列表
- 1. 列表的介绍
- 1.1 访问列表元素
- 1.2 索引从0而不是1开始
- 1.3 使用列表中的各个值
- 1.4 修改、添加和删除元素
- 1.4.1 修改列表元素
- 1.5 在列表中添加元素
- 1.5.1 在列表末尾添加元素
- 1.5.2 在列表中插入元素
- 1.6 从列表中删除元素
- 1.6.1 使用方法pop()删除元素
- 1.6.2 弹出列表中任何位置处的元素
- 1.6.3 根据值删除元素
- 2. 组织列表
- 2.1 使用方法sort()对列表进行永久性排序
- 2.2 使用函数sorted()对列表进行临时排序
- 2.3 倒着打印列表
- 2.4 确定列表的长度
列表由一系列按特定顺序排列的元素组成。也可以将任何东西加入列表中,其中的元素之间可以没有任何关系。鉴于列表通常包含多个元素,建议给列表指定一个表示复数的名称。
在python中,用[]来表示列表,并用逗号来分隔其中的元素。、
1. 列表的介绍
1.1 访问列表元素
列表是有序集合,要访问列表元素,可指出列表的名称,在指出列表的索引,并将其放在方括号中。
还可以对任何列表元素嗲用字符串方法。
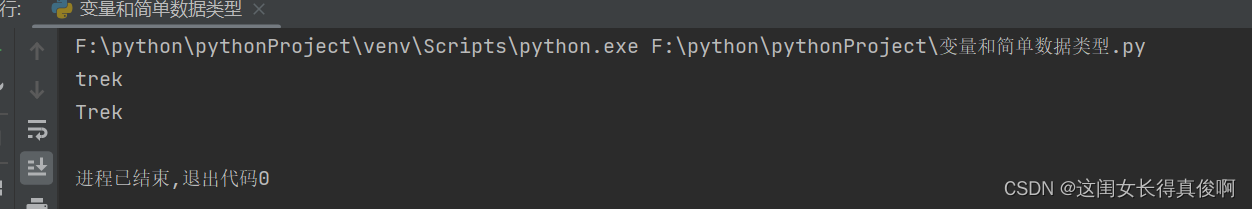
bicycles = ['trek', 'cannondale', 'redline', 'specialized']
print(bicycles[0])
print(bicycles[0].title())
1.2 索引从0而不是1开始
在python中,第一个列表元素的索引为0,而不是1.
python为访问最后一个列表元素提供了一种特殊语法。通过将索引指定为-1,可让python返回最后一个列表元素。
这种约定也适用于其他负数索引,例如,索引-2返回倒数第二个个列表元素,索引-3返回倒数第三个列表元素,以此类推。
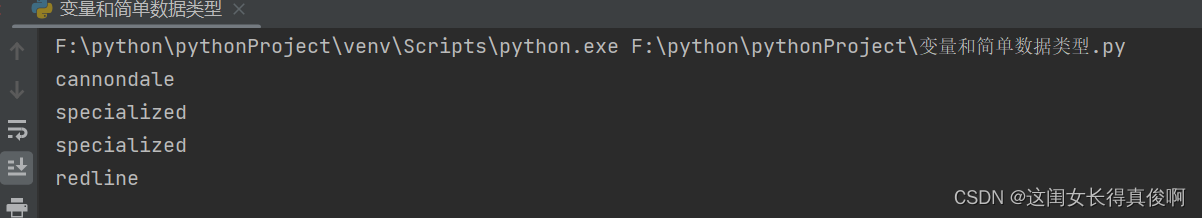
bycycles = ['trek', 'cannondale', 'redline', 'specialized']
print(bycycles[1])
print(bycycles[3])
print(bycycles[-1])
print(bycycles[-2])
1.3 使用列表中的各个值
可以向使用其他变量一样使用列表中的各个值
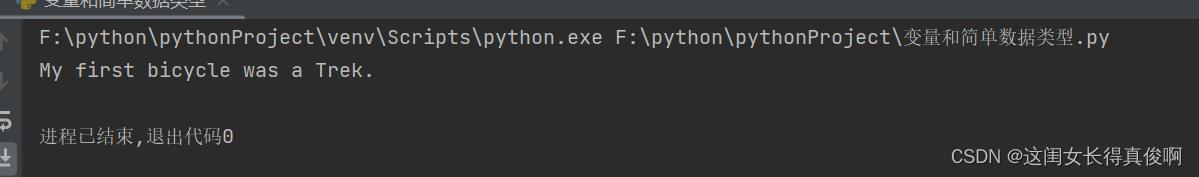
bycycles = ['trek', 'cannondale', 'redline', 'specialized']
message = "My first bicycle was a " + bycycles[0].title() + "."
