目录
- 前言
- 一、set
- 1. 简介
- 2. 成员类型
- 3. 构造函数
- (1) set()
- (2)set(InputIterator first,InputIterator last)
- (3)使用
- 4. 拷贝构造函数和赋值运算符重载
- 5. empty()
- 6. size()
- 7. insert()
- (1)pair<iterator,bool> insert(const K& key)
- (2)iterator insert(iterator pos,const K& key)
- (3)void insert(InputIterator first,InputIterator last)
- (4)综合测试set的插入接口
- 8. erase()
- (1)void erase(iterator pos)
- (2)size_t erase(const K& key)
- (3)void erase(iterator first,iterator last)
- (4)综合测试set中的删除函数接口
- 9.swap()
- 10. clear()
- 11. find()
- 12.count()
- 13. set<K>::iterator lower_bound(const K& key)
- 14. set<int>::iterator upper_bound(const K& key)
- 二、map
- 1. 简介
- 2. 成员类型
- 3. 构造函数
- 4. pair
- 5. make_pair()
- 5. 拷贝构造函数和赋值运算符重载函数
- 6. empty()
- 7. size()
- 8. operator[]
- 9. insert()
- 10. erase()
- (1) void erase(iterator pos)
- (2) size_t erase(const K& key)
- (3) void erase(iterator first,iterator last)
- (4) 综合测试erase的所有接口
- 11. swap()
- 12. clear()
- 13. find()
- 14. count()
- 15.lower_bound()
- 16.upper_bound()
前言
map和set是数据结构中非常常用的结构,这两个结构都属于二叉搜索树,set中的结点存储的是关键字,map中的结点存储的是键值对。set和map都只支持存储唯一一个关键字,不允许关键字冗余,但是其衍生出来的multiset和multimap数据结构就支持存储多个关键子,下面将通过实际代码来详细介绍这两类数据结构的使用。
一、set
1. 简介

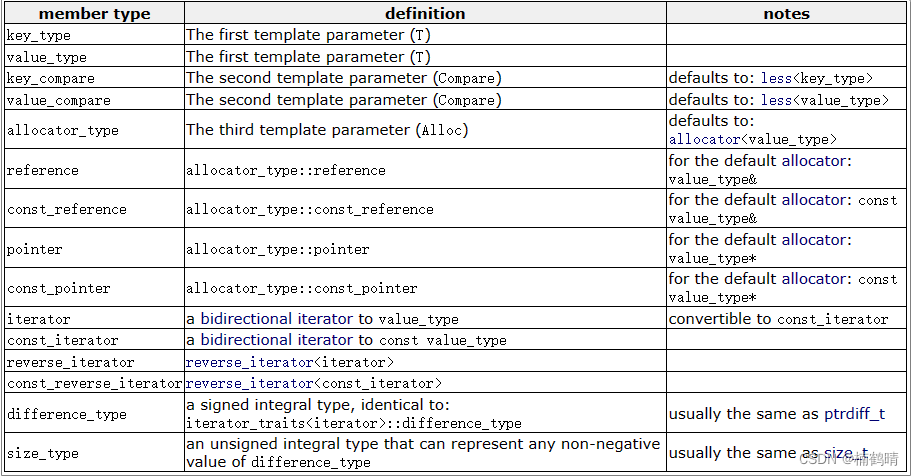
2. 成员类型
3. 构造函数
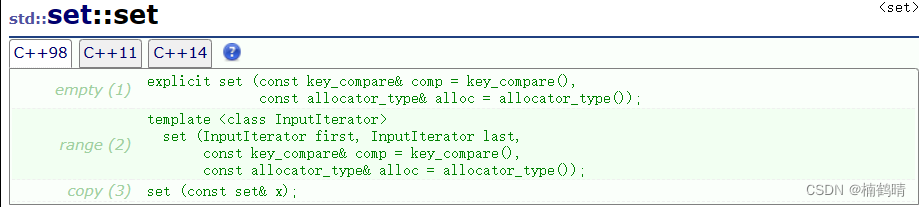
(1) set()
这个构造函数是一个无参的构造函数,是最常用的一个构造函数,其使用和之前学习的数据结构一样
(2)set(InputIterator first,InputIterator last)
这个构造函数是支持使用一段迭代器区间进行初始化,传迭代器区间的时候同样需要注意,传的必须是左闭右开的区间。
(3)使用
- 代码:
void test_set1()
{
// 使用set的构造函数
//无参构造函数
set<int> s1;
set<string> s2;
set<vector<int>> s3;
// 使用一段迭代器区间进行构造
string str("hello set(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)");
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(4);
v.push_back(5);
set<char> s4(str.begin(), str.end());
set<int> s5(v.begin(), v.end());
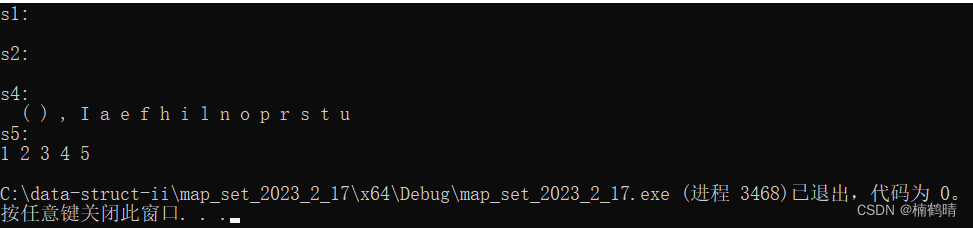
// 遍历set
cout << "s1:" << endl;
set<int>::iterator sit1 = s1.begin();
while (sit1 != s1.end())
{
cout << *sit1 << " ";
sit1++;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "s2:" << endl;
set<string>::iterator sit2 = s2.begin();
while (sit2 != s2.end())
{
cout << *sit2 << " ";
sit2++;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "s4:" << endl;
set<char>::iterator sit4 = s4.begin();
while (sit4 != s4.end())
{
cout << *sit4 << " ";
sit4++;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "s5:" << endl;
set<int>::iterator sit5 = s5.begin();
while (sit5 != s5.end())
{
cout << *sit5 << " ";
sit5++;
}
cout << endl;
