04 Android基础--RelativeLayout
- 什么是RelativeLayout?
- RelativeLayout的常见用法:
什么是RelativeLayout?
相对布局(RelativeLayout)是一种根据
父容器和兄弟控件作为参照来确定控件位置的布局方式。
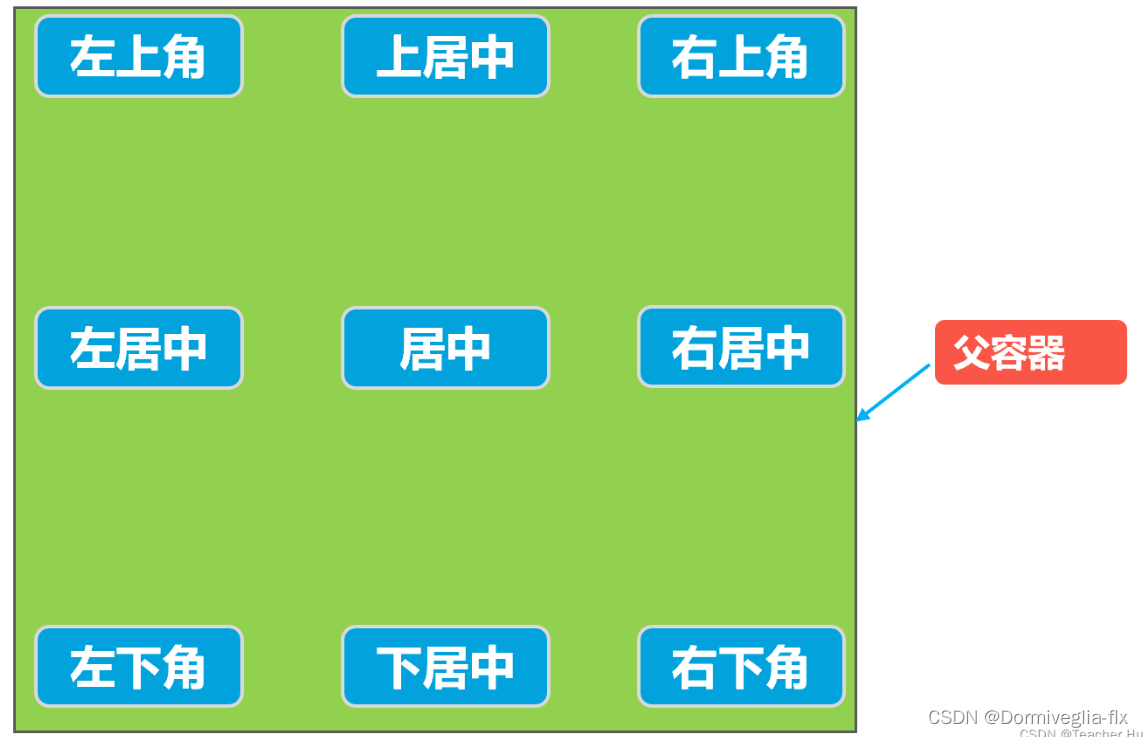
根据父容器定位
在相对布局中,可以通过以下的属性让的组合让控件处于父容器左上角、右上角、左下角、右下角、上下左右居中,正居中等九个位置。属性如下:
- android:layout_alignParentLeft=“true” 父容器左边
- android:layout_alignParentRight=“true” 父容器右边
- android:layout_alignParentTop=“true” 父容器顶部
- android:layout_alignParentBottom=“true” 父容器底部
- android:layout_centerHorizontal=“true” 水平方向居中
- android:layout_centerVertical=“true” 垂直方向居中
- android:layout_centerInParent=“true” 水平垂直都居中
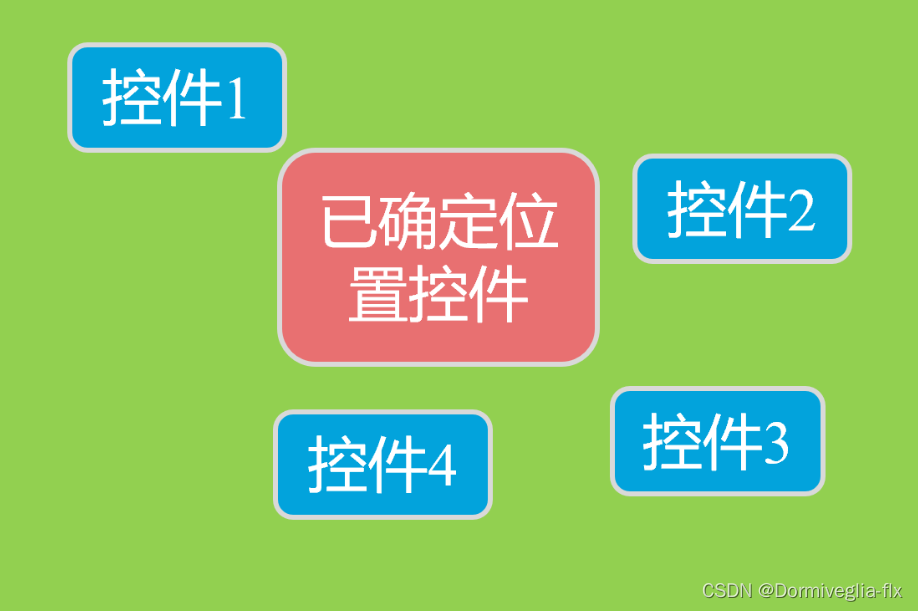
根据兄弟控件定位
在相对布局中,还支持通过已确定位置的控件作为参考来确定其他控件的位置,以下的属性让的组合让控件处于另外控件左上角、右上角、左下角、右下角、正上方、正下方、正左方、正右方等位置。属性如下:
- android:layout_toLeftOf=“@+id/button1” 在button1控件左方
- android:layout_toRightOf=“@+id/button1” 在button1控件右方
- android:layout_above=“@+id/button1” 在button1控件上方
- android:layout_below=“@+id/button1” 在button1控件下方
- android:layout_alignLeft=“@+id/button1” 与button1控件左边平齐
- android:layout_alignRight=“@+id/button1” 与button1控件右边平齐
- android:layout_alignTop=“@+id/button1” 与button1控件上边平齐
- android:layout_alignBottom=“@+id/button1” 与button1控件下边平齐
RelativeLayout的常见用法:
第一种情况:常用的列表页布局:
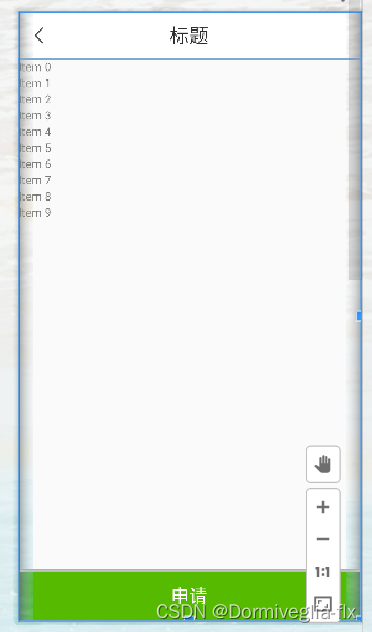
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
>
// 标题
<include
android:id="@+id/title_layout"
layout="@layout/title_layout"
/>
// 1.android:layout_below="@+id/title_layout";这个布局在title的下方
// 2.android:layout_marginBottom="60dp";指定该属性所在控件距下部最近控件的最小值;
<androidx.swiperefreshlayout.widget.SwipeRefreshLayout
android:id="@+id/sw_layout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_below="@+id/title_layout"
android:layout_marginBottom="60dp">
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/recyclerview"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</androidx.swiperefreshlayout.widget.SwipeRefreshLayout>
// 3.android:layout_alignParentBottom="true";在父容器底部
<LinearLayout
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true">
