本篇博客详细介绍list的实现&细节讲解,并且在文章末对list和vector,string进行区分和复习

list的基本结构就是双向带头循环链表,链表和顺序表的差别我们在前面数据结构的时候早就学过了,不再赘述
在使用stl库里面list时,要加上头文件
快速高效编辑查找元素 用vector
大批量增删数据 用list
目录
1.基本框架的实现
2.很细节的函数实现
3.vector和list对比
4.迭代器失效
1.基本框架的实现
定义模板T 还是表示每个节点data的类型
首先我们需要思考:
这个链表的每个节点的类型是什么?_list_node<T>
节点里面包含什么?当然 不要忘记构造函数

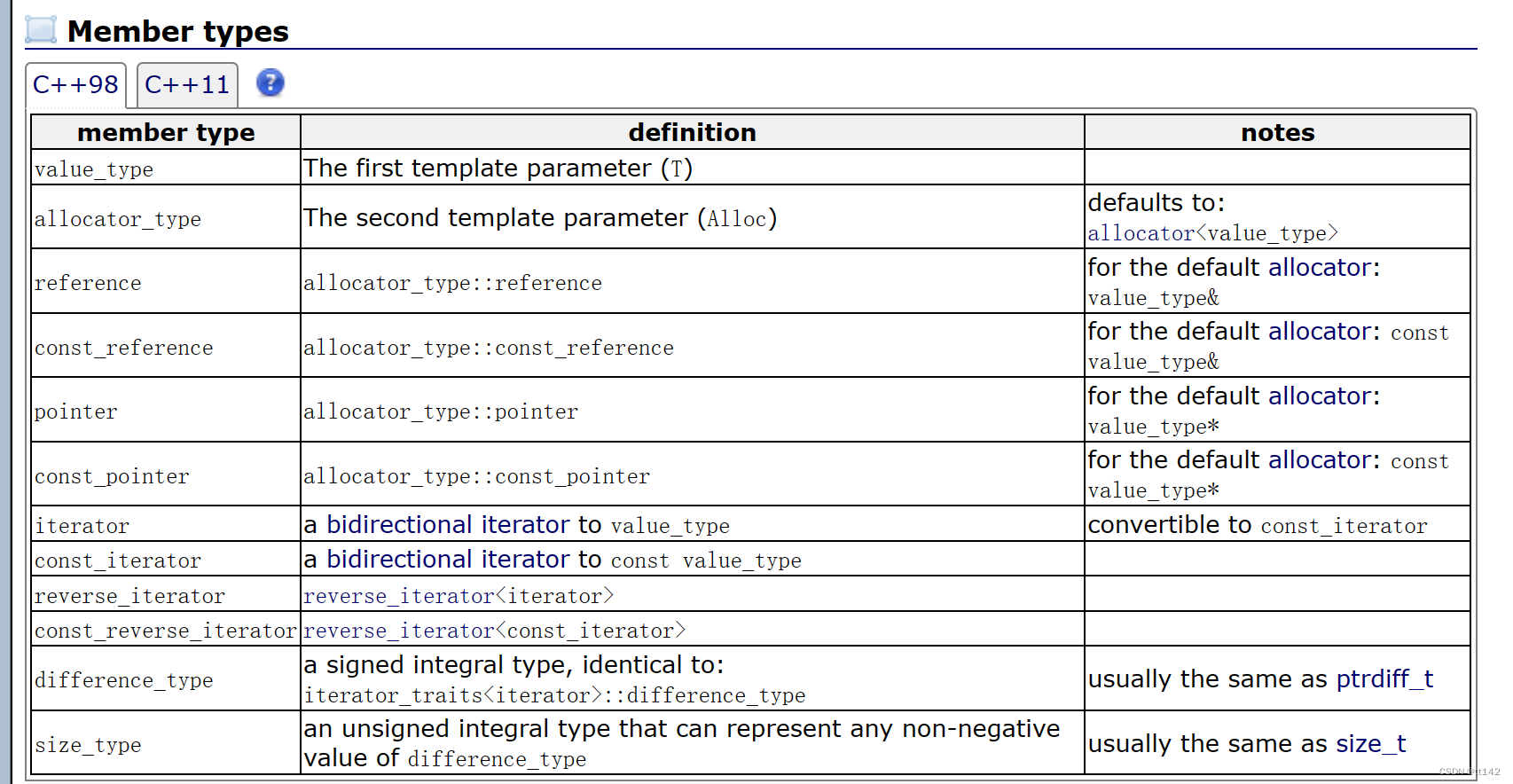
list的成员类型基本上都是迭代器,当然链表都是在用指针在玩,这里的迭代器和我们之前写顺序表就很不一样,因为之前是连续存储的结构,可以用[ ]的方式,所以迭代器是原生指针,数组的结构正好支持迭代器行为
但是这里原生指针的类型是node* ,不能满足迭代器的行为
但是我们可以用封装+运算符重载搞定
我们实现最基本的push——back()功能之后,基本上的框架就搭好了
void push_back(const T& x)
{
node* newnode = new node(x);
node* tail = head->_prev;
//head tail newnode
tail->_next = newnode;
newnode->_next = head;
newnode->_prev = tail;
head->_prev = newnode;
}目前的代码
namespace wrt
{
template <typename T>
struct _list_node
{
_list_node<T>* _prev;
_list_node<T>* _next;
T data;
_list_node(const T& x) //用x初始化节点
:_prev(nullptr)
,_next(nullptr)
,data(x)
{
}
};
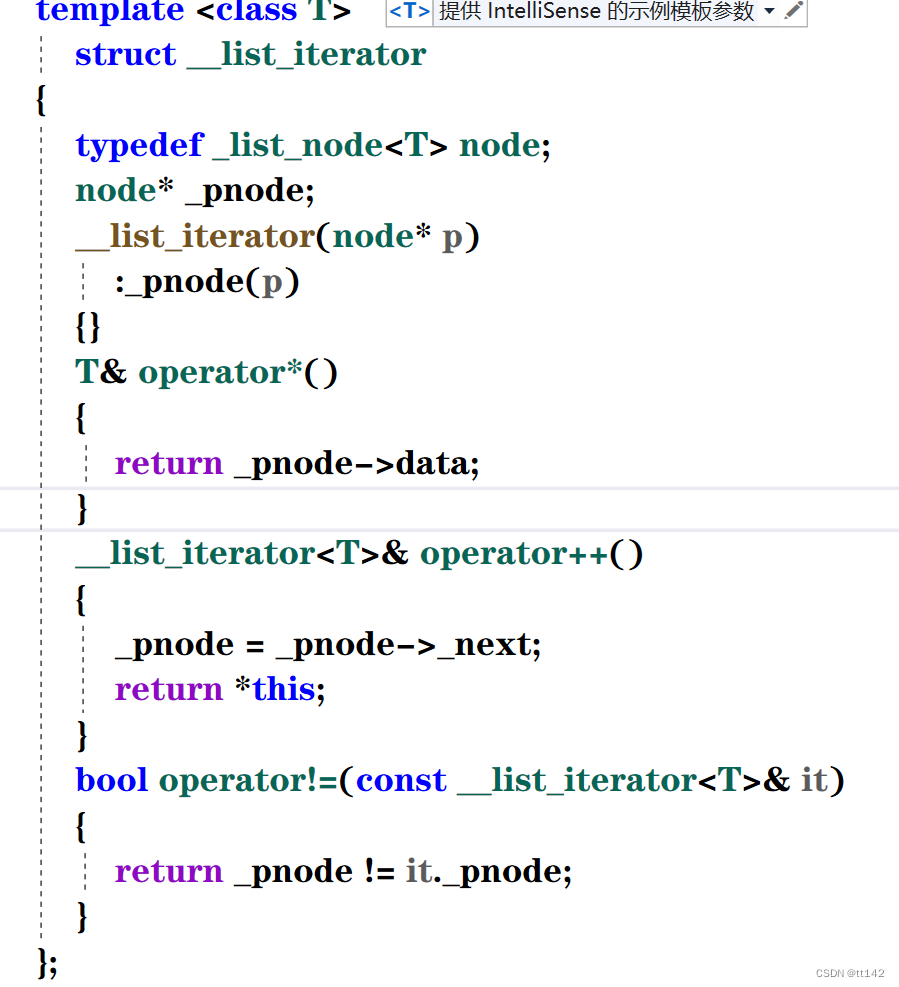
template <class T>
struct __list_iterator
{
typedef _list_node<T> node;
node* _pnode;
__list_iterator(node* p)
:_pnode(p)
{}
T& operator*()
{
return _pnode->data;
}
__list_iterator<T>& operator++()
{
_pnode = _pnode->_next;
return *this;
}
bool operator!=(const __list_iterator<T>& it)
{
return _pnode != it._pnode;
}
};
template <typename T>
class list
{
typedef _list_node<T> node;
public:
typedef __list_iterator<T> iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(head->_next);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(head);
