prometheus如何优化远程读写的性能
场景
为了解决prometheus本地存储带来的单点问题,我们一般在高可用监控架构中会使用远程存储,并通过配置prometheus的remote_write和remote_read来对接
远程写优化:remote_write
远程写的原理:
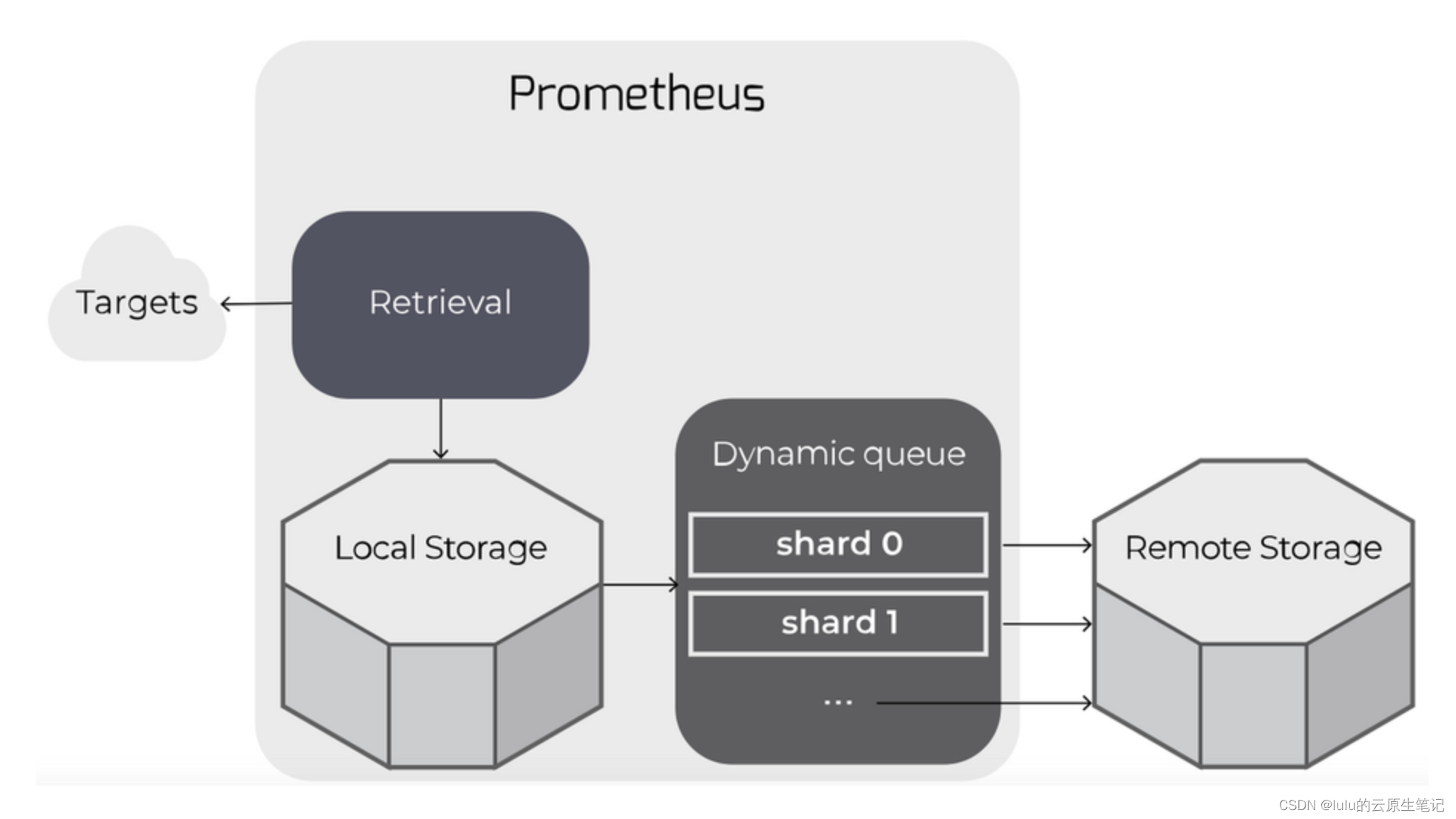
每个远程写入目标都会启动一个内存写队列(shards),这个队列从WAL中缓存数据。,通过队列去将指标数据写到有远程存储服务中,数据流如下所示:
|--> queue (shard_1) --> remote endpoint
WAL --|--> queue (shard_...) --> remote endpoint
|--> queue (shard_n) --> remote endpoint
重试机制:
当一个分片备份并填满队列时,Prometheus将阻止从WAL中读取数据到任何分片。(关于这点就涉及到对以上参数优化,后面参数capacity部分讲解)
远程端点写入失败会进行重试操作,并且保证数据不会丢失,除非远程端点保持关闭状态超过2小时,因为2小时后,WAL将被压缩,尚未发送的数据将丢失。重试时间见下面参数:min_backoff和max_backoff。
内存使用:
使用远程写入会增加Prometheus的内存占用量。大多数用户报告的内存使用量增加了约25%,但这取决于数据的形状。对于WAL中的每个系列,远程写代码都会缓存系列ID到标签值的映射,从而显着增加内存使用率。除了series缓存之外,每个分片及其队列还会增加内存使用量。当进行优化调整时,请考虑减少max_shards增加的数量,同时提高capacity和max_samples_per_send参数的大小从而避免无意间耗尽内存。默认capacity和 max_samples_per_send的取值将使得每每个shard使用内存小于100kb。
remote write queue的可调参数:
# Configures the queue used to write to remote storage.
queue_config:
# Number of samples to buffer per shard before we block reading of more
# samples from the WAL. It is recommended to have enough capacity in each
# shard to buffer several requests to keep throughput up while processing
# occasional slow remote requests.
[ capacity: <int> | default = 2500 ]
# Maximum number of shards, i.e. amount of concurrency.
[ max_shards: <int> | default = 200 ]
# Minimum number of shards, i.e. amount of concurrency.
[ min_shards: <int> | default = 1 ]
# Maximum number of samples per send.
[ max_samples_per_send: <int> | default = 500]
# Maximum time a sample will wait in buffer.
[ batch_send_deadline: <duration> | default = 5s ]
# Initial retry delay. Gets doubled for every retry.
[ min_backoff: <duration> | default = 30ms ]
# Maximum retry delay.
[ max_backoff: <duration> | default = 5s ]
# Retry upon receiving a 429 status code from the remote-write storage.
# This is experimental and might change in the future.
[ retry_on_http_429: <boolean> | default = false ]
max_shards和max_samples_per_send决定了Prometheus写入远程存储的最大TPS
参数解析:
-
1、capacity
定义:每个内存队列(shard:分片)的容量。
一旦WAL被阻塞,就无法将样本附加到任何分片,并且所有吞吐量都将停止。所以在大多数情况下,单个队列容量应足够打以避免阻塞其他分片,但是太大的容量可能会导致过多的内存消耗,并导致重新分片期间清除队列的时间更长。
-
2、max_shards
顾名思义,最大的分片数(即队列数),也可以理解为远程写的并行度。peometheus远程写的时候会使用所有的分片,只有在写队列落后于远程写的速度,使用的队列数会达到max_shards,目的在于提高远程写的吞吐量。
PS:在操作过程中,Prometheus将根据传入的采样率,未发送的未处理样本数以及发送每个样本所花费的时间,连续计算要使用的最佳分片数。(实际的分片数是动态调整的)
