在实际业务开发中经常会用到文件,字符串和控制台格式化操作,格式化操作无非就是将数据转成指定格式存储在文件或者字符串,或者显示在控制台上,或者反过来。本篇结合实际工作将C/C++语言中常用的文件,字符串和控制台常用格式化方法进行整理和介绍。
目录
1. 控制台格式化
1.1 输入格式化
1.1.1 C语言常用函数
1.1.2 C++常用函数
1.2 输出格式化
1.2.1 C语言常用函数
1.2.2 C++常用函数
2. 字符格式化
2.1 输入格式化
2.1.1 C语言常用函数
2.1.2 C++常用函数
2.2 输出格式化
2.2.1 C语言常用函数
2.2.2 C++常用函数
3. 文件格式化
3.1 输入格式化
3.1.1 C语言常用函数
3.1.2 C++常用函数
3.2 输出格式化
3.2.1 C语言常用函数
3.2.2 C++常用函数
4. 调用举例
4.1 C语言调用
4.2 C++调用
1. 控制台格式化
1.1 输入格式化
1.1.1 C语言常用函数
scanf
1.1.2 C++常用函数
cin
1.2 输出格式化
1.2.1 C语言常用函数
printf
1.2.2 C++常用函数
cout
2. 字符格式化
2.1 输入格式化
2.1.1 C语言常用函数
sscanf
2.1.2 C++常用函数
stringstream / istringstream
2.2 输出格式化
2.2.1 C语言常用函数
sprintf
2.2.2 C++常用函数
stringstream / ostringstream
3. 文件格式化
3.1 输入格式化
3.1.1 C语言常用函数
fscanf
3.1.2 C++常用函数
fstream / ifstream
3.2 输出格式化
3.2.1 C语言常用函数
fprintf
3.2.2 C++常用函数
fstream / ofstream
4. 调用举例
如下分别使用C和C++来实现对文件,字符串和控制台的格式化输入输出,用两种语言实现同样的功能以做对比
(1)对于文件:先格式化输出内容到文件,在从文件格式化输入到内存中各个对应变量中,其中会过滤到特殊字符,只提取关心的数据
(2)对于字符串:会从字符串中格式化提取到对应变量,然后再格式化输出到字符串中
(3)对于控制台:就是最常用的接收接盘输入,然后在输出
4.1 C语言调用
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
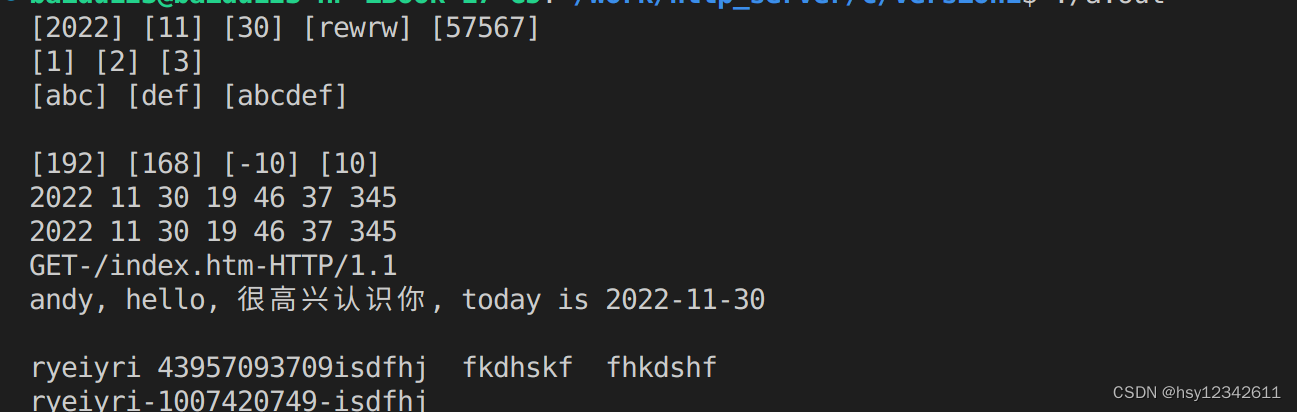
//================ C语言文件输入输出格式化 ===================
char str1[128] = {0}, str2[128] = {0}, str3[128] = {0}, str4[128] = {0};
int num1 = 0, num2 = 0, num3 = 0;
FILE *fp = fopen("test.txt", "w+");
fputs("2022 11 30 rewrw 57567\n\r", fp);
//格式化输出
fprintf(fp, "%d + %d = %d\n", 1, 2, 3);
fprintf(fp, "%s + %s = %s\n", "abc", "def", "abcdef");
rewind(fp);
fscanf(fp, "%s %s %s %s %d", str1, str2, str3, str4, &num1);
printf("[%s] [%s] [%s] [%s] [%d]\n", str1, str2, str3, str4, num1);
//fscanf(fp, "%*[\n]%*[\r]%[^ ] %*[+] %[^ ] %*[=] %[0-9]", str1, str2, str3);
// %*[\n\r]:表示过滤\r\n %*[+]:过滤+ %*[=]:过滤=
fscanf(fp, "%*[\r\n]%[0-9] %*[+] %[0-9] %*[=] %[0-9]", str1, str2, str3);
printf("[%s] [%s] [%s]\n", str1, str2, str3);
fscanf(fp, "%*[\n]%s %*[+] %s %*[=] %s", str1, str2, str3);
printf("[%s] [%s] [%s]\n\n", str1, str2, str3);
fclose(fp);
//============ C语言字符串输入输出格式化 =================
char* strIp = "192.168--10.10";
int first = 0, second = 0, third = 0, fouth = 0;
//注意其中的空格
sscanf(strIp, "%d.%d- %d.%d", &first, &second, &third, &fouth);