}
运行结果:
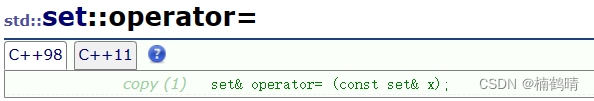
4. 拷贝构造函数和赋值运算符重载

- 代码:
void test_set2()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(4);
v.push_back(5);
v.push_back(6);
set<int> s1(v.begin(), v.end());
set<int> s2 = s1;// 调用拷贝构造函数
set<int> s3;
s3 = s2;// 调用赋值运算符重载函数
cout << "s1:" << endl;
for (auto& e : s1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "s2:" << endl;
for (auto& e : s2)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "s3:" << endl;
for (auto& e : s3)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
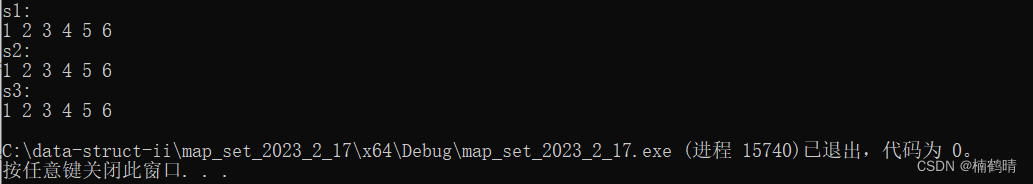
cout << endl;
}
运行结果:
5. empty()
这个函数的功能就是判断set是否为空,如果为空,则返回true,否则返回false

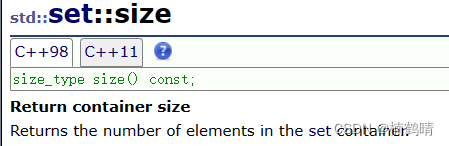
6. size()
这个函数是求set中结点的个数的
- 代码:
void test_set3()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(4);
v.push_back(5);
v.push_back(6);
set<int> s1(v.begin(), v.end());
cout << "s1:" << endl;
for (auto& e : s1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
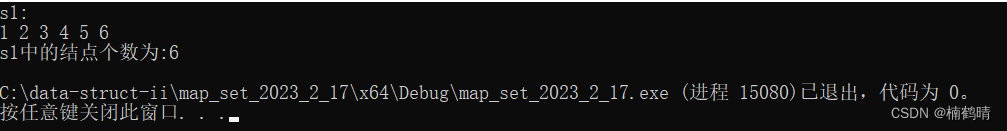
cout << endl;
cout << "s1中的结点个数为:" << s1.size() << endl;
}
运行结果:
7. insert()
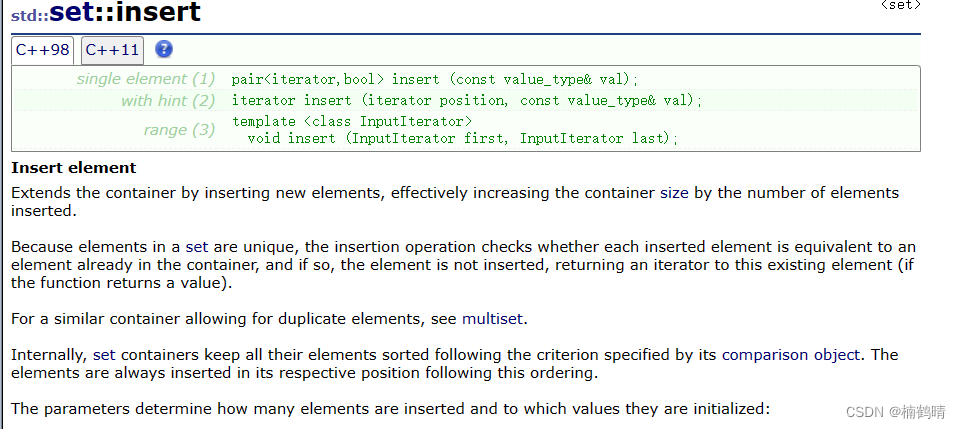
(1)pair<iterator,bool> insert(const K& key)
这个函数支持向set中插入一个key,插入之后会返回一个键值对,键值对其实本质就是一个结构体,其中存储两个值,分别叫做first和second,其中的first是iterator,也就是指向插入结点的迭代器,second是bool,标识插入是否成功,当插入的key在set中是存在的,则插入失败,返回的键值对中的迭代器指向这个已经存在的值,键值对中的bool值为false,如果插入的key不存在,则返回的键值对中的迭代器指向新插入的结点,bool值为true。
(2)iterator insert(iterator pos,const K& key)
这个函数支持在pos位置处插入一个key,返回插入位置的迭代器,这个接口平时很少用,也不太能用,因为值不能随便向set中进行插入,很容易会破坏set的结构。
(3)void insert(InputIterator first,InputIterator last)
这个函数支持向set中插入一段迭代器区间,没有返回值
(4)综合测试set的插入接口
- 代码:
void test_set4()
{
// 测试set的插入函数
set<int> s;
pair<set<int>::iterator,bool> p1 = s.insert(1);
cout << *(p1.first) << endl;
pair<set<int>::iterator, bool> p2 = s.insert(3);
cout << *(p2.first) << endl;
pair<set<int>::iterator, bool> p3 = s.insert(2);
cout << *(p3.first) << endl;
pair<set<int>::iterator, bool> p4 = s.insert(6);
cout << *(p4.first) << endl;
pair<set<int>::iterator, bool> p5 = s.insert(4);
cout << *(p5.first) << endl;
pair<set<int>::iterator, bool> p6 = s.insert(8);
cout << *(p6.first) << endl;
for (auto& e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 在3位置处插入30
set<int>::iterator pos = s.find(3);
if (pos != s.end())
{
// 找到了
set<int>::iterator pos1 = s.insert(pos, 30);
cout << *pos1 << endl;
}
else
{
// 找不到
cout << "没有找到此值" << endl;
}
// 构造一个vector
vector<int> v = { 10,7,5,40,50 };
// 向s 插入一段迭代器区间