}
list()
{
head = new node(T());
head->_next = head;
head->_prev = head;
}
void push_back(const T& x)
{
node* newnode = new node(x);
node* tail = head->_prev;
//head tail newnode
tail->_next = newnode;
newnode->_next = head;
newnode->_prev = tail;
head->_prev = newnode;
}
private :
node* head;
};
void test()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(5);
lt.push_back(6);
lt.push_back(7);
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
cout << *it <<" ";
++it;
}
cout <<endl;
}
}2.值得注意的函数
list为什么要支持sort,不可以使用algorithm文件里面的吗
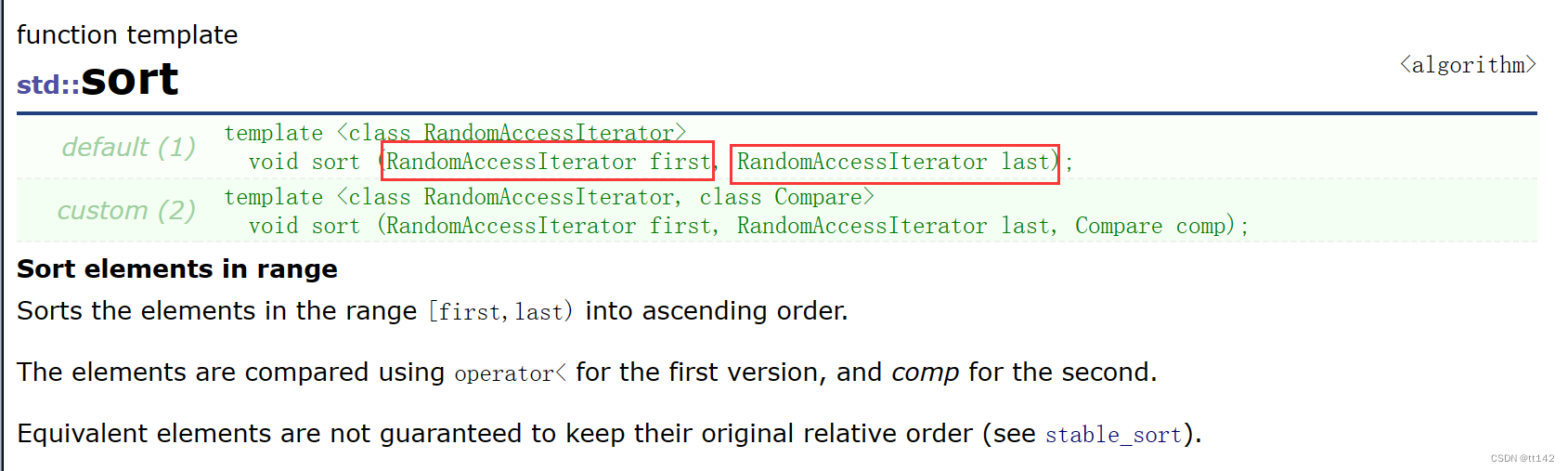
算法库里面使用了first-last 但是很显然list是不支持节点相减的
2.很细节的函数实现
一个合格的list是支持增删查改的
push_back()已经实现过了
下面看insert()
 注意到它是有返回值的 ,返回迭代器,在头部增加数据当然是可以的
注意到它是有返回值的 ,返回迭代器,在头部增加数据当然是可以的
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
node* newnode = new node(x);
node* cur = pos._pnode;
node* prev = cur->_prev;
//prev newnode cur
prev->_next = newnode;
newnode->_next = cur;
newnode->_prev = prev;
cur->_prev = newnode;
return iterator(newnode);
}对应的erase()

也是有返回值,并且不能在头结点位置删除,哨兵位不能动
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos != end());
node* cur = pos._pnode;
node* prev = cur->_prev;
node* next = cur->_next;
//prev cur next
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
delete cur;
return iterator(next);
}那么头尾的增删就可以复用啦
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
void push_back(const T& x)
{
