介绍
- ArrayList非线程安全。
- ArrayList基于动态数组,是一种线性表。随机访问友好,插入和删除效率低。
增删慢:每次删除元素,都需要改变数组长度、拷贝以及移动数组长度
查询快:由于数组在内存中是一块连续空间,因此可以根据地址+索引的方式快速获取对应位置上的元素。
存储的数据元素有序、可以重复
- 容量动态调节,有一套扩容和优化空间的机制(
基于数组存储数据的局限性:长度不可变,使用List替代数组)
ArrayList继承了AbstractList,实现了List、RandomAccess、Cloneable、Serializable接口。
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable

Serializable标记性接口
类的序列化需要实现java.io.Serializable接口,不实现此接口的类将不会使用任何状态序列化或反序列化。可序列化的所有子类都是可序列化的。序列化接口没有方法或字段,仅用于表示可串行化的语义
Cloneable标记性接口
一个类实现Cloneable接口并重写clone()方法,实现克隆
在未实现Cloneable接口的实例上调用对象的克隆方法会导致CloneNotSupportedException异常
RandomAccess标记性接口
RandomAccess接口是个空接口,作为一个标志使用,当一个类支持随机访问的时候(数组是很典型的),就可以标记这个接口。
AbstractList抽象类
ArrayList继承重写该类
常量&变量
//序列化的VersionUID
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L;
/**
* Default initial capacity.
* 默认初始容量 10,注意:调用无参构造函数时,初始容量为DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for empty instances.
* 指定初始容量为0时,返回该空数组
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We
* distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when
* first element is added.
* 不指定初始容量时,返回该空数组。
* 用于与EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA进行区分,在第一次添加元素时容量扩容为多少
*/
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any
* empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
* will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.
* 数组缓冲区 用于存储元素的容器,ArrayList的容量就是这个缓冲区的容量。
* 当elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA时,第一次添加元素后,扩容至默认容量10。
* 另外虽然这里用了transient修饰,但是其实现了readObject和writeObject,查看源码可知,是实现了序列化
*/
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
/**
* The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains).
* 元素个数,并不一定是容量
* @serial
*/
private int size;
/**
* The maximum size of array to allocate.
* Some VMs reserve some header words in an array.
* Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in
* OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit
* 最大容量,避免在某些虚拟机下可能引起的OutOfMemoryError,
* 减8的原因:数组作为一个对象,需要一定的内存存储对象头信息,对象头信息最大占用内存不可超过8字节
*/
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
构造方法
/**
* Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
* 根据给定的初始容量创建数组
* ①指定初始容量大于0时,创建初始容量大小的数组
* ②指定初始容量等于0时,创建一个空数组EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
* ③否则抛出异常IllegalArgumentException
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
//创建指定容量大小的数组
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
//创建一个空数组EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
* 在没有指定初始容量时,创建一个空数组DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
* 按照指定集合的迭代器返回元素的顺序,构造一个包含指定集合元素的list
* 构建一个Object[] 赋值给数组缓冲区
*/
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
if ((size = a.length) != 0) {
//传入的集合是ArrayList类型
if (c.getClass() == ArrayList.class) {
//直接将c的元素赋值给数组缓冲区
elementData = a;
} else {
//传入的集合不是ArrayList,Arrays.copyOf复制一个Object[] 赋值给数组缓冲区
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(a, size, Object[].class);
}
} else {
// replace with empty array.
//传入的集合长度为0,创建一个空数组
elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
内部类
Itr
Itr是ArrayList的普通内部类,实现了Iterator接口,通过ArrayList的itterator()方法得到的是Itr对象
作用:ArrayList实例对象的迭代器,用于元素的迭代遍历。
/**
* An optimized version of AbstractList.Itr
* ArrayList的内部类
*/
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
//光标 下一个要返回的元素的索引 默认值0
int cursor; // index of next element to return
//记录值 最后一个返回元素的索引,如果没有就是-1
int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such
//修改次数赋值给预期修改次数
int expectedModCount = modCount;
Itr() {}
//是否还有下一个元素
public boolean hasNext() {
//判断光标是否不等于集合的size
return cursor != size;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
//校验修改次数与预期修改次数是否一致
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
//判断光标是否合理
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
//当前容纳的所有元素
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
//再次进行下标判断,如果不一致则说明数组被修改过,就会抛出并发修改异常
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
//光标向后移动1,下个元素的下标
cursor = i + 1;
//取出下标对应的元素
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
/**
* 移除当前元素
*/
public void remove() {
//下标检查
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
//检查修改次数是否一致
checkForComodification();
try {
//调用ArrayList的remove方法, 该方法会修改操作值modCount
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
// 将下标为i的元素删除,后面的元素整体向前移动一位,i下标的元素为原来i+1下标的索引