s.insert(v.begin(), v.end());
for (auto& e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
运行结果:
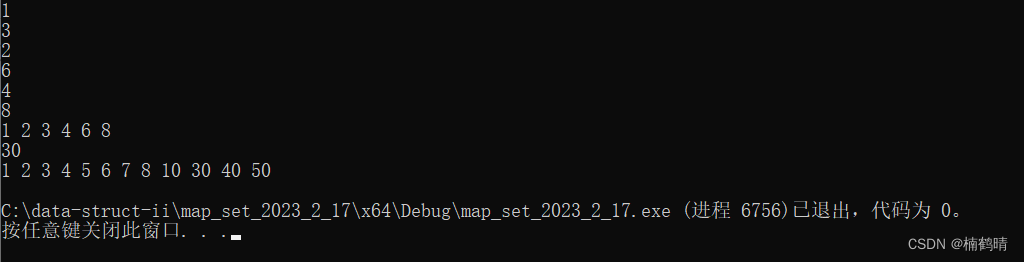
8. erase()
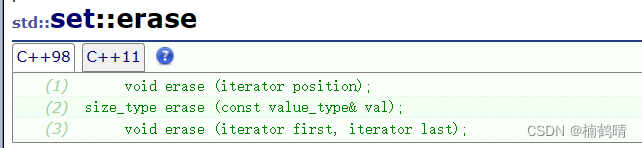
(1)void erase(iterator pos)
这个接口支持删除某个位置的值,需要提供删除值的位置(迭代器)
(2)size_t erase(const K& key)
这个接口支持删除set中的某一个值为key的结点,需要提供删除的key
(3)void erase(iterator first,iterator last)
这个接口支持删除set中的某一段连续的值
(4)综合测试set中的删除函数接口
- 代码
void test_set5()
{
//测试set中的删除函数
set<int> s;
s.insert(10);
s.insert(4);
s.insert(6);
s.insert(2);
s.insert(8);
s.insert(5);
s.insert(1);
for (auto& e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 删除某一个位置的迭代器
// 先通过find去获取这个值的迭代器
set<int>::iterator pos = s.find(4);
if (pos != s.end())
{
// 找到了
s.erase(pos);
}
for (auto& e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 删除某一个值
s.erase(10);
for (auto& e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 删除某一段区间
s.erase(s.begin(), s.end());
for (auto& e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
运行结果:
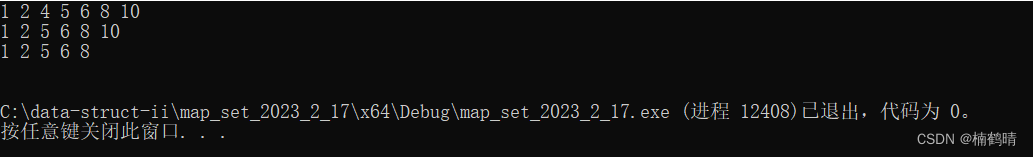
9.swap()
这个函数支持交换两个set对象的内容
- 代码:
void test_set6()
{
// 测试交换函数
set<int> s1;
s1.insert(1);
s1.insert(6);
s1.insert(5);
s1.insert(4);
s1.insert(3);
s1.insert(2);
cout << "s1:" << endl;
for (auto& e : s1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
set<int> s2;
s2.insert(10);
s2.insert(9);
s2.insert(8);
s2.insert(7);
s2.insert(6);
s2.insert(15);
cout << "s2:" << endl;
for (auto& e : s2)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
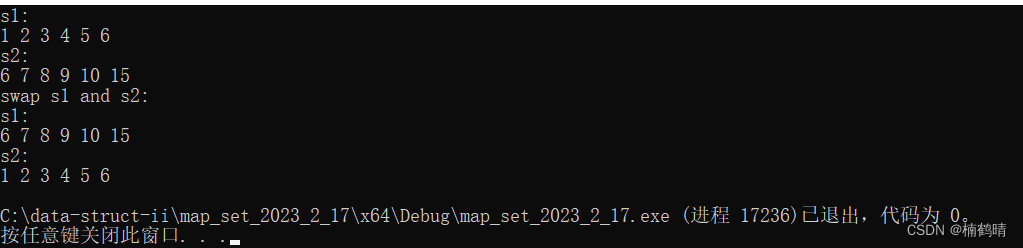
s1.swap(s2);
cout << "swap s1 and s2:" << endl;
cout << "s1:" << endl;
for (auto& e : s1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "s2:" << endl;
for (auto& e : s2)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
运行结果:
10. clear()
这个函数的功能是将set中的所有结点删除
void test_set7()
{
// 测试交换函数
set<int> s1;
s1.insert(1);
s1.insert(6);
s1.insert(5);
s1.insert(4);
s1.insert(3);
s1.insert(2);
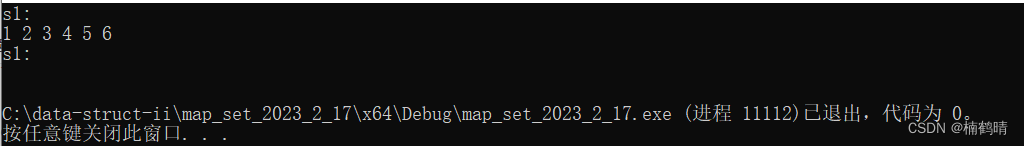
cout << "s1:" << endl;
for (auto& e : s1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
s1.clear();
cout << "s1:" << endl;
for (auto& e : s1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
运行结果:
11. find()
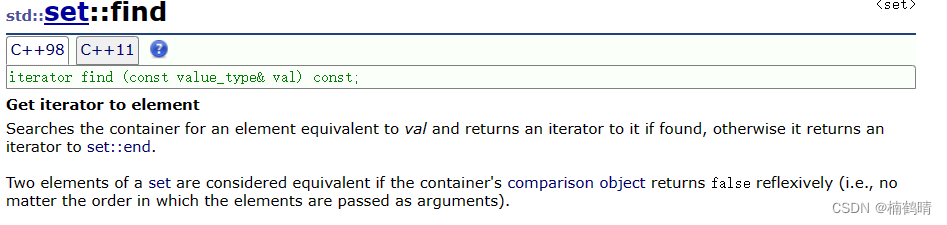
这个函数是支持在set中查找一个值,如果找到,则返回这个结点的迭代器,否则返回end()。这个find接口需要和算法中的find进行区分,set中的find函数是根据搜索树的性质进行查找的,而算法中的find是进行暴力查找的,所以这两者的查找效率是不一样的。
void test_set8()
{
//测试set中的find
vector<int> v = { 3,4,7,5,1,9,8 };
set<int> s(v.begin(),v.end());
set<int>::iterator pos;