//node* newnode = new node(x);
//node* tail = head->_prev;
head tail newnode
//tail->_next = newnode;
//newnode->_next = head;
//newnode->_prev = tail;
//head->_prev = newnode;
insert(end(), x);
}
void push_front(const T& x)
{
insert(begin(), x);
}然后就是clear(),注意头结点不能删
void clear()
{
iterator it = begin();
while(it!=end())
{
it=erase(it);
}
//头节点不能删除
}析构函数
~list()
{
clear();
//此时需要把头节点也删除
delete head;
head = nullptr;
}下面是拷贝构造
//拷贝构造
//l2=l1
list<T>& operator=(const list<T>& l)
{
if (*this != l)
{
clear();
for (const auto&e :l)
{
push_back(e);
}
}
return *this;
}为了写着更方便,把头结点的开辟封装成函数
void empty_initialize()
{
head = new node(T());
head->_next = head;
head->_prev = head;
}//l2(l1)
list(const list <T>& l)
{
empty_initialize();
for (const auto& e : l)
{
push_back(e);
}
}迭代器还有const版本怎么实现
最简单想到的就是直接在iterator类里面加上一个const修饰*运算符重载![]()
template <class T>
struct __list_iterator
{
typedef _list_node<T> node;
node* _pnode;
__list_iterator(node* p)
:_pnode(p)
{}
T& operator*()
{
return _pnode->data;
}
//在同一个类里面实现就是不行,因为const——iterator只能遍历,不能++
/* const T& operator*() const
{
return _pnode->data;
}*/
__list_iterator<T>& operator++()
{
_pnode = _pnode->_next;
return *this;
}
bool operator!=(const __list_iterator<T>& it)
{
return _pnode != it._pnode;
}
};但是这个真的对么?很显然不对,因为iterator可以遍历,++ 但是const_iterator只能遍历无法++
所以很自然想到写在两个类里面
template <class T>
struct __list_iterator
{
typedef _list_node<T> node;
node* _pnode;
__list_iterator(node* p)
:_pnode(p)
{}
T& operator*()
{