printf("[%d] [%d] [%d] [%d]\n", first, second, third, fouth);
char *strTime = "2022-11-30_19:46:37_345";
int year = 0, month = 0, day = 0, hour = 0, minute = 0, seconds = 0, mseconds = 0;
//数值输入
sscanf(strTime, "%d-%d-%d_%d:%d:%d_%d",
&year, &month, &day, &hour, &minute, &seconds, &mseconds);
printf("%d %d %d %d %d %d %d\n", year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, mseconds);
char buf1[128] = {0}, buf2[32] = {0}, buf3[32] = {0}, buf4[32] = {0}, buf5[32] = {0}, buf6[32] = {0}, buf7[32] = {0};
//字符串输入
sscanf(strTime, "%[^-]-%[^-]-%[^_]_%[^:]:%[^:]:%[^_]_%s", buf1, buf2, buf3, buf4, buf5, buf6, buf7);
printf("%s %s %s %s %s %s %s\n", buf1, buf2, buf3, buf4, buf5, buf6, buf7);
char *strHttpReq = "GET /index.htm HTTP/1.1";
sscanf(strHttpReq, "%s %s %s", buf1, buf2, buf3);
printf("%s-%s-%s\n", buf1, buf2, buf3);
sprintf(buf1, "%s, %s, %s, today is %d-%d-%s\n\n",
"andy", "hello", "很高兴认识你", 2022, 11, "30");
printf(buf1);
//================ C语言控制台格式化输入输出 =================
scanf("%s %d %s", buf1, &num1, buf2);
printf("%s-%d-%s\n", buf1, num1, buf2);
return 0;
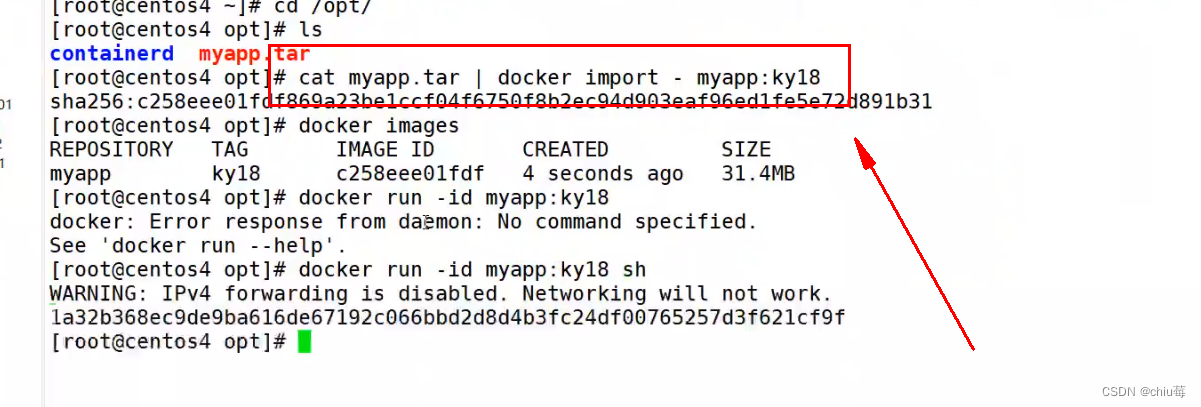
}运行结果如下:
4.2 C++调用
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <iomanip> //setw setfill
using namespace std;
int main() {
//================ C++文件输入输出格式化 ===================
std::string str1, str2, str3, str4, str5;
int num1 = 0, num2 = 0, num3 = 0, num4 = 0;
std::fstream fStream("test.txt", std::ios::out | std::ios::in);
if (fStream) {
//输出操作
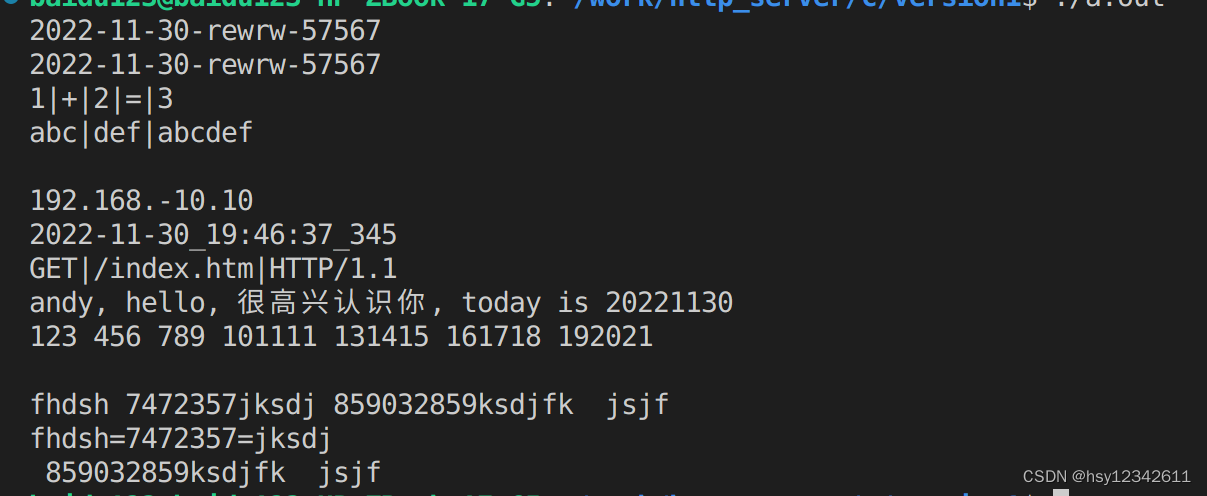
fStream << 2022 << " " << 11 << " " << 30 << " rewrw 57567" << std::endl;
fStream << 1 << " + " << 2 << " = " << 3 << std::endl;
fStream << "abc" << " " << "def" << " " << "abcdef" << std::endl;
//输入操作
fStream.seekg(0, ios::beg);
fStream >> str1 >> str2 >> str3 >> str4 >> num1;
std::cout << str1 << "-" << str2 << "-" << str3 << "-" << str4 << "-" << num1 << std::endl;
fStream.seekg(0, ios::beg);
fStream >> num1 >> num2 >> num3 >> str1 >> num4;
std::cout << num1 << "-" << num2 << "-" << num3 << "-" << str1 << "-" << num4 << std::endl;
fStream >> str1 >> str2 >> str3 >> str4 >> str5;
std::cout << str1 << "|"<< str2 << "|" << str3 << "|" << str4
