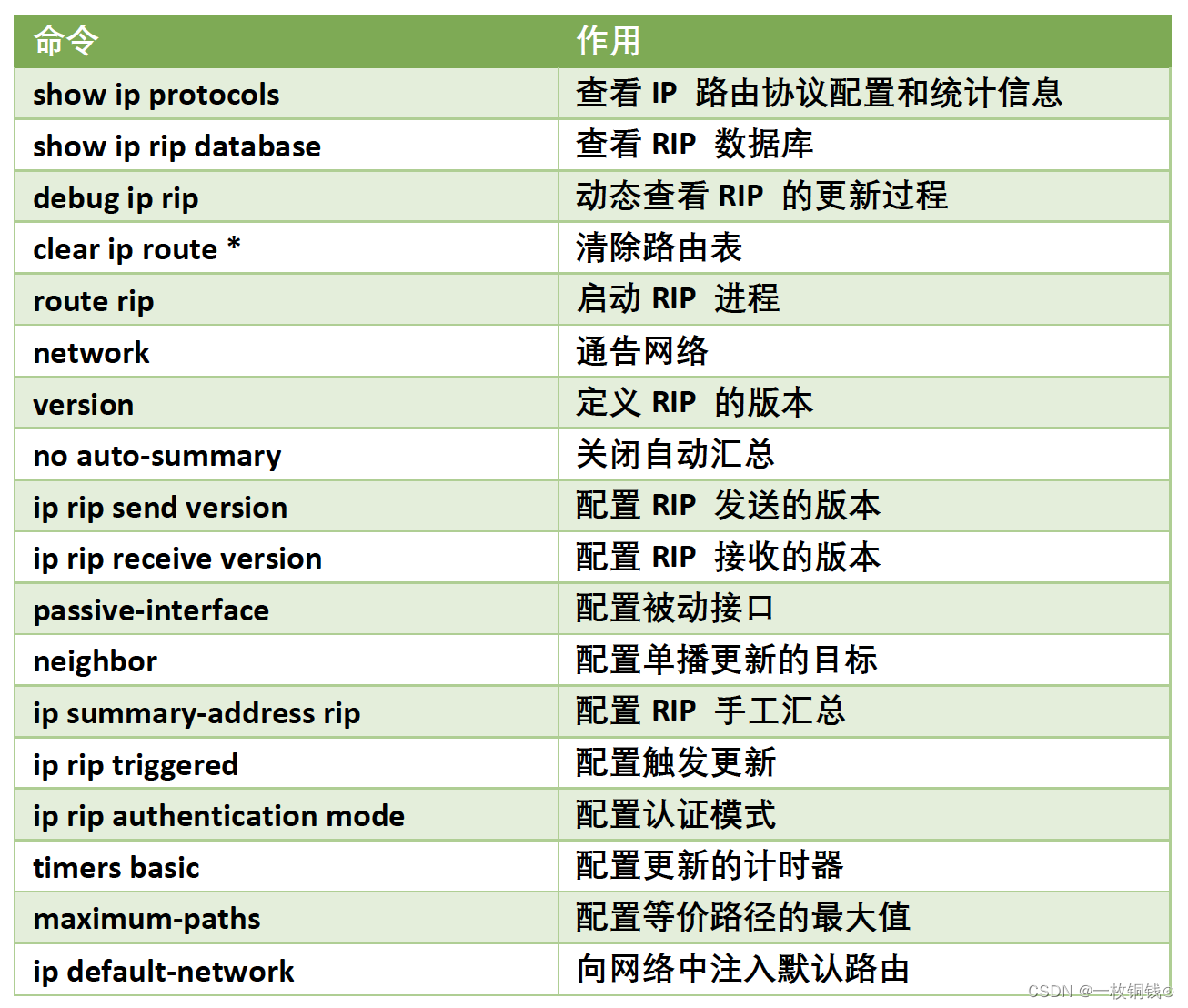
1.Simple("Hello World")
构成:生产者、消费者、消息队列
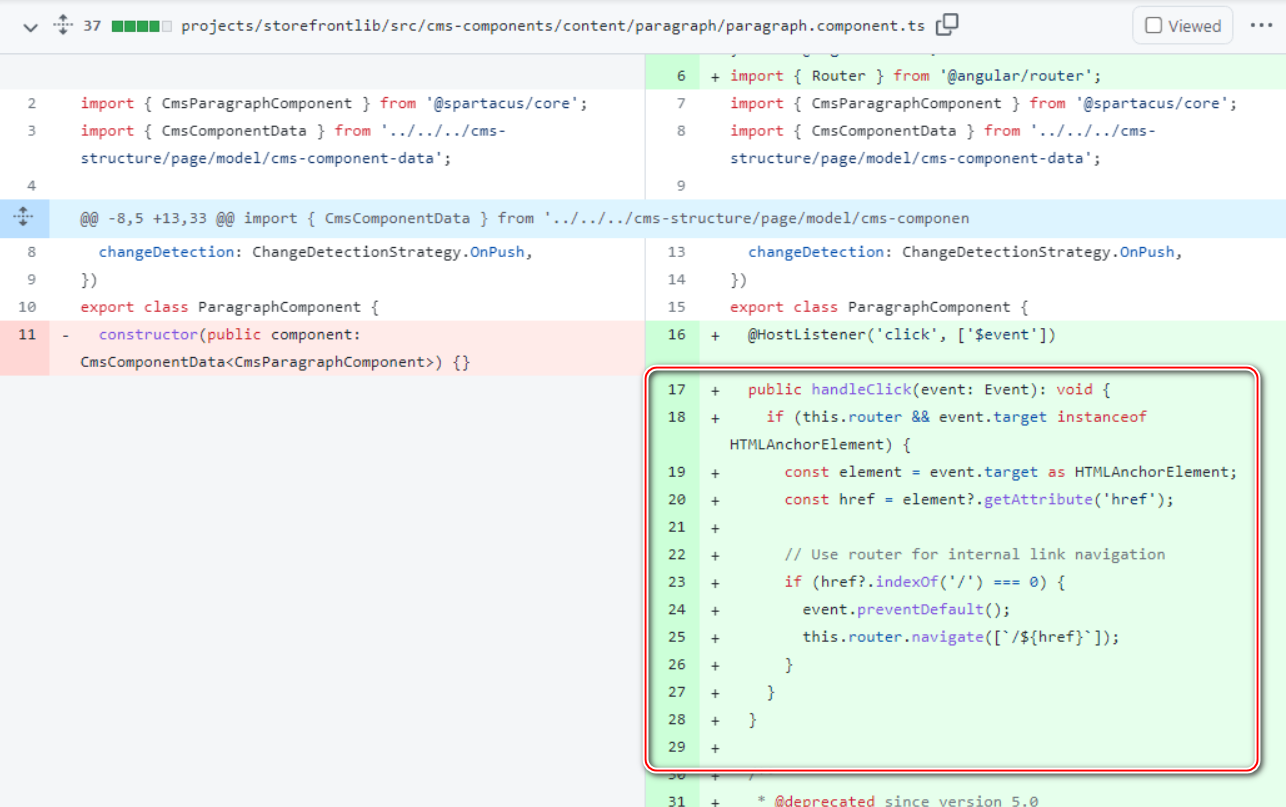
配置类
构造函数参数:name durable exclusive autoDelete
仅创建队列,不创建交换机,也不进行队列和交换机的绑定
注:配置类置于生产者端或消费者端无硬性要求,但置于消费者端更有利于测试代码,原因如下:
若先启动生产者端发送消息,再启动消费者端接收消息,则最先连接到RabbitMQ服务器的消费者将接收所有的消息,所以通常而言需要先启动消费者端;而先启动消费者端时,若将配置类置于生产者端,则可能会出现消费者端中使用,但尚未被配置到RabbitMQ的配置(若配置类在生产者端的话),所以将配置类置于消费者端更有利于测试代码,另外,在项目启动时就进行配置显然是很好的选择
@Configuration
public class HelloWorldConfiguration {
// 创建消息队列
// 不需要交换机(使用默认交换机direct)
@Bean
public Queue helloWorldQueue(){
return new Queue("hello_world_queue", true, false, false);
}
}生产者
convertAndSend方法参数:exchange routingKey message
默认交换机为direct交换机,将routingKey设置为队列名可将消息直接发送至该队列
@Service
public class SayHelloWorldService {
@Autowired
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void say(){
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("", "hello_world_queue", "hello, world");
System.out.println("消息发送成功");
}
}消费者
@RabbitListener 监听队列
@RabbitHandler 消息处理
@Service
@RabbitListener(queues = "hello_world_queue")
public class HelloWorldService {
@RabbitHandler
public void message(String message){
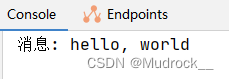
System.out.println("消息: " + message);
}
}测试
@Autowired
SayHelloWorldService sayHelloWorldService;
@Test
void helloWorld(){
sayHelloWorldService.say();
} 
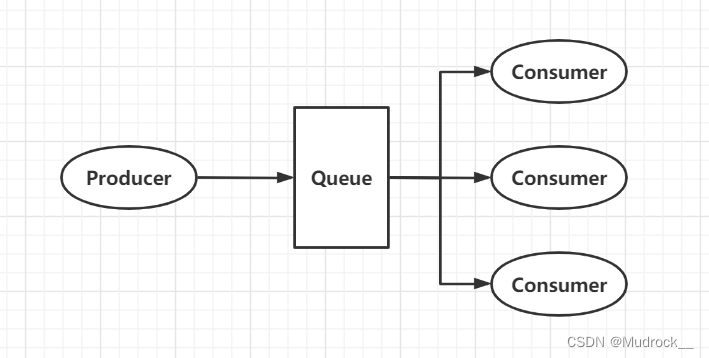
2.Work Queues(工作模式)
构成:生产者、消费者、消息队列(较Simple模式而言,存在多个消费者)
配置类
@Configuration
public class WorkQueuesConfiguration {
// 创建消息队列
// 不需要交换机(使用默认交换机direct)
@Bean
public Queue workQueue(){
return new Queue("work_queue", true, false, false);
}
}生产者
@Service
public class WorkQueuesService {
@Autowired
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void workQueues(String message){
