💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥
🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
📋📋📋本文目录如下:🎁🎁🎁
目录
💥1 概述
📚2 运行结果
🎉3 参考文献
🌈4 Python代码、数据、详细文章讲解
💥1 概述
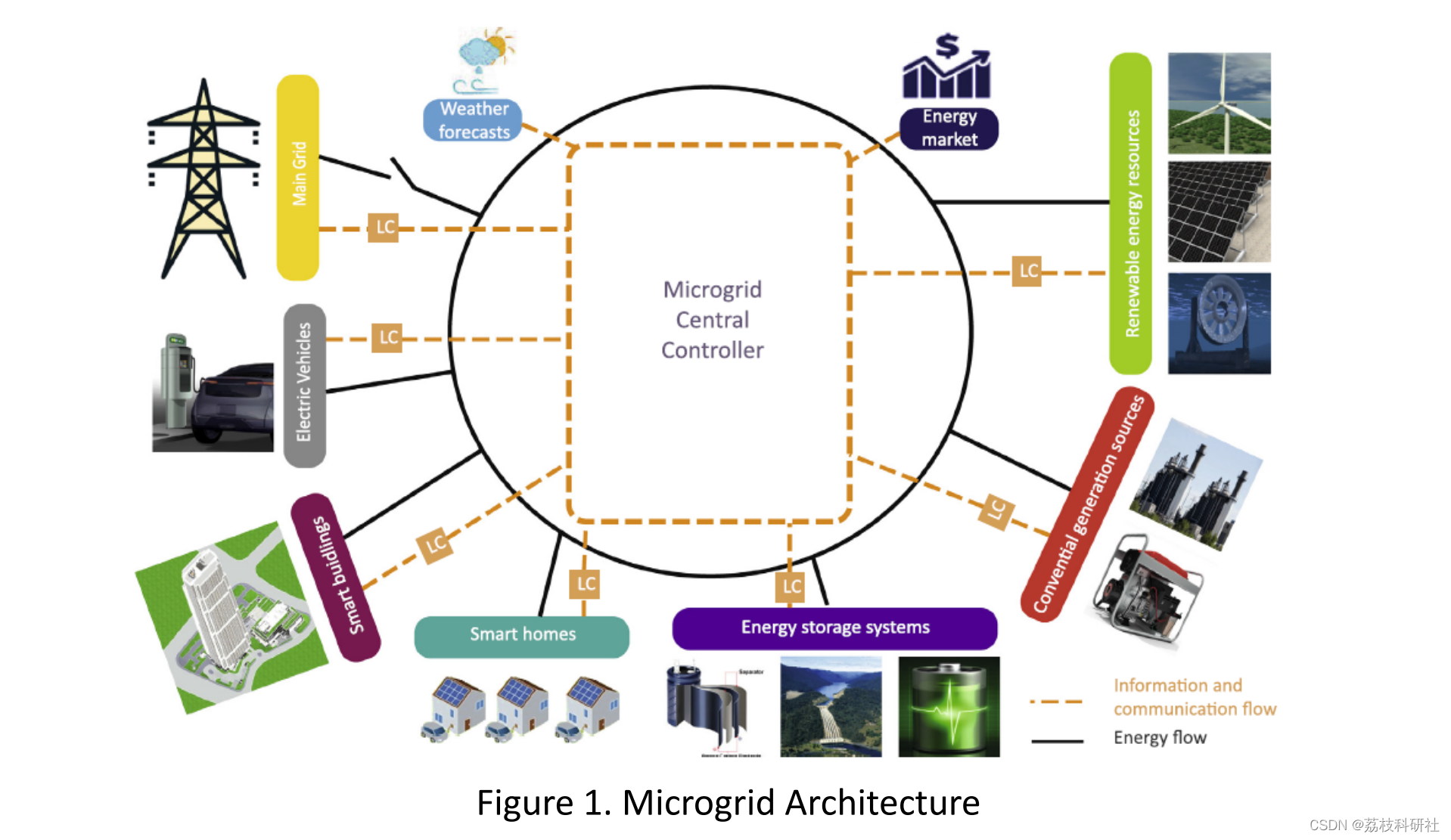

在本文中,我们提出了我们的策略和算法来管理微电网中的能量,更具体地说,在考虑消费者负荷、太阳能发电和动态电价的情况下,每小时与主电网的能量交易。 该算法的主要目标是在用户负荷、太阳能发电和电价波动的情况下,优化储能系统( ESS )的运行,最大化微电网的货币效益。除了货币收益外,该算法还考虑了需要保留的最小能量,因为这对于确保微电网中关键任务操作的连续性至关重要。研究分析了两种能量管理算法的性能:1 )具有预测未来知识的模型预测控制线性规划( MPCLPF );2 )不具有未来知识的强化学习。在MPCLPF中,分析了不同的预测算法,并对最优预测算法进行了整合。下面是文章目录:

详细文章见第4部分。
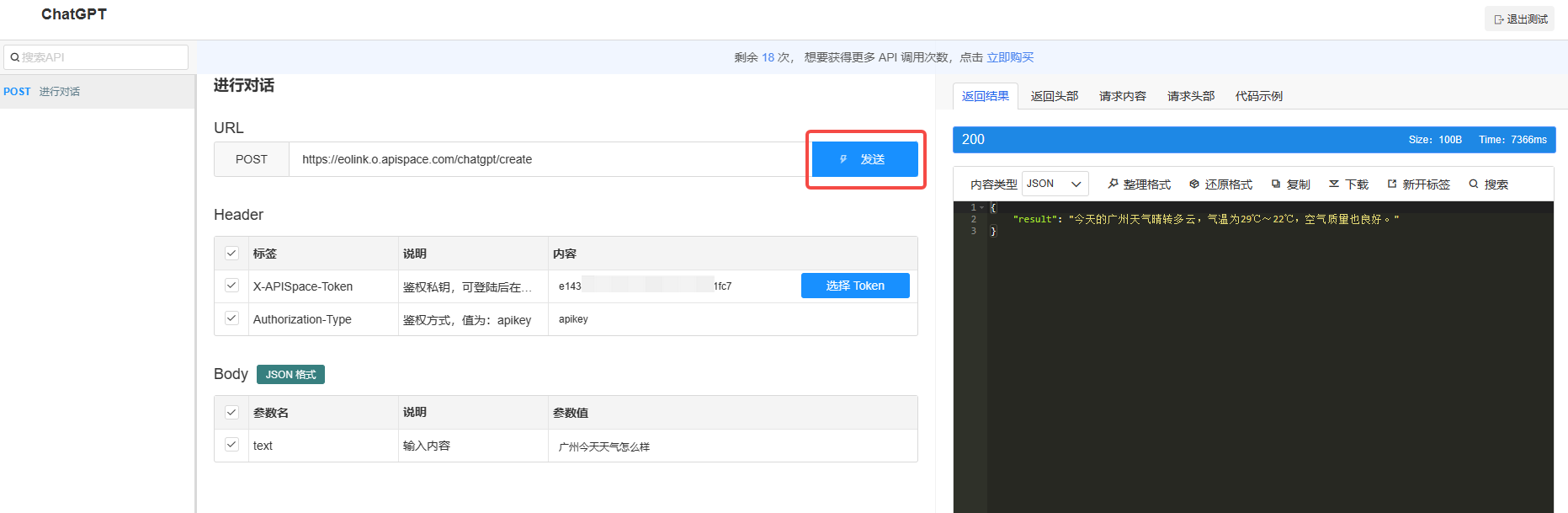
📚2 运行结果
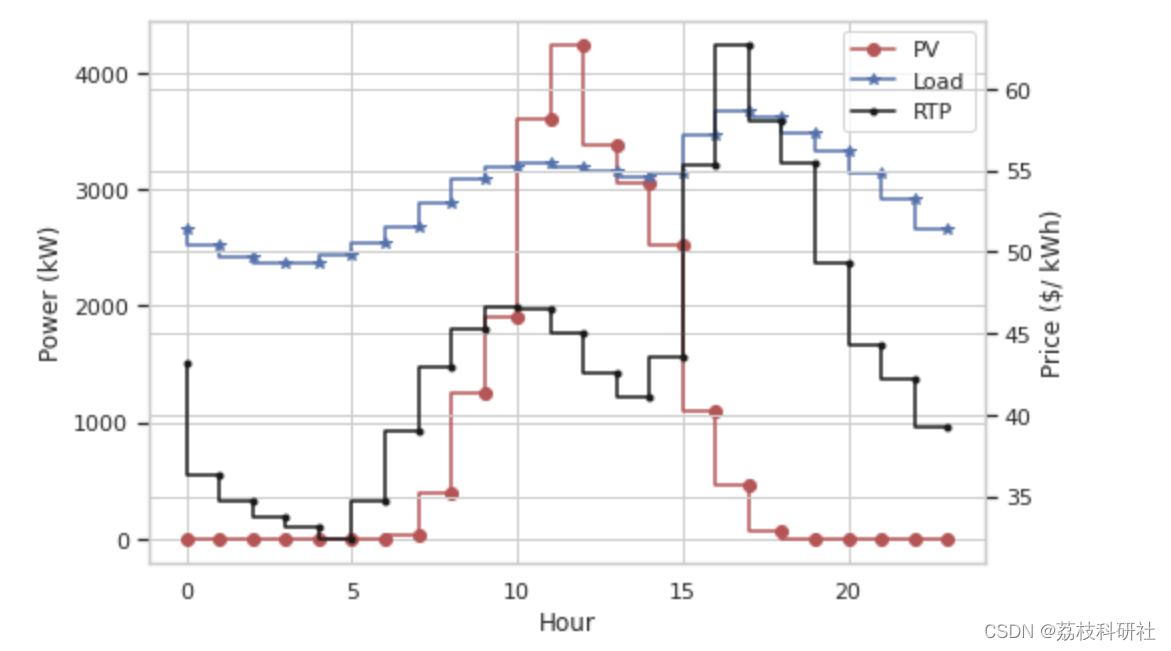