return _pnode->data;
}
//在同一个类里面实现就是不行,因为const——iterator只能遍历,不能++
/* const T& operator*() const
{
return _pnode->data;
}*/
__list_iterator<T>& operator++()
{
_pnode = _pnode->_next;
return *this;
}
bool operator!=(const __list_iterator<T>& it)
{
return _pnode != it._pnode;
}
};
template <class T>
struct __list_const_iterator
{
typedef _list_node<T> node;
node* _pnode;
__list_const_iterator(node* p)
:_pnode(p)
{}
const T& operator*() const
{
return _pnode->data;
}
__list_const_iterator<T>& operator++()
{
_pnode = _pnode->_next;
return *this;
}
bool operator!=(const __list_const_iterator<T>& it)
{
return _pnode != it._pnode;
}
};这两个类只在*运算符重载 还有名称上有区别
但是这是我们的想法,看一下源码就知道大佬果然是大佬
直接用两个模板参数解决问题
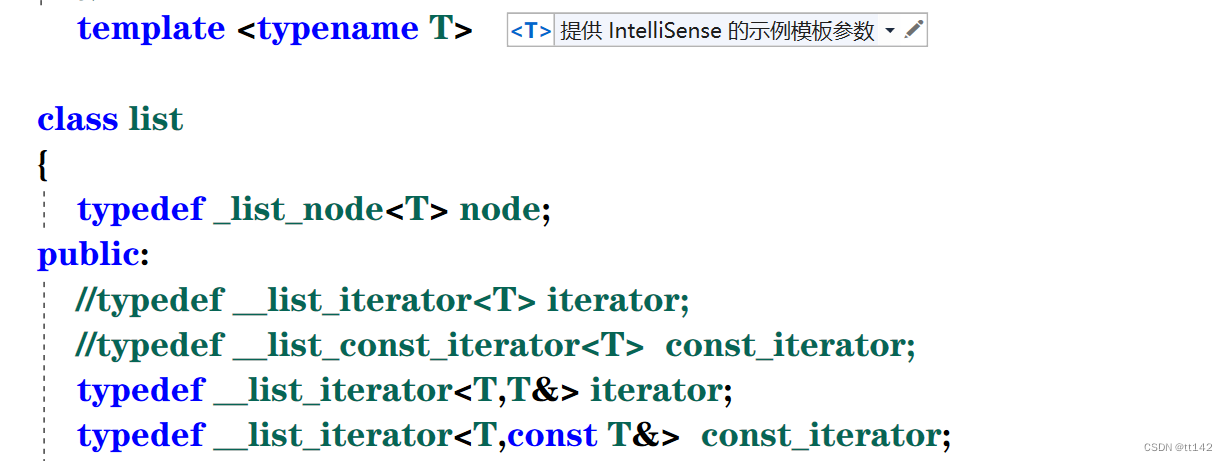
template <typename T, typename Ref>
struct __list_iterator
{
typedef _list_node<T> node;
typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref> Self;
node* _pnode;
__list_iterator(node* p)
:_pnode(p)
{}
Ref operator*()
{
return _pnode->data;
}
//在同一个类里面实现就是不行,因为const——iterator只能遍历,不能++
/* const T& operator*() const
{
return _pnode->data;
}*/
Self& operator++()
{
_pnode = _pnode->_next;
return *this;
}
Self& operator--()
{
_pnode = _pnode->_prev;
return *this;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& it)
{
return _pnode != it._pnode;
}
};拷贝构造可有现代写法哦,此时同样需要一个构造函数用迭代器初始化的

l2(l1)相比较来说,现代写法就是多一个工具人帮助复刻l1,然后把数据交换给l2,最后他自己牺牲....
首先是构造函数(用迭代器实现的)
template <class InputIterator>
