主要记录算法和数据结构学习笔记,新的一年更上一层楼!
初级算法-二叉树
- 一、递归遍历
- 二、迭代遍历
- 三、统一迭代法
- 四、层序遍历
- 五、翻转二叉树
- 六、对称二叉树
- 七、二叉树的最大深度
- 八、二叉树的最小深度
- 九、完全二叉树的节点个数
- 十、平衡二叉树
- 十一、二叉树的所有路径
- 十二、左叶子之和
- 十三、找树左下角的值
- 十四、路径总和
- 十五、从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
- 十六、最大二叉树
- 十七、合并二叉树
- 十八、二叉搜索树中的搜索
- 十九、验证二叉搜索树
- 二十、二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
- 二十一、二叉搜索树的众数
- 二十二、二叉树的最近公共祖先
- 二十三、二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
- 二十四、二叉搜索树中的插入操作
- 二十五、删除二叉搜索树中的节点
- 二十六、修剪二叉搜索树
- 二十七、将有序数组转换为高度平衡二叉搜索树
- 二十八、把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
- 满二叉树 节点数量为2k-1
- 完全二叉树除了底层以外其他层全是满的,底层从左到右连续
- 二叉搜索树左小右大
- 平衡二叉搜索树左子树和右子树的高度之差的绝对值不超过1,平衡因子为-1,0,1。在c++中map、set底层平衡二叉搜索树
- 存储方式: 链式存储、顺序存储(左孩子2i+1,右孩子2i+2)
- 深度优先搜索(前、中、后序遍历)【从某顶点,依次从它各个未被访问的邻接点出发遍历,直到所有被访问】、广度优先搜索【从某顶点访问v后,依次访问v的各个未被访问的邻接点】
- 前序遍历中左右,中序遍历左中右,后序遍历左右中
一、递归遍历
1.题目:递归遍历:leetcode144 94 145
2.解题思路:
//前序遍历
var preorderTraversal = function(root) {
let res=[];
const dfs=function(root){
if(root===null)return ;
//先序遍历所以从父节点开始
res.push(root.val);
//递归左子树
dfs(root.left);
//递归右子树
dfs(root.right);
}
//只使用一个参数 使用闭包进行存储结果
dfs(root);
return res;
};
//60ms
//41MB
//中序遍历
var inorderTraversal = function(root) {
let res=[];
const dfs=function(root){
if(root===null){
return ;
}
dfs(root.left);
res.push(root.val);
dfs(root.right);
}
dfs(root);
return res;
};
//72ms
//41MB
//后序遍历
var postorderTraversal = function(root) {
let res=[];
const dfs=function(root){
if(root===null){
return ;
}
dfs(root.left);
dfs(root.right);
res.push(root.val);
}
dfs(root);
return res;
};
//64ms
//41MB
二、迭代遍历
1.题目:迭代遍历
2.解题思路:
//前序遍历:
// 入栈 右 -> 左
// 出栈 中 -> 左 -> 右
var preorderTraversal = function(root, res = []) {
if(!root) return res;
const stack = [root];
let cur = null;
while(stack.length) {
cur = stack.pop();
res.push(cur.val);
cur.right && stack.push(cur.right);
cur.left && stack.push(cur.left);
}
return res;
};
中序遍历:
// 入栈 左 -> 右
// 出栈 左 -> 中 -> 右
var inorderTraversal = function(root, res = []) {
const stack = [];
let cur = root;
while(stack.length || cur) {
if(cur) {
stack.push(cur);
// 左
cur = cur.left;
} else {
// --> 弹出 中
cur = stack.pop();
res.push(cur.val);
// 右
cur = cur.right;
}
};
return res;
};
后序遍历:
// 入栈 左 -> 右
// 出栈 中 -> 右 -> 左 结果翻转
var postorderTraversal = function(root, res = []) {
if (!root) return res;
const stack = [root];
let cur = null;
do {
cur = stack.pop();
res.push(cur.val);
cur.left && stack.push(cur.left);
cur.right && stack.push(cur.right);
} while(stack.length);
return res.reverse();
};
三、统一迭代法
1.题目:二叉树的统一迭代法
2.解题思路:
// 前序遍历:中左右
// 压栈顺序:右左中
var preorderTraversal = function(root, res = []) {
const stack = [];
if (root) stack.push(root);
while(stack.length) {
const node = stack.pop();
if(!node) {
res.push(stack.pop().val);
continue;
}
if (node.right) stack.push(node.right); // 右
if (node.left) stack.push(node.left); // 左
stack.push(node); // 中
stack.push(null);
};
return res;
};
// 中序遍历:左中右
// 压栈顺序:右中左
var inorderTraversal = function(root, res = []) {
const stack = [];
if (root) stack.push(root);
while(stack.length) {
const node = stack.pop();
if(!node) {
res.push(stack.pop().val);
continue;
}
if (node.right) stack.push(node.right); // 右
stack.push(node); // 中
stack.push(null);
if (node.left) stack.push(node.left); // 左
};
return res;
};
// 后续遍历:左右中
// 压栈顺序:中右左
var postorderTraversal = function(root, res = []) {
const stack = [];
if (root) stack.push(root);
while(stack.length) {
const node = stack.pop();
if(!node) {
res.push(stack.pop().val);
continue;
}
stack.push(node); // 中
stack.push(null);
if (node.right) stack.push(node.right); // 右
if (node.left) stack.push(node.left); // 左
};
return res;
};
四、层序遍历
1.题目:层序遍历
2.解题思路:
var levelOrder = function(root) {
//二叉树的层序遍历
let res = [], queue = [];
queue.push(root);
if(root === null) {
return res;
}
while(queue.length !== 0) {
// 记录当前层级节点数
let length = queue.length;
//存放每一层的节点
let curLevel = [];
for(let i = 0;i < length; i++) {
