https://github.com/JintaoLee-Roger/cigsegy
一个读写 segy 格式地震数据的 python 和 c++ 工具。可以将 segy 格式文件读到内存或者直接转为二进制文件,也可以将一个 numpy 数据存储为segy格式的文件。
特点:
- 快,底层使用c++实现
- 可以在
python中使用,使用了pybind11将c++包装为python可调用的库 - 可以处理规则和不规则的地震数据,比如工区不是一个矩形(有缺失)或数据间隔不为1
- 可以使用已有的segy文件的道头进行创建新的segy文件
官方给的主要是在linux上的编译方式,在windows系统上没有详细说明。这里用visual studio 2019进行了编译,很容易就编译形成了静态库文件。其中用到了fmt格式化库
https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt
文件配置如下

通过下面代码对生成的cigsegy静态库进行了测试
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fmt/format.h>
#include "segy.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
std::cout << "Hello World!\n";
string filePath = R"(E:\test.sgy)";
segy::SegyIO segyIO(filePath);
fmt::print("texture header:n{}\n", segyIO.textual_header());
fmt::print("meta information:\n{}\n", segyIO.metaInfo());
return 0;
}
运行效果如下
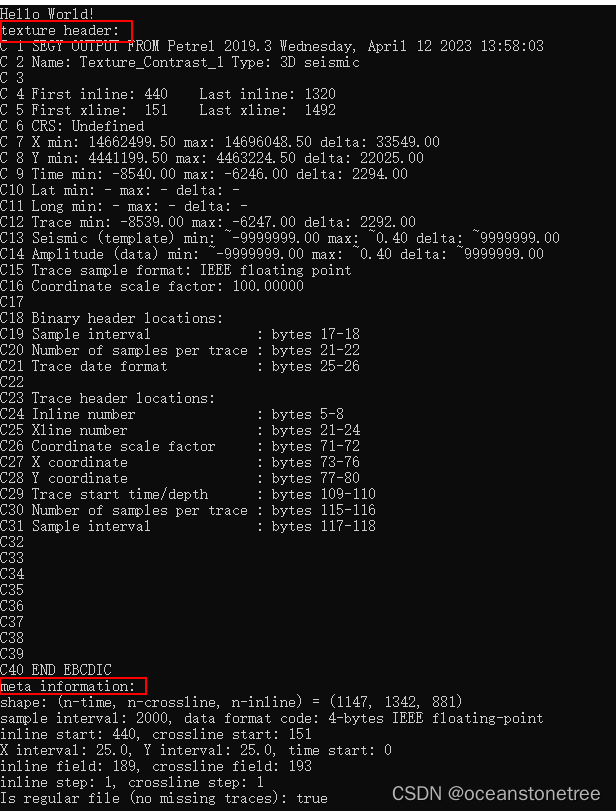
打印了seyg的文本头信息和线道号基本信息,下面列出了该库提供的其他主要接口
/*********************************************************************
** Copyright (c) 2022 Roger Lee.
** Computational and Interpretation Group (CIG),
** University of Science and Technology of China (USTC).
**
** @File: segy.h
** @Time: 2022/11/16 11:30:42
** @Version: 1.0
** @Description :
*********************************************************************/
#ifndef CIG_SEGY_H
#define CIG_SEGY_H
#include <stdexcept>
#include <vector>
// #include <omp.h>
#include "mio.hpp"
#include "utils.h"
namespace segy {
struct MetaInfo {
// count information
int32_t sizeX; // same as time
int32_t sizeY; // same as crossline
int32_t sizeZ; // same as inline
int64_t trace_count;
int16_t sample_interval; // dt
int16_t data_format; // 1 or 5
float Y_interval; // crossline interval
float Z_interval; // inline interval
int16_t start_time;
int16_t scalar;
int min_inline;
int max_inline;
int min_crossline;
int max_crossline;
bool isNormalSegy;
float fillNoValue;
// field information
int inline_field = kDefaultInlineField;
int crossline_field = kDefaultCrosslineField;
int X_field = kDefaultXField;
int Y_field = kDefaultYField;
int inline_step = 1;
int crossline_step = 1;
};
struct LineInfo {
int line_num;
uint64_t trace_start;
uint64_t trace_end;
int count;
};
struct TraceInfo {
int inline_num;
int crossline_num;
int X;
int Y;
};
class SegyIO {
public:
// read segy mode
explicit SegyIO(const std::string &segyname);
// create segy from memory
SegyIO(int sizeX, int sizeY, int sizeZ);
// create segy file from binary file
SegyIO(const std::string &binaryname, int sizeX, int sizeY, int sizeZ);
~SegyIO();
inline int shape(int dimension) {
if (dimension == 0) {
return m_metaInfo.sizeX;
} else if (dimension == 1) {
return m_metaInfo.sizeY;
} else if (dimension == 2) {
return m_metaInfo.sizeZ;
} else {
throw std::runtime_error("shape(dim), dim can be only {0, 1, 2}");
}
}
inline int64_t trace_count() { return m_metaInfo.trace_count; }
inline void set_size(int x, int y, int z) {
m_metaInfo.sizeX = x;
m_metaInfo.sizeY = y;
m_metaInfo.sizeZ = z;
if (isReadSegy) {
m_metaInfo.isNormalSegy = true;
isScan = true;
int64_t trace_count =
(m_source.size() - kTextualHeaderSize - kBinaryHeaderSize) /
(kTraceHeaderSize + x * sizeof(float));
if ((int64_t)y * z != (trace_count)) {
throw std::runtime_error("invalid shape. inline * crossline != "
"total_trace_count");
}
}
}