for (auto& e : v)
{
pos = s.find(e);
if (pos != s.end())
{
// 找到了
cout << *pos << endl;
}
else
{
// 找不到
cout << "找不到此值" << endl;
}
}
}
运行结果:
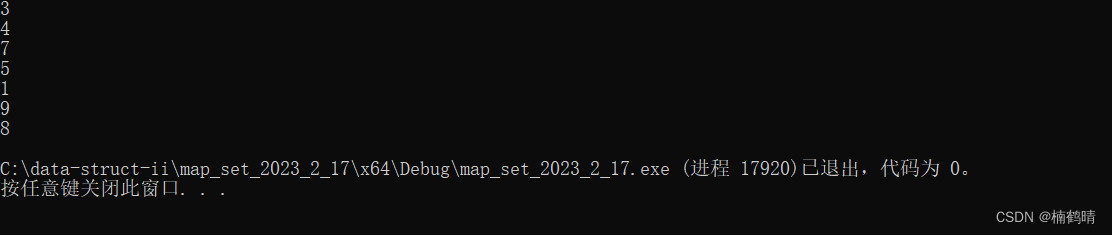
12.count()

这个函数的作用是求set中对应结点的个数,理论上set中的每一个结点在set中只能出现,所以查找的值返回的值次数理论上只能是1或者0。所以在set中,count()函数也能充当查找的功能。
void test_set9()
{
//测试set中的find
vector<int> v = { 3,4,7,5,1,9,8 };
set<int> s(v.begin(), v.end());
set<int>::iterator pos;
for (auto& e : v)
{
cout << s.count(e) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
vector<int> v1 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
for (auto& e: v1)
{
cout << e << "出现的次数:" << s.count(e) << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
运行结果:
13. set::iterator lower_bound(const K& key)
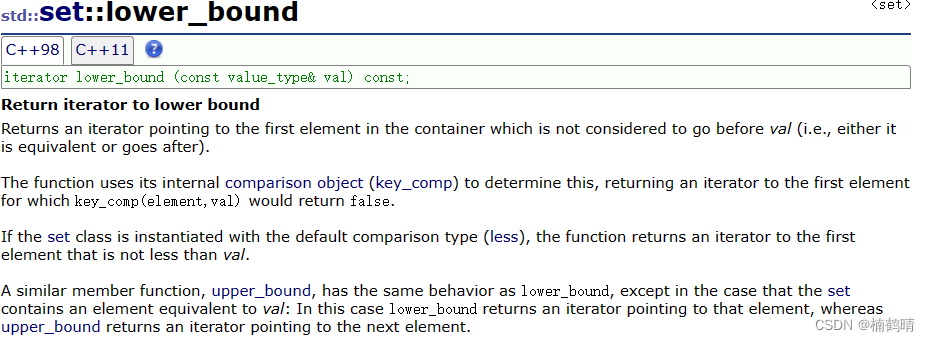
这个函数的功能是返回比key大或者相等的结点的迭代器
void test_set10()
{
// 测试lower_bound
vector<int> v = { 3,4,7,5,1,9,8 };
set<int> s(v.begin(), v.end());
// 找的值在set中存在
set<int>::iterator lowIt = s.lower_bound(4);
if (lowIt != s.end())
{
cout << *lowIt << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找不到" << endl;
}
// 找的值在set中不存在
lowIt = s.lower_bound(6);
if (lowIt != s.end())
{
cout << *lowIt << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找不到" << endl;
}
}
运行结果:
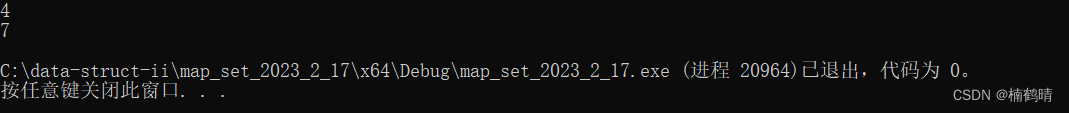
14. set::iterator upper_bound(const K& key)
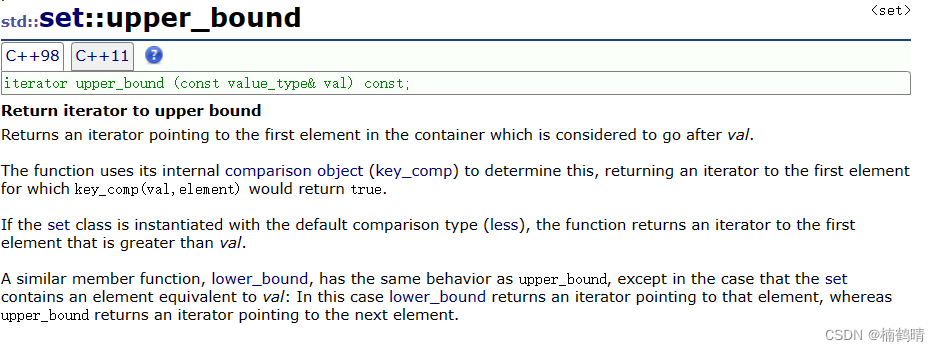
这个函数的功能是返回比key大的结点的迭代器(不包含key的结点)
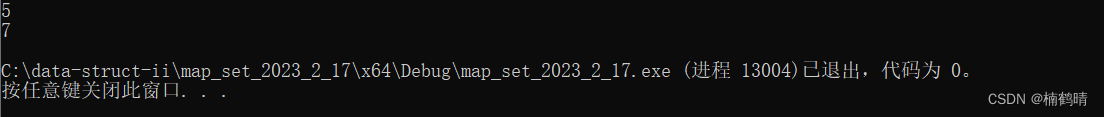
void test_set11()
{
// 测试upper_bound
vector<int> v = { 3,4,7,5,1,9,8 };
set<int> s(v.begin(), v.end());
// 找的值在set中存在
set<int>::iterator lowIt = s.upper_bound(4);
if (lowIt != s.end())
{
cout << *lowIt << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找不到" << endl;
}
// 找的值在set中不存在
lowIt = s.upper_bound(6);
if (lowIt != s.end())
{
cout << *lowIt << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找不到" << endl;
}
}
运行结果:
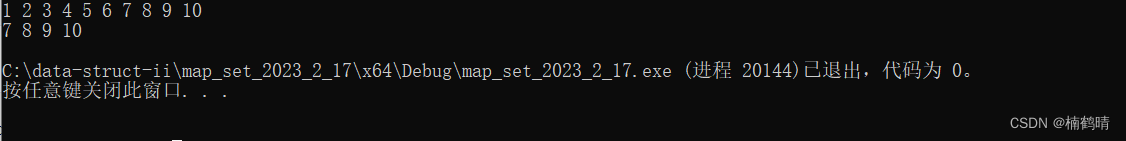
- lowerbound()和upper_bound()的综合使用场景
可以和set.erase(InputIterator first,InputIterator last)这个函数接口进行使用,删除一段迭代器区间
代码:
void test_set12()
{
// 综合测试lower_bound()和upper_bound()的使用
vector<int> v = { 2,3,5,1,7,6,4,9,8,10 };
set<int> s(v.begin(), v.end());
for (auto& e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//删除1-6的值
set<int>::iterator lowIt = s.lower_bound(1);
set<int>::iterator upIt = s.upper_bound(6);
s.erase(lowIt, upIt);
for (auto& e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
运行结果:
二、map
1. 简介

2. 成员类型