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("", "work_queue", message);
System.out.println("消息发送完成");
}
}消费者
@Service
@RabbitListener(queues = "work_queue")
public class Worker01Service {
@RabbitHandler
public void worker01(String message){
System.out.println("Worker01收到消息: " + message);
}
}@Service
@RabbitListener(queues = "work_queue")
public class Worker02Service {
@RabbitHandler
public void worker01(String message){
System.out.println("Worker02收到消息: " + message);
}
}@Service
@RabbitListener(queues = "work_queue")
public class Worker03Service {
@RabbitHandler
public void worker03(String message){
System.out.println("Worker03收到消息: " + message);
}
}测试
可以看到消息被平分给了三个消费者


3.Publish/Subscribe(发布/订阅模式)
构成:生产者、消费者、消息队列、fanout交换机
相较于上述模式,区别在于具有自定义的交换机,类型为fanout
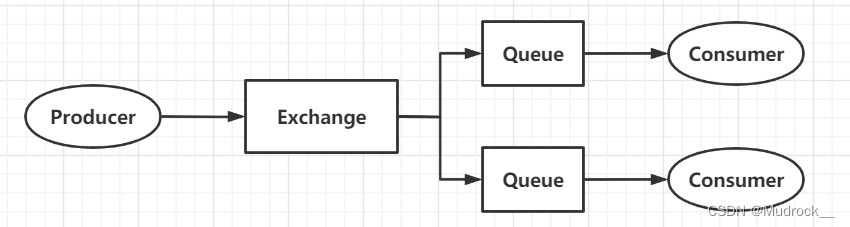
配置类
将消息队列与交换机进行绑定,当有生产者向交换机投递消息时,交换机将会把消息转发至所有与其绑定的消息队列
@Configuration
public class FanoutConfiguration {
//订单交换机
@Bean
public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange(){
return new FanoutExchange("fanout_exchange_order", true, false);
}
//消息通知队列(短信与邮件)
@Bean
public Queue fanoutSMSQueue(){
return new Queue("sms_queue", true, false, false);
}
@Bean
public Queue fanoutEmailQueue(){
return new Queue("email_queue", true, false, false);
}
//绑定交换机与队列
@Bean
public Binding fanoutSMSBinding(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutSMSQueue()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
@Bean
public Binding fanoutEmailBinding(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutEmailQueue()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
}生产者
此处routingKey为空(fanout交换机无需routingKey)
@Service
public class FanoutOrderService {
@Autowired
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void makeOrder(String userID, String producerID, int num){
// 1.根据需求查询仓库 判断是否能满足需求
