一、栈

1.1 模拟栈
实现一个栈,栈初始为空,支持四种操作:
push x – 向栈顶插入一个数 x;
pop – 从栈顶弹出一个数;
empty – 判断栈是否为空;
query – 查询栈顶元素。
现在要对栈进行 M 个操作,其中的每个操作 3 和操作 4 都要输出相应的结果。
输入格式
第一行包含整数 M,表示操作次数。
接下来 M 行,每行包含一个操作命令,操作命令为 push x,pop,empty,query 中的一种。
输出格式
对于每个 empty 和 query 操作都要输出一个查询结果,每个结果占一行。
其中,empty 操作的查询结果为 YES 或 NO,query 操作的查询结果为一个整数,表示栈顶元素的值。
数据范围
1≤M≤100000
1≤x≤109
所有操作保证合法。
输入样例:
10push5
query
push6pop
query
pop
empty
push4
query
empty输出样例:
55YES4NO代码
dada
34
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int M = 100010;
int stk[M], tt;
int m;
int main()
{
cin >> m;
while (m -- )
{
string op;
int x;
cin>>op;
if(op=="push")
{
cin >> x;
stk[ ++tt ] = x;
}
else if (op == "pop") tt--;
else if (op == "empty") cout << (tt ?"NO" : "YES") <<endl;
else cout << stk[tt] <<endl;
}
return 0;
}35
36
1.2表达式求值
给定一个表达式,其中运算符仅包含 +,-,*,/(加 减 乘 整除),可能包含括号,请你求出表达式的最终值。
注意:
数据保证给定的表达式合法。
题目保证符号 - 只作为减号出现,不会作为负号出现,例如,-1+2,(2+2)*(-(1+1)+2) 之类表达式均不会出现。
题目保证表达式中所有数字均为正整数。
题目保证表达式在中间计算过程以及结果中,均不超过 231−1。
题目中的整除是指向 0 取整,也就是说对于大于 00 的结果向下取整,例如 5/3=1,对于小于 0 的结果向上取整,例如 5/(1−4)=−15/(1−4)=−1。
C++和Java中的整除默认是向零取整;Python中的整除//默认向下取整,因此Python的eval()函数中的整除也是向下取整,在本题中不能直接使用。
输入格式
共一行,为给定表达式。
输出格式
共一行,为表达式的结果。
数据范围
表达式的长度不超过 105。
输入样例:
(2+2)*(1+1)输出样例:
8思路:
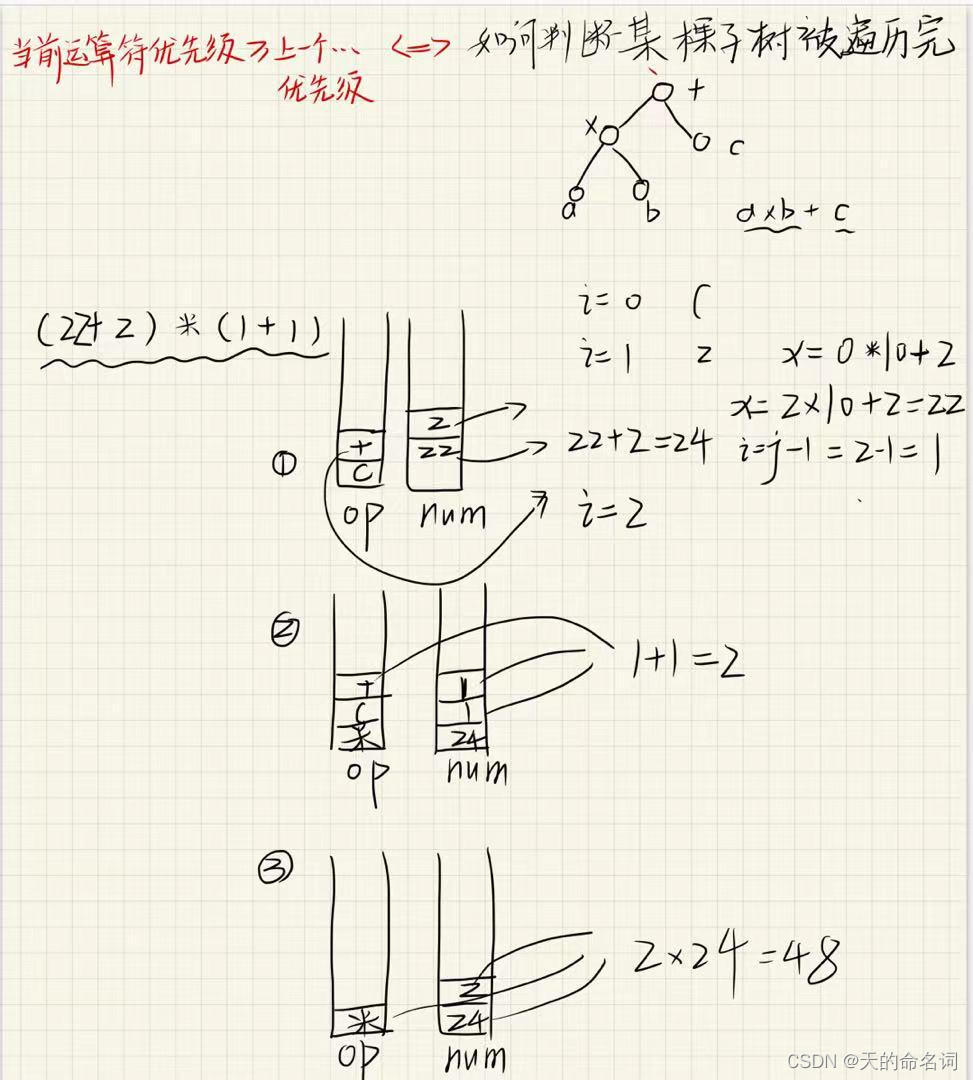