//故删除下标为i的元素,下一个元素的索引变为i,而cursor此时已经为i+1
//数据修正
cursor = lastRet;
//防止连续删除
lastRet = -1;
//避免并发修改异常,同步操作值
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) {
Objects.requireNonNull(consumer);
final int size = ArrayList.this.size;
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size) {
return;
}
final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) {
consumer.accept((E) elementData[i++]);
}
// update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic
//
cursor = i;
lastRet = i - 1;
checkForComodification();
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
ListItr
ListItr是一个具有遍历集合属性的Itr类子类,同时也是Iterator接口实现类。
ListItr的成员变量信息都继承自了父类Itr类的成员变量,ListItr并未对Itr中的hasNext()方法、next()方法、remove()方法进行覆写。覆写了ListIterator接口中的hasPrevious()、nextIndex()和previousIndex()等方法。
/**
* An optimized version of AbstractList.ListItr
* AbstractList.ListItr的优化版
*/
private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E> {
/**
* 有参构造
* 由 listIterator(int index) 、 listIterator()方法创建
* @param index
*/
ListItr(int index) {
super();
cursor = index;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor - 1;
}
/**
* 真正可以取出元素的方法,与next()含义相反,为遍历上一个
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E previous() {
//判断当前数组是否发生修改
checkForComodification();
//游标cursor指向的上一个元素的索引
int i = cursor - 1;
//cursor为0的情况,即为遍历到了当前数组的第一个元素
if (i < 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
//检测集合是否被修改过。
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
//ArrayList类本身的set(int index, E element)方法对我们的元素进行修改
ArrayList.this.set(lastRet, e);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
try {
//插入的位置
int i = cursor;
//ArrayList本类的add(int index, E element)方法来进行插入操作
ArrayList.this.add(i, e);
cursor = i + 1;
//避免重复操作
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
SubList
继承了 AbstractList 类,并实现了 RandomAccess 接口,支持随机读取
SubList返回的视图是由父类集合支持的,因此是非结构化的,所以,对SubList子集合进行操作,也会修改父类的集合。SubList类中,每个public方法(除了subList()方法)都调用checkForComodification(),用于判断父类集合是否被修改。所以,如果直接使用父类方法修改集合,则SubList子类的遍历、增加、删除等操作都会抛出异常
private class SubList extends AbstractList<E> implements RandomAccess {
// 父类的引用
private final AbstractList<E> parent;
/*
* 父类集合中的位置,如果使用SubList中的subList方法,
* 则此时父类为SubList类,不是ArrayList
*/
private final int parentOffset;
// 子类List在父类 ArrayList 中的下标位置
private final int offset;
// 视图集合的size
int size;
/**
* 构造方法,参数offset表示父类集合的下标偏移量
* @param parent
* @param offset
* @param fromIndex
* @param toIndex
*/
SubList(AbstractList<E> parent,
int offset, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
this.parent = parent;
this.parentOffset = fromIndex;
this.offset = offset + fromIndex;
this.size = toIndex - fromIndex;
this.modCount = ArrayList.this.modCount;
}
public E set(int index, E e) {
// 检查下标是否越界
rangeCheck(index);
// 检查是否有其他线程修改了父类集合
checkForComodification();
//获取该索引的旧值
E oldValue = ArrayList.this.elementData(offset + index);
// 调用父类方法替换元素,所以本质上还是在父类集合中替换元素
ArrayList.this.elementData[offset + index] = e;
return oldValue;
}
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
checkForComodification();
// 调用父类方法获取元素
return ArrayList.this.elementData(offset + index);
}
public int size() {
checkForComodification();
return this.size;
}
public void add(int index, E e) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
checkForComodification();
// 使用父类方法添加元素,
parent.add(parentOffset + index, e);
// 父类add()方法修改了modCount的值,更新subList的modCount值
this.modCount = parent.modCount;
this.size++;
}
/**
* 根据下标移除元素
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return
*/
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
checkForComodification();
E result = parent.remove(parentOffset + index);
this.modCount = parent.modCount;
this.size--;
return result;
}
/**
* 移除指定区间的元素
* @param fromIndex index of first element to be removed
* @param toIndex index after last element to be removed
*/
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
checkForComodification();
parent.removeRange(parentOffset + fromIndex,
parentOffset + toIndex);
this.modCount = parent.modCount;
this.size -= toIndex - fromIndex;
}
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(this.size, c);
}
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
int cSize = c.size();
if (cSize==0)
return false;
checkForComodification();
parent.addAll(parentOffset + index, c);
this.modCount = parent.modCount;
this.size += cSize;