print(message)
1.4 修改、添加和删除元素
创建的大多数列表都将是动态的,这意味着列表创建后,将随着程序的运行增删元素。
1.4.1 修改列表元素
要修改列表元素,可指定列表名和要修改的元素的索引,再指定该元素的新值。
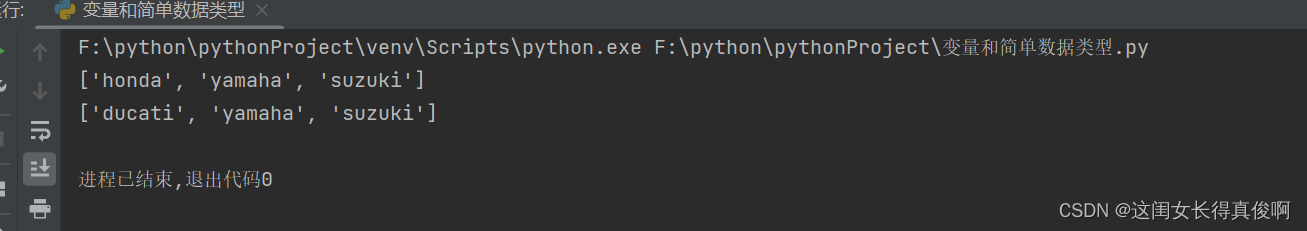
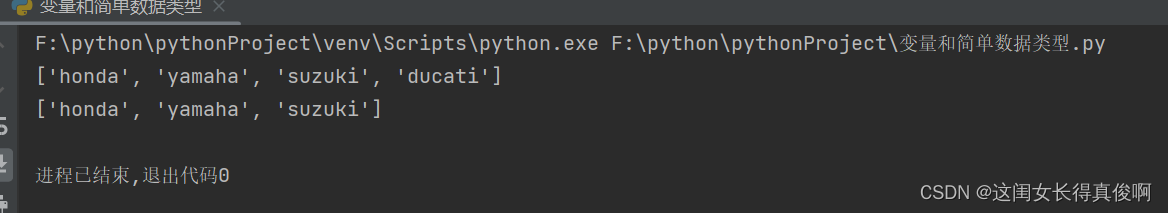
motorcycles = ['honda', 'yamaha', 'suzuki']
print(motorcycles)
motorcycles[0] = 'ducati'
print(motorcycles)
1.5 在列表中添加元素
1.5.1 在列表末尾添加元素
append()方法:可以给列表附加元素时,将新元素添加到列表末尾
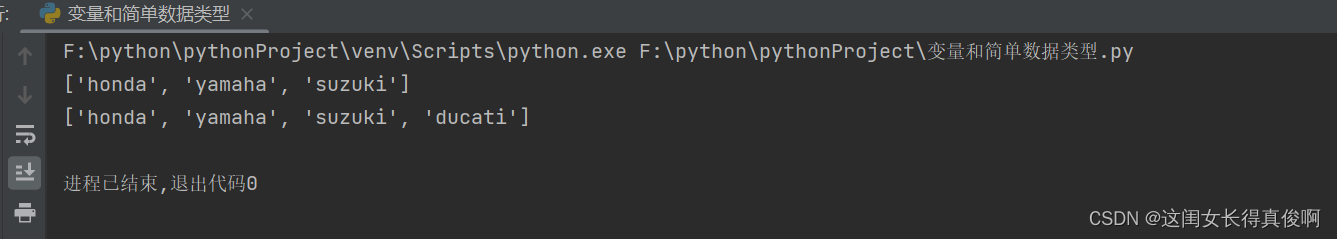
motorcycles = ['honda', 'yamaha', 'suzuki']
print(motorcycles)
motorcycles.append('ducati')
print(motorcycles)
这种创建列表的方式机及其常见,因为经常要等程序后,才知道用户要在程序中存储哪些数据。为控制用户,可首先创建一个空列表,用于存储用户将要输入的值,然后将用户提供的每个新值附加到列表中。
1.5.2 在列表中插入元素
使用方法insert()可在列表的任何位置添加新元素。你需要指定新元素的索引和值。
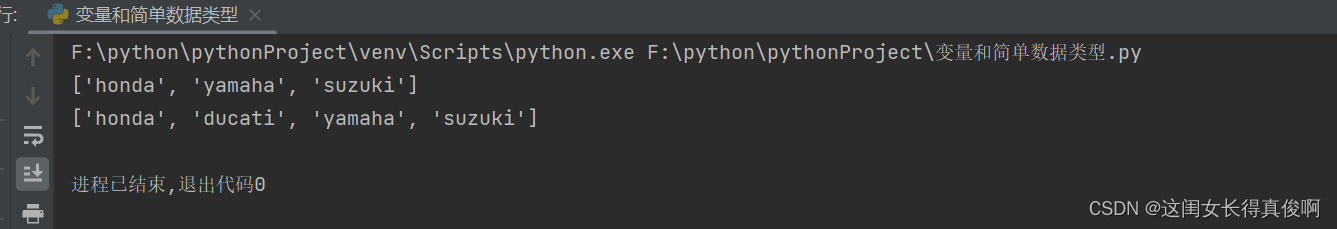
motorcycles = ['honda', 'yamaha', 'suzuki']
print(motorcycles)
motorcycles.insert(1, 'ducati')
print(motorcycles)