<Button
android:id="@+id/material_apply"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
/>
</LinearLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
第二种情况:常用的搜索抽屉布局:
搜索栏有很多,有滚动条,重置与搜索按钮在最底部。
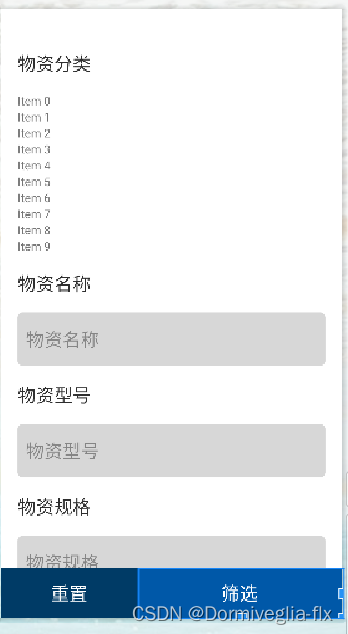
<RelativeLayout>
// 1. 添加滚动条
<androidx.core.widget.NestedScrollView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingHorizontal="20dp">
// 2. 搜索栏需要 占满全屏
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
style="@style/select_title"
android:text="@string/material_type" />
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/madetails_recyclerview"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp" />
<TextView
style="@style/select_title"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:text="@string/name_of_goods" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/madetails_name_of_goods"
style="@style/select_ed"
android:background="@drawable/select_ed_background"
android:hint="@string/name_of_goods" />
<TextView
style="@style/select_title"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:text="@string/model_of_goods" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/madetails_model_of_goods"
style="@style/select_ed"
android:background="@drawable/select_ed_background"
android:hint="@string/model_of_goods" />
<TextView
style="@style/select_title"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:text="@string/specification_of_goods" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/madetails_specification_of_goods"
style="@style/select_ed"
android:background="@drawable/select_ed_background"
android:hint="@string/specification_of_goods" />
<TextView
style="@style/select_title"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:text="@string/code_of_goods" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/madetails_code_of_goods"
style="@style/select_ed"
android:background="@drawable/select_ed_background"
android:hint="@string/code_of_goods" />
