Phaser工具(有时间就了解一下,下面还有队列)
简介
java7中引入了一种新的可重复使用的同步屏障,称为移相器Phaser。Phaser拥有与CyclicBarrier和CountDownLatch类似的功能.
但是这个类提供了更加灵活的应用。CountDownLatch和CyclicBarrier都是只适用于固定数量的参与者。移相器适用于可变数目的屏障,在这个意义上,可以在任何时间注册新的参与者。并且在抵达屏障是可以注销已经注册的参与者。因此,注册到同步移相器的参与者的数目可能会随着时间的推移而变化。
如CyclicBarrier一样,移相器可以重复使用,这意味着当前参与者到达移相器后,可以再一次注册自己并等待另一次到达.
移相器的另一个重要特征是:移相器可能是分层的,这允许你以树形结构来安排移相器以减少竞争
简单例子:
/**
* @Author: youthlql-吕
* @Date: 2020/10/11 21:57
* <p>
* 功能描述:
*/
public class PhaserTest {
private final static Random RANDOM = new Random();
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Phaser phaser = new Phaser();
//JDK8语法,相当于创建5个线程
IntStream.rangeClosed(1,5).boxed().map(i->phaser).forEach(Task::new);
//主线程也注册进去
phaser.register();
phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();//main线程 到达并等待前行
System.out.println("All of work are finished.");
}
static class Task extends Thread{
private final Phaser phaser;
Task(Phaser phaser) {
this.phaser = phaser;
phaser.register();//把自己加入计数器中
start();
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("The worker[ "+getName()+ " ]" +" is working.");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(RANDOM.nextInt(5));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();//自己完成,等待其他线程完成。 到达并等待前行
}
}
}
结果:
The worker[ Thread-1 ] is working.
The worker[ Thread-2 ] is working.
The worker[ Thread-0 ] is working.
The worker[ Thread-4 ] is working.
The worker[ Thread-3 ] is working.
All of work are finished.
重复使用的例子
/*
跑完步,需要去骑自行车,骑完自行车需要去跳高
*/
public class PhaserTest {
private final static Random RANDOM = new Random();
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Phaser phaser = new Phaser(3);
for (int i = 1; i < 4; i++) {
new Athletes(i,phaser).start();
}
}
static class Athletes extends Thread {
private final int no;
private final Phaser phaser;
Athletes(int no, Phaser phaser) {
this.no = no;
this.phaser = phaser;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(no + " start running.");
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(RANDOM.nextInt(100));
System.out.println(no + " end running.");
phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
System.out.println(no + " start bicycle.");
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(RANDOM.nextInt(100));
System.out.println(no + " end bicycle.");
phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
System.out.println(no + " start long jump.");
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(RANDOM.nextInt(100));
System.out.println(no + " end long jump.");
phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
结果:
1 start running.
2 start running.
3 start running.
3 end running.
2 end running.
1 end running.
1 start bicycle.
2 start bicycle.
3 start bicycle.
3 end bicycle.
2 end bicycle.
1 end bicycle.
1 start long jump.
2 start long jump.
3 start long jump.
2 end long jump.
1 end long jump.
3 end long jump.
可以看到栅栏被重复利用了。
动态减少
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class test {
private final static Random RANDOM = new Random();
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Phaser phaser = new Phaser(3);
for (int i = 1; i < 3; i++) {
new Athletes(i,phaser).start();
}
//假设3号运动员受伤了
new InjuredAthletes(3, phaser).start();
}
//运动员受伤了,需要减少
static class InjuredAthletes extends Thread {
private final int no;
private final Phaser phaser;
InjuredAthletes(int no, Phaser phaser) {
this.no = no;
this.phaser = phaser;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
sport(no, phaser, " start running.", " end running.");
sport(no, phaser, " start bicycle.", " end bicycle.");
System.out.println(no + "号运动员受伤了");
phaser.arriveAndDeregister();//动态减少
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
static class Athletes extends Thread {
private final int no;
private final Phaser phaser;
Athletes(int no, Phaser phaser) {
this.no = no;
this.phaser = phaser;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
sport(no, phaser, " start running.", " end running.");
sport(no, phaser, " start bicycle.", " end bicycle.");
sport(no, phaser, " start long jump.", " end long jump.");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private static void sport(int no, Phaser phaser, String x, String y) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println(no + x);
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(RANDOM.nextInt(100));
System.out.println(no + y);
phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
}
}
结果:
2 start running.
1 start running.
3 start running.
2 end running.
1 end running.
3 end running.
3 start bicycle.
1 start bicycle.
2 start bicycle.
2 end bicycle.
3 end bicycle.
1 end bicycle.
1 start long jump.
2 start long jump.
3号运动员受伤了
2 end long jump.
1 end long jump.
3号运动员受伤了,那么他就不能完成jump,3号运动员的phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance()也就无法执行,就会导致程序无法终止。因为Phaser数量是3个,只要三个线程都到了才会结束。所以说3号运动员受伤后,可以减少Phaser的数量:phaser.arriveAndDeregister();//动态减少
常用API
注册
public int register()
public int bulkRegister(int parties)
register
- 是注册一个线程数,比较常用
bulkRegister
- 可以批量注册
到达
public int arrive()
public int arriveAndDeregister()
public int arriveAndAwaitAdvance()
arrive
- 这个到达后,不会阻塞,相当于
countdown机制【因为countdown只会阻塞调用者,其它线程干完任务就可以干其他事】 - 大家要理解一点,party 数和线程是没有关系的,不能说一个线程代表一个 party,因为我们完全可以在一个线程中重复调用 arrive() 方法。这么表达纯粹是方便理解用。
arriveAndAwaitAdvance
- 到达后会阻塞,相当于
CyclicBarrier机制
arriveAndDeregister
- 当线程出现异常,不能正常到达时,可以调用该方法,
动态减少注册数
举例
public class PhaserTest {
private static final Random RANDOM = new Random();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
final Phaser phaser = new Phaser(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
new ArriveTask(i,phaser).start();
}
//等待全部任务进行完成
phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
System.out.println("The phase 1 work finish done.");
}
private static class ArriveTask extends Thread{
private final Phaser phaser;
private ArriveTask(int no,Phaser phaser) {
super(String.valueOf(no));
this.phaser = phaser;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(getName() + " start working. ");
threadSleep();
System.out.println(getName() + " The phase one is running.");
phaser.arrive();
threadSleep();
System.out.println(getName() + " keep to other thing. ");
}
}
private static void threadSleep() {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(RANDOM.nextInt(5));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
onAdvance()
这个方法是 protected 的,所以它不是 phaser 提供的 API,从方法名字上也可以看出,它会在一个 phase 结束的时候被调用。
它的返回值代表是否应该终结(terminate)一个 phaser,之所以拿出来说,是因为我们经常会见到有人通过覆写该方法来自定义 phaser 的终结逻辑,如:
protected boolean onAdvance(int phase, int registeredParties) {
return phase >= N || registeredParties == 0;
}
1、我们可以通过
phaser.isTerminated()来检测一个 phaser 实例是否已经终结了2、当一个 phaser 实例被终结以后,register()、arrive() 等这些方法都没有什么意义了,大家可以玩一玩,观察它们的返回值,原本应该返回 phase 值的,但是这个时候会返回一个负数。
监控子线程任务
public int awaitAdvance(int phase)
public int awaitAdvanceInterruptibly(int phase) throws InterruptedException
- 相当于起到监控的作用
- 如果子线程还没有执行完成,主线程就会阻塞
- 相较而言,可以不用增加注册量
举例
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
final Phaser phaser = new Phaser(4);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
new AwaitAdvance(i,phaser).start();
}
//等待全部任务进行完成
phaser.awaitAdvance(phaser.getPhase());
System.out.println("The phase 1 work finish done.");
}
强制关闭
public void forceTermination()
public boolean isTerminated()
- 强制关闭phaser,但是
如果线程陷入阻塞,不会唤醒
监控API
获取阶段数
public final int getPhase()
- 返回当前相位数。 最大相位数为Integer.MAX_VALUE
- 每增加一轮就会加一
举例
public class PhaserTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Phaser phaser = new Phaser(1);
System.out.println(phaser.getPhase());
phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
System.out.println(phaser.getPhase());
phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
System.out.println(phaser.getPhase());
phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
System.out.println(phaser.getPhase());
}
}
结果:
0
1
2
3
获取注册的数
public int getRegisteredParties()
- 获得注册的线程数,相当于Countdown初始的的计数器
- 可以动态更改
获得到达和未到达的数目
public int getArrivedParties()
public int getUnarrivedParties()
getArrivedParties
- 获得已经到达的线程数,和没有到达的线程数
getUnarrivedParties
- 获得没有到达的线程数,和没有到达的线程数
Phaser的分层结构
Tiering 这个词本身就不好翻译,大家将就一下,要表达的意思就是,将多个 Phaser 实例构造成一棵树。
1、第一个问题来了,为什么要把多个 Phaser 实例构造成一棵树,解决什么问题?有什么优点?