return true;
}
/**
* subList 中迭代器使用ListIterator()
* @return
*/
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return listIterator();
}
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(final int index) {
checkForComodification();
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
final int offset = this.offset;
return new ListIterator<E>() {
int cursor = index;
int lastRet = -1;
int expectedModCount = ArrayList.this.modCount;
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != SubList.this.size;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= SubList.this.size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (offset + i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[offset + (lastRet = i)];
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor - 1;
if (i < 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (offset + i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i;
return (E) elementData[offset + (lastRet = i)];
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) {
Objects.requireNonNull(consumer);
final int size = SubList.this.size;
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size) {
return;
}
final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (offset + i >= elementData.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) {
consumer.accept((E) elementData[offset + (i++)]);
}
// update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic
lastRet = cursor = i;
checkForComodification();
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor - 1;
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
SubList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = ArrayList.this.modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.set(offset + lastRet, e);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
SubList.this.add(i, e);
cursor = i + 1;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = ArrayList.this.modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (expectedModCount != ArrayList.this.modCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
};
}
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size);
return new SubList(this, offset, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > this.size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+this.size;
}
/**
* 检查是否有多线程修改集合
*/
private void checkForComodification() {
if (ArrayList.this.modCount != this.modCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
checkForComodification();
return new ArrayListSpliterator<E>(ArrayList.this, offset,
offset + this.size, this.modCount);
}
}
ArrayListSpliterator
ArrayList可分割的迭代器,基于二分法的可分割迭代器,是为了并行遍历元素而设计的一种迭代器,jdk1.8 中的集合框架中的数据结构都默认实现了 spliterator。
/** Index-based split-by-two, lazily initialized Spliterator */
//基于索引的、二分的、懒加载的分割器
static final class ArrayListSpliterator<E> implements Spliterator<E> {
/*
* If ArrayLists were immutable, or structurally immutable (no
* adds, removes, etc), we could implement their spliterators
* with Arrays.spliterator. Instead we detect as much
* interference during traversal as practical without
* sacrificing much performance. We rely primarily on
* modCounts. These are not guaranteed to detect concurrency
* violations, and are sometimes overly conservative about
* within-thread interference, but detect enough problems to
* be worthwhile in practice. To carry this out, we (1) lazily
* initialize fence and expectedModCount until the latest
* point that we need to commit to the state we are checking
* against; thus improving precision. (This doesn't apply to
* SubLists, that create spliterators with current non-lazy
* values). (2) We perform only a single
* ConcurrentModificationException check at the end of forEach
* (the most performance-sensitive method). When using forEach
* (as opposed to iterators), we can normally only detect
* interference after actions, not before. Further
* CME-triggering checks apply to all other possible
* violations of assumptions for example null or too-small
* elementData array given its size(), that could only have
* occurred due to interference. This allows the inner loop
* of forEach to run without any further checks, and
* simplifies lambda-resolution. While this does entail a
* number of checks, note that in the common case of
* list.stream().forEach(a), no checks or other computation
