文章目录
- 前言
- 一、R basic
- 1. R Operator
- 2. 变量赋值
- 3. c() - combine 函数
- 4. 对向量的操作
- 5. Special Numerical Values
- 二、 Built-in Functions
- 1. min, max and range
- 2. sum and prod
- 3. Cumulative Summaries
- 4. paste
- 5. list()
- 6. seq()
- 7. rep()
- 总结
前言
本系列是 STATS 782的课程笔记,主要记录使用 R 语言的一些技巧。
一、R basic
1. R Operator

①:→ 生成数字序列
> 1:50
[1] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
[18] 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34
[35] 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50
② %% → 取余(求模)
5 %% 2
# 输出结果为 1,因为 5 除以 2 的余数是 1
③ %/% → 整除
7 %/% 3
# 输出结果为 2,因为 7 除以 3 的商是 2.3333,整数部分为 2
2. 变量赋值

3. c() - combine 函数
用于创建一维向量(vector)和组合数据,可以将多个数值、字符或逻辑值组合成一个向量:
① 创建一个数值向量:
num_vector <- c(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
> num_vector
[1] 1 2 3 4 5
② 组合已有的向量:
vector1 <- c(1, 2, 3)
vector2 <- c(4, 5, 6)
combined_vector <- c(vector1, vector2)
③ The Recycling Rule:
当 c 函数合并的两个向量长度不同时,
First enlarge the shorter vector by recycling its elements, then combine the vectors element by element.
> c(1, 2, 3, 4) + c(1, 2)
[1] 2 4 4 6
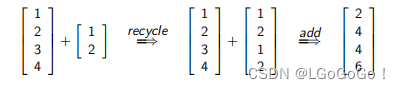
4. 对向量的操作
① 截取向量:
R语言中向量的索引从 1 开始,
> vector_total
[1] 1 0 2 4
> vector_total[1]
[1] 1
> vector_total[1:3]
[1] 1 0 2
> vector_total[c(1, 3)]
[1] 1 2
> vector_total[c(-1, -3)]
[1] 0 4
或截取满足条件的向量value:
> x = c(1, 2, 3, 4)
> x[x > 2]
[1] 3 4
② 改变向量 value
先获取向量,再赋值,即可完成修改value,
> vector_total[1:3] <- 0
> vector_total
[1] 0 0 0 4
使用 ifelse 函数修改:
> x = 1:10
> ifelse(x > 5, x, -x)
[1] -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 6 7 8 9 10
5. Special Numerical Values
① Infinity:
0 作为分母时,根据分子的正负值,得到结果正无穷 / 负无穷
> 1 / 0
[1] Inf
> -1 / 0
[1] -Inf
② NaN:
Not a Number,特殊的常量,代表 “Not a Number”(非数值)。NaN 通常是由数学运算的未定义或不可表示结果导致的:
sqrt(-1) # 对负数开平方根
# 输出结果为 NaN
0 / 0 # 0 除以 0
# 输出结果为 NaN
log(-1) # 对负数取对数
# 输出结果为 NaN
③ NA:
Not Available,indicate that a value is missing or not available:
# Any arithmetic expression which contains NA will produce NA as a result.
> 1 + sin(NA)
[1] NA
二、 Built-in Functions

1. min, max and range
The functions min and max return the minimum and maximum values contained in any of their arguments, and the function range returns a vector of length 2 containing the minimum and maximum of the values in the arguments.
> max(1:100)
[1] 100
> max(1:100, Inf)
[1] Inf
> range(1:100)
[1] 1 100
2. sum and prod
The functions sum and prod compute the sum and product of all the elements in their arguments.
> sum(1:100)
[1] 5050
> prod(1:10)
[1] 3628800
3. Cumulative Summaries
> cumsum(1:10)
[1] 1 3 6 10 15 21 28 36 45 55
> cumprod(1:6)
[1] 1 2 6 24 120 720
> cummax(1:10)
[1] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
> cummin(1:10)
[1] 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
4. paste
Strings can be “glued together” by using paste.
默认以空格分隔:
> paste("First", "Second", "Third")
[1] "First Second Third"
> paste("First", "Second", "Third", sep = ":")
[1] "First:Second:Third"
> paste("First", "Second", "Third", sep = "")
[1] "FirstSecondThird"
对向量进行操作:
> paste(s, "element", sep = "-")
[1] "initial-element" "second-element"
[3] "third-element"
> paste(s, collapse = " -> ")
[1] "initial -> second -> third"
5. list()
The elements of vectors must all be of the same basic type. Lists provide a way of storing things of different types in a single object.
> lst = list(10, "eleven", TRUE)
> lst = list(1:10, "eleven", TRUE)
> lst
[[1]]
[1] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
[[2]]
[1] "eleven"
[[3]]
[1] TRUE
6. seq()
功能与 “:” 类似,但 “:” 步进只能为 1,
> seq(0, 1, by = .1)
[1] 0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
> seq(0, 1, length = 11)
[1] 0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
> seq(0, by = .1, length = 11)
[1] 0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
> seq(to = 1, by = .1, length = 11)
[1] 0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
7. rep()
The first argument to rep gives the values to be repeated and the second specifies how many times to repeat them.
> rep(1:4, 3)
[1] 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4
> rep(1:4, c(2, 3, 2, 3))
[1] 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 4 4 4
> rep(c("A", "B", "C"), 3)
[1] "A" "B" "C" "A" "B" "C" "A" "B" "C"
总结
本文回顾了 STATS 782 第一章节的内容,介绍了R语言的基本运算符,数据类型等,以及一些常用的内置函数。