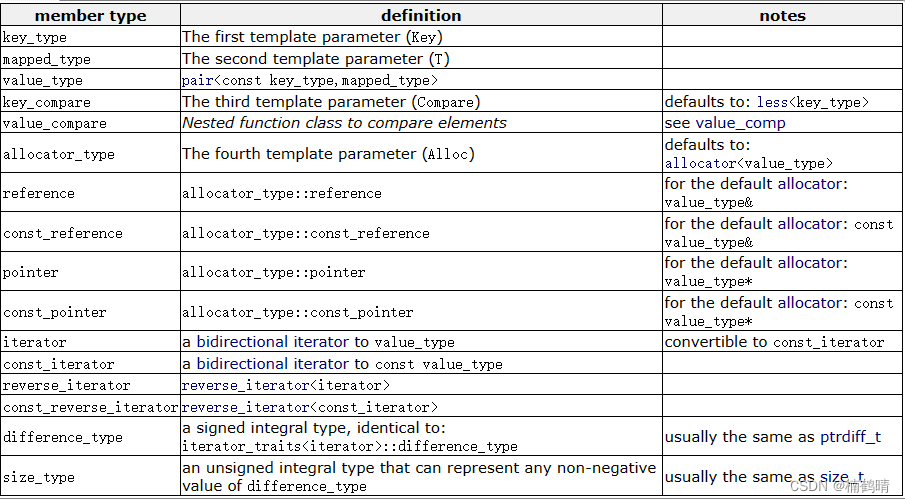
3. 构造函数
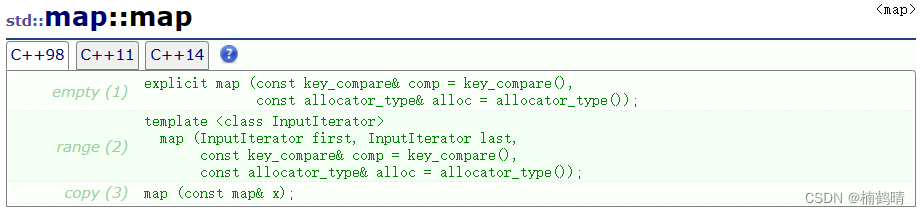
这个构造函数中比较常用的是使用无参构造函数进行创建对象
void test_map1()
{
// 无参构造函数
map<int, int> m1;
map<string, string> m2;
map<string, int> m3;
map<vector<int>, vector<int>> m4;
}
4. pair
pair是键值对的意思,其本质是一个结构体,其中包含两个成员变量first和second,使用pair的时候需要注意包头文件
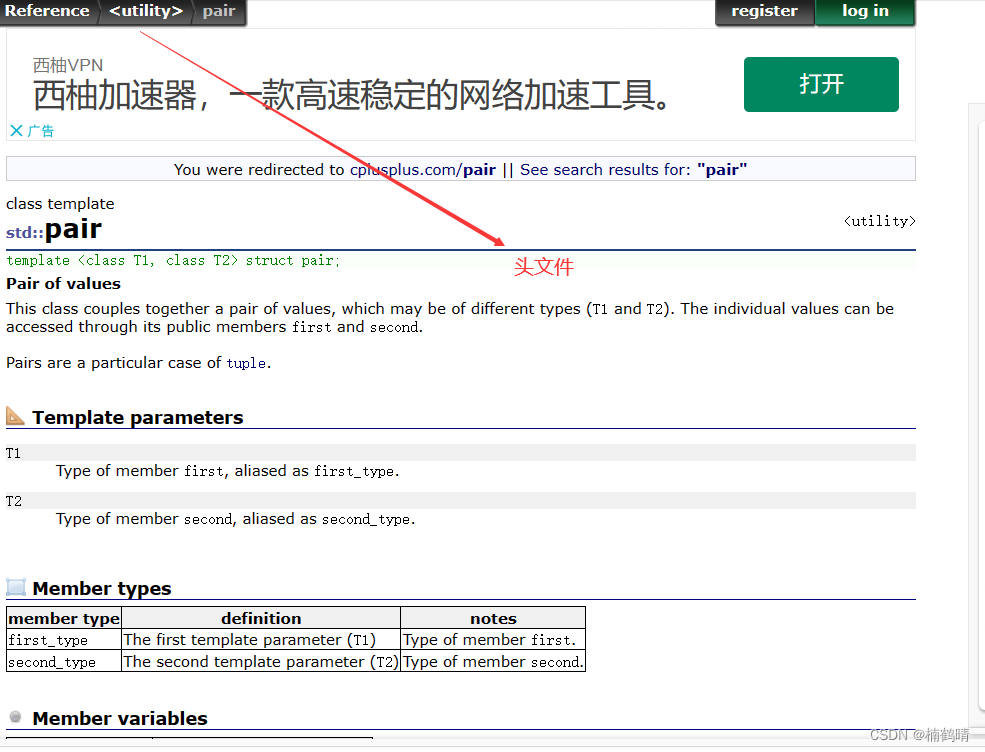
// pair
template <class K,class V>
struct pair
{
K first;
V second;
};
5. make_pair()
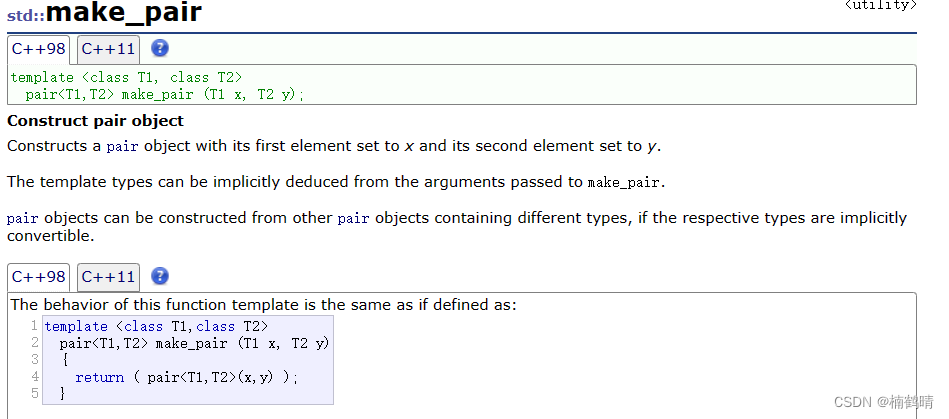
make_pair本质上是一个函数调用,就算将两个类型的值传给make_pair()然后构造出一个pair类型出来
其中需要注意,我们在传pair类型的参数的时候,是需要指明模板参数的,但是使用make_pair的时候是不需要指明模板参数的,后面的场景将会遇到
5. 拷贝构造函数和赋值运算符重载函数
使用方法和之前学习的数据结构一模一样。
void test_map14()
{
// 使用拷贝构造函数和赋值运算符重载函数
map<int, int> m;
m[1] = 1;
m[2] = 2;
m[3] = 3;
m[4] = 4;
m[5] = 5;
m[6] = 6;
m[7] = 7;
map<int, int> m1 = m;// 调用拷贝构造函数
map<int, int> m2;
m2 = m1;// 调用赋值运算符重载函数
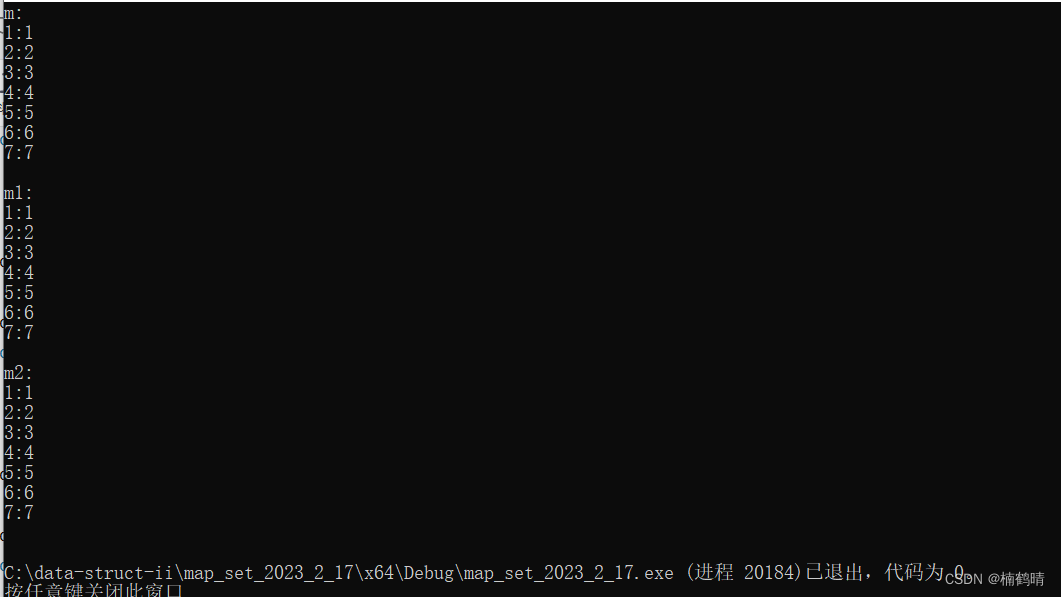
cout << "m:" << endl;
for (auto& e : m)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "m1:" << endl;
for (auto& e : m1)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "m2:" << endl;
for (auto& e : m2)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
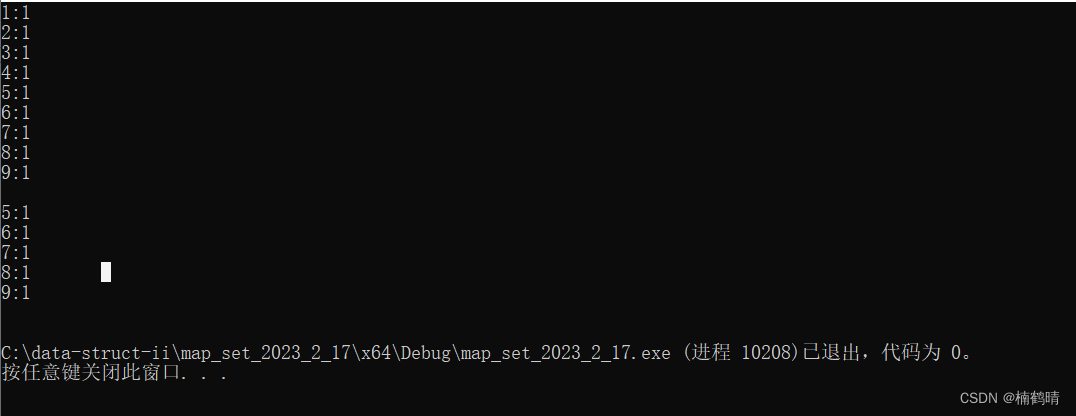
运行结果:
6. empty()
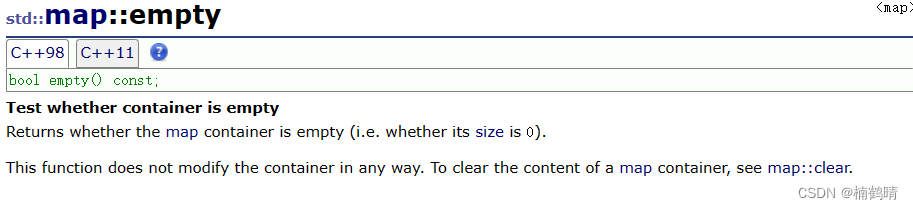
判断map是否为空,如果为空,返回true,否则,返回false
void test_map10()
{
//测试empty()
map<int, int> m;
m.insert(make_pair(1, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(2, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(3, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(4, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(5, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(6, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(7, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(8, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(9, 1));
if (m.empty())
{
cout << "该树为空" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "该树不为空" << endl;
}
m.clear();
if (m.empty())
{
cout << "该树为空" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "该树不为空" << endl;
}
}
运行结果:
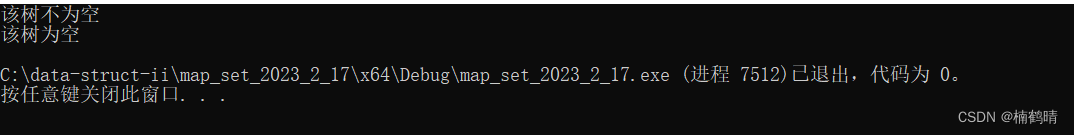
7. size()
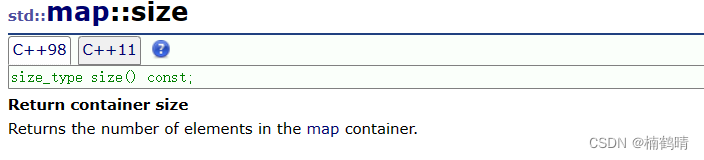
返回map中结点的个数
void test_map11()
{
// 测试size()
map<int, int> m;
m.insert(make_pair(1, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(2, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(3, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(4, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(5, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(6, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(7, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(8, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(9, 1));
