目录
一、5G/NR
1、 快速参考(Quick Reference)
2、5G Success
3、5G Challenges
4、Qualcomm Videos
二、PHY and Protocol
1、Frame Structure
2、Numerology
3、Waveform
4、Frequency Band
5、BWP
6、Synchronization
7、Beam Management
8、CSI Framework
9、Channel Mapping
10、CORESET
11、DCI
12、SLIV
13、UCI/PUCCH
14、Reference Signal
15、MAC
16、RLC
17、PDCP
18、SS Block
19、Scheduling
20、MIB / SIB
21、RACH
22、RRC Overview
23、RrcReconfiguration
24、NSA/ENDC
25、SA/Initial Attach
26、UE Capability
27、Paging
28、 Power Control
29、MIMO Config. DL
30、MIMO Config. UL
三、NAS / Core
1、Registration
2、Network Slice
3、Core Architecture
四、Misc.
1、Field Test
2、OTA(Over The Air)
3、Release 16
4、Release 17
5、Massive MIMO ?
6、WhyMassiveMIMO ?
7、Propagation Model
一、5G/NR
1、 快速参考(Quick Reference)
1) Pre 5G Chronicles
a、 What has been done/talked before the realization of 5G ?
b、 Time Table/Milestones
2) 4G to 5G Evolution**
3) 4G vs 5G
4) Post-deployment Evolution (Cell Coverage, Test Report)**
5) Post-deployment Challenges
6) 5G Definitions
7) 5G Indication : upperLayerIndication
8) 5GMM
9) 5GSM
10)5QI
11) 5G Release 16 Highlights
12) 5G Release 17 Highlights
13) 5G Release 18 Highlights
14) 5WWC/ATSSS
15) Acronyms
16) Agreed Items
17) AI/ML (Aritificial Intelligence / Machine Learning)
18) AMF
19) Antenna Ports
20) Articles on 5G (Before Deployment)
21) ATSSS/5WWC
22) Beam Failure Recovery
23) Beam Forming
24) Beam Management
25) BWP(Bandwidth Part)
26) BWP Switching
27) Call Process : SA Initial Attach
28) Carrier Aggregation
29) Carrier Bandwidth Part (BWP)
30) Cell Search / SIB1 Decoding
31) Cell Selection
32) Cell Selection Criteria
33) CBG(Code Block Group)
34) Challenges
35) Channel Coding
36) Channel Structure / Channel Mapping
37) Common Search Space(Type 0 PDCCH, RMSI-PDCCH-Config)
38) Common Search Space(Type 1 PDCCH)
39) CoMP
40) ConfiguredScheduling/SPS
41) Converged Connectivity - ATSSS/5WWC
42) Core - Network Interfaces
43) Core - AMF
44) Core - NRF
45) Core - N22 - NSSF
46) Core - SMF
47) Core - UDM
48) Core - N1 Interface
49) Core - N26 Interface
50) Core - N12,N13 - AMF,AUSF,UDM - Authentication
51) Core - N8 - Registration
52) Core - NGAP
53) Core - SCTP
51) Core - GTP
52) CORESET(Parameters, Example)
53) CORESET 0/SIB 1 decoding
54) CPRI
55) CSI Framework
56) CSI Report
57) CSI RS
58) CSI RS Codebook
59) CU/DU Separation
60) Current Activities (Who is doing what ?)
61) DCI
62) Deployment Scenario
63) DFT-s-OFDM
64) DNN / LADN
65) Downlink Preamption
66) DSS (Dynamic Spectrum Sharing)
67) eCPRI
68) EIRP
69) Enhanced Massive MIMO
70) Event and Forum
71) Field Test
72) Frame Structure
73) Frame Structure : Candidate
74) Frequency Domain Position/Resource Block Indexing
75) FR(Frequency Range) / Operating Band
76) FRC (Fixed Reference Channel)
77) General News
78) GSCN
79) HARQ(ACK/NACK)
80) HARQ-ACK Codebook
81) History of 5G (5G before 3GPP)
a、 Activities
b、 Articles/New
c、 Propagation Model
82) IAB (Integraded Access / Backhaul)
83) IP Allocation
84) K0,K1,K2,N1,N2
85) LADN / DNN
86) LTE Interworking (NSA : Non StandAlone)
87) MAC : Overview
88) MAC CE
89) MAC CE : Buffer Status Report
90) MAC CE : C-RNTI
91) MAC CE : Contention Resolution
92) MAC CE : SCell Activation/Deactivation
93) MAC CE : TCI State Indication for UE-specific PDCCH MAC CE
94) MAC CE : TCI States Activation/Deactivation for UE-specific PDSCH MAC CE
95) MAC CE : Timing Advance
96) Massive MIMO : Introduction/Definition
97) Massive MIMO : Motivation (Why We Need it ?)