let node = queue.shift();
curLevel.push(node.val);
// 存放当前层下一层的节点
node.left && queue.push(node.left);
node.right && queue.push(node.right);
}
//把每一层的结果放到结果数组
res.push(curLevel);
}
return res;
};
五、翻转二叉树
1.题目
翻转二叉树
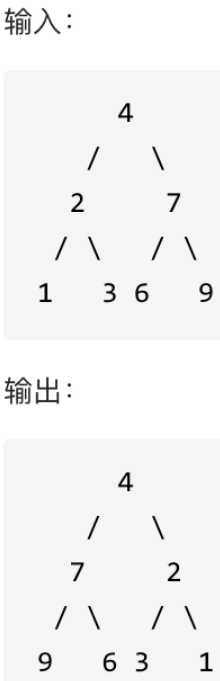
2.**解题思路**:
```javascript
//递归的前序遍历
var invertTree = function(root) {
// 终止条件
if (!root) {
return null;
}
// 交换左右节点
const rightNode = root.right;
root.right = invertTree(root.left);
root.left = invertTree(rightNode);
return root;
};
//迭代的前序遍历
var invertTree = function(root) {
//我们先定义节点交换函数
const invertNode = function(root, left, right) {
let temp = left;
left = right;
right = temp;
root.left = left;
root.right = right;
}
//使用迭代方法的前序遍历
let stack = [];
if(root === null) {
return root;
}
stack.push(root);
while(stack.length) {
let node = stack.pop();
if(node !== null) {
//前序遍历顺序中左右 入栈顺序是前序遍历的倒序右左中
node.right && stack.push(node.right);
node.left && stack.push(node.left);
stack.push(node);
stack.push(null);
} else {
node = stack.pop();
//节点处理逻辑
invertNode(node, node.left, node.right);
}
}
return root;
};
//层序遍历
var invertTree = function(root) {
//我们先定义节点交换函数
const invertNode = function(root, left, right) {
let temp = left;
left = right;
right = temp;
root.left = left;
root.right = right;
}
//使用层序遍历
let queue = [];
if(root === null) {
return root;
}
queue.push(root);
while(queue.length) {
let length = queue.length;
while(length--) {
let node = queue.shift();
//节点处理逻辑
invertNode(node, node.left, node.right);
node.left && queue.push(node.left);
node.right && queue.push(node.right);
}
}
return root;
};
六、对称二叉树
1.题目:

2.解题思路:
//递归判断
var isSymmetric = function(root) {
// 使用递归遍历左右子树 递归三部曲
// 1. 确定递归的参数 root.left root.right和返回值true false
const compareNode = function(left, right) {
// 2. 确定终止条件 空的情况
if(left === null && right !== null || left !== null && right === null) {
return false;
} else if(left === null && right === null) {
return true;
} else if(left.val !== right.val) {
return false;
}
// 3. 确定单层递归逻辑
let outSide = compareNode(left.left, right.right);
let inSide = compareNode(left.right, right.left);
return outSide && inSide;
}
if(root === null) {
return true;
}
return compareNode(root.left, root.right);
};
//队列实现迭代判断
var isSymmetric = function(root) {
// 迭代方法判断是否是对称二叉树
// 首先判断root是否为空
if(root === null) {
return true;
}
let queue = [];
queue.push(root.left);
queue.push(root.right);
while(queue.length) {
let leftNode = queue.shift(); //左节点
let rightNode = queue.shift(); //右节点
if(leftNode === null && rightNode === null) {
continue;
}
if(leftNode === null || rightNode === null || leftNode.val !== rightNode.val) {
return false;
}
queue.push(leftNode.left); //左节点左孩子入队
queue.push(rightNode.right); //右节点右孩子入队
queue.push(leftNode.right); //左节点右孩子入队
queue.push(rightNode.left); //右节点左孩子入队
}
return true;
};
//栈实现迭代判断
var isSymmetric = function(root) {
// 迭代方法判断是否是对称二叉树
// 首先判断root是否为空
if(root === null) {
return true;
}
let stack = [];
stack.push(root.left);
stack.push(root.right);
while(stack.length) {
let rightNode = stack.pop(); //左节点
let leftNode=stack.pop(); //右节点
if(leftNode === null && rightNode === null) {
continue;
}
if(leftNode === null || rightNode === null || leftNode.val !== rightNode.val) {
return false;
}
stack.push(leftNode.left); //左节点左孩子入队
stack.push(rightNode.right); //右节点右孩子入队
stack.push(leftNode.right); //左节点右孩子入队
stack.push(rightNode.left); //右节点左孩子入队
}
return true;
};
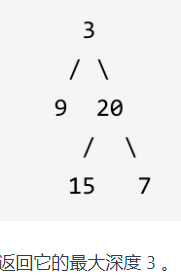
七、二叉树的最大深度
1.题目:
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
//递归遍历
var maxdepth = function(root) {
//使用递归的方法 递归三部曲
//1. 确定递归函数的参数和返回值
const getdepth = function(node) {
//2. 确定终止条件
if(node === null) {
return 0;
}
//3. 确定单层逻辑
let leftdepth = getdepth(node.left);
let rightdepth = getdepth(node.right);
let depth = 1 + Math.max(leftdepth, rightdepth);
return depth;
}
return getdepth(root);
};
//层级遍历
var maxDepth = function(root) {
if(!root) return 0
let count = 0