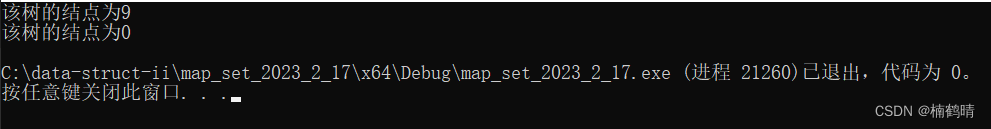
cout << "该树的结点为" << m.size() << endl;
m.clear();
cout << "该树的结点为" << m.size() << endl;
}
运行结果:
8. operator[]
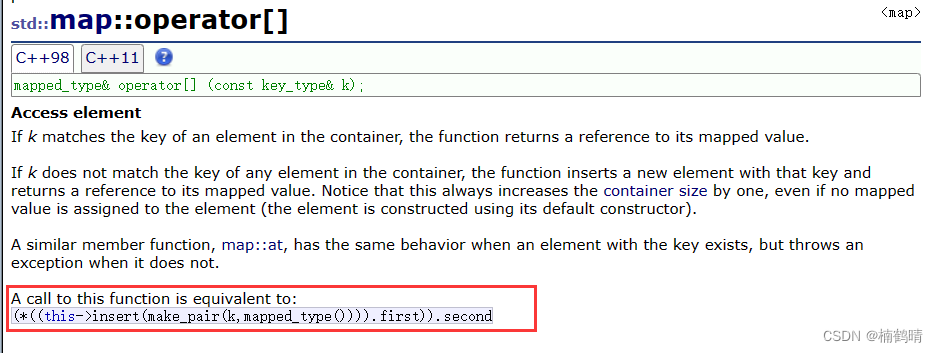
这个函数需要中单关注其返回值,其返回值是一个mapped_type&类型,也就是value的引用,所以返回值是支持修改的,其中涉及的插入过程中的细节在insert()中会进行细讲。
综上,我们可以知道,operator[]()充当的作用可以是插入,也可以是修改,也可以是仅仅访问某一个结点中的值
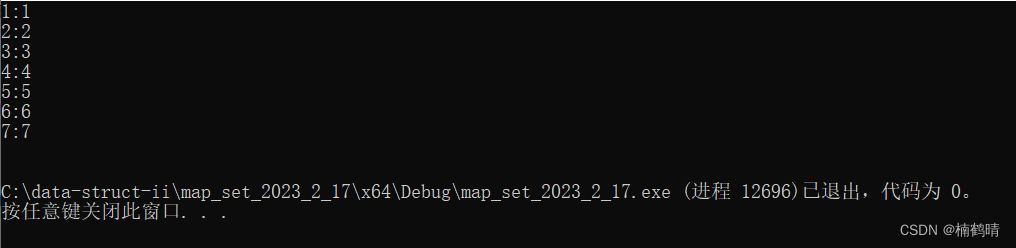
- 代码1:插入+访问
void test_map12()
{
// 测试[]
map<int, int> m;
m[1] = 1;
m[2] = 2;
m[3] = 3;
m[4] = 4;
m[5] = 5;
m[6] = 6;
m[7] = 7;
for (auto& e : m)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
运行结果:
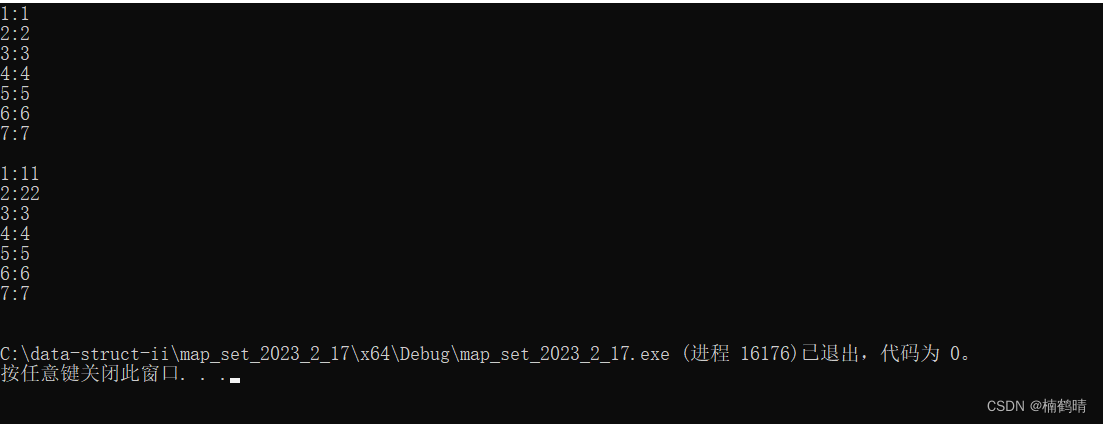
- 代码2:插入+访问+修改
void test_map13()
{
// 测试[]
map<int, int> m;
m[1] = 1;
m[2] = 2;
m[3] = 3;
m[4] = 4;
m[5] = 5;
m[6] = 6;
m[7] = 7;
for (auto& e : m)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
m[1] = 11;
m[2] = 22;
for (auto& e : m)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
运行结果:
9. insert()
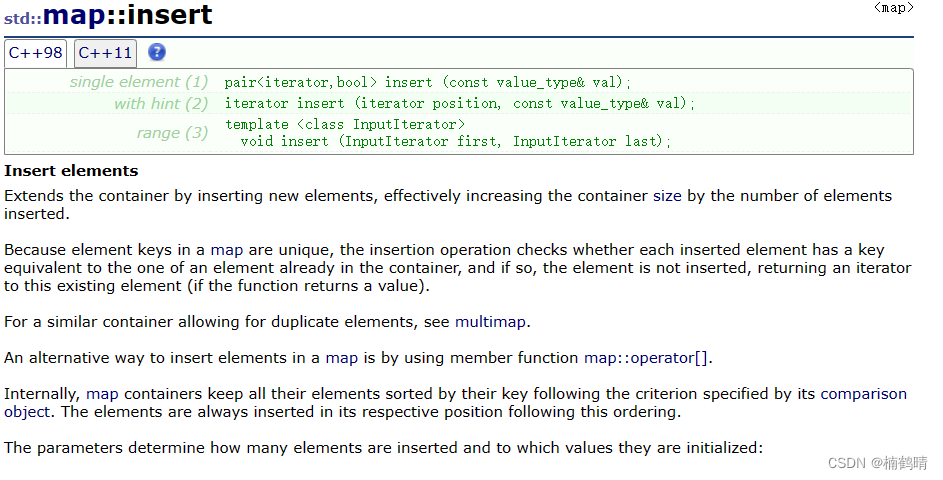
上面的接口中最常用的是插入pair类型的,这个函数需要中单关注其返回值,其返回值是一个pair<iterator,bool>类型,operator[]() 函数首先会调用 insert()函数,如果插入的值存在,则返回的pair<iterator,bool>中的iterator指向的是这个存在的结点,bool为false,表示此次插入失败,如果插入的值不存在,则成功插入,返回的pair<iterator,bool>中的iterator指向这个新插入的迭代器,bool为true,表示此次插入是成功的。
综上,我们可以知道,operator[]()充当的作用可以是插入,也可以是修改,也可以是仅仅访问某一个结点中的值使用如下:
void test_map2()
{
// std::pair<iterator,bool> set::insert(make_pair(key,value));
map<string, string> m1;
m1.insert(std::pair<string, string>("string", "字符串"));
m1.insert(make_pair("sort", "排序"));
m1.insert(make_pair("left", "左边"));
for (auto& e : m1)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
运行结果:
10. erase()
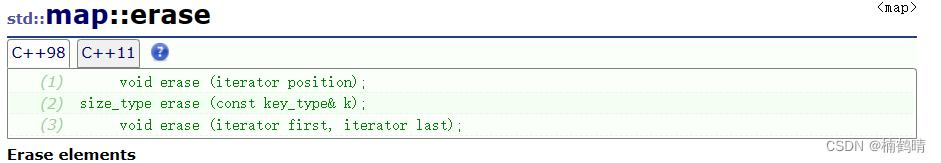
(1) void erase(iterator pos)
这个接口是支持给定迭代器,删除迭代器位置处的结点
(2) size_t erase(const K& key)
这个接口是支持删除给定的key的结点
(3) void erase(iterator first,iterator last)
这个接口支持删除一段迭代器区间,一般可以和lower_bound()和upper_bound()进行使用
(4) 综合测试erase的所有接口
- 代码:
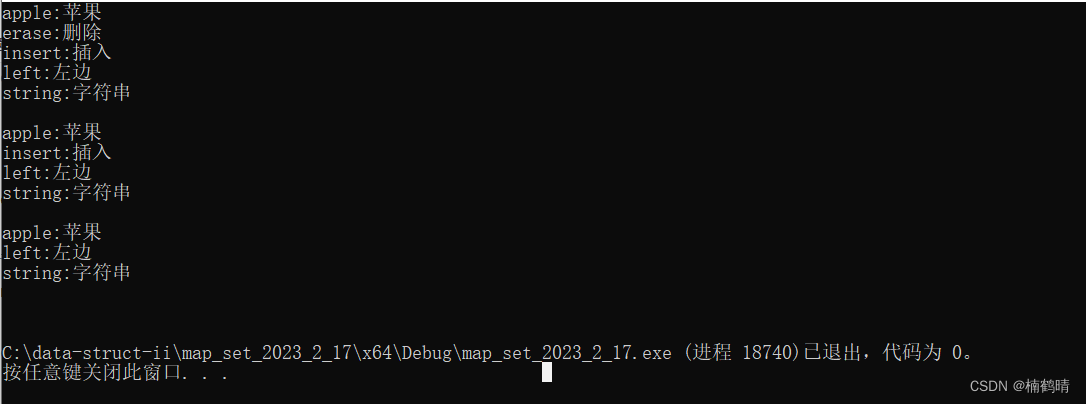
void test_map3()
{
map<string, string> m;
m.insert(make_pair("string", "字符串"));
m.insert(make_pair("left", "左边"));
m.insert(make_pair("apple", "苹果"));
m.insert(make_pair("insert", "插入"));
m.insert(make_pair("erase", "删除"));
for (auto& e : m)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
// 删除erase:支持通过key进行删除
m.erase("erase");
