前言
学习数据结构,二叉树是一大难点,也是一大重点,小伙伴们和我一起看看二叉树的知识吧!
本文代码是Java。
目录
前言
一、什么是二叉树
二、二叉树的遍历
(一)前序遍历
(二)中序遍历
(三)后序遍历
(四)层序遍历
(五)依据前序遍历和中序遍历求二叉树
(六)依据中序遍历和后序遍历求二叉树
结语
一、什么是二叉树
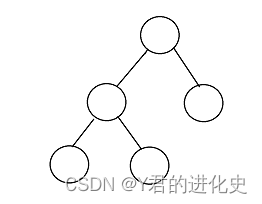
二叉树是指只有一个根节点并且只有两个孩子节点的树。
例如:
二叉树中有两种特殊的二叉树,分别是满二叉树和完全二叉树。
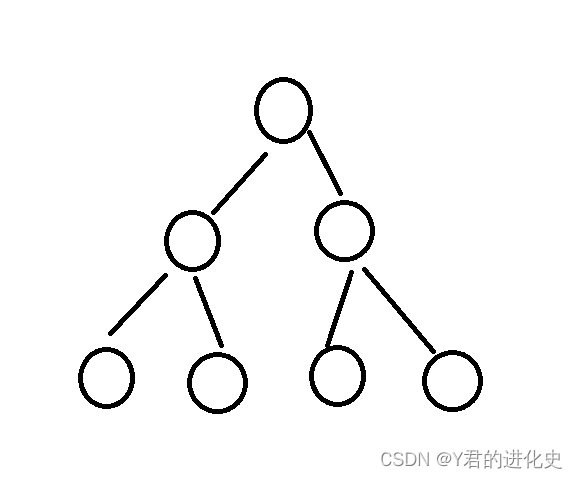
- 满二叉树:
一个二叉树,如果每一个层的结点数都达到最大值,则这个二叉树就是满二叉树。
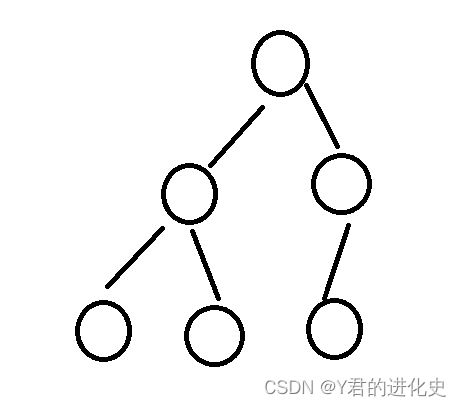
2.完全 二叉树:
一棵深度为k的有n个结点的二叉树,对树中的结点按从上至下、从左到右的顺序进行编号,如果编号为i(1≤i≤n)的结点与满二叉树中编号为i的结点在二叉树中的位置相同,则这棵二叉树称为完全二叉树。
注意事项:
- 一棵n个结点的树有n-1条边;
- 满二叉树的层数为k,则结点总数为(2^k)-1;
- 若根节点的层数为1,则非空二叉树的第i层最多(2^(i-1))-1个结点;
- 叶子节点n0,度为2的结点n2,则n0=n2+1,任何二叉树都满足这个特性;
- 具有n个结点的完全二叉树的深度k为log2(n+1)向上取整;
- 对于完全二叉树,
- 当根节点为0时,已知父节点为i,则左孩子节点为2i+1,右孩子节点为2i+2;
- 当根节点为1时,已知父节点为i,则左孩子节点为2i,右孩子节点为2i+1;
二、二叉树的遍历
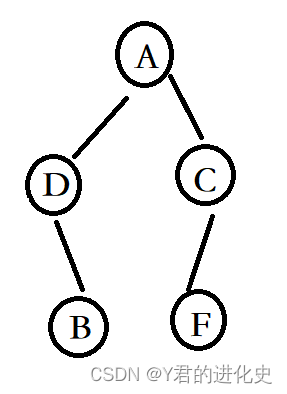
以该二叉树为例子:
(一)前序遍历
前序遍历始终遵守 根节点 -> 左节点 -> 右节点的规律;
例如此二叉树通过前序遍历得出的顺序是:ADBCF.