const queue = [root]
while(queue.length) {
let size = queue.length
/* 层数+1 */
count++
while(size--) {
let node = queue.shift();
node.left && queue.push(node.left);
node.right && queue.push(node.right);
}
}
return count
};
八、二叉树的最小深度
1.题目:
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
最小深度2
//递归遍历
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var minDepth1 = function(root) {
if(!root) return 0;
// 到叶子节点 返回 1
if(!root.left && !root.right) return 1;
// 只有右节点时 递归右节点
if(!root.left) return 1 + minDepth(root.right);
// 只有左节点时 递归左节点
if(!root.right) return 1 + minDepth(root.left);
return Math.min(minDepth(root.left), minDepth(root.right)) + 1;
};
//迭代遍历
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var minDepth = function(root) {
if(!root) return 0;
const queue = [root];
let dep = 0;
while(true) {
let size = queue.length;
dep++;
while(size--){
const node = queue.shift();
// 到第一个叶子节点 返回 当前深度
if(!node.left && !node.right) return dep;
node.left && queue.push(node.left);
node.right && queue.push(node.right);
}
}
};
九、完全二叉树的节点个数
1.题目:
给出一个完全二叉树,求出该树的节点个数。
示例
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
输出:6
示例 2:
输入:root = []
输出:0
示例 3:
输入:root = [1]
输出:1
提示:
- 树中节点的数目范围是[0, 5 * 10^4]
- 0 <= Node.val <= 5 * 10^4
- 题目数据保证输入的树是 完全二叉树
//递归遍历
var countNodes = function(root) {
//递归法计算二叉树节点数
// 1. 确定递归函数参数
const getNodeSum = function(node) {
//2. 确定终止条件
if(node === null) {
return 0;
}
//3. 确定单层递归逻辑
let leftNum = getNodeSum(node.left);
let rightNum = getNodeSum(node.right);
return leftNum + rightNum + 1;
}
return getNodeSum(root);
};
//迭代遍历
var countNodes = function(root) {
//层序遍历
let queue = [];
if(root === null) {
return 0;
}
queue.push(root);
let nodeNums = 0;
while(queue.length) {
let length = queue.length;
while(length--) {
let node = queue.shift();
nodeNums++;
node.left && queue.push(node.left);
node.right && queue.push(node.right);
}
}
return nodeNums;
};
//完全二叉树性质
var countNodes = function(root) {
//利用完全二叉树的特点
if(root === null) {
return 0;
}
let left = root.left;
let right = root.right;
let leftDepth = 0, rightDepth = 0;
while(left) {
left = left.left;
leftDepth++;
}
while(right) {
right = right.right;
rightDepth++;
}
if(leftDepth == rightDepth) {
return Math.pow(2, leftDepth+1) - 1;
}
return countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1;
};
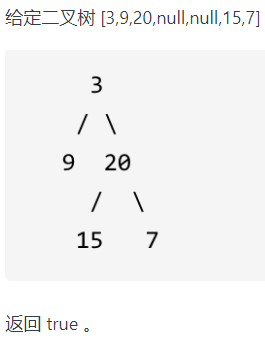
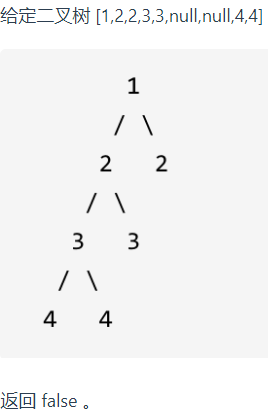
十、平衡二叉树
1.题目:
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。
本题中,一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1。
示例
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
//递归
var isBalanced = function(root) {
//还是用递归三部曲 + 后序遍历 左右中 当前左子树右子树高度相差大于1就返回-1
// 1. 确定递归函数参数以及返回值
const getDepth = function(node) {
// 2. 确定递归函数终止条件
if(node === null) return 0;
// 3. 确定单层递归逻辑
let leftDepth = getDepth(node.left); //左子树高度
// 当判定左子树不为平衡二叉树时,即可直接返回-1
if(leftDepth === -1) return -1;
let rightDepth = getDepth(node.right); //右子树高度
// 当判定右子树不为平衡二叉树时,即可直接返回-1
if(rightDepth === -1) return -1;
if(Math.abs(leftDepth - rightDepth) > 1) {
return -1;
} else {
return 1 + Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth);
}
}
return !(getDepth(root) === -1);
};
//迭代遍历
// 获取当前节点的高度
var getHeight = function (curNode) {
let stack = [];
if (curNode !== null) stack.push(curNode); // 压入当前元素
let depth = 0, res = 0;
while (stack.length) {
let node = stack[stack.length - 1]; // 取出栈顶
if (node !== null) {
stack.pop();
stack.push(node); // 中
stack.push(null);
depth++;
node.right && stack.push(node.right); // 右
node.left && stack.push(node.left); // 左
} else {
stack.pop();
node = stack[stack.length - 1];
stack.pop();
depth--;
}
res = res > depth ? res : depth;
}
return res;
}
var isBalanced = function (root) {
if (root === null) return true;
let stack = [root];
while (stack.length) {
let node = stack[stack.length - 1]; // 取出栈顶
stack.pop();
if (Math.abs(getHeight(node.left) - getHeight(node.right)) > 1) {