1.6 从列表中删除元素
如果知道要删除的元素在列表中的元素,可使用del语句
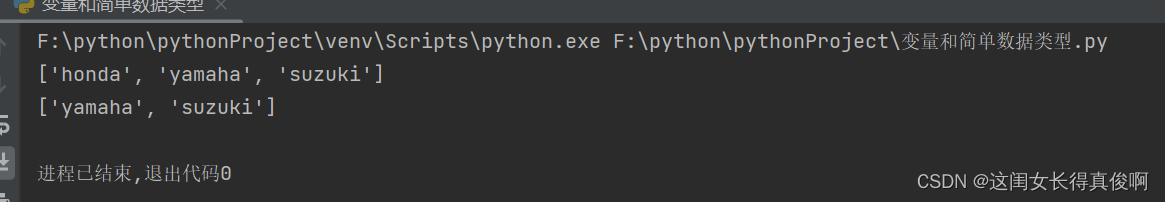
motorcycles = ['honda', 'yamaha', 'suzuki']
print(motorcycles)
del motorcycles[0]
print(motorcycles)
使用del可删除任务位置处的列表元素,条件是知道其索引
del
1.6.1 使用方法pop()删除元素
方法pop()可删除列表末尾的元素,并让你能够接着使用它。
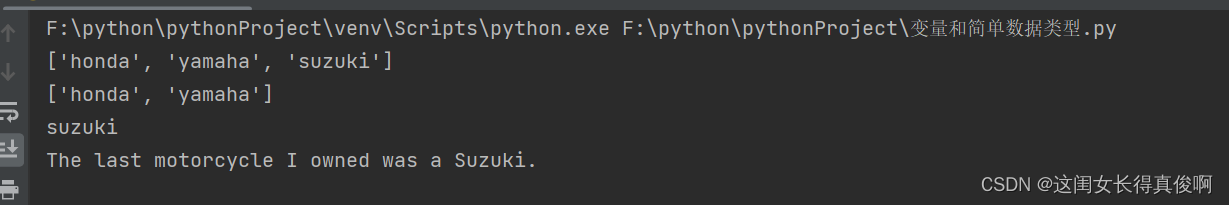
motorcycles = ['honda', 'yamaha', 'suzuki']
print(motorcycles)
poped_motorcycle = motorcycles.pop()
print(motorcycles)
print(poped_motorcycle)
print("The last motorcycle I owned was a " + poped_motorcycle.title() + ".")
1.6.2 弹出列表中任何位置处的元素
使用pop()来删除列表中任何位置的元素,只需要括号中指定要删除索引。
pop( num )
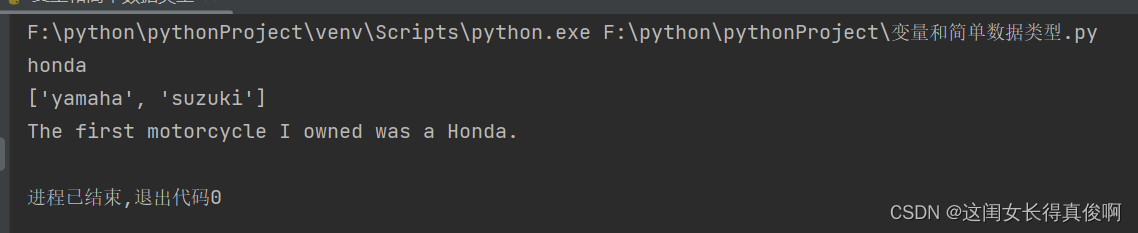
motorcycles = ['honda', 'yamaha', 'suzuki']
first_owned = motorcycles.pop(0)
print(first_owned)
print(motorcycles)
print('The first motorcycle I owned was a ' + first_owned.title() + '.')
