1.传统拷贝
FileInputStream、FileOutputStream
read:将数据从磁盘读取到内核态缓冲区,再从内核态缓冲区拷贝到用户缓冲区
write:将数据从用户缓冲区写入到socket缓冲区,再从socket缓冲区写入到网卡设备
内核空间:
主要是提供进程调度、内存分配、连接硬件资源等功能
用户空间:
提供给应用程序的空间,不具有访问内核资源的权限。如果用户程序需要使用到内核空间的资源,则需要通过系统调用来完成。进程从用户空间切换到内核空间,完成相关操作后,再从内核空间切换到用户空间。
内核态:
进程运行在内核空间,被称为进程的内核态
用户态:
进程运行在用户空间,被称为进程的用户态。
DMA技术
DMA本质上是一块主板上独立的芯片,允许外设设备和内存存储器之间直接进行IO数据传输,其过程不需要CPU的参与。
主要流程就是:CPU通知DMA将磁盘数据拷贝到内核态后,CPU就可以无需等待执行其他任务。DMA通知磁盘将数据从磁盘放到磁盘缓冲区,磁盘完成后通知DMA,DMA将数据从磁盘缓冲区放到内内核缓冲区中。完成后,通知CPU来取数据。

1.应用程序调用read函数,向操作系统发起IO调用,上下文从用户态切换至内核态
2.DMA控制器把数据从磁盘中读取到内核缓冲区
3.CPU把内核缓冲区数据拷贝到用户应用缓冲区,上下文从内核态切换至用户态,此时read函数返回
4.用户应用进程通过write函数,发起IO调用,上下文从用户态切换至内核态
5.CPU将缓冲区的数据拷贝到socket缓冲区
6.DMA控制器将数据从socket缓冲区拷贝到网卡设备,上下文从内核态切换至用户态,此时write函数返回
从这里可以看到做一次从磁盘到用户缓冲区的数据提取,需要cpu切换2次,cpu拷贝次数1次,DMA拷贝1次,如果是复制那就需要4次CPU切换,2次CPU拷贝,2次DMA拷贝,所以需要减少CPU在用户态与内核态之间的切换次数以及拷贝次数。
2. 零拷贝
什么是零拷贝?
零拷贝是指计算机执行IO操作时,CPU不需要将数据从一个存储区域复制到另一个存储区域,进而减少上下文切换以及CPU的拷贝时间,是IO操作优化技术。
虚拟内存
虚拟内存远大于物理内存空间。且多个虚拟内存可以映射同一个物理地址。这样当DAM将数据拷贝到内核缓存后,无需cpu将数据再拷贝到用户空间了。

实现零拷贝的方式
1. mmap + write
2. sendfile
3. 带有DMA收集拷贝功能的sendfile
MMAP拷贝
void *mmap(void *addr, size_t length, int prot, int flags, int fd, off_t offset);
1.用户进程通过调用mmap方法向操作系统内核发起IO调用,上下文从用户态切换至内核态
2.CPU利用DMA控制器,将数据从硬盘拷贝到内核缓冲区
3.上下文从内核态切换回用户态,mmap方法返回
4.用户进程通过调用write方法向操作系统内核再次发起IO调用,上下文从用户态切换至内核态
5.CPU将内核缓冲区的数据拷贝到socket缓冲区
6.CPU利用DMA控制器,将数据从socket缓冲器拷贝到网卡,上下文从内核态切换至用户态,write方法返回
使用mmap + write拷贝,CPU上下文切换4次,拷贝3次(1次CPU拷贝,2次DMA拷贝),由此可见减少了一次CPU拷贝。
sendfile拷贝