return false;
}
node.right && stack.push(node.right);
node.left && stack.push(node.left);
}
return true;
};
十一、二叉树的所有路径
1.题目:
给定一个二叉树,返回所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例

//递归遍历
var binaryTreePaths = function(root) {
//递归遍历+递归三部曲
let res = [];
//1. 确定递归函数 函数参数
const getPath = function(node,curPath) {
//2. 确定终止条件,到叶子节点就终止
if(node.left === null && node.right === null) {
curPath += node.val;
res.push(curPath);
return;
}
//3. 确定单层递归逻辑
curPath += node.val + '->';
node.left && getPath(node.left, curPath);
node.right && getPath(node.right, curPath);
}
getPath(root, '');
return res;
};
//迭代遍历
var binaryTreePaths = function(root) {
if (!root) return [];
const stack = [root], paths = [''], res = [];
while (stack.length) {
const node = stack.pop();
let path = paths.pop();
if (!node.left && !node.right) { // 到叶子节点终止, 添加路径到结果中
res.push(path + node.val);
continue;
}
path += node.val + '->';
if (node.right) { // 右节点存在
stack.push(node.right);
paths.push(path);
}
if (node.left) { // 左节点存在
stack.push(node.left);
paths.push(path);
}
}
return res;
};
十二、左叶子之和
1.题目:
计算给定二叉树的所有左叶子之和。
示例

//递归遍历
var sumOfLeftLeaves = function(root) {
//采用后序遍历 递归遍历
// 1. 确定递归函数参数
const nodesSum = function(node) {
// 2. 确定终止条件
if(node === null) {
return 0;
}
let leftValue = nodesSum(node.left);
let rightValue = nodesSum(node.right);
// 3. 单层递归逻辑
let midValue = 0;
if(node.left && node.left.left === null && node.left.right === null) {
midValue = node.left.val;
}
let sum = midValue + leftValue + rightValue;
return sum;
}
return nodesSum(root);
};
//迭代遍历
var sumOfLeftLeaves = function(root) {
//采用层序遍历
if(root === null) {
return null;
}
let queue = [];
let sum = 0;
queue.push(root);
while(queue.length) {
let node = queue.shift();
if(node.left !== null && node.left.left === null && node.left.right === null) {
sum+=node.left.val;
}
node.left && queue.push(node.left);
node.right && queue.push(node.right);
}
return sum;
};
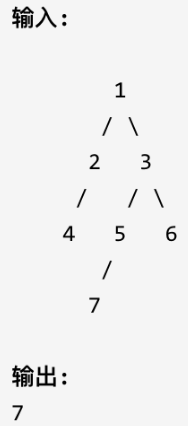
十三、找树左下角的值
1.题目:
给定一个二叉树,在树的最后一行找到最左边的值。
示例
//递归遍历
var findBottomLeftValue = function(root) {
//首先考虑递归遍历 前序遍历 找到最大深度的叶子节点即可
let maxPath = 0, resNode = null;
// 1. 确定递归函数的函数参数
const dfsTree = function(node, curPath) {
// 2. 确定递归函数终止条件
if(node.left === null && node.right === null) {
if(curPath > maxPath) {
maxPath = curPath;
resNode = node.val;
}
}
node.left && dfsTree(node.left, curPath+1);
node.right && dfsTree(node.right, curPath+1);
}
dfsTree(root,1);
return resNode;
};
//层序遍历
var findBottomLeftValue = function(root) {
//考虑层序遍历 记录最后一行的第一个节点
let queue = [];
if(root === null) {
return null;
}
queue.push(root);
let resNode;
while(queue.length) {
let length = queue.length;
for(let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
let node = queue.shift();
if(i === 0) {
resNode = node.val;
}
node.left && queue.push(node.left);
node.right && queue.push(node.right);
}
}
return resNode;
};
十四、路径总和
1.题目:
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,判断该树中是否存在根节点到叶子节点的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例
示例: 给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22,
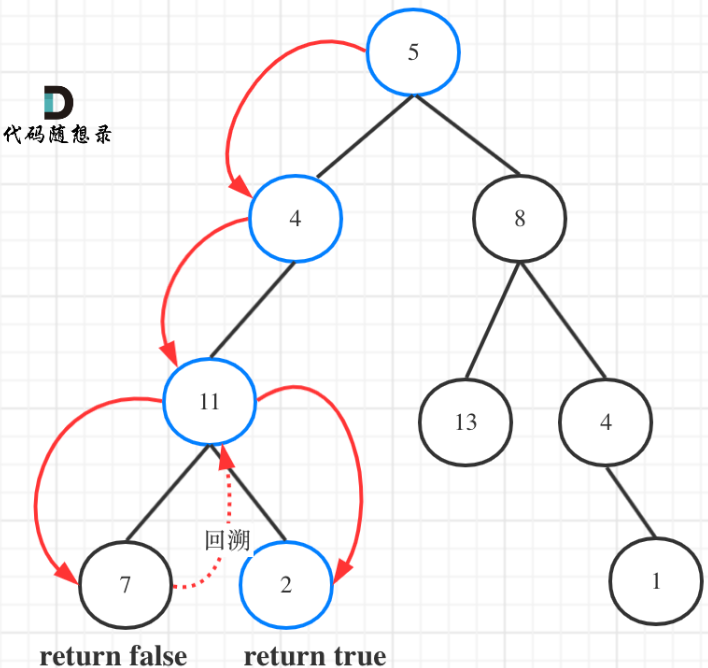
返回 true, 因为存在目标和为 22 的根节点到叶子节点的路径 5->4->11->2。
//递归遍历
/**
* @param {treenode} root
* @param {number} targetsum
* @return {boolean}
*/
let haspathsum = function (root, targetsum) {
// 递归法
const traversal = (node, cnt) => {
// 遇到叶子节点,并且计数为0
if (cnt === 0 && !node.left && !node.right) return true;
// 遇到叶子节点而没有找到合适的边(计数不为0),直接返回
if (!node.left && !node.right) return false;
// 左(空节点不遍历).遇到叶子节点返回true,则直接返回true
if (node.left && traversal(node.left, cnt - node.left.val)) return true;
// 右(空节点不遍历)
if (node.right && traversal(node.right, cnt - node.right.val)) return true;
return false;
};
if (!root) return false;
return traversal(root, targetsum - root.val);
// 精简代码:
// if (!root) return false;
// if (!root.left && !root.right && targetsum === root.val) return true;