* occur anywhere other than inside forEach itself. The other
* less-often-used methods cannot take advantage of most of
* these streamlinings.
*/
//用于存放ArrayList对象
private final ArrayList<E> list;
//起始位置(包含),advance/split操作时会修改
private int index; // current index, modified on advance/split
//结束位置(不包含),-1 表示到最后一个元素
private int fence; // -1 until used; then one past last index
//用于存放list的modCount,当fence被设值后初始化
private int expectedModCount; // initialized when fence set
/** Create new spliterator covering the given range */
/**
* 创建一个范围性的分割器
* @param list
* @param origin
* @param fence
* @param expectedModCount
*/
ArrayListSpliterator(ArrayList<E> list, int origin, int fence,
int expectedModCount) {
this.list = list; // OK if null unless traversed
this.index = origin;
this.fence = fence;
this.expectedModCount = expectedModCount;
}
/**
* 在第一次使用时实例化结束位置
* @return
*/
private int getFence() { // initialize fence to size on first use
int hi; // (a specialized variant appears in method forEach)
ArrayList<E> lst;
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
if ((lst = list) == null)
hi = fence = 0;
else {
expectedModCount = lst.modCount;
hi = fence = lst.size;
}
}
return hi;
}
/**
* 分割list,返回一个新分割出的spliterator实例,相当于二分法,这个方法会递归
* 1.ArrayListSpliterator本质上还是对原list进行操作,只是通过index和fence来控制每次处理范围
* 2.ArrayListSpliterator在遍历元素时,不能对list进行结构变更操作,否则抛错。
* @return
*/
public ArrayListSpliterator<E> trySplit() {
int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
return (lo >= mid) ? null : // divide range in half unless too small
new ArrayListSpliterator<E>(list, lo, index = mid,
expectedModCount);
}
/**
* 返回true 时,只表示可能还有元素未处理
* 返回false 时,没有剩余元素需要处理
* @return
*/
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super E> action) {
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int hi = getFence(), i = index;
if (i < hi) {
index = i + 1;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E)list.elementData[i];
action.accept(e);
if (list.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 顺序遍历处理所有剩下的元素
*/
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
int i, hi, mc; // hoist accesses and checks from loop
ArrayList<E> lst; Object[] a;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if ((lst = list) != null && (a = lst.elementData) != null) {
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
mc = lst.modCount;
hi = lst.size;
}
else
mc = expectedModCount;
if ((i = index) >= 0 && (index = hi) <= a.length) {
for (; i < hi; ++i) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) a[i];
action.accept(e);
}
if (lst.modCount == mc)
return;
}
}
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
//估算大小
public long estimateSize() {
return (long) (getFence() - index);
}
//获取特征值
public int characteristics() {
return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED;
}
}
添加
boolean add(E e)
将指定的元素追加到此列表的末尾

/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*
* add添加 添加到最后。O(1)
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
//是否触发扩容
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
//将元素存放在size索引下,size值后自增1
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
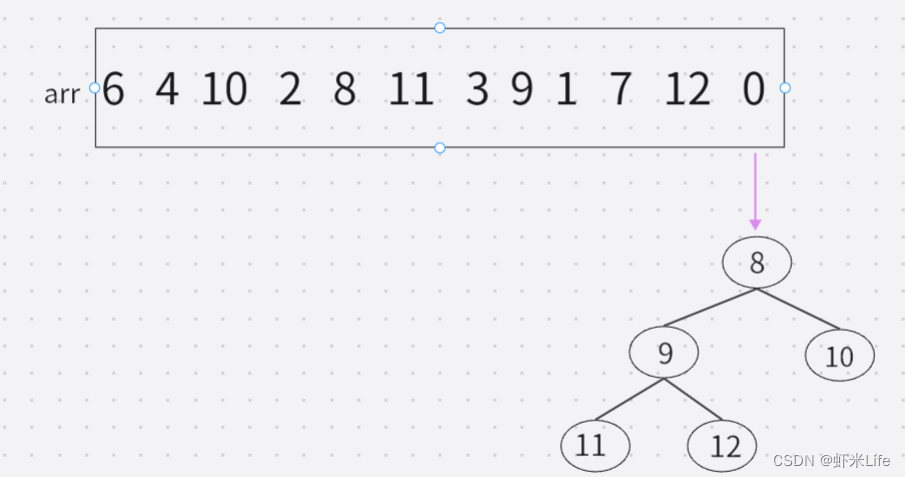
void add(int index, E element)
在此列表中的指定位置插入指定的元素
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this
* list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and
* any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* 添加到指定位置,后面依次后移。O(n)
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
//数组拷贝
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
//将元素赋值到指定索引位置
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
1.ensureCapacityInternal
确保容量,set后的容量是否超过上限,超过则进行扩容

private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
//calculateCapacity返回set后当前要存储元素的个数
//ensureExplicitCapacity set后的要存储元素的个数和容量上限比较,是否触发扩容
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
1.1calculateCapacity
当创建ArrayList时没有设置数组长度,会创建一个空数组,等到第一次add时,才会设置数组长度为10. 此时数组存储元素的个数为max(10,minCapacity)
否则直接返回minCapacity
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {
//如果创建ArrayList没有指定容量大小,max取较大值max(10,minCapacity),否则返回minCapacity
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
return minCapacity;
}
1.2ensureExplicitCapacity
//确保容量的方法 超过当前容量上限则进行扩容
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
//用于fail-fast机制,用于在并发场景下