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stack>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
stack<int> num;
stack<char> op;
void eval()
{
auto b = num.top(); num.pop();
auto a = num.top(); num.pop();
auto c = op.top(); op.pop();
int x;
if (c == '+') x = a + b;
else if (c == '-') x = a - b;
else if (c == '*') x = a * b;
else x = a / b;
num.push(x);
}
int main()
{
unordered_map<char, int> pr{{'+', 1}, {'-', 1}, {'*', 2}, {'/', 2}};
string str;
cin >> str;
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i ++ )
{
auto c = str[i];
if (isdigit(c))
{
int x = 0, j = i;
while (j < str.size() && isdigit(str[j]))
x = x * 10 + str[j ++ ] - '0';
i = j - 1;
num.push(x);
}
else if (c == '(') op.push(c);
else if (c == ')')
{
while (op.top() != '(') eval();
op.pop();
}
else
{
while (op.size() && op.top() != '(' && pr[op.top()] >= pr[c]) eval();
op.push(c);
}
}
while (op.size()) eval();
cout << num.top() << endl;
return 0;
}
1.3 单调栈
给定一个长度为 N 的整数数列,输出每个数左边第一个比它小的数,如果不存在则输出 −1−1。
输入格式
第一行包含整数 N,表示数列长度。
第二行包含 N 个整数,表示整数数列。
输出格式
共一行,包含 N 个整数,其中第 i 个数表示第 i 个数的左边第一个比它小的数,如果不存在则输出 −1−1。
数据范围
1≤N≤105
1≤数列中元素≤109
输入样例:
5
3 4 2 7 5输出样例:
-1 3 -1 2 2代码:
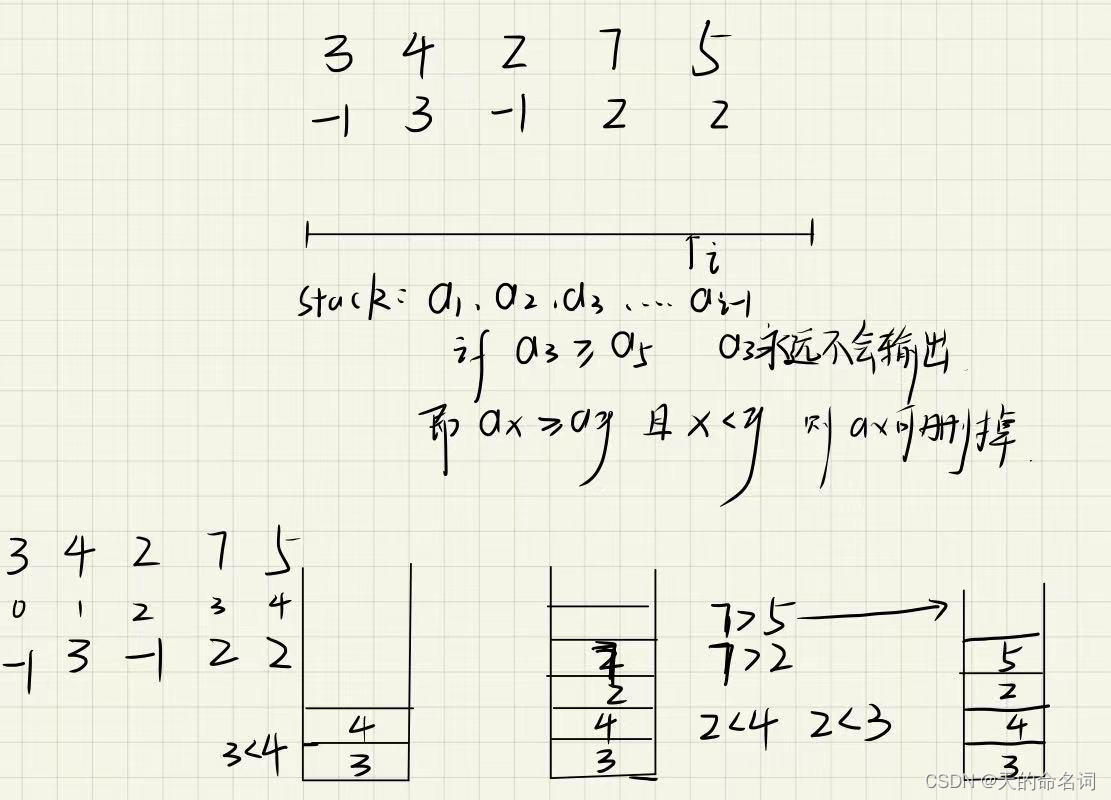
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N =1e5+10;
int st[N];
int tt;
