目录
- 参考
- 一、SPI机制
- 1、什么是SPI
- 2、使用场景?
- 3、使用介绍
- 4、代码演示
- 新建工程edevp-dfs-api的spi接口
- 新建阿里云oss实现类
- 新建minio实现类
- 新建测试工程edevp-demo
- 测试
- 5、总结
- 优点:解耦
- 缺点:
- 二、Spring Boot的扩展机制之Spring Factories
- 1.概述
- 2.实现原理是什么
- 3.Spring Factories在Spring Boot中的应用
- 3、edevp-dfs-sdk代码实现
- 新建DfsProperties
- 新建DfsClient
- 新建DfsServiceImpl
- 新建DfsAutoConfiguration启动类
- 新建`META-INF/spring.factories`
- 定义yml
- edevp-dfs-demo引入包测试
参考
可插拔组件设计机制—SPI
Spring.factories
通过S3协议实现通用的文件存储服务中间件
一、SPI机制
1、什么是SPI
SPI 的全称是Service Provider Interface,即提供服务接口;是一种服务发现机制,SPI 的本质是将接口实现类的全限定名配置在文件中,并由服务加载器读取配置文件,加载实现类。这样可以在运行时,动态为接口替换实现类。正因此特性,我们可以很容易的通过 SPI 机制为我们的程序提供拓展功能。
通过多模块分布式文件存储edevp-dfs展示SPI机制
2、使用场景?
数据库驱动加载接口实现类的加载;如:JDBC 加载Mysql,Oracle…
日志门面接口实现类加载,如:SLF4J 对log4j、logback 的支持
Spring中大量使用了SPI,特别是spring-boot 中自动化配置的实现
Dubbo 也是大量使用SPI 的方式实现框架的扩展,它是对原生的SPI 做了封装,允许用户扩展实现Filter 接口。
3、使用介绍
要使用 Java SPI,需要遵循以下约定:
当服务提供者提供了接口的一种具体实现后,需要在JAR 包的META-INF/services 目录下创建一个以“接口全限制定名”为命名的文件,内容为实现类的全限定名;
接口实现类所在的JAR放在主程序的classpath 下,也就是引入依赖。
主程序通过java.util.ServiceLoder 动态加载实现模块,它会通过扫描META-INF/services 目录下的文件找到实现类的全限定名,把类加载值JVM,并实例化它;
SPI 的实现类必须携带一个不带参数的构造方法。
示例:
4、代码演示
新建工程edevp-dfs-api的spi接口
package com.edevp.dfs.api;
/**
* @create 2023-04-11
*/
public interface DfsService {
/**
* 创建bucket
* @param bucketName 存储桶
*/
void createBucket(String bucketName);
/**
* 判断存储桶是否存在
* @param bucketName 存储桶
*/
default boolean doesBucketExist(String bucketName){return true;}
/**
* 初始化
*/
void init();
}
新建阿里云oss实现类
public class OssServiceImpl implements DfsService {
@Override
public void createBucket(String bucketName) {
if (!amazonS3.doesBucketExistV2(bucketName)) {
amazonS3.createBucket((bucketName));
}
}
public boolean doesBucketExist(String bucketName){
return enable && amazonS3.doesBucketExistV2(bucketName);
}
@PostConstruct
@Override
public void init() {
System.out.println("oss");
}
在resource下新建/META-INF/services/com.edevp.dfs.api.DfsService的文件,内容如下:
com.edevp.dfs.impl.OssServiceImpl
新建minio实现类
public class MinioServiceImpl implements DfsService {
@Override
public void createBucket(String bucketName) {
System.out.println("minio");
}
@Override
public boolean doesBucketExist(String bucketName) {
return false;
}
@Override
public void init() {