list(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
empty_initialize();
while(first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
++first;
}
}然后是swap
void swap(const list<T>& l)
{
std::swap(head, l.head); //两个链表交换只需交换头结点
}现代写法
//l2(l1)
list(const list<T>& l)
{
empty_initialize();
list<T> tmp(l.begin(), l.end());
swap(tmp); //tmp出作用域销毁
}l2=l1 这是对于一个已经存在的对象l1,无需构造头结点
//l2=l1 这是对于一个已经存在的对象l1,无需构造头结点
list <T>& operator=(const list<T>& l)
{
swap(l);
return *this;
}想象一个场景:你需要统计size(),当然这种操作不能频繁进行,因为每一次都要从头开始遍历有很多消耗,那么最简单的办法是什么?!成员变量加上size

现在凸显出复用的好处了,我虽然实现到一半开始想加上size,也只需要改动几个函数就可以完成功能





其他全是复用,爽歪歪
可以用size实现两个函数
size_t _size()
{
return size;
}
bool rmpty()
{
//return head->next==head;
return size==0;
}C++兼容c是有前置和后置的(区分于有些语言,觉得前置后置很麻烦就删去后置)
完善一下前面对于迭代器的运算符操作
//前置
Self& operator++()
{
_pnode = _pnode->_next;
return *this;
}
//后置
Self& operator++(int)
{
Self tmp(*this);
_pnode = _pnode->_next;
return tmp;
}
//前置
Self& operator--()
{
_pnode = _pnode->_prev;
return *this;
}
//后置
Self& operator--(int )
{
Self tmp(*this);
_pnode = _pnode->_prev;
return tmp;
}看起来写成这样是不是很完美,但是看一个问题
struct Pos
{
size_t _row;
size_t _col;
Pos(size_t row=0,size_t col=0) //一定要时刻记着写一个默认构造!!!!!!
:_row(row)
,_col(col)
{}
};
void test()
{
list<Pos> lt;
Pos p1(1, 1);
lt.push_back(p1);
lt.push_back(p1);
lt.push_back(p1);
lt.push_back(Pos(2, 2)); //匿名函数
lt.push_back(Pos(3, 3));
list<Pos>::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
//it->_row++;
cout << *it << " ";
}
}思考一下有什么问题???