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code 防溢出,超出容量则扩容
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
//扩容方法
grow(minCapacity);
}
1.2.1grow
扩容为原来容量的1.5倍
如果扩容后的容量依然小于要存储的个数,则数组的容量就设置为要存储的个数
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
* 私有扩容方法,确保minCapacity个数元素的存储
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
//扩容前的容量
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
//扩容后的容量 为扩容前的1.5倍
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
//如果扩容后的容量 依然小于要存储的个数,则数组的容量就等于存储的个数
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
//如果扩容后的容量超出了最大数组的长度 则取integer的最大值
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
1.2.1.1hugeCapacity
//私有 大容量分配,最大分配Integer.MAX_VALUE,最小分配MAX_ARRAY_SIZE
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
2rangeCheckForAdd
/**
* A version of rangeCheck used by add and addAll.
* 传入索引进行条件判断越界
*/
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index > size || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)
按指定集合的iterator返回的顺序将指定集合中的所有元素追加到此列表的末尾

/**
* Appends all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of
* this list, in the order that they are returned by the
* specified collection's Iterator. The behavior of this operation is
* undefined if the specified collection is modified while the operation
* is in progress. (This implies that the behavior of this call is
* undefined if the specified collection is this list, and this
* list is nonempty.)
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
* 将传入集合的所有元素添加到列表末尾
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount
//将a数组拷贝到elementData里
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew);
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
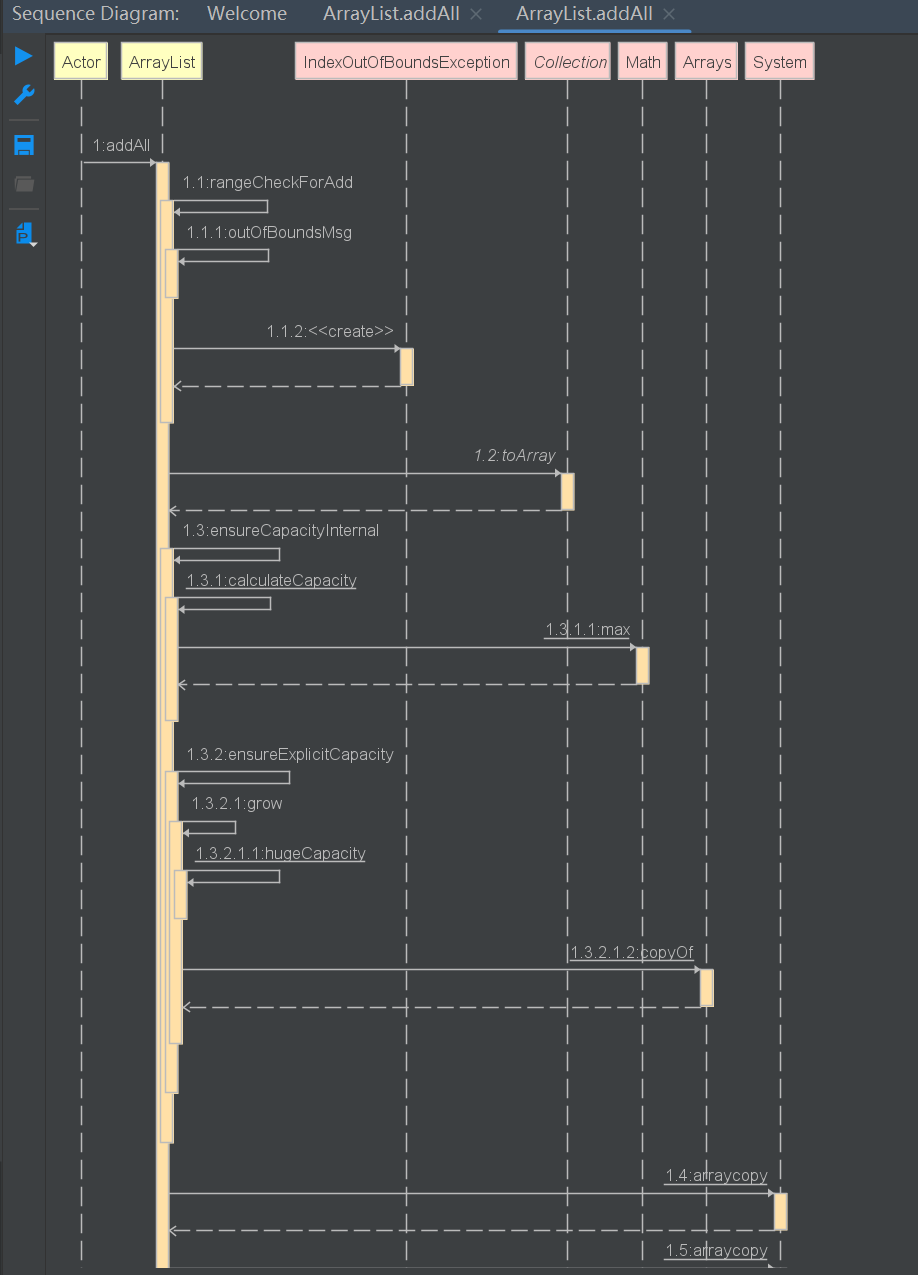
boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c)
将指定集合中的所有元素插入到此列表中,从指定的位置开始
/**
* Inserts all of the elements in the specified collection into this
* list, starting at the specified position. Shifts the element
* currently at that position (if any) and any subsequent elements to
* the right (increases their indices). The new elements will appear
* in the list in the order that they are returned by the
* specified collection's iterator.
*
* @param index index at which to insert the first element from the
* specified collection
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
* 指定位置插入集合元素
*/
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount
//需要移动的个数 = 集合真实的长度-要存储的索引位置
int numMoved = size - index;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew,
numMoved);
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
删除
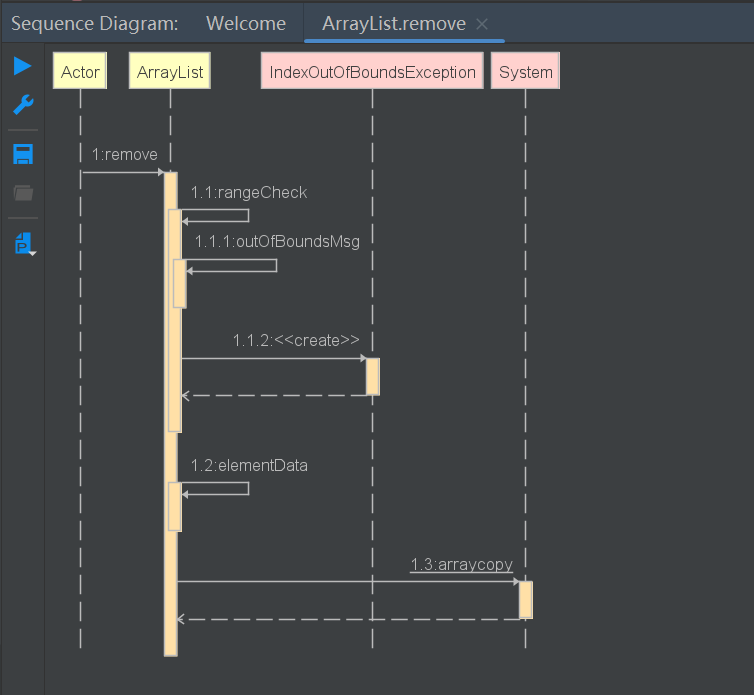
E remove(int index)
删除指定位置元素
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their
* indices).
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element that was removed from the list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* 删除指定位置元素并返回 O(n)
*/
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
//获得指定索引的元素
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
//说明该元素不是在数组最后的位置,进行数组的拷贝(将该元素后组成的数组统一前移一位)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
//数组元素个数减1,将数组最后位置置空 让gc进行回收
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
//返回旧值
return oldValue;
}
boolean remove(Object o)
删除指定元素
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list,
* if it is present. If the list does not contain the element, it is
* unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index
* <tt>i</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>
* (if such an element exists). Returns <tt>true</tt> if this list
* contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list
* changed as a result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list contained the specified element
* 删除给定obj
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
//传入null
if (o == null) {
//遍历
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
//找到第一个元素为null所在的索引
if (elementData[index] == null) {
//删除元素
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
//找到第一个元素为o所在的索引
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
//删除元素
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void fastRemove(int index)
就是remove(int index)中删除元素的逻辑
/*
* Private remove method that skips bounds checking and does not
* return the value removed.