sendfile是Linux2.1版本后内核引入 的一个系统调用函数,原型如下
ssize_t sendfile(int out_fd, int in_fd, off_t *offset, size_t count);
sendfile表示两个文件描述符之间传输数据,他是在操作系统内核中操作的,避免了数据从内核缓冲区和用户缓冲区之际七年的拷贝操作,因此可以用它来实现零拷贝。
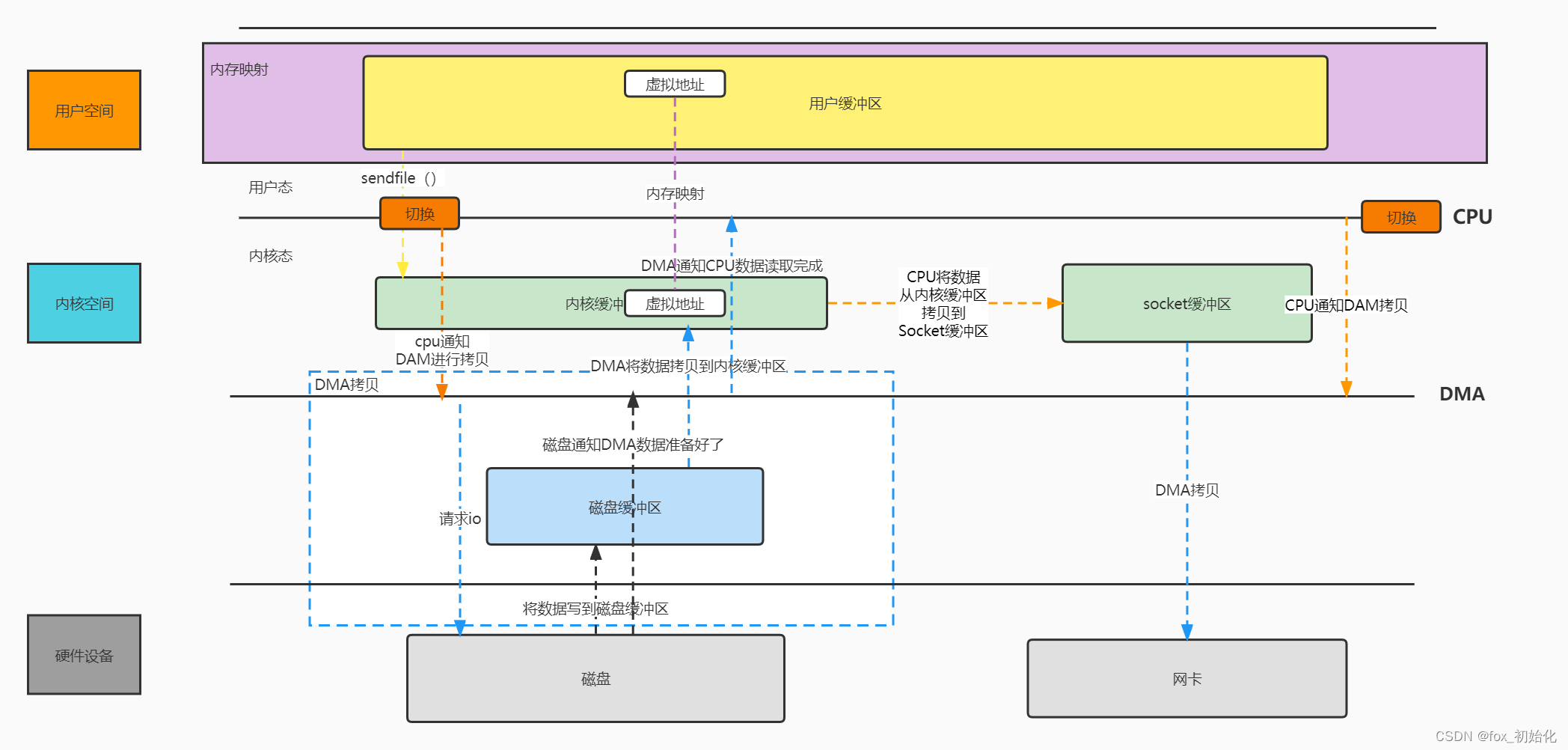
1.用户进程发起sendfile系统调用,上下文从用户态切换至内核态
2.DMA控制器将数据从硬盘拷贝到内核缓冲区
3.CPU将读缓冲区中的数据拷贝到socket缓冲区
4.DMA控制器异步把数据从socket缓冲器拷贝到网卡
5.上下文从内核态切换至用户态,sendfile函数返回
使用sendfile拷贝,CPU上下文切换2次,拷贝3次 (1次CPU拷贝,2次DMA拷贝),由此可见减少了两次CPU切换,一次CPU拷贝。
sendfile +DMA scatter/gather实现的零拷贝
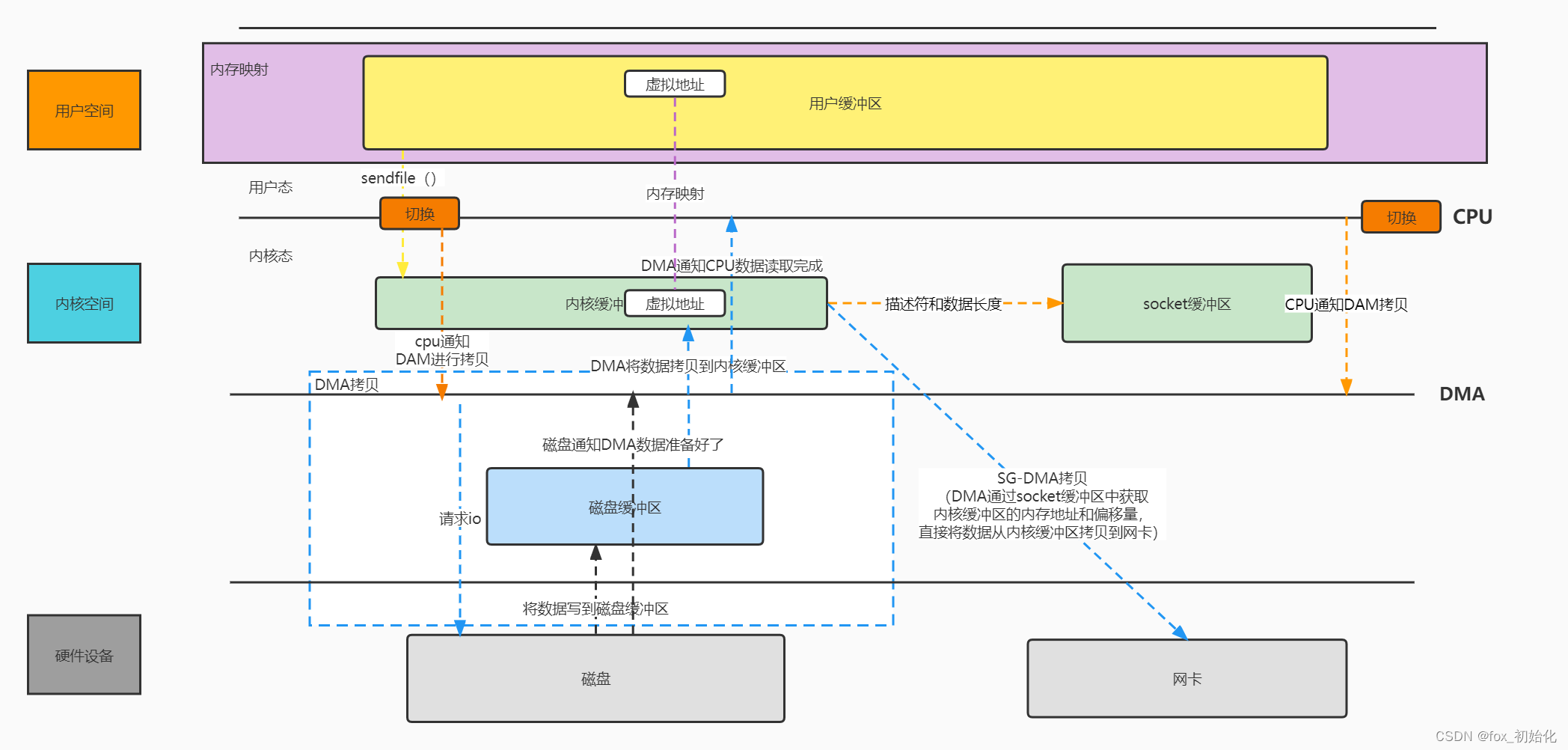
1.用户进程发起sendfile系统调用,上下文从用户态切换至内核态
2.DMA控制器将数据从磁盘拷贝到内核缓冲器
3.CPU把内核缓冲区中的文件描述符信息(包括内核缓冲区的内存地址和偏移量)直接发送到socket缓冲区
4.DMA控制器根据文件描述符信息直接把数据从内核缓冲区拷贝到网卡
5.上下文切换至用户态,sendfile返回
sendfile +DMA scatter/gather,只产生2次CPU切换,2次DMA拷贝,这才是真正意义的零拷贝。
拷贝速度对比
Java中拷贝文件的方式
使用文件大小:2657KB
使用FileInputStream、FileOutputStream传统拷贝
private static void fileCopy(){
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
Long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(new File("C:\\Users\\XXX\\IdeaProjects\\text.txt"));
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(new File("C:\\Users\\XXX\\IdeaProjects\\FileOutputStream.txt"));
int readData = 0;
byte[] buf = new byte[1024*1024*10];
while (-1 != (readData = fileInputStream.read(buf))) {
fileOutputStream.write(readData);
}
Long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(t2-t1);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
耗时:11
MMAP(FileChannle的read、write)拷贝