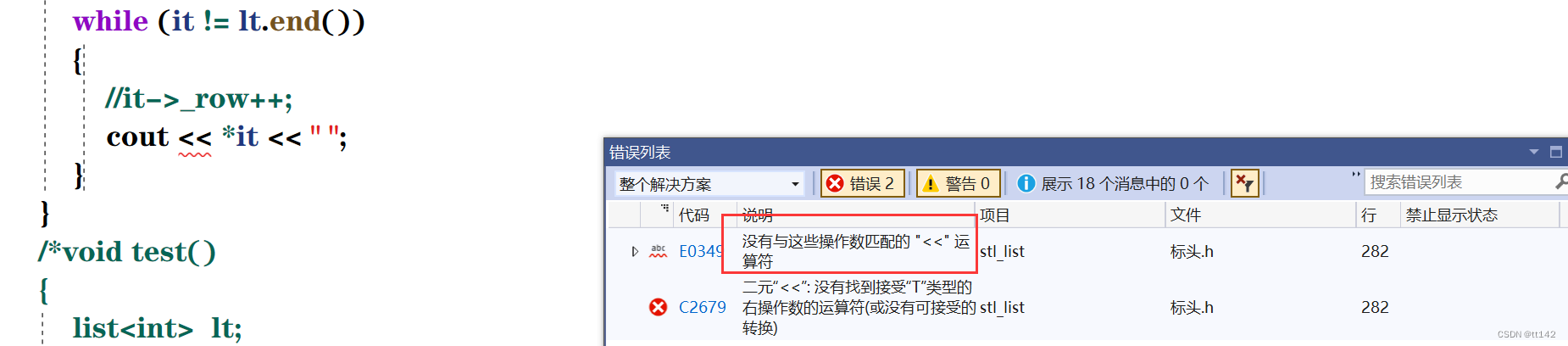
这很尴尬,首先我们思考一下,为什么C++支持cout,因为可以对内置类型可以直接识别然后输出,但是这里的it是个迭代器
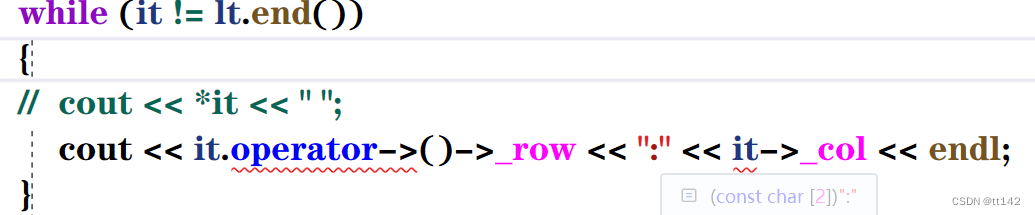
其实这样就可以啦,只需要重载一个->这个运算符
但是我们只有T这个模板类型,没有T*


然后运算符->重载这样写
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_pnode->data;
}注意:脑子一定要清醒,我们提供类T是为了list每个节点的数据类型,Ref是T&(当然还有一个const T&),Ptr是T*(还有const T*)
这里面也体现出我们typedef的智慧

这个模板我们改了很多次,但是我typedef之后,直接修改类型,不需要改名字,都是Self!!!