* 私有删除方法,不进行边界检查,不返回被删除元素
*/
private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
}
void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
删除指定范围的元素
/**
* Removes from this list all of the elements whose index is between
* {@code fromIndex}, inclusive, and {@code toIndex}, exclusive.
* Shifts any succeeding elements to the left (reduces their index).
* This call shortens the list by {@code (toIndex - fromIndex)} elements.
* (If {@code toIndex==fromIndex}, this operation has no effect.)
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if {@code fromIndex} or
* {@code toIndex} is out of range
* ({@code fromIndex < 0 ||
* fromIndex >= size() ||
* toIndex > size() ||
* toIndex < fromIndex})
* 删除[fromIndex,toIndex)的元素
*/
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - toIndex;
System.arraycopy(elementData, toIndex, elementData, fromIndex,
numMoved);
// clear to let GC do its work
//删除后新的元素个数
int newSize = size - (toIndex-fromIndex);
//删除元素
for (int i = newSize; i < size; i++) {
elementData[i] = null;
}
//更新元素个数
size = newSize;
}
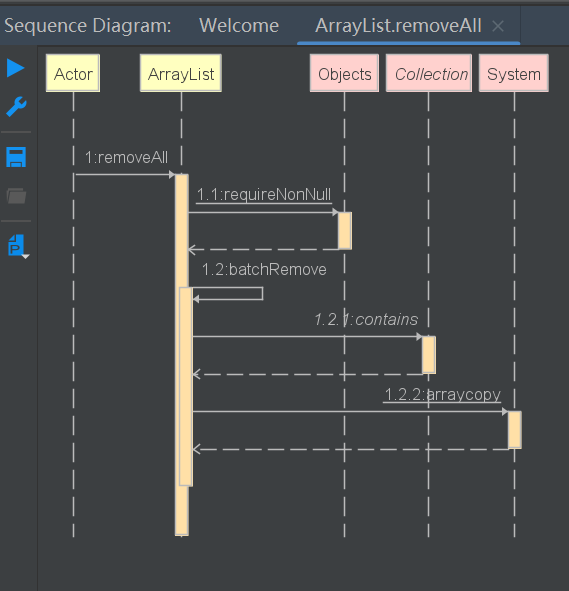
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c)
移除集合中的元素
/**
* Removes from this list all of its elements that are contained in the
* specified collection.
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be removed from this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of an element of this list
* is incompatible with the specified collection
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if this list contains a null element and the
* specified collection does not permit null elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>),
* or if the specified collection is null
* @see Collection#contains(Object)
* 移除c集合中的所有元素
*/
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
//null值判断
Objects.requireNonNull(c);
return batchRemove(c, false);
}
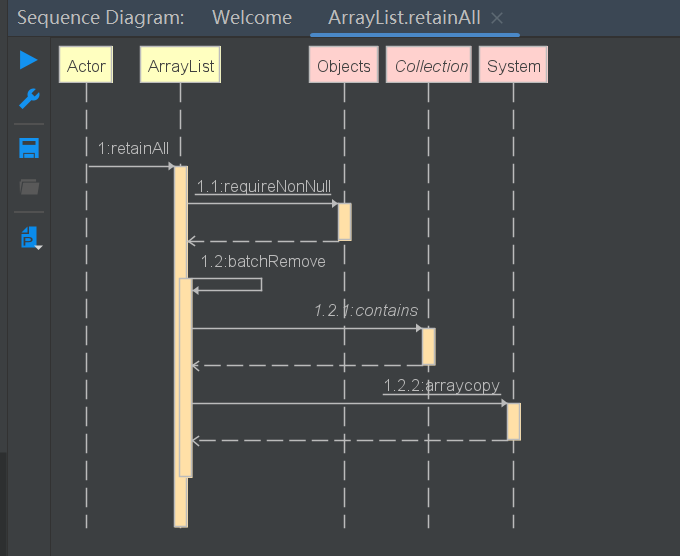
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c)
保留集合中的元素
/**
* Retains only the elements in this list that are contained in the
* specified collection. In other words, removes from this list all
* of its elements that are not contained in the specified collection.
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be retained in this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of an element of this list
* is incompatible with the specified collection
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if this list contains a null element and the
* specified collection does not permit null elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>),
* or if the specified collection is null
* @see Collection#contains(Object)
* 保留c集合中的元素
*/
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {
Objects.requireNonNull(c);
return batchRemove(c, true);
}
boolean batchRemove(Collection c, boolean complement)
removeAll方法和retainAll方法都调用了batchRemove方法,区别就在于参数complement
如果为true只保留c集合中元素,如果false,移除c集合中的元素
以removeAll为例,当complement为false
/**
* 批量移除。O(n)
* @param c
* @param complement 如果为true只保留c集合中元素,如果false,移除c集合中的元素
* @return
*/
private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) {
final Object[] elementData = this.elementData;
//两个指针,r是读取位置,w是写入位置
int r = 0, w = 0;
boolean modified = false;
try {
for (; r < size; r++)
//遍历数组,当c中不存在该元素时,边判定边写入元素
if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement)
//elementData[r] 遍历的元素
//elementData[w++] 写入的元素 写入后指针+1
elementData[w++] = elementData[r];
} finally {
// Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection,
// even if c.contains() throws.