// 2.若能满足则生成订单
String orderID = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
System.out.println("成功生成订单");
// 3.通过RabbitMQ发送消息
String exchangeName = "fanout_exchange_order";
String routingKey = "";
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, routingKey, orderID);
System.out.println("订单发送成功");
}
}消费者
@Service
// @RabbitListener 监听消息队列
@RabbitListener(queues = "email_queue")
public class EmailMessageService {
// @RabbitHandler 消息处理(接收消息)
@RabbitHandler
public void receiveEmailMessage(String message){
System.out.println("接收到Email消息: " + message);
}
}@Service
// @RabbitListener 监听消息队列
@RabbitListener(queues = "sms_queue")
public class SMSMessageService {
// @RabbitHandler 消息处理(接收消息)
@RabbitHandler
public void receiveSMSMessage(String message){
System.out.println("接收到SMS消息: " + message);
}
}测试
@Autowired
FanoutOrderService fanoutOrderService;
@Test
void fanoutOrder() {
fanoutOrderService.makeOrder("1", "1", 1);
}

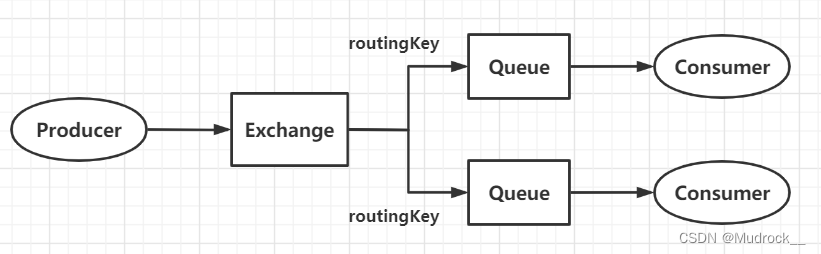
4.Routing(路由模式)
构成:生产者、消费者、消息队列、direct交换机
相较于Publish/Subscribe模式,区别在于交换机类型,direct交换机支持以routingKey标识并分类消息队列
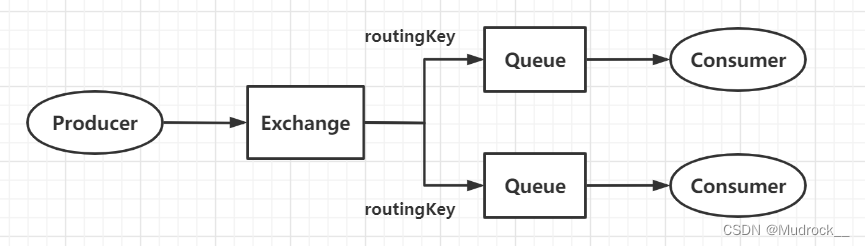
配置类
绑定消息队列与交换机时,还需要绑定routingKey,交换机将根据routingKey标识并分类消息队列;发送消息时,需要指明routingKey,交换机会根据routingKey将消息转发至对应的消息队列处
@Configuration
public class DirectConfiguration {
//订单交换机
@Bean
public DirectExchange directExchange(){
return new DirectExchange("direct_exchange_order", true, false);
}
//消息通知队列(短信与邮件)
@Bean
public Queue directSMSQueue(){
return new Queue("sms_queue", true, false, false);
}
@Bean
public Queue directEmailQueue(){
return new Queue("email_queue", true, false, false);
}
//绑定交换机与队列
@Bean
public Binding directSMSBinding(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(directSMSQueue()).to(directExchange()).with("sms");
}
@Bean