Phaser 内部用一个 state 来管理状态变化,随着 parties 的增加,并发问题带来的性能影响会越来越严重。
/**
* 0-15: unarrived
* 16-31: parties, 所以一个 phaser 实例最大支持 2^16-1=65535 个 parties
* 32-62: phase, 31 位,那么最大值是 Integer.MAX_VALUE,达到最大值后又从 0 开始
* 63: terminated
*/
private volatile long state;
通常我们在说 0-15 位这种,说的都是从低位开始的
state 的各种操作依赖于 CAS,典型的无锁操作,但是,在大量竞争的情况下,可能会造成很多的自旋。
而构造一棵树就是为了降低每个节点(每个 Phaser 实例)的 parties 的数量,从而有效降低单个 state 值的竞争。
2、第二个问题,它的结构是怎样的?
这里我们不讲源码,用通俗一点的语言表述一下。我们先写段代码构造一棵树:
Phaser root = new Phaser(5);
Phaser n1 = new Phaser(root, 5);
Phaser n2 = new Phaser(root, 5);
Phaser m1 = new Phaser(n1, 5);
Phaser m2 = new Phaser(n1, 5);
Phaser m3 = new Phaser(n1, 5);
Phaser m4 = new Phaser(n2, 5);
根据上面的代码,我们可以画出下面这个很简单的图:
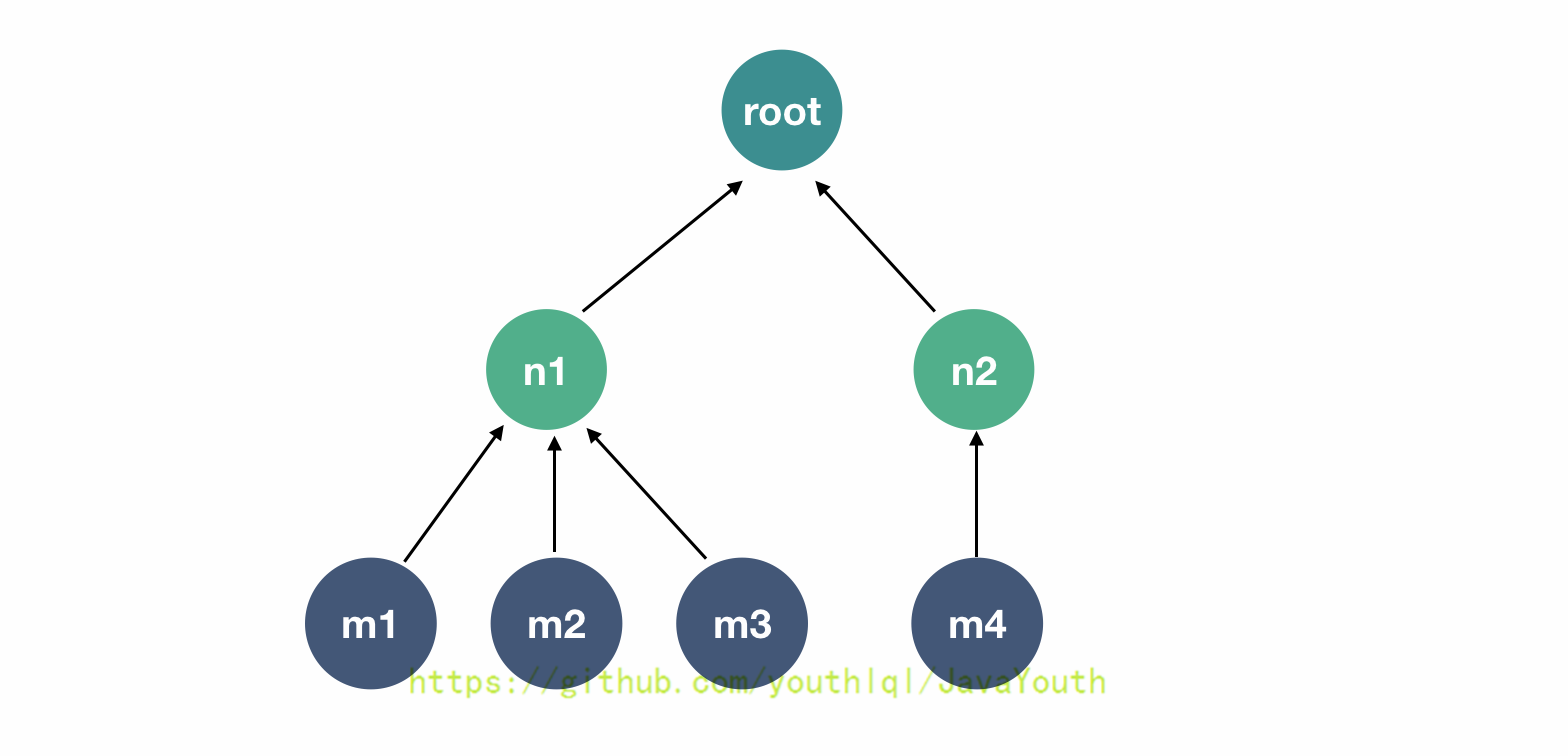
这棵树上有 7 个 phaser 实例,每个 phaser 实例在构造的时候,都指定了 parties 为 5,但是,对于每个拥有子节点的节点来说,每个子节点都是它的一个 party,我们可以通过 phaser.getRegisteredParties() 得到每个节点的 parties 数量:
- m1、m2、m3、m4 的 parties 为 5
- n1 的 parties 为 5 + 3,n2 的 parties 为 5 + 1
- root 的 parties 为 5 + 2
结论应该非常容易理解,我们来阐述一下过程。
在子节点注册第一个 party 的时候,这个时候会在父节点注册一个 party,注意这里说的是子节点添加第一个 party 的时候,而不是说实例构造的时候。
在上面代码的基础上,大家可以试一下下面的这个代码:
Phaser m5 = new Phaser(n2);
System.out.println("n2 parties: " + n2.getRegisteredParties());
m5.register();
System.out.println("n2 parties: " + n2.getRegisteredParties());
第一行代码中构造了 m5 实例,但是此时它的 parties == 0,所以对于父节点 n2 来说,它的 parties 依然是 6,所以第二行代码输出 6。第三行代码注册了 m5 的第一个 party,显然,第四行代码会输出 7。
当子节点的 parties 降为 0 的时候,会从父节点中"剥离",我们在上面的基础上,再加两行代码:
m5.arriveAndDeregister();
System.out.println("n2 parties: " + n2.getRegisteredParties());
由于 m5 之前只有一个 parties,所以一次 arriveAndDeregister() 就会使得它的 parties 变为 0,此时第二行代码输出父节点 n2 的 parties 为 6。
还有一点有趣的是,在非树的结构中,此时 m5 应该处于 terminated 状态,因为它的 parties 降为 0 了,不过在树的结构中,这个状态由 root 控制,所以我们依然可以执行 m5.register()…
3、每个 phaser 实例的 phase 周期有快有慢,怎么协调的?
