定义于头文件 <set>
| template< class Key, | (1) | |
| namespace pmr { template <class Key, class Compare = std::less<Key>> | (2) | (C++17 起) |
std::set 是关联容器,含有 Key 类型对象的已排序集。用比较函数 比较 (Compare) 进行排序。搜索、移除和插入拥有对数复杂度。 set 通常以红黑树实现。
在每个标准库使用比较 (Compare) 概念的场所,用等价关系确定唯一性。不精确地说,若二个对象 a 与 b 相互间既不比较大于亦不比较小于: !comp(a, b) && !comp(b, a) ,则认为它们等价。
std::set 满足容器 (Container) 、具分配器容器 (AllocatorAwareContainer) 、关联容器 (AssociativeContainer) 和可逆容器 (ReversibleContainer) 的要求。
修改器
插入元素或结点
std::set<Key,Compare,Allocator>::insert| std::pair<iterator,bool> insert( const value_type& value ); | (1) | |
| std::pair<iterator,bool> insert( value_type&& value ); | (2) | (C++11 起) |
| iterator insert( iterator hint, const value_type& value ); | (3) | (C++11 前) |
| iterator insert( const_iterator hint, const value_type& value ); | (C++11 起) | |
| iterator insert( const_iterator hint, value_type&& value ); | (4) | (C++11 起) |
| template< class InputIt > | (5) | |
| void insert( std::initializer_list<value_type> ilist ); | (6) | (C++11 起) |
| insert_return_type insert(node_type&& nh); | (7) | (C++17 起) |
| iterator insert(const_iterator hint, node_type&& nh); | (8) | (C++17 起) |
插入元素到容器,若容器未含拥有等价关键的元素。
1-2) 插入 value 。
3-4) 插入 value 到尽可能接近,正好前于(C++11 起) hint 的位置。
5) 插入来自范围 [first, last) 的元素。 若范围中的多个元素拥有比较等价的关键,则插入哪个元素是未指定的(待决的 LWG2844 )。
6) 插入来自 initializer_list ilist 的元素。 若范围中的多个元素拥有比较等价的关键,则插入哪个元素是未指定的(待决的 LWG2844 )。
7) 若 nh 是空的结点把柄,则不做任何事。否则插入 nh 所占有的元素到容器,若容器尚未含有拥有等价于 nh.key() 的关键的元素。若 nh 非空且 get_allocator() != nh.get_allocator() 则行为未定义。
8) 若 nh 是空的结点把柄,则不做任何事并返回尾迭代器。否则,插入 nh 所占有的元素到容器,若容器尚未含有拥有等价于 nh.key() 的关键的元素,并返回指向拥有等于 nh.key() 的关键的元素的迭代器(无关乎插入成功还是失败)。若插入成功,则从 nh 移动,否则它保持该元素的所有权。元素被插入到尽可能接近正好先于 hint 的位置。若 nh 非空且 get_allocator() != nh.get_allocator() 则行为未定义。
没有迭代器或引用被非法化。若插入成功,则在结点把柄保有元素时获得的指向该元素的指针和引用被非法化,而在提取前获得的指向元素的指针和引用变得合法。 (C++17 起)
参数
| hint | - |
| ||||
| value | - | 要插入的元素值 | ||||
| first, last | - | 要插入的元素范围 | ||||
| ilist | - | 插入值来源的 initializer_list | ||||
| nh | - | 兼容的结点把柄 | ||||
| 类型要求 | ||||||
- InputIt 必须满足遗留输入迭代器 (LegacyInputIterator) 的要求。 | ||||||
返回值
1-2) 返回由指向被插入元素(或阻止插入的元素)的迭代器和若插入发生则设为 true 的 bool 值。
3-4) 返回指向被插入元素,或阻止插入的元素的迭代器。
5-6) (无)
7) 返回 insert_return_type ,其成员初始化如下:若 nh 为空,则 inserted 为 false , position 为 end() ,而 node 为空。否则发生插入, inserted 为 true , position 指向被插入元素,而 node 为空。若插入失败,则 inserted 为 false , node 拥有 nh 的先前值,而 position 指向拥有等价于 nh.key() 的关键的元素。
8) 若 nh 为空则为尾迭代器,若插入发生则为指向被插入元素的迭代器,而若插入失败则为指向拥有等价于 nh.key() 的关键的元素的迭代器。
异常
1-4) 若任何操作抛异常,则插入无效果。
| 本节未完成 原因:情况 5-8 |
复杂度
1-2) 与容器大小成对数, O(log(size())) 。
| 3-4) 若插入恰好发生在正好后于 hint 的位置,则为均摊常数,否则与容器大小成对数。 | (C++11 前) |
| 3-4) 若插入恰好发生在正好先于 hint 的位置,则为均摊常数,否则与容器大小成对数。 | (C++11 起) |
5-6) O(N*log(size() + N)) ,其中 N 是要插入的元素数。
7) 与容器大小成对数, O(log(size())) 。
8) 若插入恰好发生在正好先于 hint 的位置,则为均摊常数,否则与容器大小成对数。
注意
有提示插入 (3,4) 不返回 bool ,这是为了与顺序容器上的定位插入,如 std::vector::insert 签名兼容。这使得可以创建泛型插入器,例如 std::inserter 。检查有提示插入是否成功的一种方式是比较插入前后的 size() 。
重载 (5,6) 通常实现为循环,其中以 end() 为 hint 调用重载 (3) ;它们对后附最小元素大于 *this 中最大元素的有序序列(例如另一 set )优化。