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize = (7.5,5))
ax2 = ax.twinx()
PV_plot = ax.step(np.arange(24), df.iloc[0:24,0], 'ro-', label = "PV")
load_plot = ax.step(np.arange(24), df.iloc[0:24,1], 'b*-', label = "Load")
price_plot = ax2.step(np.arange(24), df.iloc[0:24,2], 'k.-', label = "RTP")
# Display all label in one box
plots = PV_plot + load_plot + price_plot
labels = [plot.get_label() for plot in plots]
ax.legend(plots, labels, loc = 0)
ax.set_xlabel("Hour")
ax.set_ylabel("Power (kW)")
ax2.set_ylabel("Price ($/ kWh)")
plt.show()
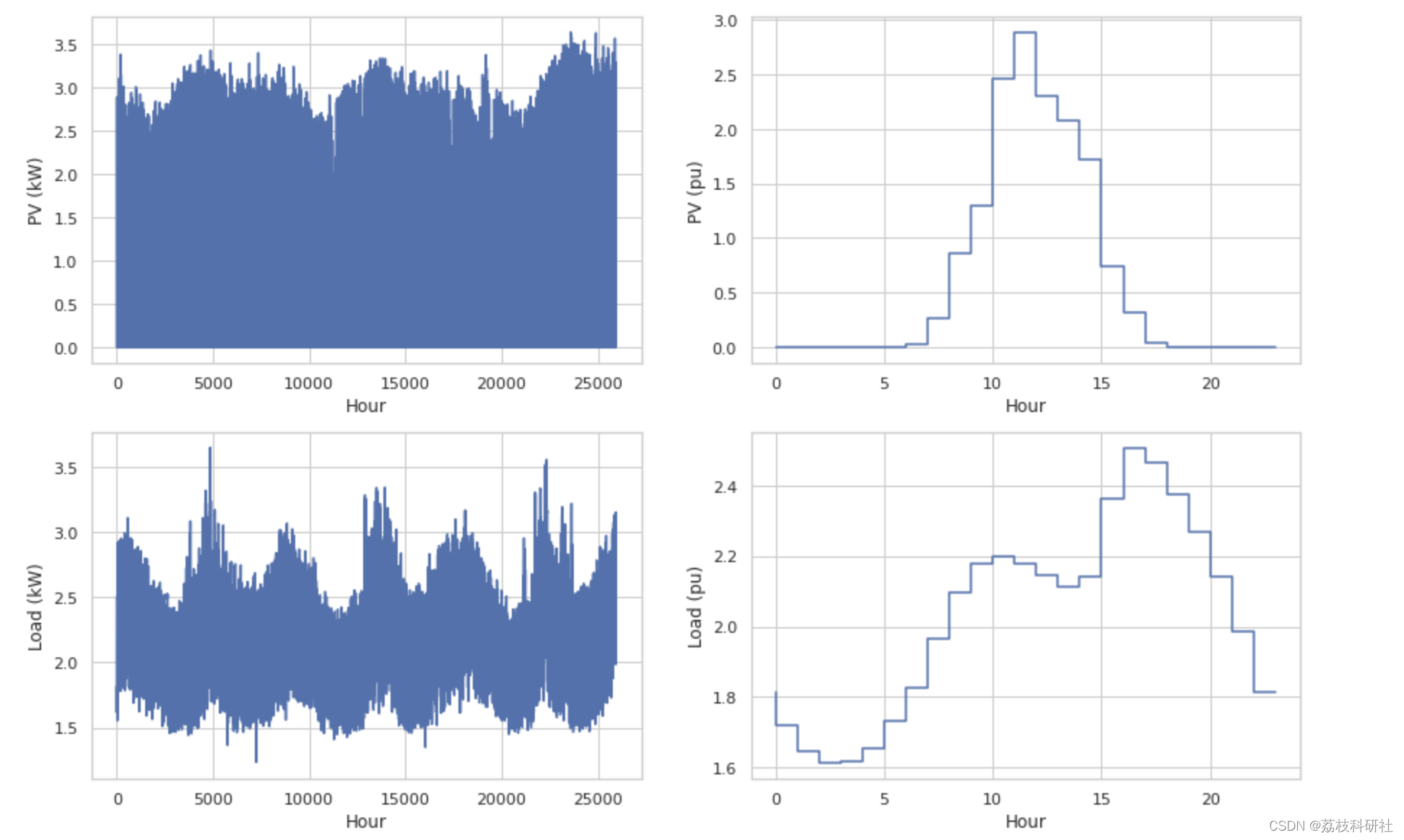
fig, ax = plt.subplots(3, 2, figsize = (15, 15))