System.out.println("minio");
}
}
在resource下新建/META-INF/services/com.edevp.dfs.api.DfsService的文件,内容如下:
com.edevp.dfs.impl.MinioServiceImpl
新建测试工程edevp-demo
引入连个子模块的jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>com.edevp</groupId>
<artifactId>edevp-dfs-api</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.edevp</groupId>
<artifactId>edevp-dfs-minio</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.edevp</groupId>
<artifactId>edevp-dfs-oss</artifactId>
</dependency>
测试
新建Application测试,通过serviceLoader加载实现类,发现有两个
public class Application {
static void invoker(){
ServiceLoader<DfsService> serviceLoader = ServiceLoader.load(DfsService.class);
Iterator<DfsService> drivers = serviceLoader.iterator();
boolean isNotFound = true;
while (drivers.hasNext()){
isNotFound = false;
drivers.next().init();
}
if(isNotFound){
throw new RuntimeException("一个驱动实现类都不存在");
}
}
public static void main( String[] args )
{
invoker();
}
}
执行发现分别输出
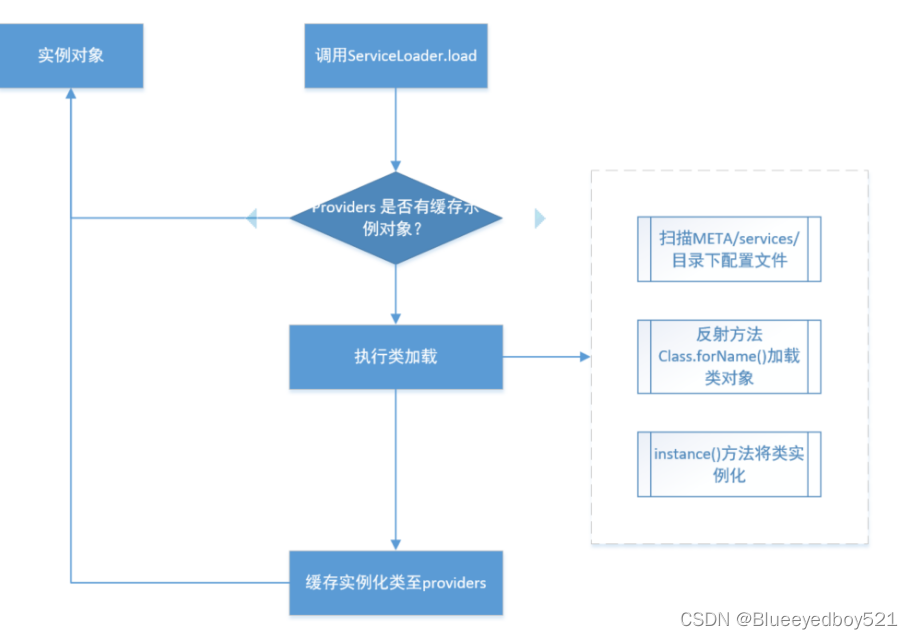
oss
minio
5、总结
优点:解耦
SPI 的使用,使得第三方服务模块的装配控制逻辑与调用者的业务代码分离,不会耦合在一起,应用程序可以根据实际业务情况来启用框架扩展和替换框架组件。
SPI 的使用,使得无须通过下面几种方式获取实现类
代码硬编码import 导入
指定类全限定名反射获取,例如JDBC4.0 之前;Class.forName(“com.mysql.jdbc.Driver”)
缺点:
虽然ServiceLoader也算是使用的延迟加载,但是基本只能通过遍历全部获取,也就是接口的实现类全部加载并实例化一遍。如果你并不想用某些实现类,它也被加载并实例化了,这就造成了浪费。获取某个实现类的方式不够灵活,只能通过Iterator形式获取,不能根据某个参数来获取对应的实现类。
二、Spring Boot的扩展机制之Spring Factories
1.概述
在 Spring Boot 项目中,怎样将 pom.xml 文件里面添加的依赖中的 bean 注册到 Spring Boot 项目的 Spring 容器中呢?
你可能会首先想到使用 @ComponentScan 注解,遗憾的是 @ComponentScan 注解只能扫描 Spring Boot 项目包内的 bean 并注册到 Spring 容器中,项目依赖包中的 bean 不会被扫描和注册,除非通过@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages = {"com.xx"})。此时,我们需要使用 @EnableAutoConfiguration 注解来注册项目依赖包中的 bean。而 spring.factories 文件,可用来记录项目包外需要注册的 bean 类名。
使用 spring.factories 文件有什么好处呢?假如我们封装了一个插件,该插件提供给其他开发人员使用。我们可以在 spring.factories 文件中指定需要自动注册到 Spring 容器的 bean 和一些配置信息。使用该插件的开发人员只需少许配置,甚至不进行任何配置也能正常使用。
在Spring中也有一种类似与Java SPI的加载机制。它在META-INF/spring.factories文件中配置接口的实现类名称,然后在程序中读取这些配置文件并实例化。
这种自定义的SPI机制是Spring Boot Starter实现的基础。
2.实现原理是什么
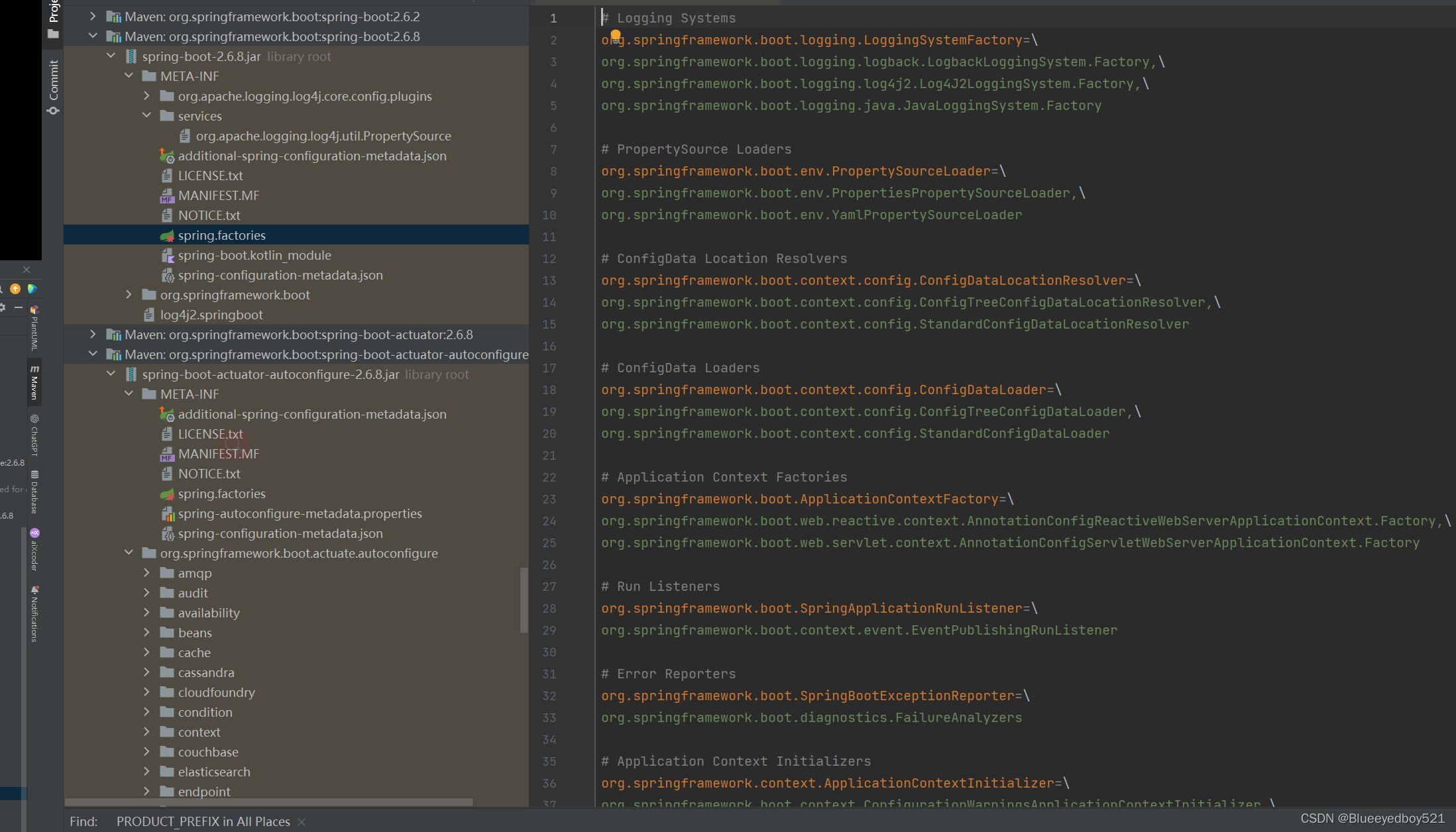
spring-core包里定义了SpringFactoriesLoader类,这个类实现了检索META-INF/spring.factories文件,并获取指定接口的配置的功能。在这个类中定义了两个对外的方法:
- loadFactories 根据接口类获取其实现类的实例,这个方法返回的是对象列表。