所以直接->访问就可以啦
他的原理就是

3.vector和list对比

4.迭代器失效
vector:insert和erase都有失效问题
lsit:erase会失效
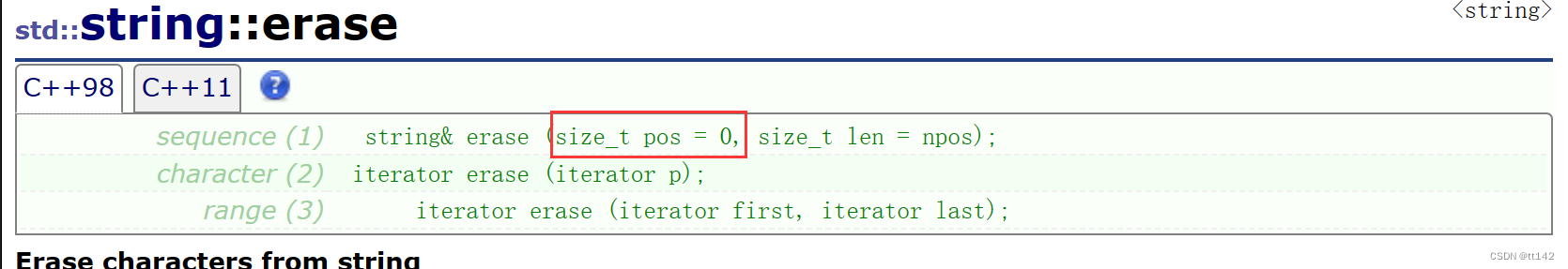
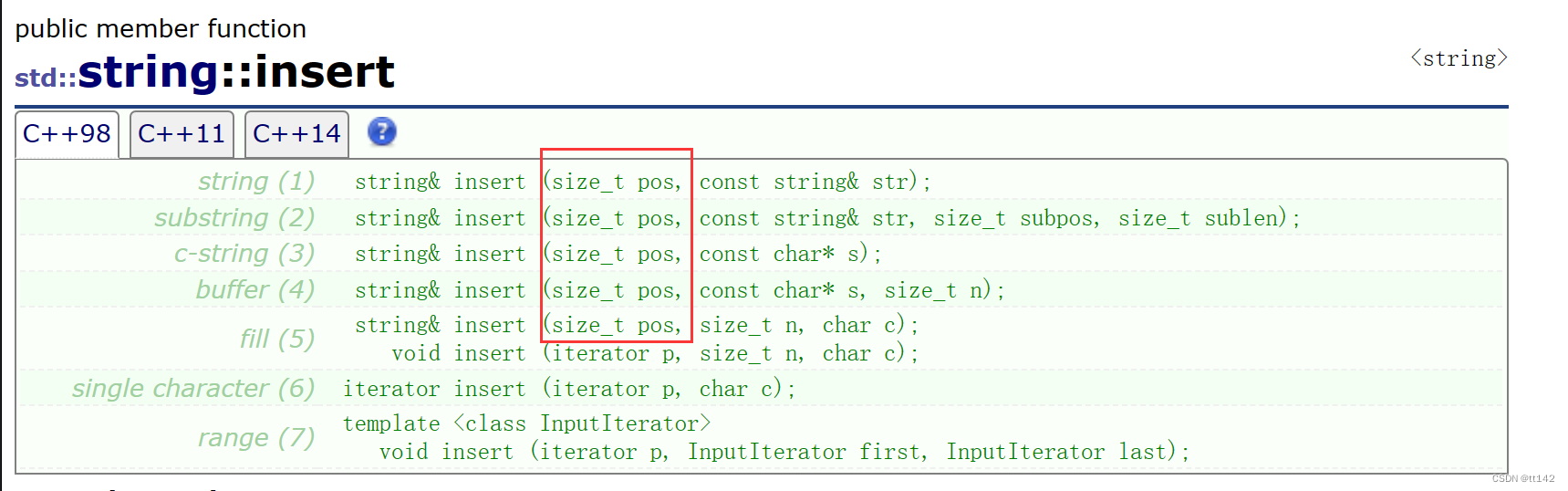
那么string会有失效问题吗?当然,insert和erase都有,和vecor类似,但是一般不关注string失效,因为string的insert和erase常用接口都是下标支持的,迭代器用的少
最后我们的list实现总代码![]()
.h文件
#pragma once
namespace wrt
{
template <typename T>
struct _list_node
{
_list_node<T>* _prev;
_list_node<T>* _next;
T data;
_list_node(const T& x) //用x初始化节点
:_prev(nullptr)
,_next(nullptr)
,data(x)
{
}
};
template <typename T, typename Ref,class Ptr>
struct __list_iterator
{
typedef _list_node<T> node;
typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref,Ptr> Self;
node* _pnode;
__list_iterator(node* p)
:_pnode(p)
{}
Ref operator*()
{
return _pnode->data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_pnode->data;
}
//在同一个类里面实现就是不行,因为const——iterator只能遍历,不能++
/* const T& operator*() const
{
return _pnode->data;
}*/
//前置
Self& operator++()
{
_pnode = _pnode->_next;
return *this;
}
//后置
Self& operator++(int)
{
Self tmp(*this);
_pnode = _pnode->_next;
return tmp;
}
//前置
Self& operator--()
{
_pnode = _pnode->_prev;
return *this;
}
//后置
Self& operator--(int )
{
Self tmp(*this);
_pnode = _pnode->_prev;
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& it)
{
return _pnode != it._pnode;
}
};
/* template <class T>
struct __list_const_iterator
{
typedef _list_node<T> node;
node* _pnode;
__list_const_iterator(node* p)
:_pnode(p)
{}
const T& operator*() const
{
return _pnode->data;
}
__list_const_iterator<T>& operator++()
{
_pnode = _pnode->_next;
return *this;
}
bool operator!=(const __list_const_iterator<T>& it)
{
return _pnode != it._pnode;
}
};*/
template <typename T>
class list
{
typedef _list_node<T> node;
public:
//typedef __list_iterator<T> iterator;
//typedef __list_const_iterator<T> const_iterator;
typedef __list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;
typedef __list_iterator<T,const T&,T*> const_iterator;
size_t _size()
{
return size;
}
bool rmpty()
{
//return head->next==head?
