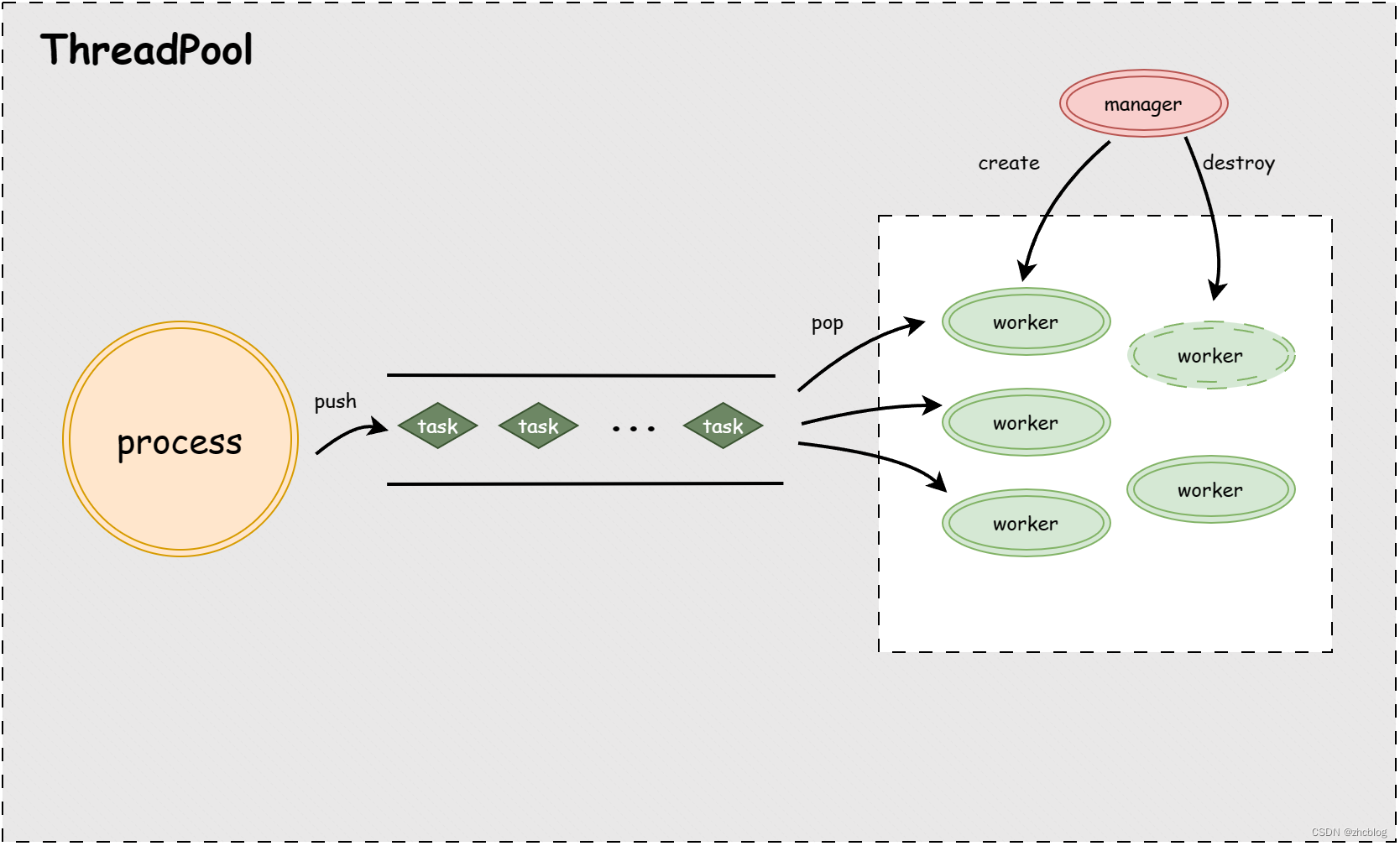
一、线程池介绍
1)应用场景
当并发数很多的时候,并且每个线程执行时间很短的任务,这样就会频繁创建线程,而这样的频繁创建和销毁线程会大大降低系统的执行效率。对于这种场景我们可以使用线程池来复用之前创建的线程,降低线程的频繁创建和销毁工作,达到提高执行效率的目的。
2)线程池原理
线程池使用者往线程池任务队列里面添加任务,线程池会根据任务的多少来自动创建或销毁工作线程取执行任务,即当任务数量比较多而线程池比较少处于忙不过来的状态时,线程池就会自动创建线程,而当仍务数量比较少而空闲线程比较多时,线程池就会自动销毁一部分空闲线程。其中任务队列、线程池使用者和工作线程组成一个生产者消费者模型,线程池使用者(消费者)检查队列已满就阻塞,否则就向任务队列添加任务并通知工作线程(消费者)取任务执行,而工作线程(消费者)取任务之后也会向线程池使用者(生产者)发送通知解阻塞。
3)线程池结构
线程池由任务队列、工作线程和管理线程三部分组成,他们的所用分别如下。
- 任务队列:
- 负责保存要执行的任务(一般每个任务就是一个回调函数);
- 线程池使用者(生产者)往任务队列里面添加任务,并通知工作线程(消费者)取任务执行;
- 工作线程(消费者)从任务队列里面获取到任务后,需要把该任务从队列中删除;
- 工作线程:
- 负责执行任务队列里面的任务;
- 当任务队列没有任务时,工作线程便自动睡眠防止占用CPU资源;
- 当由任务时唤醒工作线程,从队列中取任务执行(从队列中取出任务后,如果生产者此时阻塞的话可以通知生产者解阻塞);
- 管理线程:
- 负责控制工作线程的数量;
- 当空闲的工作线程数量比较多时,就销毁一部分线程;
- 当队列任务比较多而工作线程比较少时,新创建一部分线程;
二、程序实现
1)C语言实现
threadPool.h
#ifndef _THREAD_POOL_
#define _THREAD_POOL_
typedef struct ThreadPool ThreadPool;
// 创建并初始化线程池
ThreadPool* threadPoolCreate(int queueSize, int minNum, int maxNum);
// 销毁线程池
void threadPoolDestory(ThreadPool* pool);
// 往线程池添加任务
int threadPoolAdd(ThreadPool* pool, void (*handler)(void* arg), void* arg);
// 获取线程池当前工作线程数
int threadPoolWorkNum(ThreadPool* pool);
// 获取线程池当前存活线程数
int threadPoolLiveNum(ThreadPool* pool);
#endif // _THREAD_POOL_
threadPool.c
#include "threadPool.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <error.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define CHAGNUM 4
void* worker(void *arg);
void* manager(void *arg);
void threadExit(ThreadPool* pool);
typedef struct Task {
void (*handler)(void* arg);
void* arg;
}Task;
struct ThreadPool {
Task* taskQ;
int qCapacity;
int qSize;
int qFront;
int qBack;
pthread_t manageID;
pthread_t* workIDs;
int maxNum; // 最大线程数量
int minNum; // 最小线程数量
int workNum; // 正在执行任务的工作线程数量
int liveNum; // 当前已创建的的工作线程数量
int exitNum; // 需要销毁退出的线程数量
pthread_mutex_t mutexPool;
pthread_mutex_t mutexWork; // 锁workNum变量
pthread_cond_t hasTask; // 任务队列是否有任务
pthread_cond_t isFull; // 任务队列是否已满
int isDestory; // 线程池是否销毁
};
ThreadPool* threadPoolCreate(int queueSize, int minNum, int maxNum)
{
int i, res = 0;
// 创建线程池对象
ThreadPool* tPool = (ThreadPool*)malloc(sizeof(struct ThreadPool));
if (tPool == NULL) {
perror("tPool malloc:");
goto err;
}
// 创建任务队列
tPool->taskQ = (Task*)malloc(sizeof(struct Task) * queueSize);
if (tPool->taskQ == NULL) {
perror("taskQ malloc:");
goto err;
}
tPool->qSize = 0;
tPool->qCapacity = queueSize;
tPool->qFront = tPool->qBack = 0;
// 创建存储工作线程ID的数组
tPool->workIDs = (pthread_t*)malloc(sizeof(pthread_t) * maxNum);
if (tPool->workIDs == NULL) {
perror("workIDs malloc:");
goto err;
}
memset(tPool->workIDs, 0, sizeof(pthread_t) * maxNum);
tPool->maxNum = maxNum;
tPool->minNum = minNum;
tPool->workNum = 0;
tPool->liveNum = minNum;
tPool->exitNum = 0;
tPool->isDestory = 0;
// 初始化互斥量和条件变量
if (pthread_mutex_init(&tPool->mutexPool, NULL) != 0 ||
pthread_mutex_init(&tPool->mutexWork, NULL) != 0 ||
pthread_cond_init(&tPool->isFull, NULL) != 0 ||
pthread_cond_init(&tPool->hasTask, NULL) != 0) {
printf("mutex or cond init fail...\n");
goto err;
}
// 创建工作线程
for (i = 0; i < minNum; i++) {
res = pthread_create(&tPool->workIDs[i], NULL, worker, tPool);
if (res != 0) {
printf("thread create failed for worker, errno: %d, idx: %d\n", res, i);
goto err;
}
}
// 创建管理线程
res = pthread_create(&tPool->manageID, NULL, manager, tPool);
if (res != 0) {
printf("thread create failed for manager, errno: %d\n", res);
goto err;
}
return tPool;
err:
if (tPool && tPool->taskQ) {
free(tPool->taskQ);
tPool->taskQ = NULL;
}
if (tPool && tPool->workIDs) {
free(tPool->workIDs);
tPool->workIDs = NULL;
}
if (tPool) {
free(tPool);
}
return NULL;
}
void* worker(void *arg)
{
Task task;
ThreadPool* pool = (ThreadPool*)arg;
while(1) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool);
// 队列为空就阻塞当前线程,避免占用CPU
while(pool->qSize == 0 && !pool->isDestory) {
pthread_cond_wait(&pool->hasTask, &pool->mutexPool);
// 减少空闲线程
if (pool->exitNum > 0) {
pool->exitNum--;
if (pool->liveNum > pool->minNum) {
pool->liveNum--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
threadExit(pool);
}
}
}
// 销毁线程池
if (pool->isDestory) {
pool->liveNum--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
threadExit(pool);
}
// 取一个任务执行
task.arg = pool->taskQ[pool->qFront].arg;
task.handler = pool->taskQ[pool->qFront].handler;
pool->qFront = (pool->qFront + 1) % pool->qCapacity;
pool->qSize--;
pthread_cond_signal(&pool->isFull);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexWork);
pool->workNum++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexWork);
task.handler(task.arg);
if (task.arg) { // 释放资源 或者 用户在回调函数中释放这里就不释放了
free(task.arg);
task.arg = NULL;
}
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexWork);
pool->workNum--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexWork);
}
return NULL;
}
void* manager(void *arg)
{
int i = 0, incNum = CHAGNUM;
ThreadPool* pool = (ThreadPool*)arg;
while(!pool->isDestory) {
sleep(3);
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool);
int queueSize = pool->qSize;
int liveNum = pool->liveNum;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexWork);
int workNum = pool->workNum;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexWork);
// 数据处理不过来要增加线程
if (queueSize > liveNum) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool);
for(i = 0; i < pool->maxNum && incNum > 0; i++) {
if (pool->workIDs[i] == 0) {
pthread_create(&pool->workIDs[i], NULL, worker, pool);
incNum--;
pool->liveNum++;
printf("new thread %ld, liveNum = %d, workNum = %d\n",
pool->workIDs[i], pool->liveNum, pool->workNum);
}
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
}
// 空闲线程多了要销毁
if(workNum * 2 < liveNum &&
liveNum - CHAGNUM > pool->minNum) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool);
pool->exitNum = CHAGNUM;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
for (i = 0; i < CHAGNUM; i++) {
pthread_cond_signal(&pool->hasTask);
}
}
}
return NULL;
}
int threadPoolAdd(ThreadPool* pool, void (*handler)(void* arg), void* arg)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool);
while(pool->qSize == pool->qCapacity && !pool->isDestory) {
pthread_cond_wait(&pool->isFull, &pool->mutexPool);
}
if (pool->isDestory) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
return -1;
}
pool->taskQ[pool->qBack].arg = arg;
pool->taskQ[pool->qBack].handler = handler;
pool->qBack = (pool->qBack + 1) % pool->qCapacity;
pool->qSize++;
pthread_cond_signal(&pool->hasTask); // 通知空闲的工作线程取任务执行
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
return 0;
}
void threadExit(ThreadPool* pool)
{
int i;
pthread_t tid = pthread_self();
for(i = 0; i < pool->maxNum; i++) {
if (pool->workIDs[i] == tid) {
pool->workIDs[i] = 0;
break;
}
}
printf("thread %ld exit, liveNum = %d, workNum = %d\n",
tid, pool->liveNum, pool->workNum);
pthread_exit(0);
}
int threadPoolWorkNum(ThreadPool* pool)
{
int workNum;
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexWork);
workNum = pool->workNum;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexWork);
return workNum;
}
int threadPoolLiveNum(ThreadPool* pool)
{
int liveNum;
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool);
liveNum = pool->liveNum;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
return liveNum;
}
void threadPoolDestory(ThreadPool* pool)
{
int i;
if (pool == NULL) {
return;
}
pool->isDestory = 1;
// 销毁管理线程
pthread_join(pool->manageID, NULL);
// 销毁工作线程
for (i = 0; i < pool->maxNum; i++) {
if (pool->workIDs[i] > 0) {
pthread_cond_signal(&pool->hasTask);
}
}
for (i = 0; i < pool->maxNum; i++) {
if (pool->workIDs[i] > 0) {
pthread_join(pool->workIDs[i], NULL);
}
}
pthread_mutex_destroy(&pool->mutexPool);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&pool->mutexWork);
pthread_cond_destroy(&pool->hasTask);
if (pool->workIDs) {
free(pool->workIDs);
pool->workIDs = NULL;
}
if (pool->taskQ) {
free(pool->taskQ);
pool->taskQ = NULL;
}
free(pool);
printf("thread pool destory...\n");
}
main.c
#include "threadPool.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void myTest(void *arg)
{
printf("tid: %ld, num = %d\n", pthread_self(), *(int *)arg);
sleep(3);
}
int main()
{
int i;
ThreadPool *pool = threadPoolCreate(20, 4, 10);
for (i = 0; i < 40; i++) {
int* num = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int));
*num = i;
threadPoolAdd(pool, myTest, num);
}
sleep(10);
threadPoolDestory(pool);
return 0;
}
2)C++实现
threadPool.h
#ifndef _THREADPOOL_H
#define _THREADPOOL_H
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <queue>
struct Task {
void (*handler)(void*);
void* arg = nullptr;
};
class TaskQueue {
public:
TaskQueue();
~TaskQueue();
// 添加任务
void addTask(Task& task);
void addTask(void (*handler)(void*), void* arg);
// 取出任务
Task getTask();
// 获取任务数
inline int getTaskNum();
private:
pthread_mutex_t m_lock;
std::queue<Task> m_que;
};
class ThreadPool {
public:
ThreadPool(int max, int min);
~ThreadPool();
// 添加任务
void addTask(Task task);
// 获取工作线程数
int getWorkNum();
// 获取存活线程数
int getLiveNum();
private:
static void* worker(void* arg);
static void* manager(void* arg);
void threadExit();
private:
TaskQueue m_taskQ;
int m_maxNum;
int m_minNum;
int m_workNum;
int m_liveNum;
int m_exitNum;
static const int m_changeNum = 2;
bool m_isDestory = false;
pthread_t m_managerTid;
pthread_t* m_workTids;
pthread_cond_t m_hasTask;
pthread_mutex_t m_lock; // 锁m_workNUm、m_liveNum、m_exitNum变量
};
#endif // _THREADPOOL_H
threadPool.cpp
#include "threadPool.h"
#include <iostream>
ThreadPool::ThreadPool(int max, int min)
{
int i;
m_maxNum = max;
m_minNum = min;
m_workNum = 0;
m_liveNum = min;
m_exitNum = 0;
if (pthread_cond_init(&m_hasTask, nullptr) != 0
|| pthread_mutex_init(&m_lock, nullptr) != 0) {
std::cout << "cond or mutex init fail..." << std::endl;
return;
}
m_workTids = new pthread_t[m_maxNum];
if(m_workTids == nullptr) {
std::cout << "m_workTids malloc failed..." << std::endl;
}
memset(m_workTids, 0, sizeof(pthread_t) * m_maxNum);
// 创建工作线程
for (i = 0; i < m_minNum; i++) {
pthread_create(&m_workTids[i], nullptr, worker, this);
std::cout << "worker thread " << m_workTids[i] << " created" << std::endl;
}
// 创建管理线程
pthread_create(&m_managerTid, nullptr, manager, this);
}
ThreadPool::~ThreadPool()
{
m_isDestory = true;
pthread_join(m_managerTid, nullptr);
pthread_cond_broadcast(&m_hasTask);
for (int i = 0; i < m_maxNum; i++) {
if (m_workTids[i] != 0) {
pthread_join(m_workTids[i], nullptr);
std::cout << "thread i = " << i << " tid = " << m_workTids[i] << " exit..." << std::endl;
m_workTids[i] = 0;
}
}
pthread_mutex_destroy(&m_lock);
pthread_cond_destroy(&m_hasTask);
if (m_workTids) {
delete []m_workTids;
}
std::cout << "liveNum = "<< m_liveNum <<", workNum = "<< m_workNum <<", queSize = " << this->m_taskQ.getTaskNum() << std::endl;
}
void* ThreadPool::worker(void* arg)
{
ThreadPool* pool = static_cast<ThreadPool*>(arg);
while(1) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->m_lock);
while(pool->m_taskQ.getTaskNum() == 0 && !pool->m_isDestory) {
std::cout << "thread " << pthread_self() << " waitting..." << std::endl;
pthread_cond_wait(&pool->m_hasTask, &pool->m_lock);
// 空闲线程退出
if (pool->m_exitNum > 0) {
pool->m_exitNum--;
if(pool->m_liveNum > pool->m_minNum) {
pool->m_liveNum--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->m_lock);
pool->threadExit();
}
}
}
// 销毁线程池
if (pool->m_isDestory) {
pool->m_liveNum--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->m_lock);
pthread_exit(0); // 这里不调用threadExit是让主线程好回收资源
}
// 取任务执行
Task task = pool->m_taskQ.getTask();
pool->m_workNum++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->m_lock);
task.handler(task.arg); // 用户自己取释放arg内存
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->m_lock);
pool->m_workNum--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->m_lock);
}
return nullptr;
}
void* ThreadPool::manager(void* arg)
{
ThreadPool* pool = static_cast<ThreadPool*>(arg);
while(!pool->m_isDestory) {
sleep(3);
int liveNum;
int taskNum;
int workNum;
int i, incNum = pool->m_changeNum;
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->m_lock);
liveNum = pool->m_liveNum;
workNum = pool->m_workNum;
taskNum = pool->m_taskQ.getTaskNum();
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->m_lock);
// 任务太多忙不过来需要创建线程
if(!pool->m_isDestory && taskNum > liveNum && liveNum < pool->m_maxNum) {
for (i = 0; i < pool->m_maxNum && incNum > 0 ; i++) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->m_lock);
if (pool->m_workTids[i] == 0) {
pool->m_liveNum++;
incNum--;
pthread_create(&pool->m_workTids[i], NULL, worker, pool);
std::cout << "new thread " << pool->m_workTids[i] << " created" << std::endl;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->m_lock);
}
}
// 销毁多余的空闲线程
incNum = pool->m_changeNum;
if (!pool->m_isDestory && workNum * 2 < liveNum && liveNum > pool->m_minNum) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->m_lock);
pool->m_exitNum = pool->m_changeNum;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->m_lock);
while (incNum--) {
pthread_cond_signal(&pool->m_hasTask);
}
}
}
return nullptr;
}
void ThreadPool::addTask(Task task)
{
if (m_isDestory) {
return;
}
pthread_mutex_lock(&m_lock);
m_taskQ.addTask(task);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_lock);
pthread_cond_signal(&m_hasTask);
}
void ThreadPool::threadExit()
{
for (int i = 0; i < m_maxNum; i++) {
if (m_workTids[i] == pthread_self()) {
std::cout << "thread " << m_workTids[i] << " exit..." << std::endl;
pthread_mutex_lock(&m_lock);
m_workTids[i] = 0;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_lock);
pthread_exit(0);
}
}
}
int ThreadPool::getWorkNum()
{
int workNum = 0;
pthread_mutex_lock(&m_lock);
workNum = m_workNum;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_lock);
return m_workNum;
}
int ThreadPool::getLiveNum()
{
int liveNum = 0;
pthread_mutex_lock(&m_lock);
liveNum = m_liveNum;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_lock);
return liveNum;
}
TaskQueue::TaskQueue()
{
pthread_mutex_init(&m_lock, NULL);
}
TaskQueue::~TaskQueue()
{
pthread_mutex_destroy(&m_lock);
}
void TaskQueue::addTask(Task& task)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&this->m_lock);
m_que.push(task);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&this->m_lock);
}
void TaskQueue::addTask(void (*handler)(void*), void* arg)
{
Task task;
task.arg = arg;
task.handler = handler;
pthread_mutex_lock(&this->m_lock);
m_que.push(task);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&this->m_lock);
}
Task TaskQueue::getTask()
{
Task task;
pthread_mutex_lock(&this->m_lock);
if (m_que.size() > 0) {
task = m_que.front();
m_que.pop();
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&this->m_lock);
return task;
}
inline int TaskQueue::getTaskNum()
{
return this->m_que.size();
}
main.cpp
#include "threadPool.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void my_test(void* arg)
{
int num = *(int*)arg;
cout << "thread id: " << pthread_self() << " , num: " << num << endl;
sleep(1);
delete (int*)arg;
}
int main()
{
ThreadPool* pool = new ThreadPool(10, 4);
sleep(1);
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
Task task;
task.handler = my_test;
task.arg = new int(i);
pool->addTask(task);
}
sleep(10);
delete pool;
return 0;
}