//如果读的元素个数 不等于 数组的个数 说明在操作中抛出了异常,出错后保证数据的完整性
if (r != size) {
//数组拷贝 从出错的位置开始,将后面所有元素拷贝到写入元素的后面
System.arraycopy(elementData, r,
elementData, w,
size - r);
//写入的个数 = 真正写入的个数 + 移动元素的个数
w += size - r;
}
//说明写入的个数小于元素的个数,有元素需要删除
if (w != size) {
// clear to let GC do its work
//此时索引w 至 size-1的元素都是要删除的
for (int i = w; i < size; i++)
elementData[i] = null;
modCount += size - w;
//元素的个数为w
size = w;
//修改成功
modified = true;
}
}
return modified;
}
边遍历边赋值
比如原数组:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9;参数数组:a b c 3 5 8 d
| 循环次数 | r | w | if值 | elementData[w++] = elementData[r] | 原数组值 | 替换值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | true | elementData[0] = elementData[0] | 123456789 | 123456789 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | true | elementData[1] = elementData[1] | 123456789 | 123456789 |
| 3 | 2 | 2 | flase | |||
| 4 | 3 | 2 | true | elementData[2] = elementData[3] | 123456789 | 124456789 |
| 5 | 4 | 3 | flase | |||
| 6 | 5 | 3 | ture | elementData[3] = elementData[5] | 124456789 | 124656789 |
| 7 | 6 | 4 | true | elementData[4] = elementData[6] | 124656789 | 124676789 |
| 8 | 7 | 5 | flase | |||
| 9 | 8 | 5 | true | elementData[5] = elementData[8] | 124676789 | 124679789 |
w为5,将数组索引6,7,8元素删除,即将7,8,9删除
原数组变为1 2 4 6 7 9
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Object> src = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9));
ArrayList<Object> c = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c", 3, 5, 8, "d"));
System.out.println(src.removeAll(c));
System.out.println(src);
}
输出结果

void clear()
清空数组
/**
* Removes all of the elements from this list. The list will
* be empty after this call returns.
* 清空list,释放空间 O(n)
*/
public void clear() {
modCount++;
// clear to let GC do its work
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
elementData[i] = null;
size = 0;
}
查找
E get(int index)
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* 获取指定位置元素
*/
public E get(int index) {
//检查索引是否在条件范围内
rangeCheck(index);
//返回该索引对应的元素
return elementData(index);
}
int indexOf(Object o)
顺序查找,返回obj所在下标
/**
* Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the lowest index <tt>i</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>,
* or -1 if there is no such index.
* 顺序查找,返回首先出现的位置,找不到返-1。O(n)
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
//ArrayList可以存储null 查询的元素为null的情况
if (o == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
//不为null的情况
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
int lastIndexOf(Object o)
逆序查找,返回obj所在下标
/**
* Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the highest index <tt>i</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>,
* or -1 if there is no such index.
* 逆序查找,返回最后出现的位置,找不到返-1。O(n)
*/
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
boolean contains(Object o)
判断集合是否包含指定元素
/**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this list contains the specified element.
* More formally, returns <tt>true</tt> if and only if this list contains
* at least one element <tt>e</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e))</tt>.
*
* @param o element whose presence in this list is to be tested
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list contains the specified element
* 顺序查找实现,根据返回值判断集合是否包含元素o
*/
public boolean contains(Object o) {
//indexOf(o) >= 0 表示查找到了存储的o元素
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
}
修改
E set(int index, E element)
/**
* Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with
* the specified element.
*
* @param index index of the element to replace
* @param element element to be stored at the specified position
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* 修改指定位置元素
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
//赋值
elementData[index] = element;
//返回旧值
return oldValue;
}
迭代器
Iterator iterator()
创建一个Iterator的子类Itr
/**
* Returns an iterator over the elements in this list in proper sequence.
*
* <p>The returned iterator is <a href="#fail-fast"><i>fail-fast</i></a>.
*
* @return an iterator over the elements in this list in proper sequence
*/
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
//内部类Itr
return new Itr();
}
其他
List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
返回SubList类型的子集合
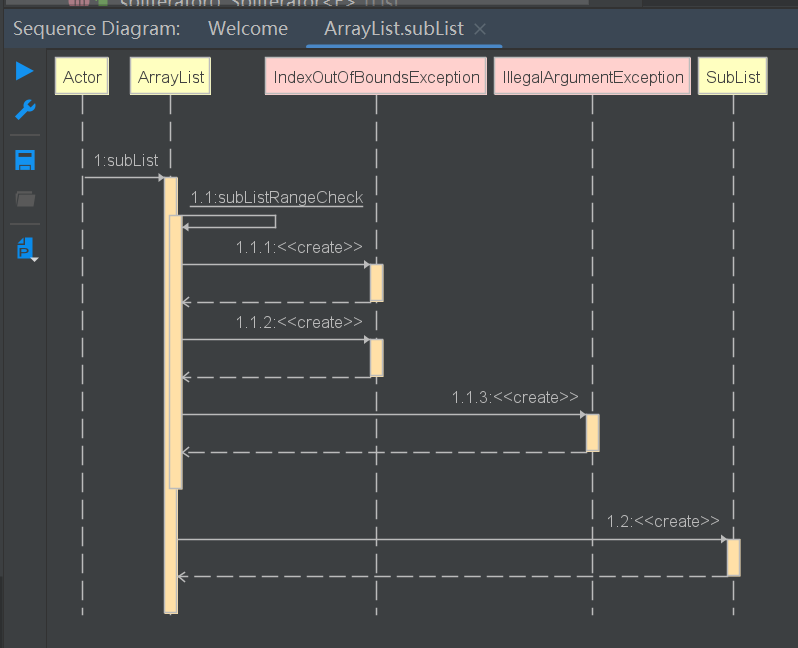
/**
* Returns a view of the portion of this list between the specified
* {@code fromIndex}, inclusive, and {@code toIndex}, exclusive. (If
* {@code fromIndex} and {@code toIndex} are equal, the returned list is
* empty.) The returned list is backed by this list, so non-structural
* changes in the returned list are reflected in this list, and vice-versa.