<< "|" << str5 << std::endl;
fStream >> str1 >> str2 >> str3;
std::cout << str1 << "|"<< str2 << "|" << str3 << std::endl << std::endl;
fStream.close();
}
//============ C++字符串输入输出格式化 =================
std::string strIp = "192.168--10.10";
int first = 0, second = 0, third = 0, fouth = 0;
std::stringstream ss(strIp);
//提取IP地址
ss >> first >> setw(1) >> str1 >> second >> setw(1) >> str2 >> third >> setw(1) >> str3 >> fouth;
std::cout << first << "." << second << "." << third << "." << fouth<< std::endl;
//提取时间
ss.clear();
std::string strTime = "2022-11-30_19:46:37_345";
ss.str(strTime);
int year = 0, month = 0, day = 0, hour = 0, minute = 0, seconds = 0, mseconds = 0;
ss >> year >> setw(1) >> str1 >> month >> setw(1) >> str1 >> day >> setw(1) >> str1 >>
hour >> setw(1) >> str1 >> minute >> setw(1) >> str1 >> seconds >> setw(1) >> str1 >> mseconds;
std::cout << year << '-' << month << '-' << day << '_' << hour <<
':' << minute << ':' << seconds << '_'<< mseconds << std::endl;
ss.clear();
ss.str("GET /index.htm HTTP/1.1");
ss >> str1 >> str2 >> str3;
std::cout << str1 << "|" << str2 << "|" << str3 << std::endl;
ss.clear();
ss.str("");
ss << "andy, " << "hello, " << "很高兴认识你, today is " << 2022 << 11 << "30";
std::cout << ss.str() << std::endl;
//拆分字符串
ss.clear();
ss.str("123|456|789|101111|131415|161718|192021");
std::string item;
//std::getline第一个参数是输入流 cin istringstream ifstream参数均可以
while (std::getline(ss, item, '|')) {
std::cout << item << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl << std::endl;
//================ C++控制台格式化输入输出 =================
std::cin >> str1 >> num1 >> str2;
std::cout << str1 << "=" << num1 << "=" << str2 << std::endl;
//从键盘获取一行文本,遇到\n结束,文本之间可以有空格
std::getline(std::cin, str1);
std::cout << str1 << std::endl;
//遇到空格就结束取值,空格(包括)的输入不会存储在str1中
//std::getline(std::cin, str1, ' ');
return 0;
}运行结果如下:
![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Django高血压分析平台](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/85d39437b9f74270ab9c9369eda7a7ee.png)








![[oeasy]python0022_框架标题的制作_banner_结尾字符串_end](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/051e69a8e4105d4ccb63ba8cd3168f7c.png)