在组织成树的这种结构中,每个 phaser 实例的 phase 已经不受自己控制了,由 root 来统一协调,也就是说,root 当前的 phase 是多少,每个 phaser 的 phase 就是多少。
那又有个问题,如果子节点的一个周期很快就结束了,要进入下一个周期怎么办?需要等!这个时候其实要等所有的节点都结束当前 phase,因为只有这样,root 节点才有可能结束当前 phase。
我觉得 Phaser 中的树结构我们要这么理解,我们要把整棵树当做一个 phaser 实例,每个节点只是辅助用于降低并发而存在,整棵树还是需要满足 Phaser 语义的。
阻塞队列
请谈谈对阻塞队列的理解
# 阻塞队列
# 阻塞队列为空时,从队列中获取元素的操作将会被阻塞
# 阻塞队列为满时,往队列里添加元素的操作将会被阻塞
# 阻塞队列的好处
# 多线程领域中,所谓阻塞,即某些情况下会挂起线程,一旦条件满足,线程唤醒。
# 为什么需要 BlockingQueue
# 我们不需要关心什么时候需要阻塞线程,什么时候需要唤醒线程了
# 在 JUC 包发布以前,多线程环境下,程序员需要自己控制这些细节,并且兼顾效率与线程安全
种类
# ArrayBlockingQueue
# 数组结构组成的有界阻塞队列
# LinkedBlockingQueue
# 由链表结构组成的有界(但大小默认值为 Integer.MAX_VALUE) 阻塞队列
# PriorityBlockingQueue
# 支持优先级排序的无界阻塞队列
对队列中的元素进行排序,如果未指定比较器,插入队列的元素必须实现Comparable接口
内部基于数组实现的最小二叉堆算法
队列的长度是可扩展的(类似ArrayList),上限为Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8
# DelayQueue
# 使用优先级队列实现的延迟无界阻塞队列
DelayQueue是一个无界的BlockingQueue,用于放置实现了Delayed接口的对象,其中的对象只能在其到期时才能从队列中取走。这种队列是有序的,即队头对象的延迟到期时间最长。注意:不能将null元素放置到这种队列中
# SynchronousQueue
# 不存储元素的阻塞队列,也即单个元素的队列(PS:实际上它不是一个真正的队列,因为SynchronousQueue没有容量。与其他BlockingQueue(阻塞队列)不同,SynchronousQueue是一个不存储元素的BlockingQueue。只是它维护一组线程,这些线程在等待着把元素加入或移出队列)
# LinkedTransferQueue
# 由链表结构组成的无界阻塞队列
# LinkedBlockingDeque
# 由链表结构组成的双向阻塞队列
核心方法
# 抛出异常组
# add(e)
# 队列满时 add 会抛出 java.lang.IllegalStateException: Queue full
# remove()
# 队列空时 remove 会抛出 java.util.NoSuchElementException
# element()
# 得到队首元素,队列为空时,抛出 java.util.NoSuchElementException
# 返回布尔值组
# offer(e)
# 往阻塞队列插入数据,成功时返回 true,失败时返回 false
# poll()
# 从阻塞队列取出数据,成功时返回 数据,队列为空时返回 null
# peek()
# 取出队首元素,成功时返回 数据,队列为空时返回 null
# 阻塞
# put(e)
# 往阻塞队列插入数据,无返回值,插入不成功时阻塞线程,直至插入成功 Or 线程中断
# take()
# 从阻塞队列取出数据,成功返回数据,不成功时阻塞线程,直至取出成功 Or 线程中断
# 超时
# offer(e,time,unit)
# 往阻塞队列插入数据,成功返回 true,不成功时线程阻塞等待超时时间,过时返回false 并放弃操作
# poll(time,unit)
# 从阻塞队列取出数据,成功返回 数据,队列为空时线程阻塞等待超时时间,过时返回false 并放弃操作
阻塞队列的使用场景
# 生产者消费者模式
# 线程池
# 消息中间件
传统版生产者消费者模式 Demo
package ProducerAndConsumer;
/**
* @Author: youthlql-吕
* @Date: 2019/9/26 14:56
* <p>
* 功能描述: 功能描述: 4个线程的if语句
* 要求:生产者线程消费一个,消费者线程消费一个。num只能为1或0
* 改用while循环的4个线程
*
*/
public class Producer_03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Consumer3 consumer = new Consumer3();
//生产者线程A
new Thread(() ->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
consumer.increment();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"生产者A").start();
new Thread(() ->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
consumer.decrement();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"消费者B").start();
new Thread(() ->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
consumer.increment();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"生产者C").start();
new Thread(() ->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
consumer.decrement();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"消费者D").start();
}
}
class Consumer3{
private Integer num = 0;
public synchronized void increment() throws InterruptedException {
while(num != 0){
this.wait();
}
num++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + num);
notifyAll();
}
public synchronized void decrement() throws InterruptedException {
while(num == 0){
this.wait();
}
num--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + num);
notifyAll();
}
}
阻塞队列版生产者消费者模式Demo
/**
* @Author: youthlql-吕
* @Date: 2019/9/26 16:04
* <p>
* 功能描述:
*/
public class Video44 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyResource myResource = new MyResource(new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(10));
new Thread(() ->{
System.out.println("----------生产者线程启动-----------");
try {
myResource.produce();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"Producer").start();
new Thread(() ->{
System.out.println("----------消费者线程启动-----------");
try {
myResource.consume();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"Consumer").start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
myResource.stop();
System.out.println("********5秒之后,main叫停生产,生产结束*********");
}
}
class MyResource{
private volatile Boolean FLAG = Boolean.TRUE;
private AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger();
private BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = null;
public MyResource(BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue){
this.blockingQueue = blockingQueue;
//打印日志一般需要看类信息
System.out.println(blockingQueue.getClass().getName());
}
public void produce() throws InterruptedException {
String data = null;
Boolean returnValue;
while(FLAG){
data = atomicInteger.incrementAndGet() + "";
returnValue = blockingQueue.offer(data, 2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (returnValue){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t\t 插入队列成功 \t" + data);
}else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t 插入超时 \t" + data);
}
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t 大老板叫停,生产者停止生产");
}
public void consume() throws InterruptedException {
String data = null;
while(FLAG){
// Thread.sleep(500);
data = blockingQueue.poll(2L,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (data == null || data.equalsIgnoreCase("")){
FLAG = false;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t 消费超时,消费者退出" );
return;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t 消费队列成功 \t" + data);
}
}
public void stop(){
this.FLAG = false;
}
}
线程池
主要优点
- 第一:降低资源消耗.通过重复利用自己创建的线程降低线程创建和销毁造成的消耗.
- 第二: 提高响应速度.当任务到达时,任务可以不需要等到线程的创建,就能立即执行.
- 第三: 提高线程的可管理性.线程是稀缺资源,如果无限的创建,不仅会消耗资源,还会较低系统的稳定性,使用线程池可以进行统一分配,调优和监控.