</LinearLayout>
</androidx.core.widget.NestedScrollView>
// 3. android:layout_alignParentBottom="true";相对于根元素布局,在根元素的底部。
<LinearLayout
style="@style/select_bottom_layout"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true">
<Button
android:id="@+id/reset_btn"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:background="@color/dark_blue"
android:text="@string/reset"
android:textColor="@color/white"
android:textSize="22dp" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/filter_btn"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="3"
android:background="@color/colorAccent"
android:text="@string/filter"
android:textColor="@color/white"
android:textSize="22dp" />
</LinearLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
类似于这种布局的做法:1.上面的元素需要
占满全屏2.下面的按钮android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"相对父元素布局,在父元素的底部。
第三种情况:子页面展示项
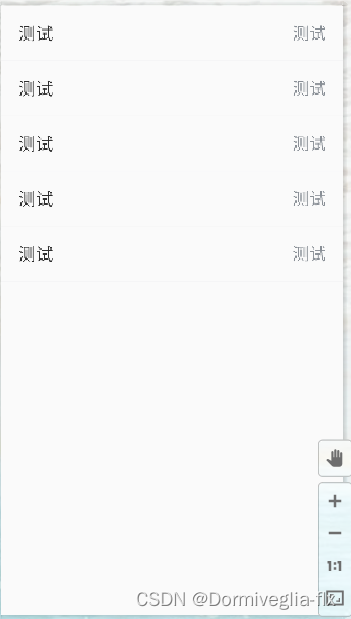
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
<!--1. android:layout_alignParentLeft="true": 父容器左边
android:layout_alignParentRight="true" 父容器右边
android:layout_centerInParent="true" 水平垂直都居中
-->
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="60px">
<TextView
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="测试" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/apply_form_tv"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
tools:text="测试" />
</RelativeLayout>
<!--测试-->
<RelativeLayout style="@style/sub_line">
<TextView
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="测试" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/apply_form_tv"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
tools:text="测试" />
</RelativeLayout>
</LinearLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
对于这种展示形布局或者说是提交型布局:1.<LinearLayout 标签可以让其下的子布局页面竖向排列 2.<RelativeLayout 标签:位于父容器左边与父容器右边,且水平竖直居中。









![[Java·算法·困难]LeetCode25. K 个一组翻转链表](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d8afa9d66cf8463d88277e112a2488b4.png)