-
3、min_shards
最小分片配置Prometheus使用的最小分片数量,并且是远程写入开始时使用的分片数量。如果远程写入落后,Prometheus将自动扩大分片的数量,因此大多数用户不必调整此参数。但是,增加最小分片数将使Prometheus在计算所需分片数时避免在一开始就落后。 -
4、max_samples_per_send
定义:每次远程写发送的最大指标数量,即批处理;
这个值依赖于远程存储系统,对于一些系统而言,在没有显著增加延迟的情况下发送更多指标数据而运行良好,然而,对于另外一些系统而言,每次请求中发送大量指标数据可能导致其出现故障,使用的默认值是适用于绝大多数系统的。
-
5、batch_send_deadline
定义:单一分片批量发送指标数据的最大等待时间;
即使排队的分片尚未达到max_samples_per_send,也会发送请求。 对于对延迟不敏感的小批量系统,可以增加批量发送的截止时间,以提高请求效率。
-
6、min_backoff
定义:远程写失败的最小等待时间;
min_backoff是第一次的重试等待时间,第二次等待时间是其2倍,以此类推,直到max_backoff的值;
-
7、max_backoff
定义:远程写失败的最大等待时间;
推荐做法:
-
当进行优化调整时,请考虑减少max_shards的数量,同时提高capacity和max_samples_per_send参数的大小从而避免无意间耗尽内存
-
max_shards和max_samples_per_send决定了Prometheus写入远程存储的最大TPS,
max_shards * max_samples_per_send决定了TPS的值,所以要考虑这两个的合理搭配
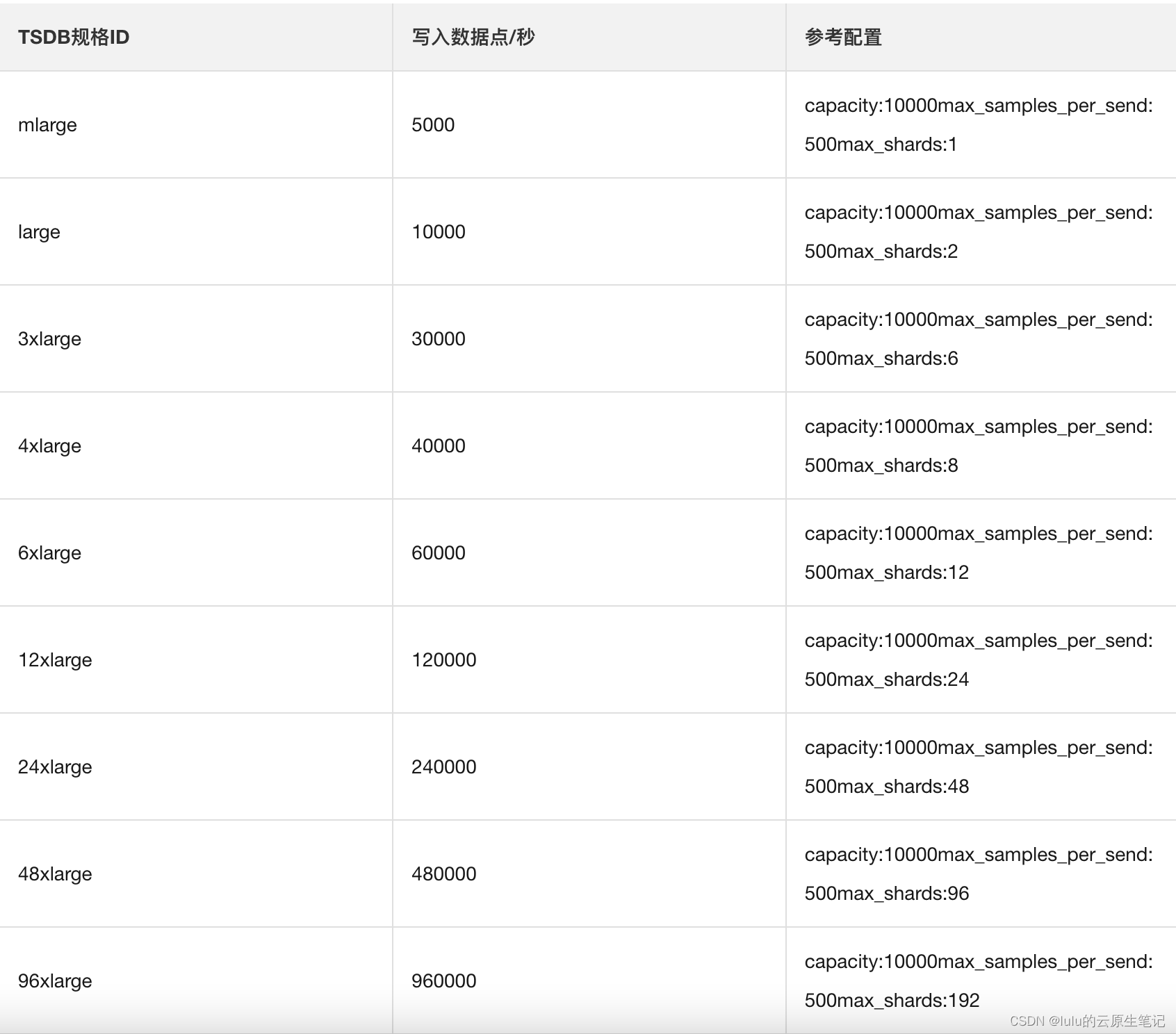
给出阿里云prometheus对接TSDB调优参考表:
远程读优化:remote_read
默认情况下,prometheus除了使用remote_write将数据发送到远程时序数据库,同时还会按照以下参数来保留数据到本地自己的时序数据库,两者取最先达到限制的:
--storage.tsdb.retention.time=30d
--storage.tsdb.retention.size=512MB
也就说默认情况下,prometheus保存了两份数据,一份到远程时序数据库,一份在本地
那么读取的时候是读取远程的还是读取本地是由read_recent参数决定
# Whether reads should be made for queries for time ranges that
# the local storage should have complete data for.
[ read_recent: <boolean> | default = false ]
read_recent作用:
- 当设置为 true 时,所有查询都将从远程和本地存储中得到答复。
- 当为 false(默认值)时,任何可以从本地存储完全回答的查询都不会发送到远程端点
推荐做法:
- 通过storage.tsdb.retention.time与storage.tsdb.retention.size控制缓存短期数据在本地
- 配置read_recent为false,使得本地能查询到的数据都优先在本地进行查询