144. 二叉树的前序遍历 - 力扣(Leetcode)
递归版本:
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
func(root);
return list;
}
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public void func(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return;
}
list.add(root.val);
func(root.left);
func(root.right);
}
}非递归版本:
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode tmp = null;
while(!stack.empty() || root!=null){
while(root != null){
stack.push(root);
list.add(root.val);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
root = root.right;
}
return list;
}
}(二)中序遍历
中序遍历始终遵守 左节点 -> 根节点 -> 右节点的规律;
例如此二叉树通过中序遍历得出的顺序是:DBAFC.
94. 二叉树的中序遍历 - 力扣(Leetcode)
递归版本:
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
func(root);
return list;
}
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public void func(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return;
}
func(root.left);
list.add(root.val);
func(root.right);
}
}非递归版本:
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
while(!stack.empty() || root!=null) {
while(root != null){
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
list.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
return list;
}
}(三)后序遍历
后序遍历始终遵守 左节点 -> 右节点 -> 根节点 的规律;
例如此二叉树通过后序遍历得出的顺序是:BDFCA.
145. 二叉树的后序遍历 - 力扣(Leetcode)
递归版本:
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
func(root);
return list;
}
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public void func(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return;
}
func(root.left);
func(root.right);
list.add(root.val);
}
}非递归版本:
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode tmp = null;
while(!stack.empty() || root != null){
while(root != null){
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
if (root.right == null || root.right == tmp) {
list.add(root.val);
tmp = root;
root = null;
} else {
stack.push(root);
root = root.right;
}
}
return list;
}
}(四)层序遍历
层序遍历始终遵守 从根节点开始遍历,一层一层往下遍历 的规律;
例如此二叉树通过层序遍历得出的顺序是:ADCBF.
102. 二叉树的层序遍历 - 力扣(Leetcode)
代码:
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
List<List<Integer>> list = new LinkedList<>();
if(root != null){
queue.offer(root);
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
List<Integer> list1 = new LinkedList<>();
int size1 = queue.size();
while(size1-- > 0){
root = queue.poll();
list1.add(root.val);
if(root.left != null){
queue.offer(root.left);
}
if(root.right != null){
queue.offer(root.right);
}
}
list.add(list1);
}
return list;
}
}(五)依据前序遍历和中序遍历求二叉树
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 - 力扣(Leetcode)
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
if(inorder == null){
return null;
}
return buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder, 0, inorder.length-1);
}
int pre = 0;
public TreeNode buildTreeChild(int[] preorder, int[] inorder, int form, int end){
if(form > end) return null;
//if(pre >= preorder.length) return null;
TreeNode tmp = new TreeNode(preorder[pre]);
int i = findTree(inorder, preorder[pre],form,end);
pre++;
tmp.left = buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder, form, i-1);
tmp.right = buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder, i+1, end);
return tmp;
}
public int findTree(int[] inorder,int k, int index, int end) {
for(int i = index; i<= end; i++){
if(inorder[i] == k){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}(六)依据中序遍历和后序遍历求二叉树
106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 - 力扣(Leetcode)
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
if(inorder.length == 1)
return new TreeNode(inorder[0]);
return buildTreeChild(inorder, postorder, 0, inorder.length-1, postorder.length-1);
}
int i = 0;
public TreeNode buildTreeChild(int[] inorder, int[] postorder, int form, int end, int len){
if(form > end) return null;
if(i > len) return null;
TreeNode tmp = new TreeNode(postorder[len-i]);
int index = findTree(inorder, postorder[len-i],form,end);
i++;
tmp.right = buildTreeChild(inorder, postorder, index+1, end, len);
tmp.left = buildTreeChild(inorder, postorder, form, index-1, len);
return tmp;
}
public int findTree(int[] inorder, int key, int form, int end){
for(int i = form; i <= end; i++){
if(inorder[i] == key)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
}结语
关于二叉树的知识点还有很多,例如红黑树、AVL树……
我们下期再见!
这篇博客如果对你有帮助,给博主一个免费的点赞以示鼓励,欢迎各位🔎点赞👍评论收藏⭐,谢谢!!!