思维导图
本文主要分析ServletWebServerApplicationContext源码
SpringBoot Web容器应用上下文(这是个人的翻译, 如有不足之处还望指出, 大佬勿喷!!!)
1.自我思考及复盘
备注: 自我思考及复盘是为了养成带着问题阅读源码及阅读完源码后总结,是个人的学习及实践见解, 如有不足之处还望指出, 大佬勿喷!!!
1.1 自我思考
- what-是什么?
servlet web 服务器(如tomcat)的应用上下文 - why-为什么,作用?
因为要支持spring boot的内嵌即外部web服务应用上下文加载、初始化、刷新、使用、停止等 - how–如何工作的?原理
- 继承、实现应用上下文初始化、刷新、使用、停止方法
- 准备刷新Servlet 服务器上下文环境,初始化Servlet 服务器 beanfactory,加载其beanfactory定义信息
- 系统配置Servlet 服务器 beanfactory,并激活BeanFactoryPostProcessors
- 注册相关的BeanPostProcessors,初始化及注册相关的MessageSource、时间广播器、事件监听器
- 热加载Servlet 服务器 单例bean,完成其刷新过程
- SpringBoot容器使用Servlet 服务器,停止调用销毁方法。
- 如果是我,将会如何设计?使用到哪些设计模式?
- 将使用模板方法:针对不同的Servlet 服务器套用对应模板,重写模板方法
- 策略模式:根据内嵌还是外置的服务器去调用对应的加载运行方法
1.2 复盘
- 用到哪些设计模式?
- 其中DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry有用到单例模式(双重检测)获取Bean,代码中未列出,补充一下:
// DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.java
public Object getSingleton(String beanName){
//参数true设置标识允许早期依赖
return getSingleton(beanName,true);
}
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
//检查缓存中是否存在实例
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
//如果为空,则锁定全局变量并进行处理。
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
//如果此bean正在加载,则不处理
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
//当某些方法需要提前初始化的时候则会调用addSingleFactory 方法将对应的ObjectFactory初始化策略存储在singletonFactories
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
//调用预先设定的getObject方法
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
//记录在缓存中,earlysingletonObjects和singletonFactories互斥
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
return (singletonObject != NULL_OBJECT ? singletonObject : null);
}
- 在AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext有用到策略模式及适配器模式:详见下文
SpringBoot(十二)启动流程分析之创建应用上下文AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
2.概述
- SpringApplication#createApplicationContext() 方法,根据不同的 Web 应用类型,创建不同的 Spring 容器,如下:
// SpringApplication.java
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
// 根据 webApplicationType 类型,获得 ApplicationContext 类型
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", ex);
}
}
// 创建 ApplicationContext 对象
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
- 本文主要分享SERVLET 类型对应的 Spring 容器类型 AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext 类,类图如下:
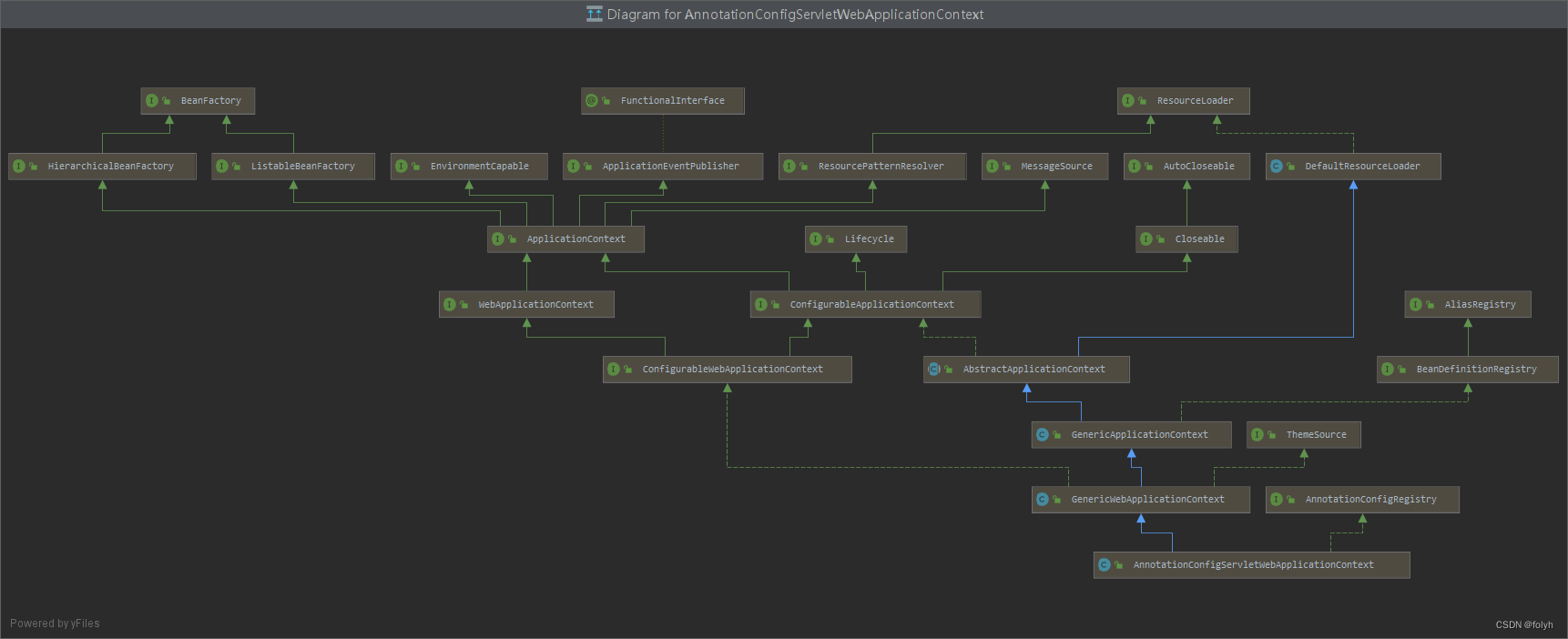
(蓝色实线是类继承关系;绿色虚线是接口实现关系;绿色实线是接口与接口之间关系–可以用extends词)
3.ServletWebServerApplicationContext
实现 ConfigurableWebServerApplicationContext 接口,获得管理 WebServer 的能力;继承 GenericWebApplicationContext 类,Spring Boot 使用 Servlet Web 服务器的 ApplicationContext 实现类。
核心方法refresh()向上继承了AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()方法
// AbstractApplicationContext.java
// `#refresh()` 方法
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
.......
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // <1>
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh(); // <2>
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh(); // <3>
}
........
}
3.1 #refresh() 方法
备注:#refresh() 方法本质还是调用上面AbstractApplicationContext的核心#refresh(),这里另外做了异常处理
3.1.1 初始化Spring 容器
// ServletWebServerApplicationContext.java
@Override
public final void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
try {
super.refresh();
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
// <X> 如果发生异常,停止 WebServer
stopAndReleaseWebServer();
throw ex;
}
}
3.1.2 #stopAndReleaseWebServer()方法停止 WebServer
// ServletWebServerApplicationContext.java
private void stopAndReleaseWebServer() {
// 获得 WebServer 对象,避免被多线程修改了
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
if (webServer != null) {
try {
