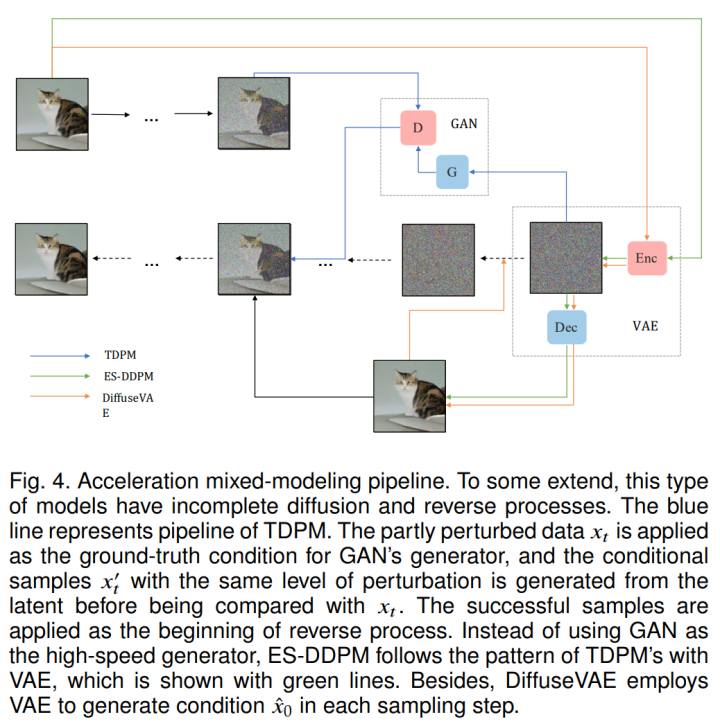
In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is an equation which imposes relations between the various partial derivatives of a multivariable function.
The function is often thought of as an “unknown” to be solved for, similarly to how x is thought of as an unknown number to be solved for in an algebraic equation like x2 − 3x + 2 = 0. However, it is usually impossible to write down explicit formulas for solutions of partial differential equations. There is, correspondingly, a vast amount of modern mathematical and scientific research on methods to numerically approximate solutions of certain partial differential equations using computers. Partial differential equations also occupy a large sector of pure mathematical research, in which the usual questions are, broadly speaking, on the identification of general qualitative features of solutions of various partial differential equations, such as existence, uniqueness, regularity, and stability.[citation needed] Among the many open questions are the existence and smoothness of solutions to the Navier–Stokes equations, named as one of the Millennium Prize Problems in 2000.
Partial differential equations are ubiquitous in mathematically oriented scientific fields, such as physics and engineering. For instance, they are foundational in the modern scientific understanding of sound, heat, diffusion, electrostatics, electrodynamics, thermodynamics, fluid dynamics, elasticity, general relativity, and quantum mechanics (Schrödinger equation, Pauli equation, etc). They also arise from many purely mathematical considerations, such as differential geometry and the calculus of variations; among other notable applications, they are the fundamental tool in the proof of the Poincaré conjecture from geometric topology.
Partly due to this variety of sources, there is a wide spectrum of different types of partial differential equations, and methods have been developed for dealing with many of the individual equations which arise. As such, it is usually acknowledged that there is no “general theory” of partial differential equations, with specialist knowledge being somewhat divided between several essentially distinct subfields.[1]
Ordinary differential equations form a subclass of partial differential equations, corresponding to functions of a single variable. Stochastic partial differential equations and nonlocal equations are, as of 2020, particularly widely studied extensions of the “PDE” notion. More classical topics, on which there is still much active research, include elliptic and parabolic partial differential equations, fluid mechanics, Boltzmann equations, and dispersive partial differential equations.
Navier–Stokes differential equations used to simulate airflow around an obstruction
Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Well-posedness
- 2.1 The energy method
- 2.2 Existence of local solutions
- 3 Classification
- 3.1 Notation
- 3.2 Equations of first order
- 3.3 Linear and nonlinear equations
- 3.3.1 Linear equations
- 3.3.2 Nonlinear equations
- 3.4 Linear equations of second order
- 3.5 Systems of first-order equations and characteristic surfaces
- 4 Analytical solutions
- 4.1 Separation of variables
- 4.2 Method of characteristics
- 4.3 Integral transform
- 4.4 Change of variables
- 4.5 Fundamental solution
- 4.6 Superposition principle
- 4.7 Methods for non-linear equations
- 4.8 Lie group method
- 4.9 Semianalytical methods
- 5 Numerical solutions
- 5.1 Finite element method
- 5.2 Finite difference method
- 5.3 Finite volume method
- 6 See also



![Matplotlib入门[05]——注释与标签](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/72b8144eed174762bc6d6d8cbf9a846b.png)