private static void mmapCopy() {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
FileChannel readChannel = null;
FileChannel wirteChannel = null;
try {
Long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(new File("C:\\Users\\xxx\\IdeaProjects\\text.txt"));
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(new File("C:\\Users\\xxx\\IdeaProjects\\MMAP.txt"));
readChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
wirteChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
int n = 0;
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024*1024*10);
while (readChannel.read(buf) != -1) {
buf.flip();
wirteChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear();
wirteChannel.force(true);
}
Long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(t2 - t1);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
readChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
wirteChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}耗时:27
sendfile拷贝(FileChannle的transferTo)
private static void senfileCopy() {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
FileChannel readChannel = null;
FileChannel wirteChannel = null;
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(new File("C:\\Users\\XXX\\IdeaProjects\\text.txt"));
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(new File("C:\\Users\\XXX\\IdeaProjects\\SendFile.txt"));
readChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
wirteChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
Long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
long len = readChannel.size();
long position = readChannel.position();
readChannel.transferTo(position,len,wirteChannel);
Long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(t2 - t1);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
readChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
wirteChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}耗时:3
在小数据量下传统方式和mmap方式没有太大的区别,但是sendFile方式差距还是比较明显的。
| 传统拷贝 | mmap+write | sendfile | sendfile+scatter、gather | |
| CPU切换次数 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| CPU拷贝次数 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| DMA拷贝次数 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 原因 | 存在用户缓冲区和内核缓冲区,使用DMA技术,CPU需要将数据从内核缓冲区到用户缓冲区来回读取 | 增加虚拟内存地址映射,CPU直接通过映射招到内核态的数据copy到Socket缓冲区 | 使用sendfile减少CPU的切换次数 | 使用sendfile减少CPU的切换次数,且CPU不再将数据复制到Socket缓冲区,而是把数据的位置和长度给到Socket缓冲区,由DMA根据位置和长度直接从内核缓冲区复制到磁盘 |
| 系统调用 | read/write | mmap/write | senfile | sendfile+scatter/gather |

![Error: [mobx-miniprogram] no store specified (小程序全局数据共享bug)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a6c080dfd68b47339d9d86ae64b156ea.png)
![[附源码]计算机毕业设计springboot区域医疗服务监管可视化系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d6b3e33168b145d5aba8041a6bd4fd03.png)



![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Django高血压分析平台](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/85d39437b9f74270ab9c9369eda7a7ee.png)