Java 中的线程池是通过 Executor 框架实现的,该框架中用到了 Executor、Executors、ExecutorService、ThreadPoolExecutor 这几个类。
线程池七大参数入门简介
流程举例
一个银行网点 <线程池>,共 10* 个窗口 <maximumPoolSize 最大线程数>,开放 5* 个窗口 <corePoolSize 核心线程数>
。今天办理业务的特别多,其余5个窗口加班一天 <keepAliveTime + unit 多余线程存活时间+单位>,办理业务的人在窗口前排队* <workQueue 请求任务的阻塞队列>。银行里的A职员、B职员… 给办理业务 <threadFactory 产生线程、线程名、线程序数…>最多排10个,来了11个,并且每个窗口都有人在办理业务,多的人怎么拒绝呢?<handler 拒绝策略>
七大参数
-
corePoolSize 线程池中的常驻核心线程数
创建线程池后,当有请求任务进来,就安排池中的线程去执行请求任务
当线程池中的线程数目达到 corePoolSize 后,就会把到达的任务放到缓存队列中 -
maximumPoolSize
线程池能够容纳同时执行的最大线程数,此值必须大于等于1(讲的语焉不详,PS:当缓存队列满了之后,就会使用这些线程) -
keepAliveTime 多余的空闲线程的存活时间
当前线程池数量超过 corePoolSize 时,当空闲时间达到 keepAliveTime 值时,
多余空闲线程会被销毁直到只剩下 corePoolSize 个线程为止 -
unit
keepAliveTime 的单位 -
workQueue
任务队列,被提交但尚未被执行的任务 -
threadFactory,表示生成线程池中工作线程的线程工厂<线程名字、线程序数…>,用于创建线程一般用默认的即可
-
handler,拒接策略,表示当队列满了并且工作线程大于等于线程池的最大线程数(maximumPoolSize)时,如何拒绝新的任务
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class ThreadPoolDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService threadPool =
new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,
5,
1L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<Runnable>(3),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
for(int i = 1;i <= 9; i++ )
threadPool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t 办理业务" );
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
线程池的底层工作流程
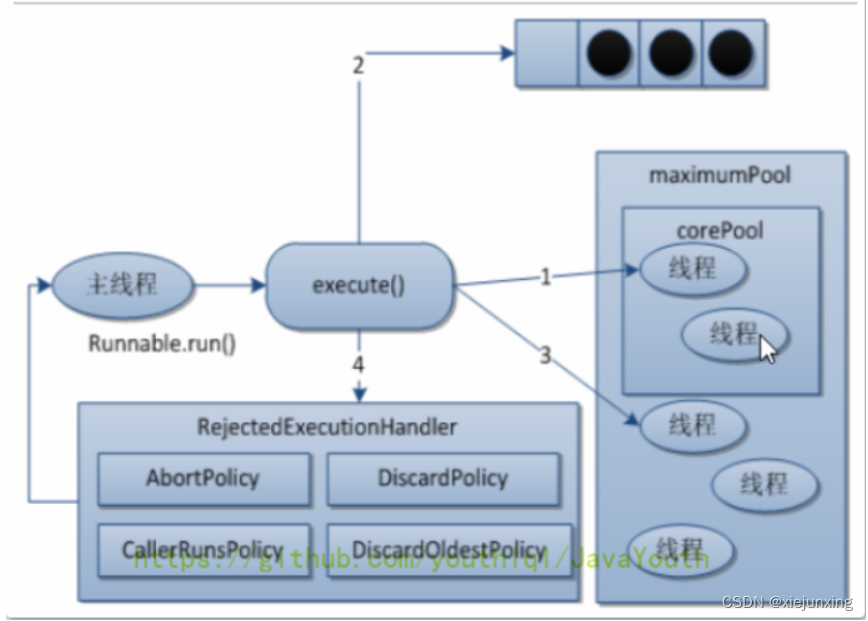
1、创建线程池后,等待请求任务
2、当调用 execute() 方法添加请求任务时,线程池做如下判断
- 如果正在运行的线程数量小于 corePoolSize,马上创建线程执行请求任务
- 如果正在运行的线程数量大于或等于 corePoolSize,将请求任务放入阻塞队列
- 如果阻塞队列满了,且正在运行的线程数小于 mamimumPoolSize,创建非核心线程执行请求任务
- 如果队列满了且线程池线程达到最大线程数,线程池启动饱和拒绝策略来执行
3、当一个线程完成任务时,从阻塞队列中取出下一个任务来执行
4、当一个线程无事可做超过一定时间时,线程池会判断
- 如果当前运行的线程数大于 corePoolSize,该线程被销毁
- 所以,线程池完成所有请求任务后,最终会收缩到 corePoolSize 的大小
线程池的4种拒绝策略
JDK 内置的拒绝策略
-
AbortPolicy(默认)
- 直接抛出 RejectedExecutionException 异常阻止系统正常运行
-
CallerRunsPolicy
- “调用者运行” 一种调节机制
- 该策略既不会抛弃任务,也不会抛出异常
- 而是将某些任务回退到调用者,从而降低新任务的流量
-
DiscardOldestPolicy
- 抛弃队列中等待最久的任务
- 然后把当前任务中加入队列中尝试再次提交当前任务
-
DiscardPolicy
- 直接丢弃任务,不予任何处理也不抛出异常
- 如果允许任务丢失,这是最好的一种方案
以上拒绝策略都是实现了 RejectedExecutionHandler 接口
线程池在实际生产中使用哪一个
后文会介绍Java内置的几个线程池
阿里巴巴 Java 开发手册
线程池不允许使用 Executors 创建,而是通过 ThreadPoolExecutor 的方式
FixedThreadPool 和 SingleThreadPool
允许的阻塞队列容量为 Integer.MAX_VALUE,可能会堆积大量的请求,导致 OOM
CachedThreadPool 和 ScheduledThreadPool
允许的创建线程数量为 Integer.MAX_VALUE,可能会创建大量的线程,导致 OOM
线程池合理配置参数
1、CPU 密集型
意思是该任务需要大量的运算,而没有阻塞,CPU 一直全速运行
CPU 密集任务只有在真正的多核 CPU 上才可能得到加速(通过多线程)
CPU 密集型任务配置尽可能少的线程数量
一般公式 : CPU 核数 + 1个线程的线程池最大线程数
2、IO 密集型
由于 IO 密集型任务线程并不是一直在执行任务,则应配置尽可能多的线程
一般公式 : CPU 核数* 2
3、IO 密集型 2
IO 密集型、即该任务需要大量的 IO,即大量的堵塞
在单线程上运行 IO 密集型的任务会导致浪费大量的 CPU 算力浪费在等待上
所以,IO 密集型任务中使用多线程可以大大的加速程序运行,即时在单核 CPU 上
这种加速主要就是利用了被浪费掉的阻塞时间
参考公式 : CPU 核数 / (1 - 阻塞系数)
例: 8 核CPU 8/(1-0.9) = 80 个线程数
线程池的状态
线程池状态含义如下
• RUNNING 接受新任务并且处理阻塞队列里的任务
• SHUTDOWN :拒绝新任务但是处理阻塞队列里的任务
• STOP :拒绝新任务并且放弃阻塞队列里的任务,同时会中断正在处理的任务。
• TIDYING:所有任务都执行完(包含阻塞队列里面的任务)后,当前线程池活动线程,数为0,将要调用 terminated 方法
• TERMINATED:终止状态,terminated 方法调用完成以后的状态
线程池状态转换列举如下
• RUNNING -> SHUTDOWN 显式调用shutdown () 方法 或者隐式调用了 finalize()方法里面的 shutdown() 方法
• RUNNING或SHUTDOWN) -> STOP 显式调用 shutdownNow() 方法
• SHUTDOWN ->TIDYING 当线程池和任务队列都为空时
• STOP -> TIDYING 当线程池为空时
• TIDYING -> TERMNATED terminated() hook 方法执行完成
线程池的关闭
关闭有两个方法:shutdown和shutdownNow
shutdown
public void shutdown() {
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
checkShutdownAccess();
advanceRunState(SHUTDOWN);
interruptIdleWorkers();
onShutdown(); // hook for ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
tryTerminate();
}
private void interruptIdleWorkers() {
interruptIdleWorkers(false);
}
private void interruptIdleWorkers(boolean onlyOne) {
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
for (Worker w : workers) {
Thread t = w.thread;
if (!t.isInterrupted() && w.tryLock()) {
try {
t.interrupt();
} catch (SecurityException ignore) {
} finally {
w.unlock();
}
}
if (onlyOne)
break;
}
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
}
- 从源码可以看出,本质上执行的是
interrupt方法 - 如果线程是空闲的,执行的是Condition的await的方法,会被直接打断,被回收
- 如果正在工作,该线程会被打上一个标记,等任务执行后被回收
shutdownNow
public List<Runnable> shutdownNow() {
List<Runnable> tasks;
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
checkShutdownAccess();
advanceRunState(STOP);
interruptWorkers();//先打断
tasks = drainQueue();//再把任务队列没有执行的任务取出
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
tryTerminate();//不断的打断
return tasks;
}
- 先打断空闲的打断
- 然后清空任务队列
- 然后不断的尝试打断正在执行的线程
- 最后会返回一个List集合,包含还没有执行的任务
awaitTermination 操作
当线程调用awaitTermination方法后,当前线程会被阻塞,直到线程池状态变为TERMINATED 才返回 或者等待时间超时才返回。