- loadFactoryNames 根据接口获取其接口类的名称,这个方法返回的是类名的列表。
从代码中我们可以知道,在这个方法中会遍历整个ClassLoader中所有jar包下的spring.factories文件。也就是说我们可以在自己的jar中配置spring.factories文件,不会影响到其它地方的配置,也不会被别人的配置覆盖。
spring.factories的是通过Properties解析得到的,所以我们在写文件中的内容都是安装下面这种方式配置的:
com.xxx.interface=com.xxx.classname
3.Spring Factories在Spring Boot中的应用
在Spring Boot的很多包中都能够找到spring.factories文件,接下来我们以spring-boot包为例进行介绍
在日常工作中,我们可能需要实现一些SDK或者Spring Boot Starter给被人使用时,
我们就可以使用Factories机制。Factories机制可以让SDK或者Starter的使用只需要很少或者不需要进行配置,只需要在服务中引入我们的jar包即可。
3、edevp-dfs-sdk代码实现
新建DfsProperties
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = DfsProperties.PREFIX)
public class DfsProperties {
public DfsProperties(){
System.out.println("===DfsProperties====");
}
/**
* 配置前缀
*/
public static final String PREFIX = "dfs";
/**
* 是否启用 oss,默认为:true
*/
private boolean enable = true;
/**
* 对象存储服务的URL
*/
private String endpoint;
/**
* 自定义域名
*/
private String customDomain;
/**
* true path-style nginx 反向代理和S3默认支持 pathStyle {<a href="http://endpoint/bucketname">...</a>} false
* supports virtual-hosted-style 阿里云等需要配置为 virtual-hosted-style
*/
private Boolean pathStyleAccess = true;
/**
* 区域
*/
private String region;
/**
* Access key就像用户ID,可以唯一标识你的账户
*/
private String accessKey;
/**
* Secret key是你账户的密码
*/
private String secretKey;
/**
* 默认的存储桶名称
*/
private String bucketName;
}
新建DfsClient
@Slf4j
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class DfsClient{
private final DfsProperties ossProperties;
private AmazonS3 amazonS3;
/**
* 创建bucket
*
* @param bucketName bucket名称
*/
public void createBucket(String bucketName) {
if (!amazonS3.doesBucketExistV2(bucketName)) {
amazonS3.createBucket((bucketName));
}
}
public boolean doesBucketExist(String bucketName){
return amazonS3.doesBucketExistV2(bucketName);
}
@PostConstruct
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
try{
ClientConfiguration clientConfiguration = new ClientConfiguration();
AwsClientBuilder.EndpointConfiguration endpointConfiguration = new AwsClientBuilder.EndpointConfiguration(
ossProperties.getEndpoint(), ossProperties.getRegion());
AWSCredentials awsCredentials = new BasicAWSCredentials(ossProperties.getAccessKey(),
ossProperties.getSecretKey());
AWSCredentialsProvider awsCredentialsProvider = new AWSStaticCredentialsProvider(awsCredentials);
