文章目录
- 一【题目类别】
- 二【题目难度】
- 三【题目编号】
- 四【题目描述】
- 五【题目示例】
- 六【题目提示】
- 七【解题思路】
- 八【时间频度】
- 九【代码实现】
- 十【提交结果】
一【题目类别】
- 栈
二【题目难度】
- 简单
三【题目编号】
- 1475.商品折扣后的最终价格
四【题目描述】
- 给你一个数组 prices ,其中 prices[i] 是商店里第 i 件商品的价格。
- 商店里正在进行促销活动,如果你要买第 i 件商品,那么你可以得到与 prices[j] 相等的折扣,其中 j 是满足 j > i 且 prices[j] <= prices[i] 的 最小下标 ,如果没有满足条件的 j ,你将没有任何折扣。
- 请你返回一个数组,数组中第 i 个元素是折扣后你购买商品 i 最终需要支付的价格。
五【题目示例】
-
示例 1:
- 输入:prices = [8,4,6,2,3]
- 输出:[4,2,4,2,3]
- 解释:
- 商品 0 的价格为 price[0]=8 ,你将得到 prices[1]=4 的折扣,所以最终价格为 8 - 4 = 4 。
- 商品 1 的价格为 price[1]=4 ,你将得到 prices[3]=2 的折扣,所以最终价格为 4 - 2 = 2 。
- 商品 2 的价格为 price[2]=6 ,你将得到 prices[3]=2 的折扣,所以最终价格为 6 - 2 = 4 。
- 商品 3 和 4 都没有折扣。
-
示例 2:
- 输入:prices = [1,2,3,4,5]
- 输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
- 解释:在这个例子中,所有商品都没有折扣。
-
示例 3:
- 输入:prices = [10,1,1,6]
- 输出:[9,0,1,6]
六【题目提示】
- 1 < = p r i c e s . l e n g t h < = 500 1 <= prices.length <= 500 1<=prices.length<=500
- 1 < = p r i c e s [ i ] < = 1 0 3 1 <= prices[i] <= 10^3 1<=prices[i]<=103
七【解题思路】
- 利用单调栈的思想
- 使用栈存储数组下标,如果栈空或者“某件商品”后面的价格都比它高,那么就把“这件商品”的数组下标入栈
- 如果栈不空,并且栈顶元素对应的“商品价格”大于或等于后面“某个商品”的价格,就说明“这件商品”有折扣,将计算后的折扣的价格保存到原数组中,并且将“这件商品”的数组下标弹出栈,说明已经找到折扣了
- 最后返回原数组即可
八【时间频度】
- 时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n), n n n为传入数组的长度
- 空间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n), n n n为传入数组的长度
九【代码实现】
- Java语言版
class Solution {
public int[] finalPrices(int[] prices) {
Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i = 0;i<prices.length;i++){
while(!stack.isEmpty() && prices[stack.peek()] >= prices[i]){
prices[stack.pop()] -= prices[i];
}
stack.push(i);
}
return prices;
}
}
- C语言版
int* finalPrices(int* prices, int pricesSize, int* returnSize)
{
int* stack = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * pricesSize);
int top = -1;
for(int i = 0;i<pricesSize;i++)
{
while(top != -1 && prices[stack[top]] >= prices[i])
{
prices[stack[top--]] -= prices[i];
}
stack[++top] = i;
}
*returnSize = pricesSize;
return prices;
}
- Python语言版
class Solution:
def finalPrices(self, prices: List[int]) -> List[int]:
stack = [0]
for i in range(0,len(prices)):
while len(stack) > 1 and prices[stack[-1]] >= prices[i]:
prices[stack.pop()] -= prices[i]
stack.append(i)
return prices
- C++语言版
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> finalPrices(vector<int>& prices) {
stack<int> st;
for(int i = 0;i<prices.size();i++){
while(!st.empty() && prices[st.top()] >= prices[i]){
int temp = st.top();
prices[temp] -= prices[i];
st.pop();
}
st.push(i);
}
return prices;
}
};
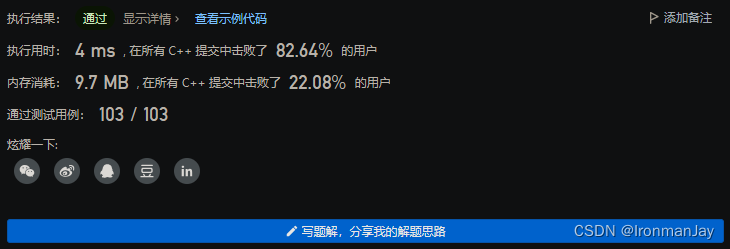
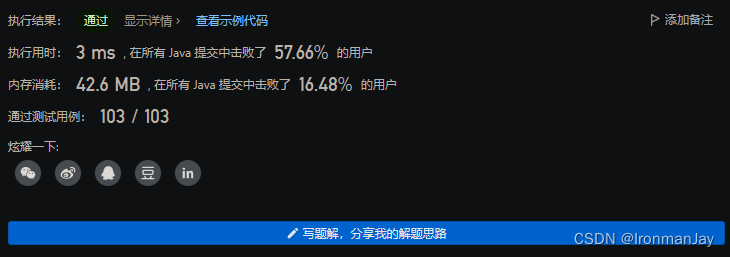
十【提交结果】
-
Java语言版
-
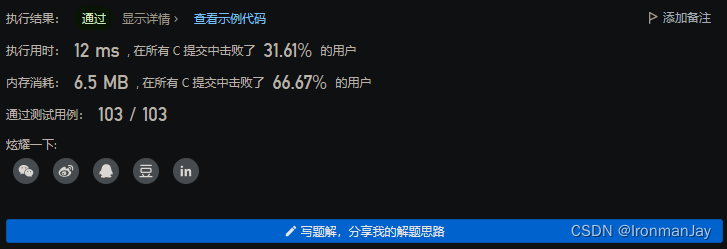
C语言版
-
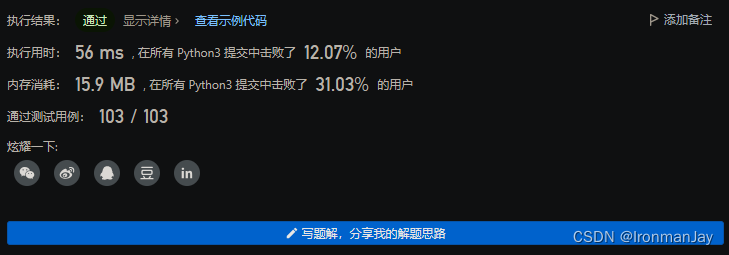
Python语言版
-
C++语言版