Executors
内置线程池用的不多,不用太在意
简介
Java通过Executors提供五种线程池,分别为:
-
newCachedThreadPool:创建一个可缓存线程池,如果线程池长度超过处理需要,可灵活回收空闲线程,若无可回收,则新建线程。 -
newFixedThreadPool:创建一个定长线程池,可控制线程最大并发数,超出的线程会在队列中等待。 -
newScheduledThreadPool:创建一个定长线程池,支持定时及周期性任务执行。和一个线程的区别
newSingleThreadExecutor Thread 任务执行完成后,不会自动销毁,可以复用 任务执行完成后,会自动销毁 可以将任务存储在阻塞队列中,逐个执行 无法存储任务,只能执行一个任务 -
newSingleThreadExecutor:创建一个单线程化的线程池,它只会用唯一的工作线程来执行任务,保证所有任务按照指定顺序(FIFO, LIFO, 优先级)执行。 -
newWorkStealingPool:创建一个ForkJoin线程池,线程数是CPU核数,可以充分利用CPU资源。从1.8开始有的
简单例子:
/**
* @Author: youthlql-吕
* @Date: 2020/4/23 10:49
* <p>
* 功能描述: 线程池的三个常用方式
*/
public class Video47 {
public static void main(String[] args){
/**
* 一池5个处理线程
*/
//ExecutorService threadPool= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
/**
* 一池一线程
*/
// ExecutorService threadPool= Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
/**
* 一池N线程
*/
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
//模拟10个用户来办理业务 没有用户就是来自外部的请求线程.
try {
for (int i = 1; i <= 20; i++) {
threadPool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t 办理业务");
});
try {
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
}
有三个内置线程池比较简单,下面介绍下稍复杂的两个内置线程池。
newWorkStealingPool
public static ExecutorService newWorkStealingPool(int parallelism) {
return new ForkJoinPool
(parallelism,
ForkJoinPool.defaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory,
null, true);
}
public static ExecutorService newWorkStealingPool() {
return new ForkJoinPool
(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(),
ForkJoinPool.defaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory,
nul, true);
}
//Returns the number of processors available to the Java virtual machine.
Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()
分析源码我们可以得知
- 采用的ForkJoin框架,可以将任务进行分割,同时线程之间会互相帮助
- 最大的线程数是CPU核数,充分利用CPU资源
newScheduledThreadPool
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);
}
- 创建的是一个定时的任务,每隔一段时间就会运行一次
首先可以对比的就是Timer这个类
public class ExecutorsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Timer timer = new Timer();
final TimerTask task = new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("=====" + System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
//1秒执行一次
timer.schedule(task,0,1000);
}
}
结果
=====1602597314888
=====1602597316897
=====1602597318898
=====1602597320898
=====1602597322899
=====1602597324899
可以发现:如果任务时间超过了定时时长,就无法按照预定的时间执行
其他工具的解决方式:
crontab定时处理器为了确保时间的正确性,会重新启一个线程
有三个方法
-
schedule(commod,delay,unit) ,这个方法是说系统启动后,需要等待多久执行,delay是等待时间。只执行一次,没有周期性。
-
scheduleAtFixedRate(commod,initialDelay,period,unit),这个是以period为固定周期时间,按照一定频率来重复执行任务,initialDelay是说系统启动后,需要等待多久才开始执行。例如:如果设置了period为5秒,线程启动之后执行了大于5秒,线程结束之后,立即启动线程的下一次,如果线程启动之后只执行了3秒就结束了那执行下一次,需要等待2秒再执行。这个是优先保证任务执行的频率,
-
scheduleWithFixedDelay(commod,initialDelay,delay,unit),这个是以delay为固定延迟时间,按照一定的等待时间来执行任务,initialDelay意义与上面的相同。例如:设置了delay为5秒,线程启动之后不管执行了多久,结束之后都需要先生5秒,才能执行下一次。这个是优先保证任务执行的间隔。
ExecutorService
public class Video53 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
2,
5,
1L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<Runnable>(3),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
//默认抛出异常
//new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()
//回退调用者
//new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy()
//处理不来的不处理
//new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy()
new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy()
);
//模拟10个用户来办理业务 没有用户就是来自外部的请求线程.
try {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
threadPool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t 办理业务");
});
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
//threadPoolInit();
}
}
ExecutorService一般就是用来作为我们自定义线程池的引用。
API
1、getActiveCount():获取当前线程池中活跃的线程个数;若是没有execute(Runnable)任务的话,是不会创建线程的;提交一个任务,也只会创建一个线程去执行,而不会一次性直接创建corePoolSize个线程。
2、allowCoreThreadTimeOut(true):当任务执行完成的时候,释放线程池;若使用的线程池的keepAliveTime为0,需要手动修改,因为不允许keepAliveTime为0的线程池,调用此方法;
3、invokeAny(Call<T>):此方法是一个同步方法,会阻塞调用线程;若其中有一个任务返回了,则其它的任务取消,不会继续执行; 此方法也存在超时设置重构方法;防止线程一直等待;无法结束。
Future
Future API
1、get():此方法是阻塞的,但是抛出了InterruptedException,所以是可以被打断的;使用interrupt()进行打断的时候,打断的是调用get()的线程,让当前线程不再阻塞的等待获取数据;并不是真正执行任务的那个线程。
2、get(TimeOut):若是获取数据超时了,但是任务还是依旧执行,只是不再等待任务的返回值。
3、isDone():执行任务期间不管是否执行成功了,还是执行失败了(抛出异常)。只要结束,isDone()就会返回true。
4、boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning):取消任务。
返回false的情况:1.任务已经执行完成了,是无法被取消的。2.之前已经被cancel过
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
testCancel();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void testCancel() throws InterruptedException {
// 把线程设置为守护线程, 根据启动线程dead.