98) Massive MIMO : FD-MIMO
99) Massive MIMO : MU-MIMO
100) Massive MIMO : Channel Model
a、 Scaling up MIMO : Opportunities and Challenges with Very Large Arrays
b、 Massive MIMO and Small Cells : Improving Energy Efficiency by Optimal Soft-Cell Coordination
c、 Multi-Layer Precoding for Full-Dimensional Massive MIMO Systems
d、 MU-MIMO Channel Estimation
101) Massive MIMO : Reciever Model
102) Massive MIMO : in 3GPP
103) Massive MIMO : Technical Challenges/Further Studies
104) Matlab Toolbox : 5G Library : SS/PBCH Block
105) Matlab Toolbox : 5G Library : PDSCH/DMRS
106) Matlab Toolbox : 5G Library : PUCCH Format 0
107) Matlab Toolbox : 5G Library : PUCCH Format 1
108) Matlab Toolbox : 5G Library : Slot Structure : Downlink / All Channels
109) Matlab Toolbox : 5G Library : Slot Structure : Uplink
110) Matlab Toolbox : 5G Library : PRACH / FR2 (120 Khz)
111) Matlab Toolbox : 5G Library : SRS (120 Khz)
112) Matlab Toolbox : 5G Library : CSI-RS
113) Matlab Toolbox : 5G Library : CSI Codebook
114) Matlab Toolbox : 5G Library : Spectrogram : Downlink (SSB, PDCCH,PDSCH,CSI-RS)
115) Matlab Toolbox : 5G Library : NR Synchronization in TDL Channel
116) Matlab Toobox : 5G Library : NR Synchronization in CDL Channel
117) Max Throughput Estimation
118) MCS/TBS/Code Rate
119) Measurement
120) MIB / SIB
121) Mini Slot
122) MIMO : Downlink
123) MIMO : Uplink
124) mmWave
125) mmWave Antenna on UE
126) N1 mode / S1 mode
127) N1 Interface
128) N2 Interface
129) N8 Interface
130) N22 Interface
131) N26 Interface
132) NAS : 5GMM
133) NAS : 5GSM
134) NAS : Registration / Reject / Reject Cause
135) NAS : PDU Session Establishment
136) NAS : Service Setup
137) NAS : UAC (Unified Access Control)
138) Network Architecture / Network Interfaces
139) Network Architecture / Network Interface - N1
140) Network Slicing
141) New Waveform Cadidate : Introduction
142) New Waveform Candidate : FBMC
143) New Waveform Candidate : f-OFDM
144) New Waveform Candidate : GFDM
145) New Waveform Candidate : UFMC
146) New Waveform Candidate : DFT-s-OFDM
147) NGAP
148) NPN(Non-Public Network)
149) NRF
150) NR Indication : upperLayerIndication
151) NR-Light/RedCap
152) NRU (NR Unlicensed)
153) NTN (Non Terestrial Network)
154) Numerology
155) NWDAF
156) OpenRAN - Overview
157) OpenRAN - Architecture
158) OpenRAN - Where to Split
159) OSI (Other SI) Scheduling
160) OTA(Over The Air) Measurement
161) Paging
162) Parameter Structure : PHY
163) PBCH
164) PBCH DMRS
165) PBCH Decoding Process
166) PCO (Protocol Configuration Option)
167) PDCCH
168) PDCCH Common
169) PDSCH
170) PDSCH AggregationFactor
171) PDSCH DMRS
172) PDSCH PTRS
173) PDSCH/PUSCH Mapping Type (Type A, Type B)
174) PDCP
175) PDU Session Establishment (IP Allocation, QoS)
176) Physical Layer : Beam Management
177) Physical Layer : Frame Structure
178) Physical Layer : Numerology
179) Physical Layer : Pseudo Random Sequence
180) Physical Layer : Reference Signals
181) Physical Layer : SS Block, SS/PBCH
182) Physical Layer : Synchronization
183) Physical Layer : Timing Units
184) Physical Layer : Uplink Transmission Timing
185) Physical Layer : Waveform
186) Physical Layer Signal : PBCH DMRS
187) Physical Layer Signal : PDSCH DMRS
188) Physical Layer Signal : PSS (Primary Synchronization Signal)
189) Physical Layer Signal : SSS (Secondary Synchronization Signal)
190) Pyhsical Layer Channel : PBCH
191) Physical Layer Channel : PDCCH
192) Physical Layer Channel : PDSCH
193) Physical Layer Channel : PUCCH
194) Physical Layer Channel : PUSCH
195) PointA, OffsetToPointA
196) Positioning
197) Power Control
198) Power Definition / Measurement (RSRP, RSRQ, SINR)
199) Power Saving
200) Pre Trial : Overview
