
#include "times.h"
#include "types.h"
#include "util_pcl.h"
#include <queue>
#include <mutex>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
using namespace indem;
template <typename T> void clear(std::queue<T> &q) {
std::queue<T> empty;
swap(empty, q);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
auto m_pSDK = new CIMRSDK();
MRCONFIG config = {0};
config.bSlam = false;
config.imgResolution = IMG_640;
config.imgFrequency = 50;
config.imuFrequency = 1000;
m_pSDK->Init(config);
std::queue<cv::Mat> points_queue;
std::mutex mutex_points;
int points_count = 0;
if (m_pSDK->EnablePointProcessor()) {
// m_pSDK->EnableLRConsistencyCheck();
// m_pSDK->SetDepthCalMode(DepthCalMode::HIGH_ACCURACY);
m_pSDK->RegistPointCloudCallback(
[&points_count, &points_queue, &mutex_points](double time, cv::Mat points) {
if (!points.empty()) {
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex_points);
points_queue.push(points);
}
++points_count;
}
});
}
PCViewer pcviewer;
auto &&time_beg = times::now();
while (true) {
if (!points_queue.empty()) {
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex_points);
pcviewer.Update(points_queue.front());
// 保存点云图到本地
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr pointcloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcviewer.ConvertMatToPointCloud(points_queue.front(), pointcloud);
std::string filename = "point_cloud.pcd";
pcviewer.SavePointCloudToFile(filename, pointcloud);
clear(points_queue);
}
char key = static_cast<char>(cv::waitKey(1));
if (key == 27 || key == 'q' || key == 'Q') { // ESC/Q
break;
}
if (pcviewer.WasStopped()) {
break;
}
}
delete m_pSDK;
auto &&time_end = times::now();
float elapsed_ms =
times::count<times::microseconds>(time_end - time_beg) * 0.001f;
#ifdef __linux
LOG(INFO) << "Time beg: " << times::to_local_string(time_beg)
<< ", end: " << times::to_local_string(time_end)
<< ", cost: " << elapsed_ms << "ms";
LOG(INFO) << "depth count: " << points_count
<< ", fps: " << (1000.f * points_count / elapsed_ms);
#endif
return 0;
}