* The returned list supports all of the optional list operations.
*
* <p>This method eliminates the need for explicit range operations (of
* the sort that commonly exist for arrays). Any operation that expects
* a list can be used as a range operation by passing a subList view
* instead of a whole list. For example, the following idiom
* removes a range of elements from a list:
* <pre>
* list.subList(from, to).clear();
* </pre>
* Similar idioms may be constructed for {@link #indexOf(Object)} and
* {@link #lastIndexOf(Object)}, and all of the algorithms in the
* {@link Collections} class can be applied to a subList.
*
* <p>The semantics of the list returned by this method become undefined if
* the backing list (i.e., this list) is <i>structurally modified</i> in
* any way other than via the returned list. (Structural modifications are
* those that change the size of this list, or otherwise perturb it in such
* a fashion that iterations in progress may yield incorrect results.)
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
* 取子list,返回Sublist这个ArrayList的内部类,
* 这是个坑,注意SubList和其他List实现类的区别
*/
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size);
return new SubList(this, 0, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
/**
* 越界判断
* @param fromIndex
* @param toIndex
* @param size
*/
static void subListRangeCheck(int fromIndex, int toIndex, int size) {
if (fromIndex < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("fromIndex = " + fromIndex);
if (toIndex > size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("toIndex = " + toIndex);
if (fromIndex > toIndex)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromIndex(" + fromIndex +
") > toIndex(" + toIndex + ")");
}
void sort(Comparator<? super E> c)
/**
* 传入Compartor,用Arrays.sort()实现,主要是LegacyMergeSort和Timsort
* @param c the {@code Comparator} used to compare list elements.
* A {@code null} value indicates that the elements'
* {@linkplain Comparable natural ordering} should be used
*/
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
//实现排序的方法
Arrays.sort((E[]) elementData, 0, size, c);
//排序完,再次判断,防止并发修改
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
modCount++;
}
boolean isEmpty()
判断集合是否为空
/**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this list contains no elements.
*
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list contains no elements
* 判空,直接看size就行了
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
Object clone()
克隆拷贝
/**
* Returns a shallow copy of this <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance. (The
* elements themselves are not copied.)
*
* @return a clone of this <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance
* 克隆,主要拷贝elementData数组 ArrayLis的clone方法返回类型为ArrayList的类型
*/
public Object clone() {
try {
//调用父类Object的clone方法,强转为ArrayList
ArrayList<?> v = (ArrayList<?>) super.clone();
//将原集合的元素赋值给新的集合,指定新集合的长度
v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
//重置修改次数
v.modCount = 0;
return v;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable
throw new InternalError(e);
}
}
void trimToSize()
/**
* Trims the capacity of this <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance to be the
* list's current size. An application can use this operation to minimize
* the storage of an <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance.
* 拷贝到新数组中,释放多余空间
*/
public void trimToSize() {
modCount++;
//存储元素小于数组的长度
if (size < elementData.length) {
elementData = (size == 0)
//空数组
? EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
//拷贝
: Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
}
}
String toString()
ArrayList本身是没有toString方法,调用其父类AbstractCollection的toString方法
AbstractCollection.java
AbstractCollection.java
/**
* Returns a string representation of this collection. The string
* representation consists of a list of the collection's elements in the
* order they are returned by its iterator, enclosed in square brackets
* (<tt>"[]"</tt>). Adjacent elements are separated by the characters
* <tt>", "</tt> (comma and space). Elements are converted to strings as
* by {@link String#valueOf(Object)}.
*
* @return a string representation of this collection
*/
public String toString() {
//获取迭代器
Iterator<E> it = iterator();
//判断迭代器是否有元素
if (! it.hasNext())
return "[]";
//字符串拼接
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append('[');
//无限循环
for (;;) {
E e = it.next();
sb.append(e == this ? "(this Collection)" : e);
//已经没有元素了,返回拼接的字符串
if (! it.hasNext())
return sb.append(']').toString();
sb.append(',').append(' ');
}
}
答疑
1 ArrayList频繁扩容导致添加性能急剧下降,该如何处理
ArrayList(int initialCapacity) 构造具有指定初始容量的空列表。可以根据业务场景创建一个适当初始容量的集合,避免了扩容的性能影响。