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
AtomicBoolean running = new AtomicBoolean(true);
Future<Integer> future = executorService.submit(() -> {
while (running.get()){
//模拟一个执行很久的任务
}
System.out.println("1111111");
return 10;
});
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
System.out.println(future.cancel(true));
System.out.println(future.isCancelled());
System.out.println(future.isDone());
}
输出:
true
true
true
根据例子我们可以看到,cancel虽然取消了任务,但是任务任然在执行,这是为什么呢?
https://blog.csdn.net/stephen8341/article/details/50433656
其实我们如果查看FutureTask的源码就会发现cancel只不过是调用了Thread的interrupt方法,而interrupt只能是停掉线程中有sleep,wait,join逻辑的线程,抛出一个InterruptException。这样看来FutureTask的cancel方法并不能停掉一切正在执行的异步任务。但是这里我们有一个妥协的做法就是在判断条件中加!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()这个判断即可.
改进代码1
private static void testCance2() throws InterruptedException {
// 把线程设置为守护线程, 根据启动线程dead.
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Future<Integer> future = executorService.submit(() -> {
while (!Thread.interrupted()){
//模拟一个执行很久的任务
}
System.out.println("1111111");
return 10;
});
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
System.out.println(future.cancel(true));
System.out.println(future.isCancelled());
System.out.println(future.isDone());
}
输出:
true
true
true
1111111
可以看到任务是真正被终止了。
还有一个场景
while (!Thread.interrupted()){
//模拟一个执行很久的任务
}
在上面改进代码的第一步,第一行代码是个IO操作,假设耗时非常长,那就根本没有机会判断while条件。此时如果cancel,一样不会真正的终止任务的执行。
改进代码2
private static void testCance3() throws InterruptedException {
// 把线程设置为守护线程, 根据启动线程dead.
AtomicBoolean running = new AtomicBoolean(true);
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool( r -> {
Thread t = new Thread(r);
t.setDaemon(true);
return t;
});
Future<Integer> future = executorService.submit(() -> {
// while (!Thread.interrupted()){
// //模拟一个执行很久的任务
// }
while (running.get()){
//模拟一个执行很久的任务
}
System.out.println("1111111");
return 10;
});
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
System.out.println(future.cancel(true)); // 可以取消掉任务, 但是无法终止任务的执行.
System.out.println(future.isCancelled());
System.out.println(future.isDone());
}
控制台输出:
true
true
trueProcess finished with exit code 0
可以看到直接结束了,思想就是将线程设置为守护线程,一旦主线程执行完,守护线程无论在干什么都会马上结束。所以后面的System.out.println("1111111");都没有打印
已经被cancel的任务,是否还能拿到结果?
private static void testCance2() throws Exception {
// 把线程设置为守护线程, 根据启动线程dead.
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Future<Integer> future = executorService.submit(() -> {
while (!Thread.interrupted()){
//模拟一个执行很久的任务
}
System.out.println("1111111");
return 10;
});
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
System.out.println(future.cancel(true));
System.out.println(future.isCancelled());
System.out.println(future.isDone());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println(future.get());
}
输出:
true
true
true
1111111
java.util.concurrent.CancellationException
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.report(FutureTask.java:121)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.get(FutureTask.java:192)
at Future.FutureExample1.testCance2(FutureExample1.java:63)
at Future.FutureExample1.main(FutureExample1.java:19)
输出了111111,说明程序已经走到了return那一行,但是可以看到拿不到了爆出了异常。
Future的缺陷以及解决方案
1、缺陷一:使用Future可以保证任务的异步执行;但是,只要去获取任务的结果,就会导致程序的阻塞;从而,从异步再次变为了同步。
2、缺陷二:假设批量执行一些异步任务,大部分任务都是几秒完成的,有少许任务是几个小时才完成。那你get()的时候,万一拿到了几个小时执行的任务,就会一直阻塞,导致几秒完成的任务拿不到结果。
3、像netty会有回调的callback
缺陷代码
private static void futureExecSomeTask() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
final List<Callable<Integer>> callableList = Arrays.asList(
() -> {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
System.out.println("Thread 10 finished!");
return 10;
},
() -> {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(20);
System.out.println("Thread 20 finished!");
return 20;
}
);
// invokeAll会阻塞等待所有的future执行完成.
List<Future<Integer>> futureList = executorService.invokeAll(callableList);
for (Future<Integer> future : futureList) {
System.out.println(future.get());
}
}
JDK7解决方案
private static void futureDefect() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
final List<Callable<Integer>> callableList = Arrays.asList(
() -> {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
System.out.println("Thread 10 finished!");
return 10;
},
() -> {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(20);
System.out.println("Thread 20 finished!");
return 20;
}
);
List<Future<Integer>> futureList = new ArrayList<>();
futureList.add(executorService.submit(callableList.get(0)));
futureList.add(executorService.submit(callableList.get(1)));
for (Future<Integer> future : futureList) {// 其实相当于把批量任务, 单个的提交给线程池去执行.
System.out.println(future.get());
}
}
JDK8解决方案
CompletionService:具体见下面
CompletionService
简介
-
CompletionService的实现目标是任务先完成可优先获取到,即结果按照完成先后顺序排序。
-
ExecutorCompletionService类是常用的CompletionService实现类,该类只有三个成员变量:
public class ExecutorCompletionService<V> implements CompletionService<V> {
private final Executor executor;
private final AbstractExecutorService aes;
private final BlockingQueue<Future<V>> completionQueue;
....
}
- 可以看到ExecutorCompletionService主要是增强executor线程池的。
- Task包装后被塞入completionQueue,当Task结束,其Future就可以从completionQueue中获取到。
执行流程:
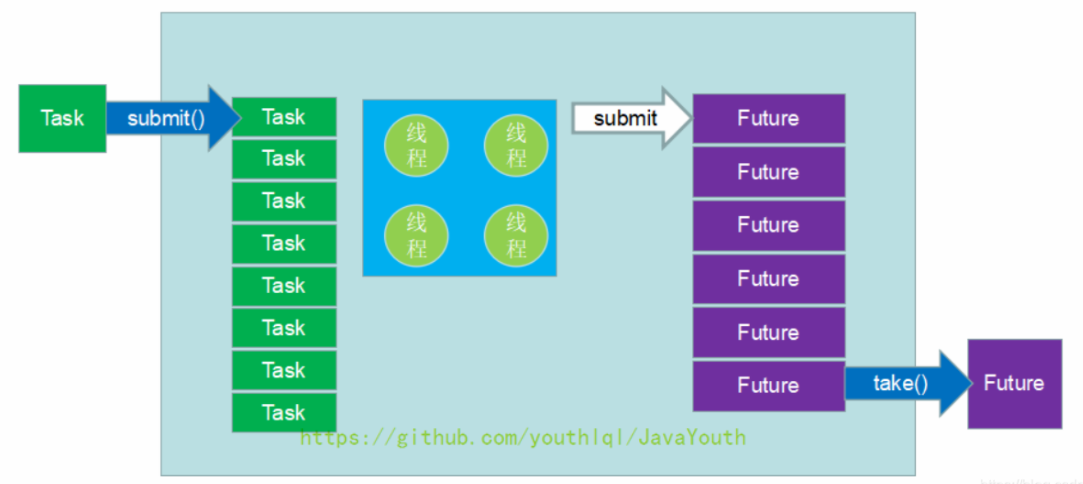
阻塞和非阻塞获取
public Future<V> take()throws InterruptedException
public Future<V> poll()
public Future<V> poll(long timeout,TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException
1234
阻塞获取
take方法回使调用者阻塞,可以保证一定会有Future取出
非阻塞获取
poll方法会去查看是否有任务完成,有则取出;没有,就会返回一个null
代码解决Future缺陷
public class CompletionServiceExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
testCompleteExecutorService();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void testCompleteExecutorService() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
final List<Callable<Integer>> callableList = Arrays.asList(
() -> {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(200);
System.out.println("Thread 10 finished!");
return 10;
},
() -> {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(400);
System.out.println("Thread 20 finished!");
return 20;
}
);
// 参数值为线程池对象.