for (auto& e : m)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
// 删除insert:通过iterator 进行删除
// 找到insert的迭代器
map<string, string>::iterator pos = m.find("insert");
if (pos != m.end())
{
// 找到了
m.erase(pos);
}
else
{
// 找不到
cout << "找不到" << endl;
}
for (auto& e : m)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
// 删除全部的结点:使用迭代器区间进行删除
m.erase(m.begin(), m.end());
for (auto& e : m)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
运行结果:
11. swap()
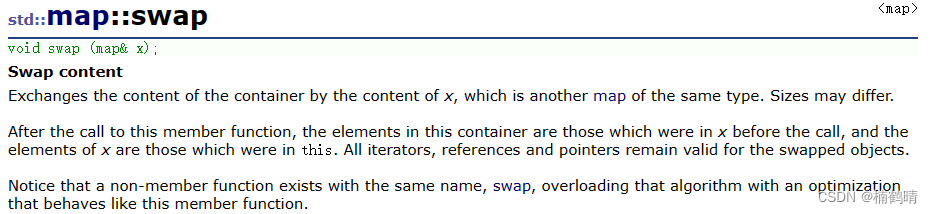
这个交换函数的底层是交换两个map中的根节点指针,std中的交换函数实现的是深拷贝,这个要区分开来。
void test_map4()
{
// 测试交换函数
map<string, string> m;
m.insert(make_pair("string", "字符串"));
m.insert(make_pair("left", "左边"));
m.insert(make_pair("apple", "苹果"));
m.insert(make_pair("insert", "插入"));
m.insert(make_pair("erase", "删除"));
map<string, string> m1;
m1.insert(std::pair<string, string>("string", "字符串"));
m1.insert(make_pair("sort", "排序"));
m1.insert(make_pair("left", "左边"));
cout << "m:" << endl;
for (auto& e : m)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "m1:" << endl;
for (auto& e : m1)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
m1.swap(m);
cout << "m:" << endl;
for (auto& e : m)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "m1:" << endl;
for (auto& e : m1)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
运行结果:
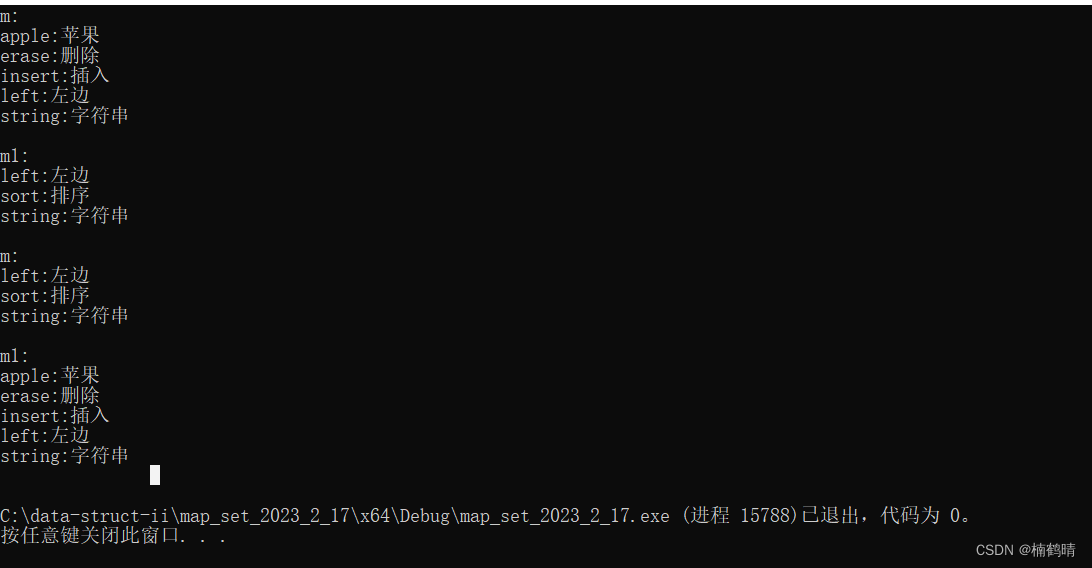
12. clear()

这个函数的功能是完成map中结点资源的清理
void test_map5()
{
// 测试clear
map<string, string> m;
m.insert(make_pair("string", "字符串"));
m.insert(make_pair("left", "左边"));
m.insert(make_pair("apple", "苹果"));
m.insert(make_pair("insert", "插入"));
m.insert(make_pair("erase", "删除"));
for (auto& e : m)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
m.clear();
for (auto& e : m)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
运行结果:
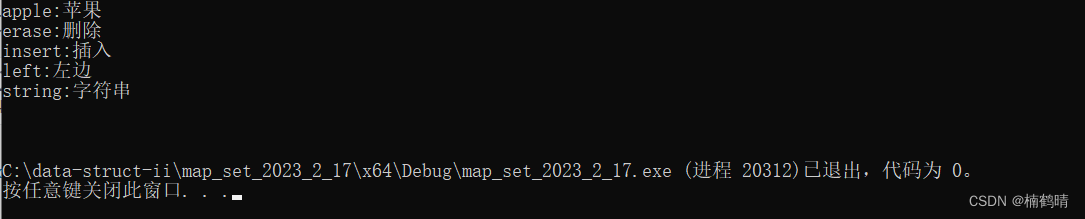
13. find()

这个函数的功能是通过key去找迭代器,所以find函数返回的是找的结点的迭代器,如果找到,返回找的结点的迭代器,否则,返回end()
void test_map6()
{
map<string, string> m;
m.insert(make_pair("string", "字符串"));
m.insert(make_pair("left", "左边"));
m.insert(make_pair("apple", "苹果"));
m.insert(make_pair("insert", "插入"));
m.insert(make_pair("erase", "删除"));
for (auto& e : m)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
map<string, string>::iterator pos = m.find("apple");
if (pos != m.end())
{
// 找到了
cout << pos->first << ":" << pos->second << endl;
}
else
{
// 找不到
cout << "找不到" << endl;
}
}
运行结果:

14. count()
计算map中结点出现的个数,理论上对于map,因为map中的数据不能出现冗余,所以map中count的返回值只可能是0或者1