this.amazonS3 = AmazonS3Client.builder().withEndpointConfiguration(endpointConfiguration)
.withClientConfiguration(clientConfiguration).withCredentials(awsCredentialsProvider)
.disableChunkedEncoding().withPathStyleAccessEnabled(ossProperties.getPathStyleAccess()).build();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
新建DfsServiceImpl
@AllArgsConstructor
public class DfsServiceImpl implements DfsService {
private final DfsClient dfsClient;
@Override
public void createBucket(String bucketName) {
dfsClient.createBucket(bucketName);
}
@Override
public boolean doesBucketExist(String bucketName) {
return dfsClient.doesBucketExist(bucketName);
}
@Override
public void init() {
}
}
新建DfsAutoConfiguration启动类
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "dfs.enable", havingValue = "true")
@EnableConfigurationProperties({DfsProperties.class})
@Import({DfsClient.class, DfsServiceImpl.class})
public class DfsAutoConfiguration {
public DfsAutoConfiguration(){
System.out.println("===DfsAutoConfiguration====");
}
@Resource
private DfsProperties dfsProperties;
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("===DfsAutoConfiguration==init=="+dfsProperties);
}
}
注意:
- @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false):此值默认是true哦,需要显示改为false才算是Lite模式,运行时不再需要给对应类生成CGLIB子类,提高了运行性能,降低了启动时间。可以参考
- @AutoConfigureAfter:在加载配置的类之后再加载当前类
- @EnableConfigurationProperties:注入配置类DfsProperties
- @Import 实例化DfsClient和DfsServiceImpl
新建META-INF/spring.factories
内容如下
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration = \com.edevp.dfs.sdk.config.DfsAutoConfiguration
定义yml
dfs:
enable: true
endpoint: http://192.168.0.44:9080
access-key: minioadmin
secret-key: minioadmin
edevp-dfs-demo引入包测试
用@Resouce,如果dfs.enable是false,则启动报错依赖注入,如果用@Autowired(required=false)即使dfs.enable是false也不会报错
@Slf4j
@Component
public class StartRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired(required=false)
private DfsService dfsService;
@Autowired(required=false)
private DfsProperties dfsProperties;
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
log.info(ossService+"======StartRunner======"+dfsProperties);
if(dfsService!= null){
dfsService.createBucket("test");
}
}
}