void collect(float *data, int *header);
std::string textual_header();
std::string metaInfo();
inline std::vector<LineInfo> line_info() { return m_lineInfo; }
inline MetaInfo get_metaInfo() { return m_metaInfo; }
void setInlineLocation(int loc);
void setCrosslineLocation(int loc);
void setXLocation(int loc);
void setYLocation(int loc);
void setInlineStep(int step);
void setCrosslineStep(int step);
void setSteps(int istep, int xstep);
// read segy
void setFillNoValue(float noValue);
void scan();
void tofile(const std::string &binary_out_name);
void read(float *dst, int startX, int endX, int startY, int endY, int startZ,
int endZ);
void read(float *dst);
void read_inline_slice(float *dst, int iZ);
void read_cross_slice(float *dst, int iY);
void read_time_slice(float *dst, int iX);
void read_trace(float *dst, int iY, int iZ);
// binary header & trace header
void get_TraceInfo(int n, int *traceinfo);
// create segy
void setSampleInterval(int interval);
void setDataFormatCode(int fdormat);
void setStartTime(int start_time);
void setXInterval(float dz);
void setYInterval(float dy);
void setMinInline(int in);
void setMinCrossline(int cross);
void create(const std::string &segy_out_name, const float *src);
void create(const std::string &segy_out_name);
void close_file();
private:
bool isReadSegy{};
bool isScan = false;
mio::mmap_source m_source;
mio::mmap_sink m_sink;
std::vector<LineInfo> m_lineInfo;
MetaInfo m_metaInfo;
void scanBinaryHeader();
void initMetaInfo();
void initTraceHeader(TraceHeader *trace_header);
void write_textual_header(char *dst, const std::string &segy_out_name);
void write_binary_header(char *dst);
void write_trace_header(char *dst, TraceHeader *trace_header, int32_t iY,
int32_t iZ, int32_t x, int32_t y);
inline void _get_TraceInfo(uint64_t n, TraceInfo &tmetaInfo) {
const char *field =
m_source.data() + kTextualHeaderSize + kBinaryHeaderSize +
n * (kTraceHeaderSize + m_metaInfo.sizeX * sizeof(float));
tmetaInfo.inline_num =
swap_endian(*(int32_t *)(field + m_metaInfo.inline_field - 1));
tmetaInfo.crossline_num =
swap_endian(*(int32_t *)(field + m_metaInfo.crossline_field - 1));
tmetaInfo.X = swap_endian(*(int32_t *)(field + m_metaInfo.X_field - 1));
tmetaInfo.Y = swap_endian(*(int32_t *)(field + m_metaInfo.Y_field - 1));
}
};
void read_ignore_header(const std::string &segy_name, float *dst, int sizeX,
int sizeY, int sizeZ, int format = 5);
void tofile_ignore_header(const std::string &segy_name,
const std::string &out_name, int sizeX, int sizeY,
int sizeZ, int format = 5);
void tofile(const std::string &segy_name, const std::string &out_name,
int iline = kDefaultInlineField, int xline = kDefaultCrosslineField,
int istep = 1, int xstep = 1);
void read(const std::string &segy_name, float *dst,
int iline = kDefaultInlineField, int xline = kDefaultCrosslineField,
int istep = 1, int xstep = 1);
void create_by_sharing_header(const std::string &segy_name,
const std::string &header_segy, const float *src,
int sizeX, int sizeY, int sizeZ, int iline = 189,
int xline = 193, int istep = 1, int xstep = 1);
void create_by_sharing_header(const std::string &segy_name,
const std::string &header_segy,
const std::string &src_file, int sizeX, int sizeY,
int sizeZ, int iline = 189, int xline = 193,
int istep = 1, int xstep = 1);
} // namespace segy
#endif