// return haspathsum(root.left, targetsum - root.val) || haspathsum(root.right, targetsum - root.val);
};
//迭代遍历
let hasPathSum = function(root, targetSum) {
if(root === null) return false;
let nodeArr = [root];
let valArr = [0];
while(nodeArr.length) {
let curNode = nodeArr.shift();
let curVal = valArr.shift();
curVal += curNode.val;
// 为叶子结点,且和等于目标数,返回true
if (curNode.left === null && curNode.right === null && curVal === targetSum) {
return true;
}
// 左节点,将当前的数值也对应记录下来
if (curNode.left) {
nodeArr.push(curNode.left);
valArr.push(curVal);
}
// 右节点,将当前的数值也对应记录下来
if (curNode.right) {
nodeArr.push(curNode.right);
valArr.push(curVal);
}
}
return false;
};
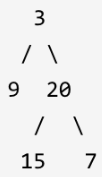
十五、从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
1.题目:
根据一棵树的中序遍历与后序遍历构造二叉树。
注意: 你可以假设树中没有重复的元素。
示例
例如,给出
中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
后序遍历 postorder = [9,15,7,20,3] 返回如下的二叉树:
var buildTree = function(inorder, postorder) {
if (!inorder.length) return null;
const rootVal = postorder.pop(); // 从后序遍历的数组中获取中间节点的值, 即数组最后一个值
let rootIndex = inorder.indexOf(rootVal); // 获取中间节点在中序遍历中的下标
const root = new TreeNode(rootVal); // 创建中间节点
root.left = buildTree(inorder.slice(0, rootIndex), postorder.slice(0, rootIndex)); // 创建左节点
root.right = buildTree(inorder.slice(rootIndex + 1), postorder.slice(rootIndex)); // 创建右节点
return root;
};
//从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
var buildTree = function(preorder, inorder) {
if (!preorder.length) return null;
const rootVal = preorder.shift(); // 从前序遍历的数组中获取中间节点的值, 即数组第一个值
const index = inorder.indexOf(rootVal); // 获取中间节点在中序遍历中的下标
const root = new TreeNode(rootVal); // 创建中间节点
root.left = buildTree(preorder.slice(0, index), inorder.slice(0, index)); // 创建左节点
root.right = buildTree(preorder.slice(index), inorder.slice(index + 1)); // 创建右节点
return root;
};
十六、最大二叉树
1.题目:
给定一个不含重复元素的整数数组。一个以此数组构建的最大二叉树定义如下:
- 二叉树的根是数组中的最大元素。
- 左子树是通过数组中最大值左边部分构造出的最大二叉树。
- 右子树是通过数组中最大值右边部分构造出的最大二叉树。
通过给定的数组构建最大二叉树,并且输出这个树的根节点。
示例

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var constructMaximumBinaryTree = function (nums) {
const BuildTree = (arr, left, right) => {
if (left > right)
return null;
let maxValue = -1;
let maxIndex = -1;
for (let i = left; i <= right; ++i) {
if (arr[i] > maxValue) {
maxValue = arr[i];
maxIndex = i;
}
}
let root = new TreeNode(maxValue);
root.left = BuildTree(arr, left, maxIndex - 1);
root.right = BuildTree(arr, maxIndex + 1, right);
return root;
}
let root = BuildTree(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
return root;
};
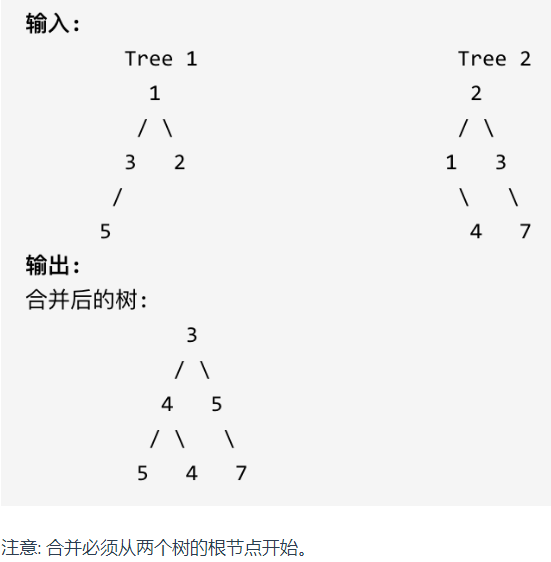
十七、合并二叉树
1.题目:
给定两个二叉树,想象当你将它们中的一个覆盖到另一个上时,两个二叉树的一些节点便会重叠。
你需要将他们合并为一个新的二叉树。合并的规则是如果两个节点重叠,那么将他们的值相加作为节点合并后的新值,否则不为 NULL 的节点将直接作为新二叉树的节点。
示例
//递归法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root1
* @param {TreeNode} root2
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var mergeTrees = function (root1, root2) {
const preOrder = (root1, root2) => {
if (!root1)
return root2
if (!root2)
return root1;
root1.val += root2.val;
root1.left = preOrder(root1.left, root2.left);
root1.right = preOrder(root1.right, root2.right);
return root1;
}
return preOrder(root1, root2);
};
//迭代法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root1
* @param {TreeNode} root2
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var mergeTrees = function(root1, root2) {
if (root1 === null) return root2;
if (root2 === null) return root1;
let queue = [];
queue.push(root1);
queue.push(root2);
while (queue.length) {
let node1 = queue.shift();
let node2 = queue.shift();;
node1.val += node2.val;
if (node1.left !== null && node2.left !== null) {
queue.push(node1.left);
queue.push(node2.left);
}
if (node1.right !== null && node2.right !== null) {
queue.push(node1.right);
queue.push(node2.right);
}
if (node1.left === null && node2.left !== null) {
node1.left = node2.left;
}
if (node1.right === null && node2.right !== null) {