a、 Pre Trial : Frame Structure
b、 Pre Trial : Matlab : Frame Structure / Resource Element Mapping
c、 Pre Trial : Physical Signal : PSS
d、 Pre Trial : Physical Signal : SSS
e、 Pre Trial : Physical Signal : ESS
f、 Pre Trial : Physical Signal : BRS
g、 Pre Trial : Physical Signal : BRRS
h、 Pre Trial : Pseudo Random Sequence
i、 Pre Trial : Basic Procedure : Power On Procedure
j、 Pre Trial : RRC : MIB/SIB
k、 Pre Trial : RACH
201) Private Network (LTE)
202) Private Network/NPN(Non-Public Network) (NR)
203) Pseudo Random Sequence
204) Propagation Model
205) Protocol Configuration Option(PCO)
206) PSS (Primary Synchronization Signal)
207) PTRS - PDSCH
208) PUCCH
209) PUSCH AggregationFactor
210) PUSCH Channel Coding and Transmssion Process
211) PUSCH DMRS
212) PUSCH Precoding / Transmission Mode (Codebook vs Non-Codebook based)/UL Transmission Scheme
213) QCL (Quasi Co Location)/TCI
214) QoS / QFI / QRI
215) RACH
216) RACH-2 Step
217) Radio Protocol Architecture
218) RAN Architecture
219) RateMatchPattern
220) Reference Signal
221) RedCap/NR-Light
222) Registration - RegistrationRequest / RegistrationAccept
223) Release 16 Highlights
224) Release 17 Highlights
225) Release 18 Highlights
226) Resource Allocation (Time [K0,K1,K2])
227) Resource Allocation Type (RA Type 0, RA Type 1)
228) Resource Allocation Units (RE, REG, REG Bundle, CCE, Aggregation Level, CORESET)
229) Resource Allocation - Applicable Time Domain Resource Allocation
230) Resource Block Indexing/Frequency Domain Position
231) Resource Grid
232) RLC
233) RMSI-PDCCH-Config/Type 0 PDCCH Common Search Space
234) RNTI
235) RRC CONNECTED <-> INACTIVE Transition
236) RRC Constraints
237) RRC Overview
238) RRC INACTIVE
239) RRC Reconfiguration
240) SCG-Failure
241) Scheduling : Overview
242) Scheduling : Dynamic / L2 Scheduling
243) SDL (Supplimentary Downlink)
244) Security for 5G
245) Security for Cellular Ingeneral
246) Search Space
247) Self-Contained Slot
248) Service Setup
249) SIB 1 decoding
250) Sidelink
251) SLIV
252) Slot Configuration
253) Slot Format Combination
254) SMF
255) Software Defined Network (SDN) : Overview
256) Software Defined Network (SDN) : OpenFlow
257) Split Bearer
258) SPS/ConfiguredScheduling
259) SR(Scheduling Request)
260) SRB(Signaling Radio Bearer)
261) SRS/Antenna Switching
262) SS Block, SS/PBCH
263) SSS (Secondary Synchronization Signal)
264) SUL(Supplementary Uplink)
265) Synchronization
266) TBS Determination
267) TCI/QCL
268) TDD DL/UL Common Configuration(TDD-UL-DL-ConfigCommon)
269) TDD DL/UL Dedicated Configuration(TDD-UL-DL-ConfigDedicated)
270) Technical Challenges
271) Tech Viedos for 5G
272) Test : Equipment : Concept and Idea
273) Test : RF Connection Method
274) Throughput Estimation
275) Time Table (MileStones to 5G)
276) Timing Advance
277) Timing Units
278) TRS (Tracking Reference Signal)
279) Type 0 PDCCH Common Search Space/RMSI-PDCCH-Config
280) Type 1 PDCCH Common Search Space
281) Two Step RACH (2 step RACH)
282) UAC (Unified Access Control)
283) UCI (Uplink Control Information)
284) UDM
285) UE Assistance Information
286) UE Capability
287) UE ID
288) UL Transmission Scheme / PUSCH Precoding / Transmission Mode (Codebook vs Non-Codebook based)
289) URLLC
290) VoNR
291) Wake Up Signal(WUS)
292) Waveform
293) WhitePapers and Forums/Summits (Before 5G Deployment)
294) WUS (Wake Up Signal)
一、5G/NR
1、 快速参考(Quick Reference)
7) 5G Indication : upperLayerIndication(NR Indication : upperLayer Indication)
为了使NR工作,应该保证(guarantee)UE和NW都支持NR能力。也就是说,NW应该知道UE是否支持NR能力,并且UE应该知道NW是否支持NR功能。
对于NW来说,有一种众所周知的机制来判断(figure out)UE是否能够进行NR。它是通过UE capability enquiry and information机制实现的。
那么,UE如何判断NW是否支持NR,尤其是NSA?
UE可以通过检查称为上层指示(upperLayerIndication)的特定(specific)SIB2(LTE SIB2)IE来找出(figure out)它。我知道。。。听起来并不清楚它到底是什么意思。实际上(Practically),这意味(imply)着如果LTE SIB2将upperLayerIndication-r15设置为true,则NW支持ENDC能力。这意味着存在与LTE小区共存(colocate)的NR小区。IE:upperLayerIndication将在未来的版本中指示(indicate)一些其他事情(例如,除了共存NR小区的存在之外),但至少在ENDC环境中,该IE指示共存NR小区存在。
以下是指示5G(NSA)可支持性(supportability)的SIB2的示例。
message c1: systemInformation: {
criticalExtensions systemInformation-r8: {
sib-TypeAndInfo {
sib2: {
.....
plmn-InfoList-r15 {
{
upperLayerIndication-r15 true
}
}
},
For further details, refer to R2-1801529.
8) 5GMM
● 5GMM(5G移动管理:5G Mobility Management)
5G移动管理主要涉及NAS注册过程(registration process),从核心网络接口(core network interface)的角度来看,它主要与 N1/N2 interface相关(be associated with)。5GMM的一些主要功能(functionality)如下(如24.501-5.1.2所述)。
▶ 注册登记(registration)
▶ 注销注册登记(de-registration)
▶ eCall非活动程序 (eCall inactivity procedure)
▶ 连接模式程序 (connected mode procedure)
▷ 网络启动的NAS传输 (network-initiated NAS transport)
▷ 初级身份验证和密钥协商程序 (primary authentication and key agreement procedure)
▷ 安全模式控制 (security mode control)
▷ 通用UE配置更新 (generic UE configuration update)
▷ 识别 (identification)
▷ UE发起的NAS传输 (UE-initiated NAS transport)
▶ 连接管理程序(connection management procedure)
▷ 服务请求(service request)
▷ 寻呼 (paging)
▷ 通知(notification)
● 5GMM状态机(5GMM Statemachine)
5GMM是一个非常复杂的(complicated)过程,24.501中有大约150页描述,如果你直接阅读细节,你很容易迷路(get lost)。我的建议(recommendation)是尽量熟悉(get familiar with)下面的状态机(statemachine),这样你就可以手工绘制状态机,然后根据需要阅读规范。
▶ UE中的5GMM主要状态(5GMM main states in the UE)
UE侧的GMM状态被指定/总结如下。
<24.501图5.1.3.2.1.1.1:5GMM在UE中的主要状态(24.501 Figure 5.1.3.2.1.1.1: 5GMM main states in the UE)>
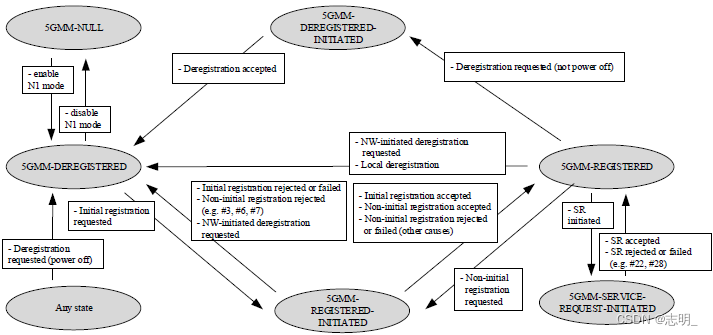
以下是对每个状态的简要描述(brief description)。了解每个状态和转换触发器(transition trigger)的详细信息将有助于您从UE日志(log)中排除(troubleshoot)各种NAS问题。
▷ 5GMM-NULL:此状态表示(represent)UE通电或重置时的初始(initial)状态。在这种状态下,5GS服务在UE中被禁用(be disabled)。在此状态下,不得执行(perform)5GS移动管理(mobility management)功能。UE没有注册(register)到任何5G网络,并且没有在网络中存储UE的上下文(context)。对于移动端接的(mobile-terminated)服务,UE是不可访问(reachable)的。
▷ 5GMM-DEREGISTERED:在此状态下,UE未注册到任何5G网络。尚未建立(establish)5GMM上下文,并且网络不知道UE位置(location),因此(hence)网络无法访问(unreachable)该位置。为了(In order to)建立5GMM上下文,UE应当开始初始注册过程( initial registration procedure)。它要么已关闭(switch off),要么已超出覆盖(coverage)范围,要么由于某种原因已从网络上注销(deregister)。对于移动端接的服务,UE是不可到达的,并且在网络中没有为UE存储上下文。
▷ 5GMM-DEREGISTERED-INITIATED:此状态表示(indicate)UE已启动(initiate)注销过程(deregistration process),但尚未完成。UE正在与网络交换消息以完成注销(deregistration)。
▷ 5GMM-REGISTERD-INITIATED:在此状态下,UE已启动注册过程(registration process),但尚未完成。UE正在与网络交换消息以完成注册。