return size == 0 ;
}
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(head->_next);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(head);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return iterator(head->_next);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return iterator(head);
}
void push_back(const T& x)
{
//node* newnode = new node(x);
//node* tail = head->_prev;
head tail newnode
//tail->_next = newnode;
//newnode->_next = head;
//newnode->_prev = tail;
//head->_prev = newnode;
insert(end(), x);
}
void push_front(const T& x)
{
insert(begin(), x);
}
~list()
{
clear();
//此时需要把头节点也删除
delete head;
head = nullptr;
size = 0;
}
//拷贝构造
//l2=l1
/*list<T>& operator=(const list<T>& l)
{
if (*this != l)
{
clear();
for (const auto&e :l)
{
push_back(e);
}
}
return *this;
}*/
void empty_initialize()
{
head = new node(T());
head->_next = head;
head->_prev = head;
size = 0;
}
list()
{
empty_initialize();
}
//l2(l1)
/* list(const list <T>& l)
{
empty_initialize();
for (const auto& e : l)
{
push_back(e);
}
}*/
//拷贝构造的现代写法
template <class InputIterator>
list(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
empty_initialize();
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
++first;
}
}
void swap(const list<T>& l)
{
std::swap(head, l.head); //两个链表交换只需交换头结点
}
//l2(l1)
list( list<T>& l)
{
empty_initialize();
list<T> tmp(l.begin(), l.end());
swap(tmp); //tmp出作用域销毁
}
//l2=l1 这是对于一个已经存在的对象l1,无需构造头结点
list <T>& operator=(const list<T>& l)
{
swap(l);
return *this;
}
void clear()
{
iterator it = begin();
while(it!=end())
{
it=erase(it);
}
//头节点不能删除
size = 0;
}
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
node* newnode = new node(x);
node* cur = pos._pnode;
node* prev = cur->_prev;
//prev newnode cur
prev->_next = newnode;
newnode->_next = cur;
newnode->_prev = prev;
cur->_prev = newnode;
++size;
return iterator(newnode);
}
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos != end());
node* cur = pos._pnode;
node* prev = cur->_prev;
node* next = cur->_next;
//prev cur next
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
delete cur;
--size;
return iterator(next);
}
private :
node* head;
size_t size;
};
struct Pos
{
size_t _row;
size_t _col;
Pos(size_t row=0,size_t col=0) //一定要时刻记着写一个默认构造!!!!!!
:_row(row)
,_col(col)
{}
};
void test()
{
list<Pos> lt;
Pos p1(1, 1);
lt.push_back(p1);
lt.push_back(p1);
lt.push_back(p1);
lt.push_back(Pos(2, 2)); //匿名函数
lt.push_back(Pos(3, 3));
list<Pos>::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
// cout << *it << " ";
//cout << it.operator->()->_row << ":" << it->_col << endl;
cout << it->_row << ":" << it->_col << ":" << endl;
}
}
/*void test()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(5);
lt.push_back(6);
lt.push_back(7);
lt.insert(lt.begin(), 5);
lt.erase(lt.begin());
lt.push_back(40);
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
cout << *it <<" ";
++it;
}
cout <<endl;
cout << lt._size() << endl;
}*/
}.cpp文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <assert.h>
using namespace std;
#include "标头.h"
int main()
{
wrt::test();
return 0;
}







![[1.3_2]计算机系统概述——中断和异常](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d13cbc2731014ff4acd0a40eb10e5841.png)