ExecutorCompletionService<Integer> completionService = new ExecutorCompletionService<>(executorService);
// 提交需要执行的任务.
callableList.stream().forEach(item -> completionService.submit(item));
Future<Integer> future;
// 阻塞的获取任务结果. 但是, 不是等待全部任务完成, 而是, 完成一个任务, 获取一个任务结果.
while ((future = completionService.take()) != null) {
System.out.println(future.get());
}
//因为take阻塞住了,所以你是看不到下面这个打印的
System.out.println("Main is finished!");
}
}
结果:
Thread 10 finished!
10
Thread 20 finished!
20
稍微改一下就可以打印出来了
public class CompletionServiceExample3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
testCompleteExecutorService();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void testCompleteExecutorService() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
final List<Callable<Integer>> callableList = Arrays.asList(
() -> {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(200);
System.out.println("Thread 10 finished!");
return 10;
},
() -> {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(400);
System.out.println("Thread 20 finished!");
return 20;
}
);
// 参数值为线程池对象.
ExecutorCompletionService<Integer> completionService = new ExecutorCompletionService<>(executorService);
// 提交需要执行的任务.
callableList.stream().forEach(item -> completionService.submit(item));
int taskCount = callableList.size();
for (int i = 0; i < taskCount; i++) {
Integer result = completionService.take().get();
System.out.println(result);
}
//
System.out.println("Main is finished!");
//记得关闭线程池
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
结果:
Thread 10 finished!
10
Thread 20 finished!
20
Main is finished!
Process finished with exit code 0
按完成顺序获取结果验证
public class CompletionServiceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//开启3个线程
ExecutorService exs = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
try {
int taskCount = 10;
// 结果集
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// 1.定义CompletionService
CompletionService<Integer> completionService = new ExecutorCompletionService<Integer>(exs);
// 2.添加任务
for(int i=0;i<taskCount;i++){
completionService.submit(new Task(i+1));
}
// 3.获取结果
for(int i=0;i<taskCount;i++){
Integer result = completionService.take().get();
list.add(result);
}
System.out.println("list="+list);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭线程池
exs.shutdown();
}
}
static class Task implements Callable<Integer> {
Integer i;
public Task(Integer i) {
super();
this.i=i;
}
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
if(i==5) {
Thread.sleep(5000);
}else{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
System.out.println("线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"任务i="+i+",执行完成!");
return i;
}
}
}
控制台输出:
线程:pool-1-thread-2任务i=2,执行完成!
线程:pool-1-thread-3任务i=3,执行完成!
线程:pool-1-thread-1任务i=1,执行完成!
线程:pool-1-thread-4任务i=4,执行完成!
线程:pool-1-thread-1任务i=8,执行完成!
线程:pool-1-thread-4任务i=9,执行完成!
线程:pool-1-thread-2任务i=6,执行完成!
线程:pool-1-thread-3任务i=7,执行完成!
线程:pool-1-thread-1任务i=10,执行完成!
线程:pool-1-thread-5任务i=5,执行完成!
list=[2, 3, 1, 4, 8, 9, 6, 7, 10, 5]
Process finished with exit code 0
CompleableFuture(重要,很常用)
为什么会出现CompletableFuture?
1、使用Future获得异步执行结果时,要么调用阻塞方法get(),要么轮询看isDone()是否为true,这两种方法都不是很好,因为主线程也会被迫等待。
2、从Java 8开始引入了CompletableFuture,它针对Future做了改进,可以传入回调对象,当异步任务完成或者发生异常时,自动调用回调对象的回调方法。
优点:
- 可以利用结果进行级联的执行
- 支持callback会自动回调给调用者
- 执行一批任务时,可以按照任务执行的顺序,获得结果
- 可以并行的获取结果,只拿最先获取的结果级联的执行
简介及注意点
1、CompletableFuture相当于是Future和ExecutorService的结合体,CompleableFuture依然是对Executor的封装,看构造函数的源码,可以知道一般情况下会创建一个ForkJoinPool,同时ThreadFactory会设置为守护线程。这就意味着:一旦主线程结束,线程池就会关闭。。可能导致回调函数还未执行, 便停止了。
如下:
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).whenComplete((v,t)->{
System.out.println("Done");
});
Thread.currentThread().join();
}
}
控制台输出:
Done
2、可以改为此方法runAsync(Runnable, Executors), 让线程池去去管理线程. 不会跟随调用线程消失; 但是, 需要注意关闭线程池.
public static void testrunAsync() {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("starting");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("end!");
}, threadPool).whenComplete((v, t) -> {
System.out.println("Finished!");
});
System.out.println("All finished!");
threadPool.shutdown();
}
控制台输出:
starting
All finished!
end!
Finished!Process finished with exit code 0
构造CompleableFuture
创建CompleableFuture不建议使用构造方法,而是使用静态的工厂方法构建。
public static CompletableFuture<Void> allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs)
public static CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs)
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> completedFuture(U value)
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable,Executor executor)
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)
allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs):这个方法会返回一个全新的CompletableFuture,传递进去的所有CompletableFuture执行完才算是执行完成。anyOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs):这个方法会返回一个全新的CompletableFuture,只要传递进去的有一个CompletableFuture执行完,就算是执行完成completedFuture(U value):可以假设一个执行出了一个结果,进行下面的级联操作。runAsync:异步的执行Runnable,没有返回值。supplyAsync:异步的执行Supplier实例,会有返回值。
runAsync
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable,Executor executor)
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)
特点就是没有返回值,并且参数是Runnable。比一般的提交一个Runnable相比,可以更加灵活点使用,级联、并联等操作
举例:
public class Test_runAsync {
public static ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("main....start....");
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("运行结果:" + i);
}, executor);
//通过前面的睡眠5秒,也可以验证出,shutdown会处理已经在阻塞队列里的
executor.shutdown();
}
}
结果:
main....start....
当前线程:12
运行结果:5
Process finished with exit code 0
supplyAsync
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)
需要给supplyAsync提供一个Supplier
举例:
public class Test_supplyAsync {
public static ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
System.out.println("main....start....");
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
int i = 10 / 0;
System.out.println("运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, executor).whenComplete((res, excption) -> { //虽然能得到异常信息,但是没法修改返回数据
System.out.println("异步任务成功完成了...结果是:" + res + ";异常信息是" + excption);
}).exceptionally(throwable -> { //可以感知异常,同时返回默认值
return 10;
}); //成功以后干啥事
System.out.println("future获取结果:" + future.get());
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
int i = 10 / 4;
System.out.println("运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, executor).handle((res, thr) -> {
if (res != null) {
return res * 2;
}
if (thr != null) { //异常不等于空了,就返回0
return 0;
}
return 0;
});
System.out.println("future1获取结果:" + future1.get());
executor.shutdown();
}
}
结果:
main....start....