▷ 5GMM-REGISTRED:此状态表示UE已成功注册到5G网络。在这种状态下,UE可以接收移动端接的服务,并且网络维护(maintain)UE的上下文(context)信息。这种状态意味着UE已经成功地完成了注册过程,并且现在可以利用(utilize)网络服务。
▷ 5GMM-SERVICE-REQUEST-INITIATED:在此状态下,UE已向网络发起服务请求以建立连接。这通常发生(occur)在UE需要接入(access)特定网络服务或资源时(例如,启动(initiate)数据会话(data session)或语音呼叫(voice call))。UE保持(remain)在这种状态,直到服务请求被网络准许(grant)或拒绝(reject)。
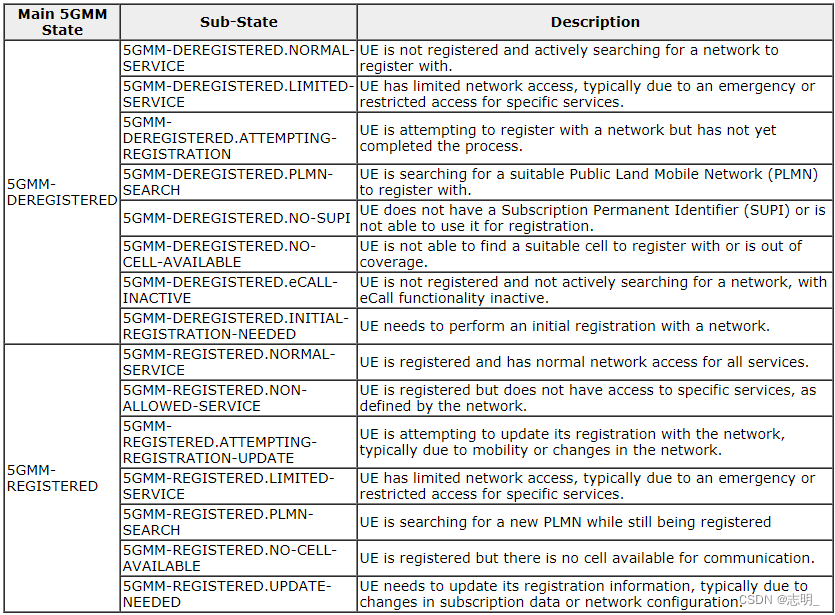
根据(According to)24.501-5.1.3.2.1.3和5.1.3.2.1.4,各种子状态(substatus)定义如下。
▶ 5GMM网络中的主要状态(5GMM main states in the network)
网络侧(on Network side)的GMM状态如下所示。
<24.501图5.1.3.2.3.1.1:5GMM网络中的主要状态(24.501 Figure 5.1.3.2.3.1.1: 5GMM main states in the network)>
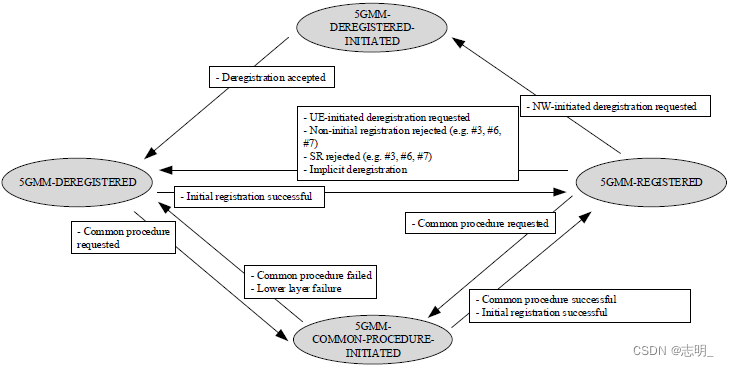
以下是对每个状态的简要描述(brief description )
▷ 5GMM-DEREGISTERED:
i)UE:未注册(register)到网络,无法访问(access)网络服务。
ii)网络:在这种状态下,网络不向UE提供任何服务。网络仍然可以监视(monitor for)来自UE的注册尝试(registration attempt),并且准备(be ready to)好处理任何传入的(incoming)注册请求。如果UE早些时候具有有效注册(valid registration)并且需要到达以进行传入通信,则网络也可以发起(initiate)寻呼(page)。
▷ 5GMM-DEREGISTERED-INITIATED:
i)UE:已启动与网络的注销过程(deregistration process)。
ii)网络:在这种状态下,网络处理注销请求,更新(update)UE的上下文信息,并释放(release)任何分配的(allocated)资源。如果需要,网络还可以确认注销过程的完成或启动(initiate)重新注册(re-registration)过程。
▷ 5GMM-COMMON-PROCEDURE-INITIATED:
i)UE:与网络启动了一个或多个通用过程(common procedure)。