node1.right = node2.right;
}
}
return root1;
};
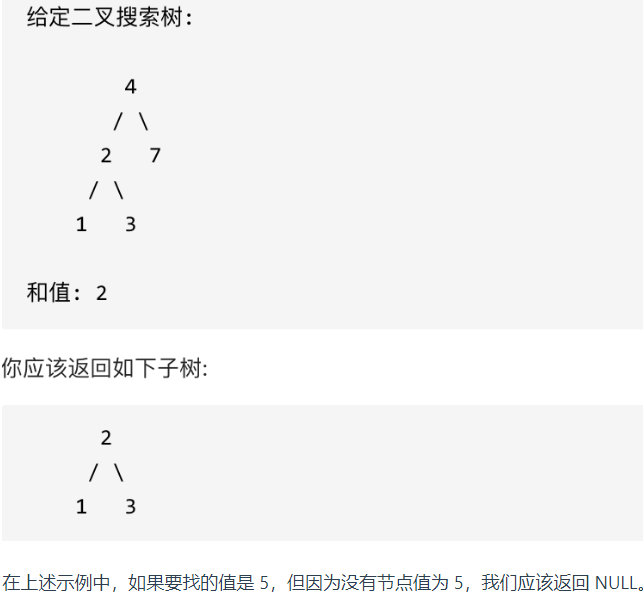
十八、二叉搜索树中的搜索
1.题目:
给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点和一个值。 你需要在BST中找到节点值等于给定值的节点。 返回以该节点为根的子树。 如果节点不存在,则返回 NULL。
示例
//递归
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} val
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var searchBST = function (root, val) {
if (!root || root.val === val) {
return root;
}
if (root.val > val)
return searchBST(root.left, val);
if (root.val < val)
return searchBST(root.right, val);
};
//迭代
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} val
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var searchBST = function (root, val) {
while (root !== null) {
if (root.val > val)
root = root.left;
else if (root.val < val)
root = root.right;
else
return root;
}
return null;
};
十九、验证二叉搜索树
1.题目:
给定一个二叉树,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。
假设一个二叉搜索树具有如下特征:
- 节点的左子树只包含小于当前节点的数。
- 节点的右子树只包含大于当前节点的数。
- 所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。
示例

//辅助数组
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isValidBST = function (root) {
let arr = [];
const buildArr = (root) => {
if (root) {
buildArr(root.left);
arr.push(root.val);
buildArr(root.right);
}
}
buildArr(root);
for (let i = 1; i < arr.length; ++i) {
if (arr[i] <= arr[i - 1])
return false;
}
return true;
};
//递归
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {boolean}
*/
let pre = null;
var isValidBST = function (root) {
let pre = null;
const inOrder = (root) => {
if (root === null)
return true;
let left = inOrder(root.left);
if (pre !== null && pre.val >= root.val)
return false;
pre = root;
let right = inOrder(root.right);
return left && right;
}
return inOrder(root);
};
二十、二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
1.题目:
给你一棵所有节点为非负值的二叉搜索树,请你计算树中任意两节点的差的绝对值的最小值。
示例

//递归 先转换为有序数组
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var getMinimumDifference = function (root) {
let arr = [];
const buildArr = (root) => {
if (root) {
buildArr(root.left);
arr.push(root.val);
buildArr(root.right);
}
}
buildArr(root);
let diff = arr[arr.length - 1];
for (let i = 1; i < arr.length; ++i) {
if (diff > arr[i] - arr[i - 1])
diff = arr[i] - arr[i - 1];
}
return diff;
};
// 递归 在递归过程中更新最小值
var getMinimumDifference = function(root) {
let res = Infinity
let preNode = null
// 中序遍历
const inorder = (node) => {
if(!node) return
inorder(node.left)
// 更新res
if(preNode) res = Math.min(res, node.val - preNode.val)
// 记录前一个节点
preNode = node
inorder(node.right)
}
inorder(root)
return res
}
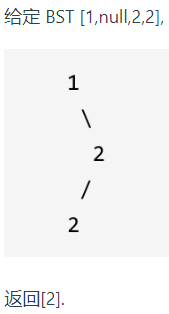
二十一、二叉搜索树的众数
1.题目:
给定一个有相同值的二叉搜索树(BST),找出 BST 中的所有众数(出现频率最高的元素)。
假定 BST 有如下定义:
- 结点左子树中所含结点的值小于等于当前结点的值
- 结点右子树中所含结点的值大于等于当前结点的值
- 左子树和右子树都是二叉搜索树
示例
//额外空间,map
var findMode = function(root) {
// 使用递归中序遍历
let map = new Map();
// 1. 确定递归函数以及函数参数
const traverTree = function(root) {
// 2. 确定递归终止条件
if(root === null) {
return ;
}
traverTree(root.left);
// 3. 单层递归逻辑
map.set(root.val,map.has(root.val)?map.get(root.val)+1:1);
traverTree(root.right);
}
traverTree(root);
//上面把数据都存储到map
//下面开始寻找map里面的
// 定义一个最大出现次数的初始值为root.val的出现次数
let maxCount = map.get(root.val);
// 定义一个存放结果的数组res
let res = [];
for(let [key,value] of map) {
// 如果当前值等于最大出现次数就直接在res增加该值
if(value === maxCount) {
res.push(key);
}
// 如果value的值大于原本的maxCount就清空res的所有值,因为找到了更大的
if(value>maxCount) {
res = [];
maxCount = value;
res.push(key);
}
}
return res;
};
//不使用额外空间,二叉树的中序遍历
var findMode = function(root) {
// 不使用额外空间,使用中序遍历,设置出现最大次数初始值为1
let count = 0,maxCount = 1;
let pre = root,res = [];
// 1.确定递归函数及函数参数
const travelTree = function(cur) {
// 2. 确定递归终止条件
if(cur === null) {
return ;
}
travelTree(cur.left);
// 3. 单层递归逻辑
if(pre.val === cur.val) {
count++;
}else {
count = 1;
}
pre = cur;
if(count === maxCount) {
res.push(cur.val);
}
if(count > maxCount) {
res = [];
maxCount = count;
res.push(cur.val);
}
travelTree(cur.right);
}
travelTree(root);
return res;
};
二十二、二叉树的最近公共祖先
1.题目:
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
示例
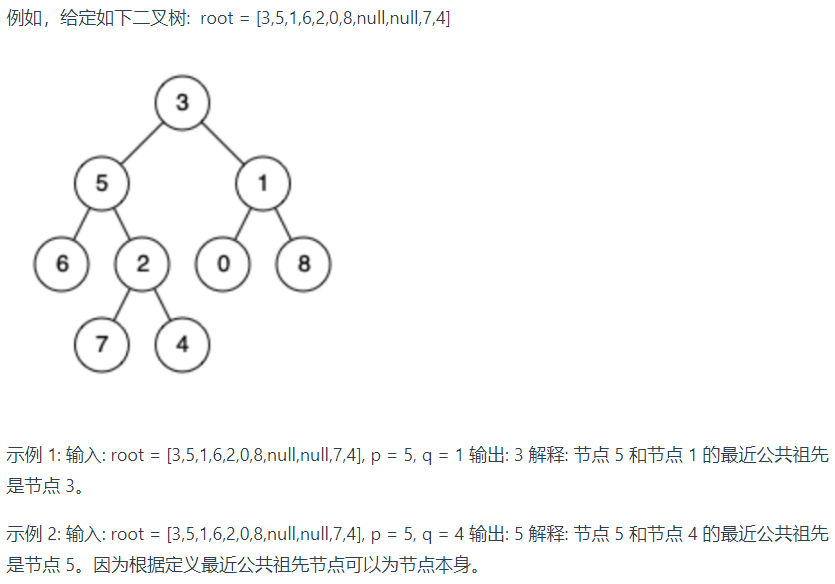
说明:
所有节点的值都是唯一的。
p、q 为不同节点且均存在于给定的二叉树中。
var lowestCommonAncestor = function(root, p, q) {
// 使用递归的方法
// 需要从下到上,所以使用后序遍历
// 1. 确定递归的函数
const travelTree = function(root,p,q) {
// 2. 确定递归终止条件
if(root === null || root === p || root === q) {
return root;
}
// 3. 确定递归单层逻辑
let left = travelTree(root.left,p,q);
let right = travelTree(root.right,p,q);
if(left !== null && right !== null) {
return root;
}
if(left === null) {
return right;
}
return left;
}
return travelTree(root,p,q);
};
二十三、二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
1.题目:
给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
示例
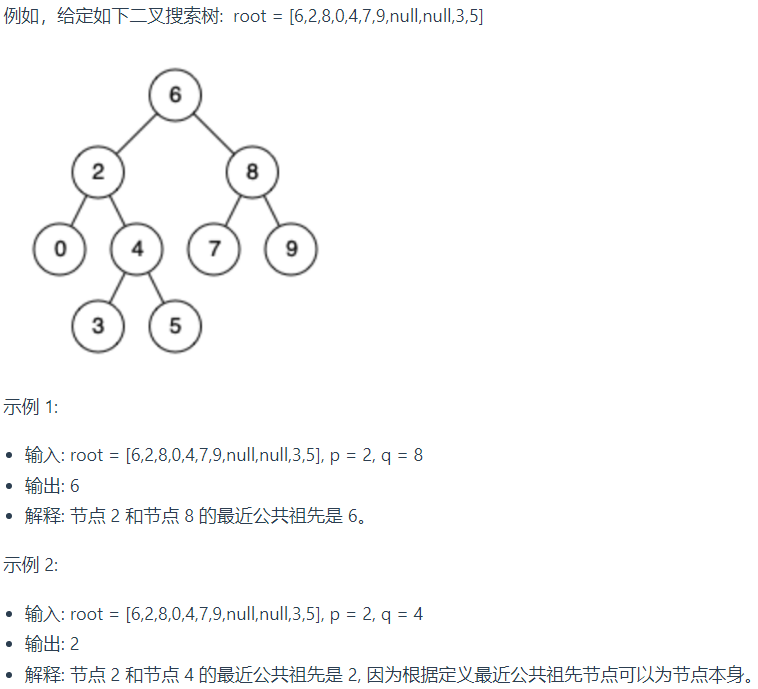
说明:
- 所有节点的值都是唯一的。
- p、q 为不同节点且均存在于给定的二叉搜索树中。
//递归法
var lowestCommonAncestor = function(root, p, q) {
// 使用递归的方法
// 1. 使用给定的递归函数lowestCommonAncestor
// 2. 确定递归终止条件
if(root === null) {
return root;
}
if(root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val) {
// 向左子树查询
return root.left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
}
if(root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val) {
// 向右子树查询
return root.right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
}
return root;
};
//迭代法
var lowestCommonAncestor = function(root, p, q) {
// 使用迭代的方法
while(root) {
if(root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val) {
root = root.left;
}else if(root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val) {
root = root.right;
}else {
return root;
}
}
return null;
};
二十四、二叉搜索树中的插入操作
1.题目:
给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点和要插入树中的值,将值插入二叉搜索树。 返回插入后二叉搜索树的根节点。 输入数据保证,新值和原始二叉搜索树中的任意节点值都不同。
注意,可能存在多种有效的插入方式,只要树在插入后仍保持为二叉搜索树即可。 你可以返回任意有效的结果。
示例
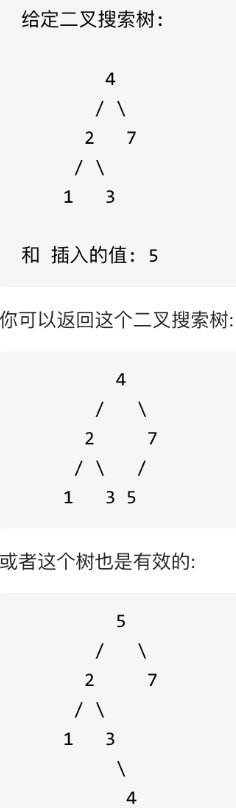
//有返回值的递归写法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} val
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var insertIntoBST = function (root, val) {
const setInOrder = (root, val) => {
if (root === null) {
let node = new TreeNode(val);
return node;
}
if (root.val > val)
root.left = setInOrder(root.left, val);
else if (root.val < val)
root.right = setInOrder(root.right, val);
return root;
}
return setInOrder(root, val);
};
//无返回值的递归
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} val
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var insertIntoBST = function (root, val) {
let parent = new TreeNode(0);
const preOrder = (cur, val) => {
if (cur === null) {
let node = new TreeNode(val);
if (parent.val > val)
parent.left = node;
else
parent.right = node;
return;
}
parent = cur;
if (cur.val > val)
preOrder(cur.left, val);
if (cur.val < val)
preOrder(cur.right, val);
}
if (root === null)
root = new TreeNode(val);
preOrder(root, val);
return root;
};
二十五、删除二叉搜索树中的节点
1.题目:
给定一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root 和一个值 key,删除二叉搜索树中的 key 对应的节点,并保证二叉搜索树的性质不变。返回二叉搜索树(有可能被更新)的根节点的引用。
一般来说,删除节点可分为两个步骤:
首先找到需要删除的节点; 如果找到了,删除它。 说明: 要求算法时间复杂度为 O ( h ) O(h) O(h),h 为树的高度。
示例

//递归
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} key
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var deleteNode = function(root, key) {
if (!root) return null;
if (key > root.val) {
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key);
return root;
} else if (key < root.val) {
root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key);
return root;
} else {
// 场景1: 该节点是叶节点
if (!root.left && !root.right) {
return null
}
// 场景2: 有一个孩子节点不存在
if (root.left && !root.right) {
return root.left;
} else if (root.right && !root.left) {
return root.right;
}
// 场景3: 左右节点都存在
const rightNode = root.right;
// 获取最小值节点
const minNode = getMinNode(rightNode);
// 将待删除节点的值替换为最小值节点值
root.val = minNode.val;
// 删除最小值节点
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, minNode.val);
return root;
}
};
function getMinNode(root) {
while (root.left) {
root = root.left;
}
return root;
}
//迭代
var deleteNode = function (root, key) {
const deleteOneNode = target => {
if (!target) return target
if (!target.right) return target.left
let cur = target.right
while (cur.left) {
cur = cur.left
}
cur.left = target.left
return target.right
}
if (!root) return root
let cur = root
let pre = null
while (cur) {
if (cur.val === key) break
pre = cur
cur.val > key ? cur = cur.left : cur = cur.right
}
if (!pre) {
return deleteOneNode(cur)
}
if (pre.left && pre.left.val === key) {
pre.left = deleteOneNode(cur)
}
if (pre.right && pre.right.val === key) {
pre.right = deleteOneNode(cur)
}
return root
}
二十六、修剪二叉搜索树
1.题目:
给定一个二叉搜索树,同时给定最小边界L 和最大边界 R。通过修剪二叉搜索树,使得所有节点的值在[L, R]中 (R>=L) 。你可能需要改变树的根节点,所以结果应当返回修剪好的二叉搜索树的新的根节点。
示例
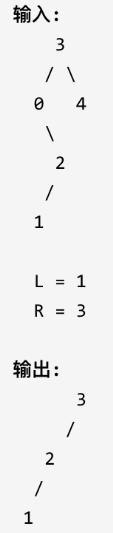
//递归
var trimBST = function (root,low,high) {
if(root === null) {
return null;
}
if(root.val < low) {
let right = trimBST(root.right, low, high);
return right;
}
if(root.val > high) {
let left = trimBST(root.left, low, high);
return left;
}
root.left = trimBST(root.left, low, high);
root.right = trimBST(root.right, low, high);
return root;
}
//迭代
var trimBST = function(root, low, high) {
if(root === null) {
return null;
}
while(root !== null && (root.val < low || root.val > high)) {
if(root.val < low) {
root = root.right;
}else {
root = root.left;
}
}
let cur = root;
while(cur !== null) {
while(cur.left && cur.left.val < low) {
cur.left = cur.left.right;
}
cur = cur.left;
}
cur = root;
//判断右子树大于high的情况
while(cur !== null) {
while(cur.right && cur.right.val > high) {
cur.right = cur.right.left;
}
cur = cur.right;
}
return root;
};
二十七、将有序数组转换为高度平衡二叉搜索树
1.题目:
将一个按照升序排列的有序数组,转换为一棵高度平衡二叉搜索树。
本题中,一个高度平衡二叉树是指一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1。
示例

//递归
var sortedArrayToBST = function (nums) {
const buildTree = (Arr, left, right) => {
if (left > right)
return null;
let mid = Math.floor(left + (right - left) / 2);
let root = new TreeNode(Arr[mid]);
root.left = buildTree(Arr, left, mid - 1);
root.right = buildTree(Arr, mid + 1, right);
return root;
}
return buildTree(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
};
//迭代
var sortedArrayToBST = function(nums) {
if(nums.length===0) {
return null;
}
let root = new TreeNode(0); //初始根节点
let nodeQue = [root]; //放遍历的节点,并初始化
let leftQue = [0]; //放左区间的下标,初始化
let rightQue = [nums.length-1]; // 放右区间的下标
while(nodeQue.length) {
let curNode = nodeQue.pop();
let left = leftQue.pop();
let right = rightQue.pop();
let mid = left + Math.floor((right-left)/2);
curNode.val = nums[mid]; //将下标为mid的元素给中间节点
// 处理左区间
if(left <= mid-1) {
curNode.left = new TreeNode(0);
nodeQue.push(curNode.left);
leftQue.push(left);
rightQue.push(mid-1);
}
// 处理右区间
if(right >= mid+1) {
curNode.right = new TreeNode(0);
nodeQue.push(curNode.right);
leftQue.push(mid+1);
rightQue.push(right);
}
}
return root;
};
二十八、把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
1.题目:
给出二叉 搜索 树的根节点,该树的节点值各不相同,请你将其转换为累加树(Greater Sum Tree),使每个节点 node 的新值等于原树中大于或等于 node.val 的值之和。
提醒一下,二叉搜索树满足下列约束条件:
节点的左子树仅包含键 小于 节点键的节点。 节点的右子树仅包含键 大于 节点键的节点。 左右子树也必须是二叉搜索树。
示例
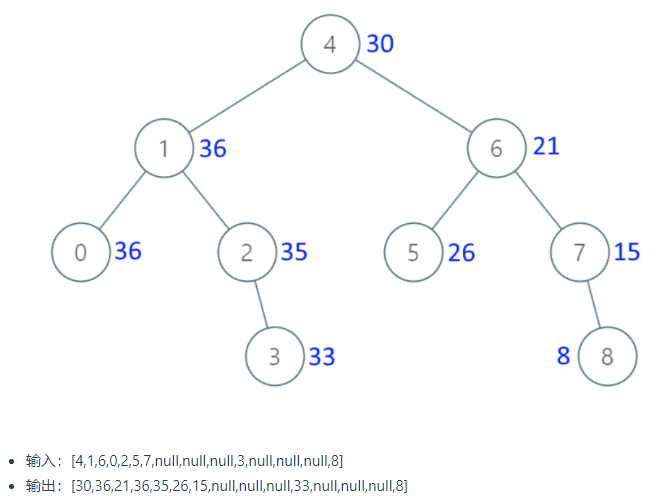
提示:
- 树中的节点数介于 0 和 104 之间。
- 每个节点的值介于 -104 和 104 之间。
- 树中的所有值 互不相同 。
- 给定的树为二叉搜索树。
//递归
var convertBST = function(root) {
let pre = 0;
const ReverseInOrder = (cur) => {
if(cur) {
ReverseInOrder(cur.right);
cur.val += pre;
pre = cur.val;
ReverseInOrder(cur.left);
}
}
ReverseInOrder(root);
return root;
};
//迭代
var convertBST = function (root) {
let pre = 0;
let cur = root;
let stack = [];
while (cur !== null || stack.length !== 0) {
while (cur !== null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.right;
}
cur = stack.pop();
cur.val += pre;
pre = cur.val;
cur = cur.left;
}
return root;
};


![[STM32F103C8T6]基于LCD和DHT11、HC08的温湿度检测系统并上传服务器](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/56b74c5caf734ea0ace2b278adf33153.png)