当前线程:pool-1-thread-1
异步任务成功完成了...结果是:null;异常信息是java.util.concurrent.CompletionException: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
future获取结果:10
当前线程:pool-1-thread-2
运行结果:2
future1获取结果:4
Process finished with exit code 0
anyOf
public static CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs)
举例:
public class Test_anyOf {
public static ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
CompletableFuture<String> futureImg = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("查询商品的图片信息");
return "hello.jpg";
},executor);
CompletableFuture<String> futureAttr = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("查询商品的属性");
return "黑色+256G";
},executor);
CompletableFuture<String> futureDesc = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("查询商品的介绍");
return "华为";
},executor);
/**
* 1、因为anyOf是等待最早的一个CompletableFuture就能结束,所以返回值是最早执行完的那个任务。
* 2、直接通过原来的future.get()可能会有空指针异常
*/
CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf = CompletableFuture.anyOf(futureImg, futureAttr, futureDesc);
anyOf.get();//等待所有结果完成
System.out.println("最早完成的任务返回值为:"+anyOf.get());
executor.shutdown();
}
}
结果:
查询商品的介绍
最早完成的任务返回值为:华为
查询商品的图片信息
查询商品的属性
这个例子中,前两个CompletableFuture都睡了两秒,所以执行最快的肯定是第三个,从结果中也得到了验证。
需要注意一点,虽然是异步的从一个地方取值,但是其他任务依然会执行完成,而并非不再执行了。
allOf
public static CompletableFuture<Void> allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs)
public class Test_allOf {
public static ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<String> futureImg = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("查询商品的图片信息");
return "hello.jpg";
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<String> futureAttr = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("查询商品的属性");
return "黑色+256G";
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<String> futureDesc = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("查询商品的介绍");
return "华为";
}, executor);
System.out.println("等待Future返回------");
//因为allOf是等待所有CompletableFuture完成才能结束,所以没有返回值,直接通过原来的future.get()就一定会有返回值
CompletableFuture<Void> allOf = CompletableFuture.allOf(futureImg, futureAttr, futureDesc);
System.out.println("最终得到的结果:" + futureImg.get() + "=>" + futureAttr.get() + "=>" + futureDesc.get());
executor.shutdown();
}
}
结果:
等待Future返回------
查询商品的图片信息
查询商品的介绍
查询商品的属性
最终得到的结果:hello.jpg=>黑色+256G=>华为
Process finished with exit code 0
组合方法
组合两个任务,同时处理两个结果
public <U> CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBoth(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,
BiConsumer<? super T,? super U> action)
public <U> CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,
BiConsumer<? super T,? super U> action)
public <U> CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,
BiConsumer<? super T,? super U> action,
Executor executor)
举例:
public class Test_Accept {
public static ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "我是任务1");
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "我是任务2");
completableFuture1.thenAcceptBothAsync(completableFuture2, (s, i) -> {
System.out.println(s + "==>" + i);
}, executor);
executor.shutdown();
}
}
结果:
我是任务1==>我是任务2
Process finished with exit code 0
分析
- 可以看出是两个任务组合,然后同时将两个结果一起处理
组合两个任务,任务完成后做的操作
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterBoth(CompletionStage<?> other,
Runnable action)
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,
Runnable action)
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,
Runnable action)
当两个任务任意一个执行完成后,执行一个操作
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterEither(CompletionStage<?> other,
Runnable action)
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,
Runnable action)
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,
Runnable action,Executor executor))
举例
public class Test_runAfterEither {
public static ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("我是任务1");
return "a";
},executor);
CompletableFuture<Void> future = completableFuture.runAfterEitherAsync(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("我是任务2");
return "b";
}),
() -> System.out.println("两个任务执行完,我才执行"),executor);
System.out.println("end");
executor.shutdown();
}
}
结果:
我是任务1
我是任务2
end
两个任务执行完,我才执行
Process finished with exit code 0
组合两个任务,处理后,返回一个结果
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombine(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,
BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn)
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,
BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn)
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,
BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn,, Executor executor)
举例
public class Test_thenCombine {
public static ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "a");
CompletableFuture<Boolean> future = completableFuture.thenCombineAsync(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 100),
(s, i) -> {
System.out.println("s: " + s + " , i : " + i);
return true;
}, executor);
System.out.println(future.get());
executor.shutdown();
}
}
结果:
s: a , i : 100
true
Process finished with exit code 0
第一个任务的输出是第二个任务的输入
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenCompose(Function<? super T,? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T,? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T,? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn, Executor executor)
相当于一次级联操作
举例:
public class Test_thenCompose {
public static ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
/**
* public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T,? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn, Executor executor)
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "我是任务1");
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "我是任务2");
CompletableFuture<String> future = completableFuture1.thenComposeAsync(s -> completableFuture2, executor);
System.out.println(future.get());
executor.shutdown();
}
}
结果:
我是任务2
Process finished with exit code 0
中转方法
有返回值
当执行完成时执行的操作
public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action)
public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action)
public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action, Executor executor)
举例
public class Test_whenComplete {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello");
CompletableFuture<String> future = completableFuture.whenComplete((v, t)
-> {
System.out.println(v + " World !");
//这个t是Throwable,只有报错了才会打印
System.out.println(t);
});
System.out.println("future:" + future.get());
Thread.currentThread().join();
}
}
结果
Hello World !
Hello
分析
-
当执行完成时执行的回调方法
-
该方法会接收执行的结果以及异常
-
回调完成会,会把原来任务执行的结果传递回去
-
whenCompleteAsync是异步的;whenComplete是同步的,会卡住主线程
-
需要传递一个
BiConsumer接口,如下所示:public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action)l;
public interface BiConsumer<T, U> {
void accept(T t, U u);
}
- T是执行的结果,U是执行时产生的异常
级联操作
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn,Executor executor)
举例
public class Test_thenApplyAsync {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello");
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = completableFuture.thenApplyAsync(t -> {
String s = t + " World !";
System.out.println(s);
return s.length();
});
System.out.println(future.get());
Thread.currentThread().join();
}
}
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn);
public interface Function<T, R> {
R apply(T t);
}
结果
Hello World !
13
Process finished with exit code -1
分析
- 是一个级联操作,即拿着上个任务的结果,做下个任务,同时返回一个新的结果
处理结果的操作
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handle(BiFunction<? super T,Throwable,? extends U> fn)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T,Throwable,? extends U> fn)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T,Throwable,? extends U> fn,Executor executor)
举例
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello");
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = completableFuture.handleAsync((s,t) -> {
String aaa = t + " World !";
System.out.println(aaa);
return aaa.length();
});
System.out.println(future.get());
Thread.currentThread().join();
}
}
结果:
Hello World !
13
分析:
- 相比于
whenComplete返回值可以自己处理,相当于一次级联 - 相比于
thenApply,可以处理异常
无返回值
处理结果
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action)
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action)
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action,Executor executor)
举例
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello");
CompletableFuture<Void> future = completableFuture.thenAccept(t -> {
String aaa = t + " World !";
System.out.println(aaa);
});
System.out.println(future.get());
Thread.currentThread().join();
}
}
结果
Hello World !
null
分析
- 相当于一次级联,但是没有返回值
执行完全部任务
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action)
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action)
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action,Executor executor)
分析
- 相较
thenAccept,不处理任务的执行结果
终结方法
处理异常
public CompletableFuture<T> exceptionally(Function<Throwable,? extends T> fn)
public class Test_exceptionally {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int a = 1 / 0;
return "World ";
});
completableFuture.exceptionally(Throwable::getMessage).thenAccept(t -> {
System.out.println(t);
});
Thread.currentThread().join();
}
}
结果:
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
Process finished with exit code -1
立马获取结果
public T getNow(T valueIfAbsent)
举例
public class Test_getNow {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "World";
});
String now = completableFuture.getNow("Hello");
System.out.println(now);
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());
Thread.currentThread().join();
}
}
结果
Hello
World
Process finished with exit code -1
分析
- 如果结果完成返回结果,如果未完成,返回传入进去的值
判断结果是否完成,如果未完成则赋予结果
public boolean complete(T value)
判断结果是否完成,如果未完成返回异常
public boolean completeExceptionally(Throwable ex)
后续获取结果会产生异常
public void obtrudeException(Throwable ex)
总结
thenAccept()处理正常结果;exceptionally()处理异常结果;thenApplyAsync()用于串行化另一个CompletableFuture;anyOf()和allOf()用于并行化多个CompletableFuture。
参考:
《Java并发编程之美》
https://www.cnblogs.com/yuandengta/p/12887361.html