15.lower_bound()
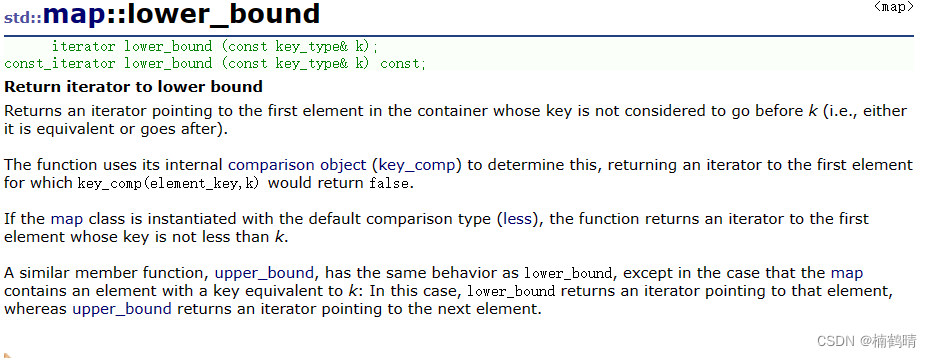
通过key,调用lower_bound()函数返回大于等于key的结点的迭代器
void test_map7()
{
// 测试lower_bound()
map<int, int> m;
m.insert(make_pair(1, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(2, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(3, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(4, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(5, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(6, 1));
// map中存在的值
map<int, int>::iterator lowIt = m.lower_bound(2);
if (lowIt != m.end())
{
// 找到了
cout << lowIt->first << ":" << lowIt->second << endl;
}
else
{
// 找不到
cout << "找不到" << endl;
}
// map中不存在的值
lowIt = m.lower_bound(0);
if (lowIt != m.end())
{
// 找到了
cout << lowIt->first << ":" << lowIt->second << endl;
}
else
{
// 找不到
cout << "找不到" << endl;
}
}
运行结果:

16.upper_bound()

通过key,调用lower_bound()函数返回大于key的结点的迭代器
void test_map8()
{
// 测试upper_bound()
map<int, int> m;
m.insert(make_pair(1, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(2, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(3, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(4, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(5, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(6, 1));
// map中存在的值
map<int, int>::iterator upIt = m.upper_bound(2);
if (upIt != m.end())
{
// 找到了
cout << upIt->first << ":" << upIt->second << endl;
}
else
{
// 找不到
cout << "找不到" << endl;
}
// map中不存在的值
upIt = m.upper_bound(0);
if (upIt != m.end())
{
// 找到了
cout << upIt->first << ":" << upIt->second << endl;
}
else
{
// 找不到
cout << "找不到" << endl;
}
}
运行结果:
- 综合使用lower_bound()和upper_bound()
void test_map9()
{
map<int, int> m;
m.insert(make_pair(1, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(2, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(3, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(4, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(5, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(6, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(7, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(8, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(9, 1));
// 删除前遍历一次
for (auto& e : m)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
// 要求删除1-4的值
map<int, int>::iterator lowIt = m.lower_bound(1);
map<int, int>::iterator upIt = m.upper_bound(4);
// 调用erase()
m.erase(lowIt, upIt);
// 删除后遍历一次
for (auto& e : m)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
运行结果: