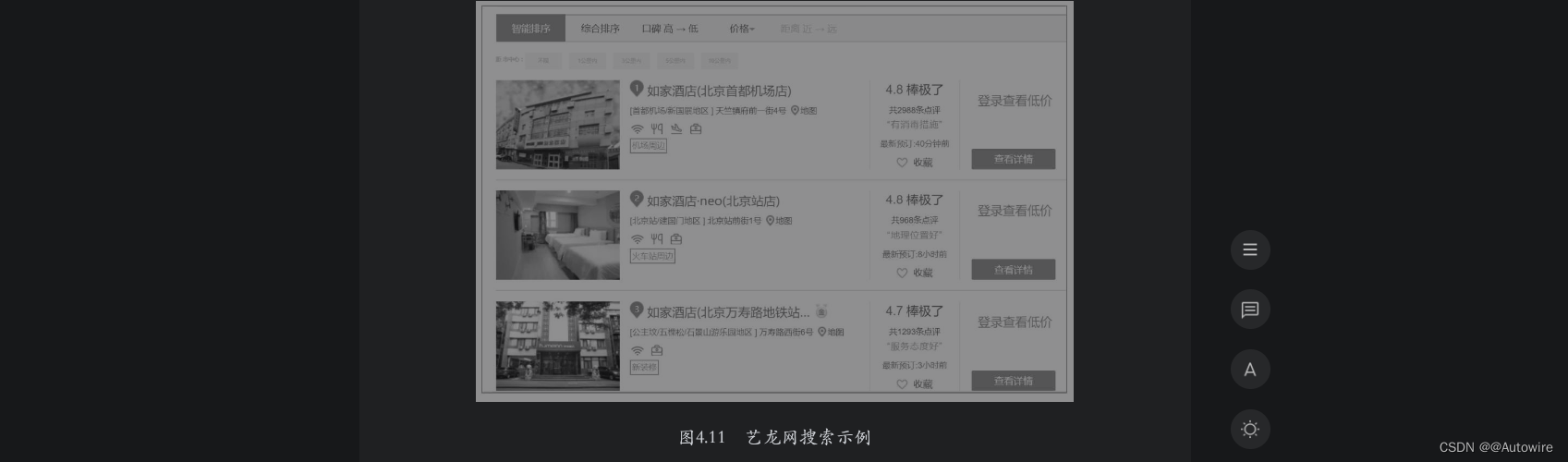
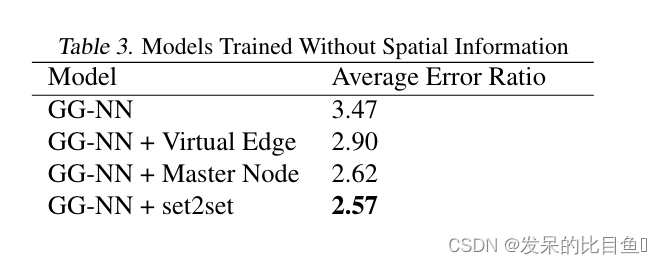
PyTorch学习笔记:nn.SmoothL1Loss——平滑L1损失
torch.nn.SmoothL1Loss(size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean', beta=1.0)
功能:创建一个平滑后的
L
1
L_1
L1损失函数,即Smooth L1:
l
(
x
,
y
)
=
L
=
{
l
1
,
…
,
l
N
}
T
l(x,y)=L=\{l_1,\dots,l_N\}^T
l(x,y)=L={l1,…,lN}T
其中,
l
n
=
{
1
2
β
(
x
n
,
y
n
)
2
,
∣
x
n
−
y
n
∣
<
β
∣
x
n
−
y
n
∣
−
1
2
β
,
otherwise
\begin{aligned} l_n=\left\{ \begin{matrix} & \frac{1}{2\beta}(x_n,y_n)^2, \quad |x_n-y_n|<\beta\\ &|x_n-y_n|-\frac12\beta,\quad \text{otherwise} \end{matrix} \right. \end{aligned}
ln={2β1(xn,yn)2,∣xn−yn∣<β∣xn−yn∣−21β,otherwise
如果绝对值误差低于 β \beta β,则创建一个平方项的损失( L 2 L_2 L2),否则使用绝对值损失( L 1 L_1 L1),此损失对异常值的敏感性低于 L 2 L_2 L2损失,即当 x x x与 y y y相差过大时,该损失数值要小于 L 2 L_2 L2损失数值,在某些情况下该损失可以防止梯度爆炸,损失图如下所示:

输入:
size_average与reduce已经被弃用,具体功能可由reduction替代reduction:指定损失输出的形式,有三种选择:none|mean|sum。none:损失不做任何处理,直接输出一个数组;mean:将得到的损失求平均值再输出,会输出一个数;sum:将得到的损失求和再输出,会输出一个数beta:指定该损失在 L 1 L_1 L1与 L 2 L_2 L2之间变化的阈值,默认 1.0 1.0 1.0
注意:
- Smooth L1损失与 L 1 L_1 L1损失类似,但是随着 ∣ x − y ∣ < β |x-y|<\beta ∣x−y∣<β,即随着 x x x与 y y y的靠近,损失形式逐渐向 L 2 L_2 L2损失的形式靠近
代码案例
一般用法
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
# reduction设为none便于逐元素对比损失值
loss = nn.SmoothL1Loss(reduction='none')
x = torch.randn(10)
y = torch.randn(10)
loss_value = loss(x, y)
print(x)
print(y)
print(loss_value)
输出
# x
tensor([ 0.7584, 1.0724, 0.8966, -1.0947, -1.8141, -1.8305, -1.5329, -0.3077,
0.6814, -0.2394])
# y
tensor([ 0.5081, -0.1718, 0.7817, -0.8019, -0.6405, -1.4802, 2.3039, 1.4522,
1.1861, -0.2443])
# loss
tensor([3.1319e-02, 7.4427e-01, 6.6015e-03, 4.2872e-02, 6.7358e-01, 6.1354e-02,
3.3368e+00, 1.2598e+00, 1.2736e-01, 1.1723e-05])
注:画图程序
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
loss = nn.SmoothL1Loss(reduction='none')
x = torch.tensor([0]*100)
y = torch.from_numpy(np.linspace(-3,3,100))
loss_value = loss(x,y)
plt.plot(y, loss_value)
plt.savefig('SmoothL1Loss.jpg')
官方文档
nn.SmoothL1Loss:https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.SmoothL1Loss.html#torch.nn.SmoothL1Loss