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
int x;
cin >> x;
while ( tt && st[tt] >= x)
{
tt--;
}
if(tt) cout << st[tt] << ' ';
else cout << -1 << ' ';
st[++tt] = x;
}
return 0;
}
二、队列
2.1 模拟队列
实现一个队列,队列初始为空,支持四种操作:
push x – 向队尾插入一个数 x;
pop – 从队头弹出一个数;
empty – 判断队列是否为空;
query – 查询队头元素。
现在要对队列进行 M 个操作,其中的每个操作 3 和操作 4 都要输出相应的结果。
输入格式
第一行包含整数 M,表示操作次数。
接下来 M 行,每行包含一个操作命令,操作命令为 push x,pop,empty,query 中的一种。
输出格式
对于每个 empty 和 query 操作都要输出一个查询结果,每个结果占一行。
其中,empty 操作的查询结果为 YES 或 NO,query 操作的查询结果为一个整数,表示队头元素的值。
数据范围
1≤M≤100000,
1≤x≤109,
所有操作保证合法。
输入样例:
10
push
6
empty
query
pop
empty
push 3
push 4
pop
query
push 6输出样例:
NO
6
YES
4代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5+10;
int q[N];
int hh, tt = -1;
int main()
{
int m;
cin >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++ )
{
string str;
int x;
cin >> str;
if (str == "push")
{
cin >> x;
q[ ++ tt ] = x;
}
else if (str == "pop")
{
hh++;
}
else if (str == "empty")
{
if(hh <= tt)
{
cout << "NO" <<endl;
}
else
{
cout << "YES" << endl;
}
}
else
{
cout << q[hh] << endl;
}
}
}
2.2 单调队列
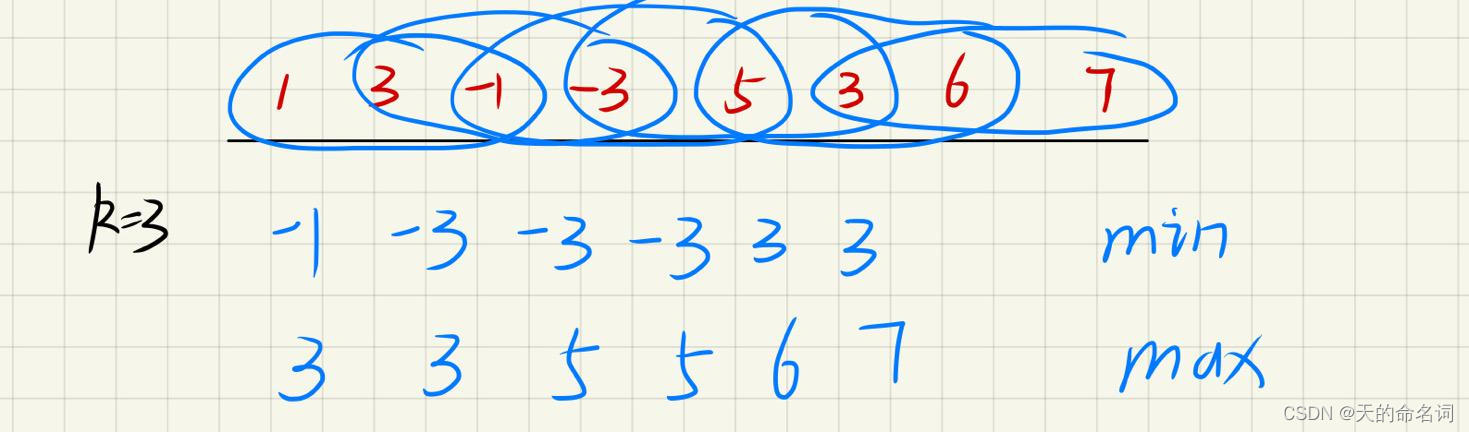
单调队列:队列内的元素值是单调的,递增或递减。本题用单调队列存储当前窗口内单调递减的元素,并日队头是窗口内的最大值,队尾是窗口内的尾元素。也就是说,队列从队头到队尾对应窗口内从最大值到尾元素的一个子序列。
1.队头出队:当队头的元素从窗口滑出时,队头元素出队(head++)
2. 队尾入队: 当新元素滑入窗口时,要把新元素从队尾插入,分两种情况:
第一种:
直接插入: 如果新元素小于队尾元素,那就百接从队尾插入 ( ++tail),因为它可能在前面的最大值滑出窗口后成为最大值;
第二种:
先删后插:如果新元素大于等于队尾元素,那就先删除队尾元素(因为它不可能成为窗口中的最大值),删除方法是tail--,即从队尾出队。循环删除,直到队空或遇到一个大于新元素的值,插
入其后 (++tail)
这样做,每次都能从队头取得窗口中的最大值。
给定一个大小为 n≤106 的数组。
有一个大小为 k 的滑动窗口,它从数组的最左边移动到最右边。
你只能在窗口中看到 k 个数字。
每次滑动窗口向右移动一个位置。
以下是一个例子:
该数组为 [1 3 -1 -3 5 3 6 7],k 为 3。
窗口位置 | 最小值 | 最大值 |
[1 3 -1] -3 5 3 6 7 | -1 | 3 |
1 [3 -1 -3] 5 3 6 7 | -3 | 3 |
1 3 [-1 -3 5] 3 6 7 | -3 | 5 |
1 3 -1 [-3 5 3] 6 7 | -3 | 5 |
1 3 -1 -3 [5 3 6] 7 | 3 | 6 |
1 3 -1 -3 5 [3 6 7] | 3 | 7 |
你的任务是确定滑动窗口位于每个位置时,窗口中的最大值和最小值。
输入格式
输入包含两行。
第一行包含两个整数 n 和 k,分别代表数组长度和滑动窗口的长度。
第二行有 n 个整数,代表数组的具体数值。
同行数据之间用空格隔开。
输出格式
输出包含两个。
第一行输出,从左至右,每个位置滑动窗口中的最小值。
第二行输出,从左至右,每个位置滑动窗口中的最大值。
输入样例:
8 3
1 3 -1 -3 5 3 6 7输出样例:
-1 -3 -3 -3 3 3
3 3 5 5 6 7代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6+10;
int q[N], a[N], tt = -1, hh=0;
int n,k;
int main()
{
cin >> n>> k;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
if(hh<= tt && q[hh] < i-k+1) hh++;
while (hh <= tt && a[q[tt]] >=a[i]) tt--;
q[ ++ tt] = i;
if( i >= k-1) cout << a[q[hh]]<<" ";
}
puts("");
hh = 0, tt = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
if(hh<= tt && q[hh] < i-k+1) hh++;
while (hh <= tt && a[q[tt]] <=a[i]) tt--;
q[ ++ tt] = i;
if( i >= k-1) cout << a[q[hh]]<<' ';
}
puts("");
}