// 停止 WebServer 对象
webServer.stop();
// 置空 webServer
this.webServer = null;
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
}
}
3.2 #postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory)方法
覆写 #postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) 方法,代码如下:
@Override
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// <1.1> 注册 WebApplicationContextServletContextAwareProcessor
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new WebApplicationContextServletContextAwareProcessor(this));
// <1.2> 忽略 ServletContextAware 接口。
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletContextAware.class);
// <2> 注册 ExistingWebApplicationScopes
registerWebApplicationScopes();
}
3.2.1 <1.1> 处,注册 WebApplicationContextServletContextAwareProcessor 。
- WebApplicationContextServletContextAwareProcessor 的作用,主要是处理实现 ServletContextAware 接口的 Bean 。
- 在这个处理类,初始化这个 Bean 中的 ServletContext 属性。
- 这样在实现 ServletContextAware 接口的 Bean 中就可以拿到 ServletContext 对象了,Spring 中 Aware 接口就是这样实现的。
- 这样,就可以从 webApplicationContext 中,获得 ServletContext 和 ServletConfig 属性。
代码如下:
// WebApplicationContextServletContextAwareProcessor.java
public class WebApplicationContextServletContextAwareProcessor extends ServletContextAwareProcessor {
private final ConfigurableWebApplicationContext webApplicationContext;
public WebApplicationContextServletContextAwareProcessor(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext webApplicationContext) {
Assert.notNull(webApplicationContext, "WebApplicationContext must not be null");
this.webApplicationContext = webApplicationContext;
}
@Override
protected ServletContext getServletContext() {
ServletContext servletContext = this.webApplicationContext.getServletContext();
return (servletContext != null) ? servletContext : super.getServletContext();
}
@Override
protected ServletConfig getServletConfig() {
ServletConfig servletConfig = this.webApplicationContext.getServletConfig();
return (servletConfig != null) ? servletConfig : super.getServletConfig();
}
}
3.2.2 <1.2> 处,忽略 ServletContextAware 接口
- 因为实现 ServletContextAware 接口的 Bean 在 <1.1> 中的 WebApplicationContextServletContextAwareProcessor 中已经处理了。
3.2.3 <2> 处,注册 ExistingWebApplicationScopes 方法
调用 #registerWebApplicationScopes() ,代码如下:
private void registerWebApplicationScopes() {
// 创建 ExistingWebApplicationScopes 对象
ExistingWebApplicationScopes existingScopes = new ExistingWebApplicationScopes(getBeanFactory());
// 注册 ExistingWebApplicationScopes 到 WebApplicationContext 中
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes(getBeanFactory());
// 恢复
existingScopes.restore();
}
3.3 #onRefresh()方法
在容器初始化时,完成 WebServer 的创建(不包括启动),代码如下:
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
// <1> 调用父方法
super.onRefresh();
try {
// <2>创建 WebServer
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
3.3.1 #createWebServer() 方法
创建 WebServer 对象
// ServletWebServerApplicationContext.java
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
// <1> 如果 webServer 为空,说明未初始化
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
// <1.1> 获得 ServletWebServerFactory 对象
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
// <1.2> 获得 ServletContextInitializer 对象
// <1.3> 创建(获得) WebServer 对象
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
}
else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", ex);
}
}
// <3> 初始化 PropertySource
initPropertySources();
}
(1)<1> 处,如果 webServer 为空,说明未初始化。
- <1.1> 处,调用 #getWebServerFactory() 方法,获得 ServletWebServerFactory 对象。
-
默认情况下,此处返回的会是 org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory 对象。
-