public Binding directEmailBinding(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(directEmailQueue()).to(directExchange()).with("email");
}
}生产者
此处需要指明routingKey
@Service
public class DirectOrderService {
@Autowired
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void makeOrder(String userID, String producerID, int num){
// 1.根据需求查询仓库 判断是否能满足需求
// 2.若能满足则生成订单
String orderID = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
System.out.println("成功生成订单");
// 3.通过RabbitMQ发送消息
String exchangeName = "direct_exchange_order";
String routingKey01 = "sms";
String routingKey02 = "email";
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, routingKey01, orderID + " sms");
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, routingKey02, orderID + " email");
System.out.println("订单发送成功");
}
}消费者
@Service
// @RabbitListener 监听消息队列
@RabbitListener(queues = "email_queue")
public class EmailMessageService {
// @RabbitHandler 消息处理(接收消息)
@RabbitHandler
public void receiveEmailMessage(String message){
System.out.println("接收到Email消息: " + message);
}
}@Service
// @RabbitListener 监听消息队列
@RabbitListener(queues = "sms_queue")
public class SMSMessageService {
// @RabbitHandler 消息处理(接收消息)
@RabbitHandler
public void receiveSMSMessage(String message){
System.out.println("接收到SMS消息: " + message);
}
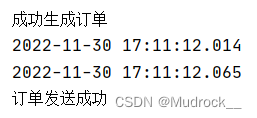
}测试
@Autowired
DirectOrderService directOrderService;
@Test
void directOrder() {
directOrderService.makeOrder("1", "1", 1);
}
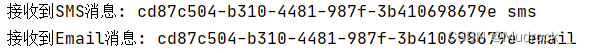
5.Topic(主题模式)
构成:生产者、消费者、消息队列、topic交换机
相较于Routing模式,区别在于交换机类型,topic交换机可模糊匹配routingKey
关于模糊匹配规则
* 表示仅一级 #表示零级或多级(以.分级 级的内容可以为空) 举例:队列1 2的routing key分别为 *.number.* 与 #.number.# x.number.y 将匹配队列1 2 .number. 将匹配队列2 x.number. 将匹配队列2 .number.y 将匹配队列2
配置类
此处routingKey以模糊匹配规则定义
@Configuration
public class TopicConfiguration {