如果要使用从列表中的一个元素,且不再以任何方式使用它,就使用del语句;
如果删除元素后还要继续使用它,就使用方法pop()
1.6.3 根据值删除元素
如果你只知道要删除的元素的值,可使用方法remove()
使用 remove()从列表中删除元素时,也可以接着使用它的值。
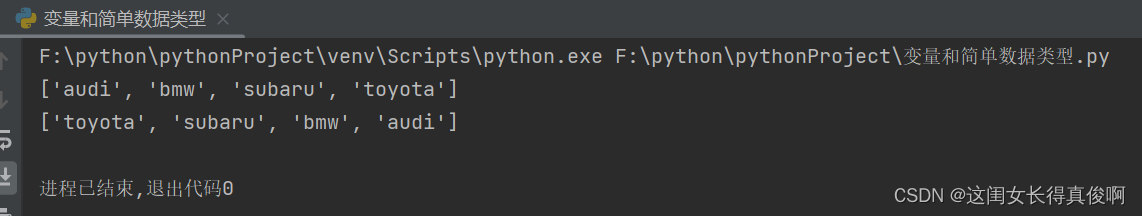
motorcycles = ['honda', 'yamaha', 'suzuki', 'ducati']
print(motorcycles)
too_expensive = 'ducati'
motorcycles.remove(too_expensive)
print(motorcycles)
print("\nA " + too_expensive.title() + " is expensive for me." )
方法remove() 只删除第一个指定的值。如果要删除的值可能在列表中出现多次,就需要使用循环来判断是否删除了所有这样的值。
2. 组织列表
2.1 使用方法sort()对列表进行永久性排序
sort()让你能够较为轻松地对列表进行排序。
sort(reverse=True)按与字母顺序相反的顺序排列列表元素
cars = ['bmw', 'audi', 'toyota', 'subaru']
cars.sort()
print(cars)
cars.sort(reverse=True)
print(cars)
2.2 使用函数sorted()对列表进行临时排序
要保留列表元素原来的排列顺序,同时以特定的顺序呈现他们,可以使用函数sorted()。
如果要按与字母顺序相反的顺序显示列表,也可以使用sorted(reverse=True)
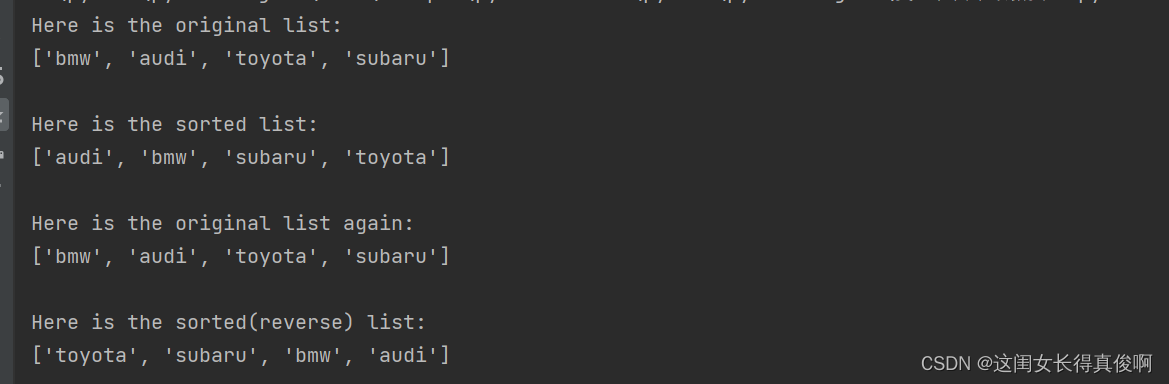
cars = ['bmw', 'audi', 'toyota', 'subaru']
print("Here is the original list:")
print(cars)
print("\nHere is the sorted list:")
print(sorted(cars))
print("\nHere is the original list again:")
print(cars)
print("\nHere is the sorted(reverse) list:")
print(sorted(cars, reverse=True)) #注意使用的函数格式
2.3 倒着打印列表
要反转列表元素的排列顺序,可使用方法reverse()
方法reverse()永久性地修改列表元素的排列顺序,可以随时恢复到原来的顺序,只需要再执行一次就行
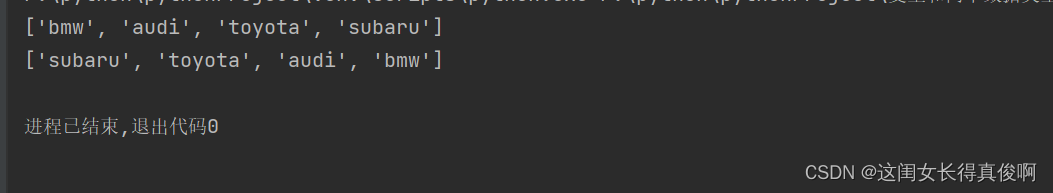
cars = ['bmw', 'audi', 'toyota', 'subaru']
print(cars)
cars.reverse()
print(cars)
2.4 确定列表的长度
使用函数len()可快速获悉列表的长度
cars = ['bmw', 'audi', 'toyota', 'subaru']
print(len(cars))
4 #输出内容


![[golang 微服务] 4. gRPC介绍,Protobuf结合gRPC 创建微服务](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/18a78106536bfc73c7eddbce236a6287.png)