在我们引入 spring-boot-starter-web 依赖时,默认会引入 spring-boot-starter-tomcat 依赖。此时,org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration 在自动配置时,会配置出 TomcatServletWebServerFactory Bean 对象。因此,此时会获得 TomcatServletWebServerFactory 对象。
-
代码如下:
// ServletWebServerApplicationContext.java
protected ServletWebServerFactory getWebServerFactory() {
// Use bean names so that we don't consider the hierarchy
// 获得 ServletWebServerFactory 类型对应的 Bean 的名字们
String[] beanNames = getBeanFactory().getBeanNamesForType(ServletWebServerFactory.class);
// 如果是 0 个,抛出 ApplicationContextException 异常,因为至少要一个
if (beanNames.length == 0) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to missing "
+ "ServletWebServerFactory bean.");
}
// 如果是 > 1 个,抛出 ApplicationContextException 异常,因为不知道初始化哪个
if (beanNames.length > 1) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to multiple "
+ "ServletWebServerFactory beans : " + StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString(beanNames));
}
// 获得 ServletWebServerFactory 类型对应的 Bean 对象
return getBeanFactory().getBean(beanNames[0], ServletWebServerFactory.class);
}
- <1.2> 处,调用 #getSelfInitializer() 方法,获得 ServletContextInitializer 对象。
返回的是 ServletContextInitializer 匿名对象,内部会调用 #selfInitialize(servletContext) 方法。该方法会在 WebServer 创建后,进行初始化。
代码如下:
// ServletWebServerApplicationContext.java
private org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletContextInitializer getSelfInitializer() {
return this::selfInitialize; // 和下面等价
// return new ServletContextInitializer() {
//
// @Override
// public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
// selfInitialize(servletContext);
// }
//
// };
}
- <1.3> 处,创建(获得) WebServer 对象。
调用 ServletWebServerFactory#getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer) 方法。
(2)<3> 处,调用父 #initPropertySources() 方法,初始化 PropertySource
3.3.2 #selfInitialize()
初始化 WebServer ,代码如下:
// ServletWebServerApplicationContext.java
private void selfInitialize(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
// <1> 添加 Spring 容器到 servletContext 属性中。
prepareWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
// <2> 注册 ServletContextScope
registerApplicationScope(servletContext);
// <3> 注册 web-specific environment beans ("contextParameters", "contextAttributes")
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(getBeanFactory(), servletContext);
// <4> 获得所有 ServletContextInitializer ,并逐个进行启动
for (ServletContextInitializer beans : getServletContextInitializerBeans()) {
beans.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
(1)<1> 处,添加 Spring 容器到 servletContext 属性中。
调用 #prepareWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) 方法,
- 通过 处,从 servletContext 的属性种,可以拿到其拥有的 Spring 容器。
- 通过 处,Spring 容器的 servletContext 属性,可以拿到 ServletContext 对象。
代码如下:
protected void prepareWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
// 如果已经在 ServletContext 中,则根据情况进行判断。
Object rootContext = servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE);
if (rootContext != null) {
// 如果是相同容器,抛出 IllegalStateException 异常。说明可能有重复的 ServletContextInitializers 。
if (rootContext == this) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - "
+ "check whether you have multiple ServletContextInitializers!");
}
// 如果不同容器,则直接返回
return;
}
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring embedded WebApplicationContext");
try {
// <X> 设置当前 Spring 容器到 ServletContext 中
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this);
// 打印日志
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Published root WebApplicationContext as ServletContext attribute with name ["
+ WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE + "]");
}
// <Y> 设置到 `servletContext` 属性中。
setServletContext(servletContext);
// 打印日志
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - getStartupDate();
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
}
(2)<2> 处,注册 ServletContextScope
调用 #registerApplicationScope(ServletContext servletContext) 方法,代码如下:
// ServletWebServerApplicationContext.java
private void registerApplicationScope(ServletContext servletContext) {
ServletContextScope appScope = new ServletContextScope(servletContext);
getBeanFactory().registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_APPLICATION, appScope);
// Register as ServletContext attribute, for ContextCleanupListener to detect it.
servletContext.setAttribute(ServletContextScope.class.getName(), appScope);
}
(3)<3> 处,注册 web-specific environment beans。
- 调用 WebApplicationContextUtils#registerEnvironmentBeans(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory bf, ServletContext sc) 方法
- 这样,从 BeanFactory 中,也可以获得到 servletContext
代码如下:
public static void registerEnvironmentBeans(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory bf, @Nullable ServletContext servletContext, @Nullable ServletConfig servletConfig) {
if (servletContext != null && !bf.containsBean("servletContext")) {
bf.registerSingleton("servletContext", servletContext);
}
if (servletConfig != null && !bf.containsBean("servletConfig")) {
bf.registerSingleton("servletConfig", servletConfig);
}
HashMap attributeMap;
Enumeration attrNameEnum;
String attrName;
if (!bf.containsBean("contextParameters")) {
attributeMap = new HashMap();
if (servletContext != null) {
attrNameEnum = servletContext.getInitParameterNames();
while(attrNameEnum.hasMoreElements()) {
attrName = (String)attrNameEnum.nextElement();
attributeMap.put(attrName, servletContext.getInitParameter(attrName));
}
}
if (servletConfig != null) {
attrNameEnum = servletConfig.getInitParameterNames();
while(attrNameEnum.hasMoreElements()) {
attrName = (String)attrNameEnum.nextElement();
attributeMap.put(attrName, servletConfig.getInitParameter(attrName));
}
}
bf.registerSingleton("contextParameters", Collections.unmodifiableMap(attributeMap));
}
if (!bf.containsBean("contextAttributes")) {
attributeMap = new HashMap();
if (servletContext != null) {
attrNameEnum = servletContext.getAttributeNames();
while(attrNameEnum.hasMoreElements()) {
attrName = (String)attrNameEnum.nextElement();
attributeMap.put(attrName, servletContext.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
bf.registerSingleton("contextAttributes", Collections.unmodifiableMap(attributeMap));
}
}
3.4 finishRefresh()
在容器初始化完成时,启动 WebServer 。覆写 #finishRefresh() 方法,代码如下:
// ServletWebServerApplicationContext.java
@Override
protected void finishRefresh() {
// <1> 调用父方法
super.finishRefresh();
// <2> 启动 WebServer
WebServer webServer = startWebServer();
// <3> 如果创建 WebServer 成功,发布 ServletWebServerInitializedEvent 事件
if (webServer != null) {
publishEvent(new ServletWebServerInitializedEvent(webServer, this));
}
}
3.4.1 <1> 处,调用 #finishRefresh() 方法,执行父逻辑
protected void finishRefresh() {
// Clear context-level resource caches (such as ASM metadata from scanning).
clearResourceCaches();
// Initialize lifecycle processor for this context.
initLifecycleProcessor();
// Propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first.
getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();
// Publish the final event.
publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));
// Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active.
LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this);
}
3.4.2 <2> 处,启动 WebServer
调用 #startWebServer() 方法,代码如下:
// ServletWebServerApplicationContext.java
private WebServer startWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
if (webServer != null) {
webServer.start();
}
return webServer;
}
3.5 onClose() 关闭 WebServer
// ServletWebServerApplicationContext.java
@Override
protected void onClose() {
// 调用父方法
super.onClose();
// 停止 WebServer
stopAndReleaseWebServer();
}
private void stopAndReleaseWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
if (webServer != null) {
try {
webServer.stop();
this.webServer = null;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
}
}
4.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
- 继承 ServletWebServerApplicationContext 类,实现 AnnotationConfigRegistry 接口,进一步提供了两个功能:
- 从指定的 basePackages 包中,扫描 BeanDefinition 们。
- 从指定的 annotatedClasses 注解的配置类(Configuration)中,读取 BeanDefinition 们。
4.1 构造方法
// AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext.java
private final AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader reader;
private final ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner;
private final Set<Class<?>> annotatedClasses = new LinkedHashSet<>();
private String[] basePackages;
/**
* 需要被 {@link #reader} 读取的注册类们
*/
public AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext() {
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
/**
* 需要被 {@link #scanner} 扫描的包
*/
public AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
super(beanFactory);
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
public AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext(Class<?>... annotatedClasses) {
this();
// <1> 注册指定的注解的类们
register(annotatedClasses);
// 初始化 Spring 容器
refresh();
}
public AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext(String... basePackages) {
this();
// <2> 扫描指定包
scan(basePackages);
// 初始化 Spring 容器
refresh();
}
}
4.1.1 <1> 处,注册指定的注解的类们.
- 如果已经传入 annotatedClasses 参数,则调用 #register(Class<?>… annotatedClasses) 方法,设置到 annotatedClasses 中。
- 然后,调用 #refresh() 方法,初始化 Spring 容器。
代码如下:
// AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext.java
@Override
// 实现自 AnnotationConfigRegistry 接口
public final void register(Class<?>... annotatedClasses) {
Assert.notEmpty(annotatedClasses, "At least one annotated class must be specified");
this.annotatedClasses.addAll(Arrays.asList(annotatedClasses));
}
4.1.2 <2> 处扫描指定包
- 如果已经传入 basePackages 参数,则调用 #scan(String… basePackages) 方法,设置到 annotatedClasses 中。
- 然后,调用 #refresh() 方法,初始化 Spring 容器。代码如下:
@Override
public final void scan(String... basePackages) {
Assert.notEmpty(basePackages, "At least one base package must be specified");
this.basePackages = basePackages;
}
4.2 prepareRefresh
- 在 Spring 容器初始化前,需要清空 scanner 的缓存。
- 覆写 #prepareRefresh() 方法,代码如下:
// AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext.java
@Override // 实现自 AbstractApplicationContext 抽象类
protected void prepareRefresh() {
// 清空 scanner 的缓存
this.scanner.clearCache();
// 调用父类
super.prepareRefresh();
}
4.3 postProcessBeanFactory
- 覆写 #postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) 方法,执行 BeanDefinition 的读取。代码如下:
// AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext.java
@Override
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 调用父类
super.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 扫描指定的包
if (this.basePackages != null && this.basePackages.length > 0) {
this.scanner.scan(this.basePackages);
}
// 注册指定的注解的类们定的
if (!this.annotatedClasses.isEmpty()) {
this.reader.register(ClassUtils.toClassArray(this.annotatedClasses));
}
}
上一篇跳转—Java源码(二)Spring Application Context 下一篇跳转—Java源码(三)SpringBoot Web容器应用上下文
本篇文章主要参考链接如下:
参考链接-芋道源码
持续更新中…
随心所往,看见未来。Follow your heart,see light!
欢迎点赞、关注、留言,一起学习、交流!