//订单交换机
@Bean
public TopicExchange topicExchange(){
return new TopicExchange("topic_exchange_order", true, false);
}
//消息通知队列(短信与邮件)
@Bean
public Queue topicSMSQueue(){
return new Queue("sms_queue", true, false, false);
}
@Bean
public Queue topicEmailQueue(){
return new Queue("email_queue", true, false, false);
}
//绑定交换机与队列
@Bean
public Binding topicSMSBinding(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicSMSQueue()).to(topicExchange()).with("*.sms.*");
}
@Bean
public Binding topicEmailBinding(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicEmailQueue()).to(topicExchange()).with("#.email.#");
}
}生产者
@Service
public class TopicOrderService {
@Autowired
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void makeOrder(String userID, String producerID, int num){
// 1.根据需求查询仓库 判断是否能满足需求
// 2.若能满足则生成订单
String orderID = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
System.out.println("成功生成订单");
// 3.通过RabbitMQ发送消息
String exchangeName = "topic_exchange_order";
String routingKey01 = "xxx.sms.yyy";
String routingKey02 = ".email.";
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, routingKey01, orderID + " sms");
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, routingKey02, orderID + " email");
System.out.println("订单发送成功");
}
}消费者
@Service
// @RabbitListener 监听消息队列
@RabbitListener(queues = "email_queue")
public class EmailMessageService {
// @RabbitHandler 消息处理(接收消息)
@RabbitHandler
public void receiveEmailMessage(String message){
System.out.println("接收到Email消息: " + message);
}
}@Service
// @RabbitListener 监听消息队列
@RabbitListener(queues = "sms_queue")
public class SMSMessageService {
// @RabbitHandler 消息处理(接收消息)
@RabbitHandler
public void receiveSMSMessage(String message){
System.out.println("接收到SMS消息: " + message);
}
}测试
可以看到,模糊匹配成功