调用示例
#include <iostream>
#include <forward_list>
#include <string>
#include <iterator>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <time.h>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
struct Cell
{
int x;
int y;
Cell() = default;
Cell(int a, int b): x(a), y(b) {}
Cell &operator +=(const Cell &cell)
{
x += cell.x;
y += cell.y;
return *this;
}
Cell &operator +(const Cell &cell)
{
x += cell.x;
y += cell.y;
return *this;
}
Cell &operator *(const Cell &cell)
{
x *= cell.x;
y *= cell.y;
return *this;
}
Cell &operator ++()
{
x += 1;
y += 1;
return *this;
}
bool operator <(const Cell &cell) const
{
if (x == cell.x)
{
return y < cell.y;
}
else
{
return x < cell.x;
}
}
bool operator >(const Cell &cell) const
{
if (x == cell.x)
{
return y > cell.y;
}
else
{
return x > cell.x;
}
}
bool operator ==(const Cell &cell) const
{
return x == cell.x && y == cell.y;
}
};
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Cell &cell)
{
os << "{" << cell.x << "," << cell.y << "}";
return os;
}
int main()
{
std::cout << std::boolalpha;
auto generate = []()
{
int n = std::rand() % 10 + 100;
Cell cell{n, n};
return cell;
};
std::set<Cell> set1;
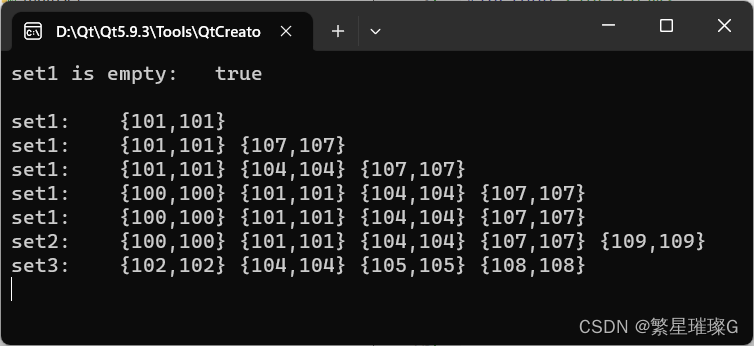
std::cout << "set1 is empty: " << set1.empty() << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
//插入元素到容器
//1-2) 插入 value 。若容器拥有带等价关键的元素,则插入到范围上界。
set1.insert(generate());
std::cout << "set1: ";
std::copy(set1.begin(), set1.end(), std::ostream_iterator<Cell>(std::cout, " "));
std::cout << std::endl;
Cell cell = generate();
// 移动语义
set1.insert(std::move(cell));
std::cout << "set1: ";
std::copy(set1.begin(), set1.end(), std::ostream_iterator<Cell>(std::cout, " "));
std::cout << std::endl;
//3-4) 插入 value 到尽可能接近,正好前于(C++11 起) hint 的位置。
set1.insert(set1.end(), generate());
std::cout << "set1: ";
std::copy(set1.begin(), set1.end(), std::ostream_iterator<Cell>(std::cout, " "));
std::cout << std::endl;
set1.insert(set1.cend(), generate());
std::cout << "set1: ";
std::copy(set1.begin(), set1.end(), std::ostream_iterator<Cell>(std::cout, " "));
std::cout << std::endl;
// 移动语义
set1.insert(set1.cend(), std::move(cell));
std::cout << "set1: ";
std::copy(set1.begin(), set1.end(), std::ostream_iterator<Cell>(std::cout, " "));
std::cout << std::endl;
//5) 插入来自范围 [first, last) 的元素。
std::set<Cell> set2{generate()};
set2.insert(set1.begin(), set1.end());
std::cout << "set2: ";
std::copy(set2.begin(), set2.end(), std::ostream_iterator<Cell>(std::cout, " "));
std::cout << std::endl;
//6) 插入来自 initializer_list ilist 的元素。
std::set<Cell> set3{generate()};
set3.insert({generate(), generate(), generate(), generate(), generate()});
std::cout << "set3: ";
std::copy(set3.begin(), set3.end(), std::ostream_iterator<Cell>(std::cout, " "));
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
}输出




![[云原生] 破局微服务通信:探索MegaEase服务网格的创新之路](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6e7bd1e4bbbe44fbadb98a8f03969864.png)