ii)网络:在这种状态下,网络处理UE对常见过程的请求,如注册、服务请求和寻呼(page)。网络还可以发起(initiate)这些过程,分配(allocate)资源,并管理UE的上下文信息。此外(Additionally),网络可以处理(handle)在这些过程中可能发生(occur)的任何错误或异常(exception)。
▷ 5GMM-REGISTERED:
i)UE:已成功注册到网络,可以访问网络服务。
ii)网络:在这种状态下,网络向注册的UE提供服务,例如数据和语音通信。当UE在不同网络区域之间移动时,网络还可以通过更新其注册(registration)来管理UE的移动性(mobility)。网络可以发起(initiate)诸如定期(periodic)注册更新、跟踪区域(tracking area)更新或寻呼之类的过程,以维持(maintain)与UE的连接。此外(Furthermore),网络可以对注册的UE实施(enforce)接入限制(access restriction)、服务质量和安全策略(security policy)。
● GMM处理的NAS信令过程(NAS Signaling Procedures Handled by 5GMM)
以下是5GMM处理的NAS信令signaling(OTA过程)的列表。我认为这些消息(流程)列表将为大多数读者提供更具体的(concrete)想法,因为分析OTA消息将是非常常见的做法(common practice)。我将为每个过程创建单独的注释,并在完成注释时放置链接。。。但不确定完成所有这些需要多长时间,但我会尽量尽早(as early as possible)完成至少5G特定的流程。对于大多数其他程序,我认为您可以应用(apply)您的LTE知识。24.501-8.2中描述了这些过程中涉及的每个NAS消息。
▶ 身份验证(Authentication)
▶ 注册登记(Registration)
▶ 上行/下行NAS传输(UL/DL NAS Transport)
▶ 取消注册(De-Registration)
▶ 服务设置(Service Setup)
▶ 配置更新(Configuration Update)
▶ 标识查询(Identify Query)
▶ 通知(Notification)
▶ 安全模式设置(Security Mode Setup)
▶ 5GMM状态(5GMM Status)
Reference
5GMM States - PDFCOFFEE
9) 5GSM(5G Session Management)
● 5GSM状态机(5GSM Statemachine)
5GSM是一个非常复杂的过程(complicated process),24.501-6中描述了大约100页的总体功能(overall functionality),24.501-8.3中描述了5GSM处理的NAS信令消息,大约40页。如果你直接阅读细节,你很容易迷路。我的建议是尽量熟悉下面的状态机,这样你就可以手工绘制状态机,然后根据需要阅读规范。
<24.501-Figure 6.1.3.2.1.1: The 5GSM sublayer states for PDU session handling in the UE (overview) >
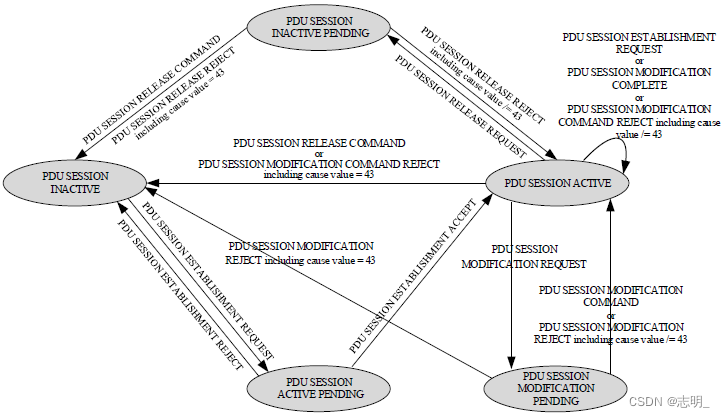
< 24.501-Figure 6.1.3.3.1.1: The 5GSM sublayer states for PDU session handling in the network (overview) >
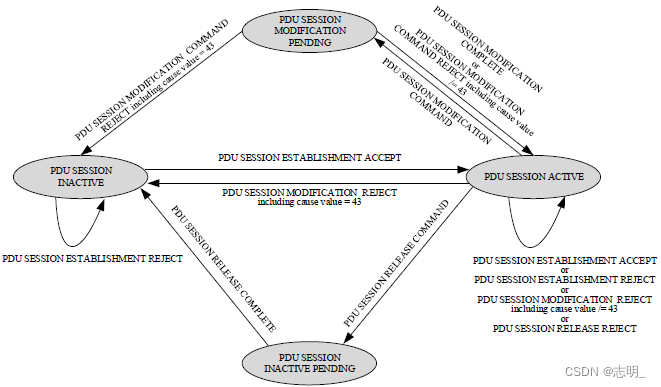
● 5GSM处理的NAS信令过程(NAS Signaling Procedures Handled by 5GSM)
以下是5GSM处理的NAS信令(OTA过程)列表。我认为这些消息(流程)列表将为大多数读者提供更具体的想法,因为分析OTA消息将是非常常见的做法。我将为每个过程创建单独的注释,并在完成注释时放置链接。。。但不确定完成所有这些需要多长时间,但我会尽量尽早完成至少5G特定的流程。对于大多数其他程序,我认为您可以应用您的LTE知识。24.501-8.3中描述了这些过程中涉及的每个NAS消息。正如您所看到的(As you see),5GSM只是关于PDU会话(session)。
▶ PDU会话建立(PDU Session Establishment)
▶ PDU会话身份验证(PDU Session Authentication)
▶ PDU会话修改(PDU Session Modification)
▶ PDU会话发布(PDU Session Release)
▶ 5GSM状态(5GSM Status)
Reference
5G Session Management Signalling Analysis (Dec 2021)
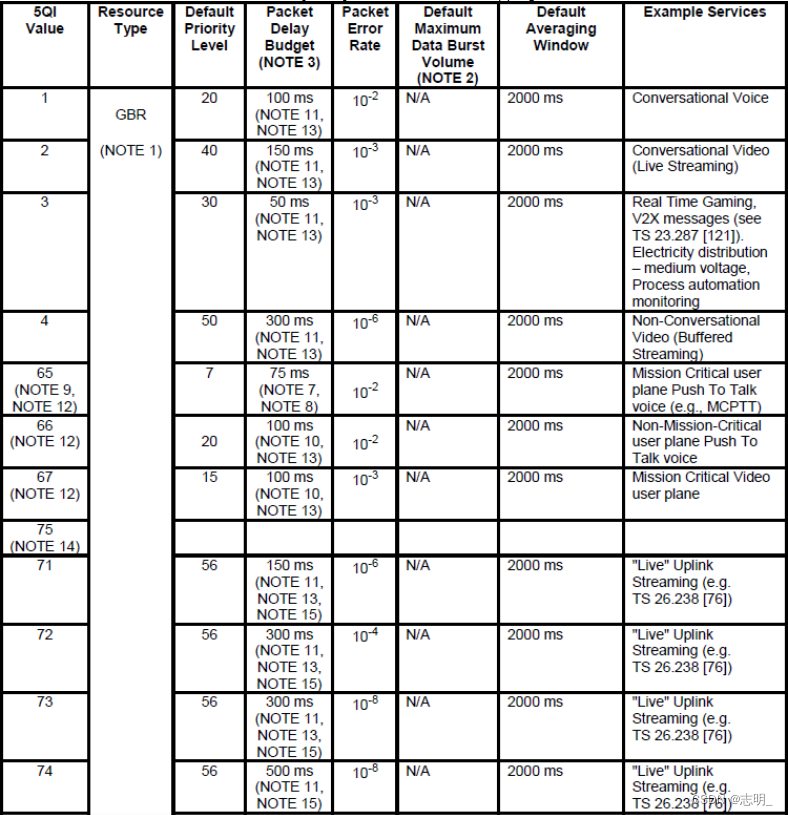
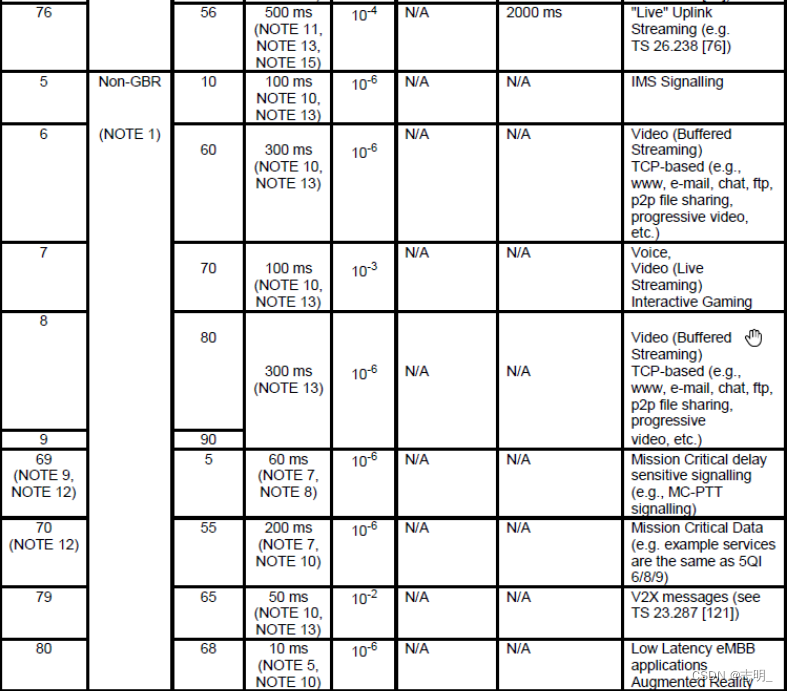
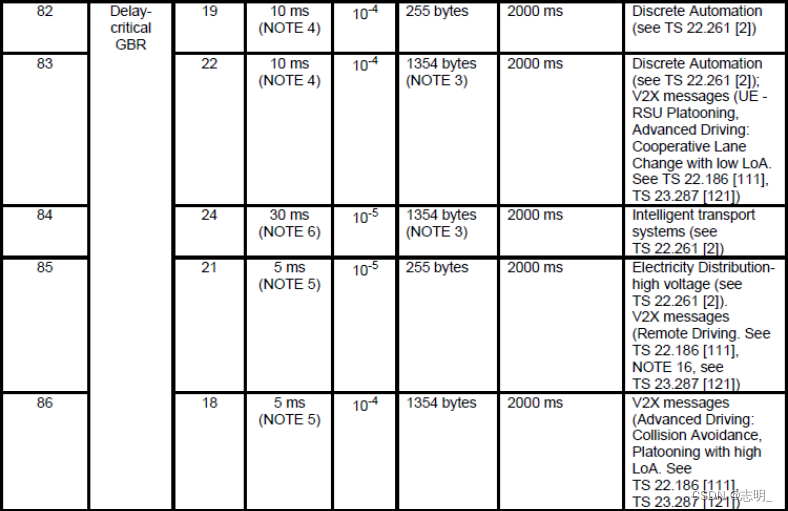
10)5QI
5QI相当于(be equivalent to)QCI in LTE。它只是有更多的选择和粒度(option and granularity)。这是一个表示(represent)服务质量水平的指标(indicator),如下所示。
< 23.501 - Table 5.7.4-1: Standardized 5QI to QoS characteristics mapping >