ax[0, 0].step(np.arange(len(x[:,0])), x[:,0])
ax[0, 0].set_xlabel("Hour")
ax[0, 0].set_ylabel("PV (kW)")
ax[0, 1].step(np.arange(len(x[0:24,0])), x[0:24,0])
ax[0, 1].set_xlabel("Hour")
ax[0, 1].set_ylabel("PV (pu)")
ax[1, 0].step(np.arange(len(x[:,1])), x[:,1])
ax[1, 0].set_xlabel("Hour")
ax[1, 0].set_ylabel("Load (kW)")
ax[1, 1].step(np.arange(len(x[0:24,1])), x[0:24,1])
ax[1, 1].set_xlabel("Hour")
ax[1, 1].set_ylabel("Load (pu)")
ax[2, 0].step(np.arange(len(x[:,2])), x[:,2])
ax[2, 0].set_xlabel("Hour")
ax[2, 0].set_ylabel("Price ($/kWh)")
ax[2, 1].step(np.arange(len(x[0:24,2])), x[0:24,2])
ax[2, 1].set_xlabel("Hour")
ax[2, 1].set_ylabel("Price (pu)")
plt.show()
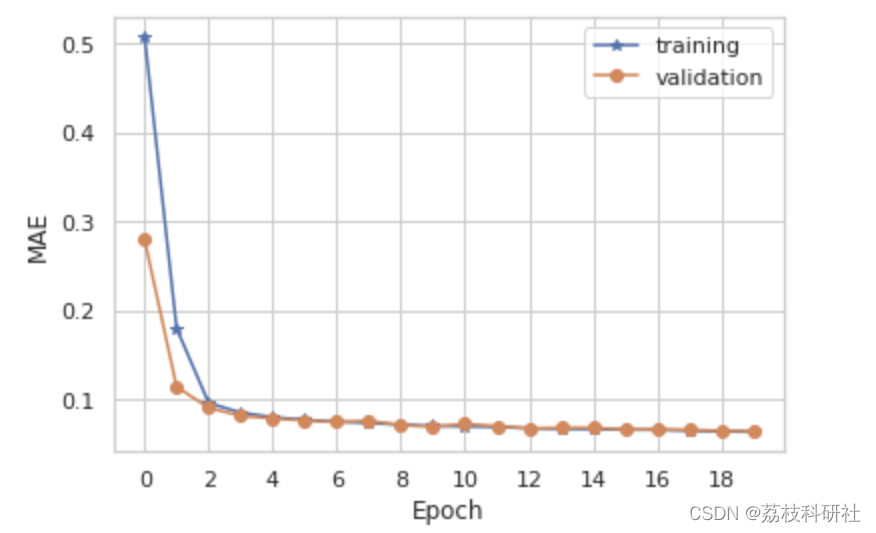
plt.plot(lstm.history.history["loss"], "-*", label="training")
plt.plot(lstm.history.history["val_loss"], "-o", label="validation")
plt.xticks(np.arange(0, 20, 2), np.arange(0, 20, 2))
plt.xlabel("Epoch")
plt.ylabel("MAE")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
encoder.load_weights(encoder.weights_dir)
decoder.load_weights(decoder.weights_dir)
y_train_pred, attentions = predict(x_train, y_train)
print ("Training MAE: {:.4f} pu\n".format(mae(y_train[:, :, 0], y_train_pred[:, :, 0])))
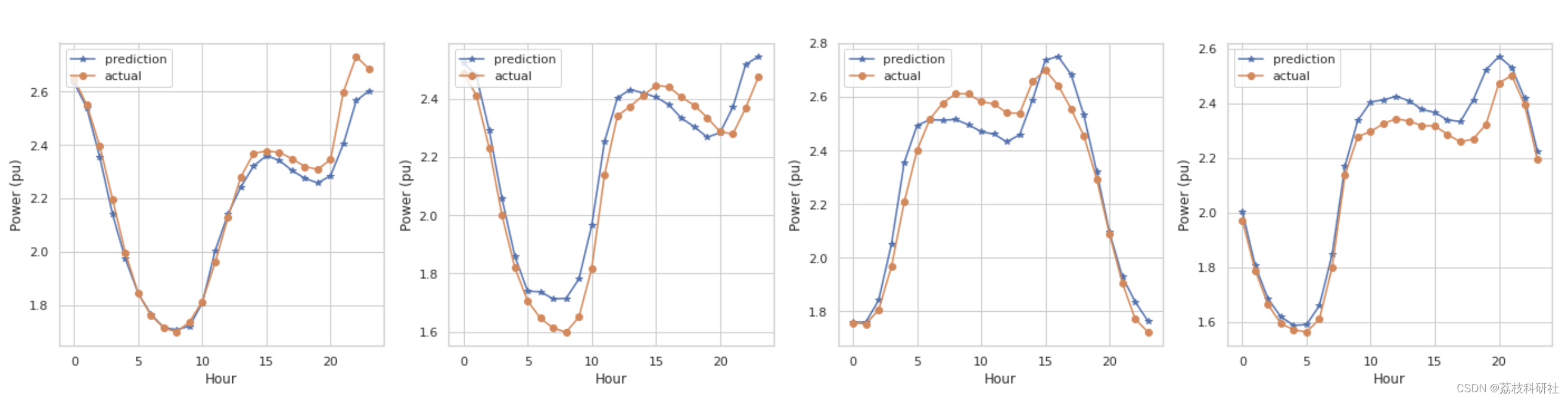
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(24, 5))
for idx, i in enumerate([0, 1000, 2000, 3000]):
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 4, idx+1)
ax.plot(y_train_pred[i], "-*", label="prediction")
ax.plot(y_train[i, :, 0], "-o", label="actual")
ax.set_xlabel("Hour")
ax.set_ylabel("Power (pu)")
ax.legend(loc=2)
plt.show()
plt.plot(lstm.history.history["loss"], "-*", label="training")
plt.plot(lstm.history.history["val_loss"], "-o", label="validation")
plt.xticks(np.arange(0, 20, 2), np.arange(0, 20, 2))
plt.xlabel("Epoch")
plt.ylabel("MAE")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
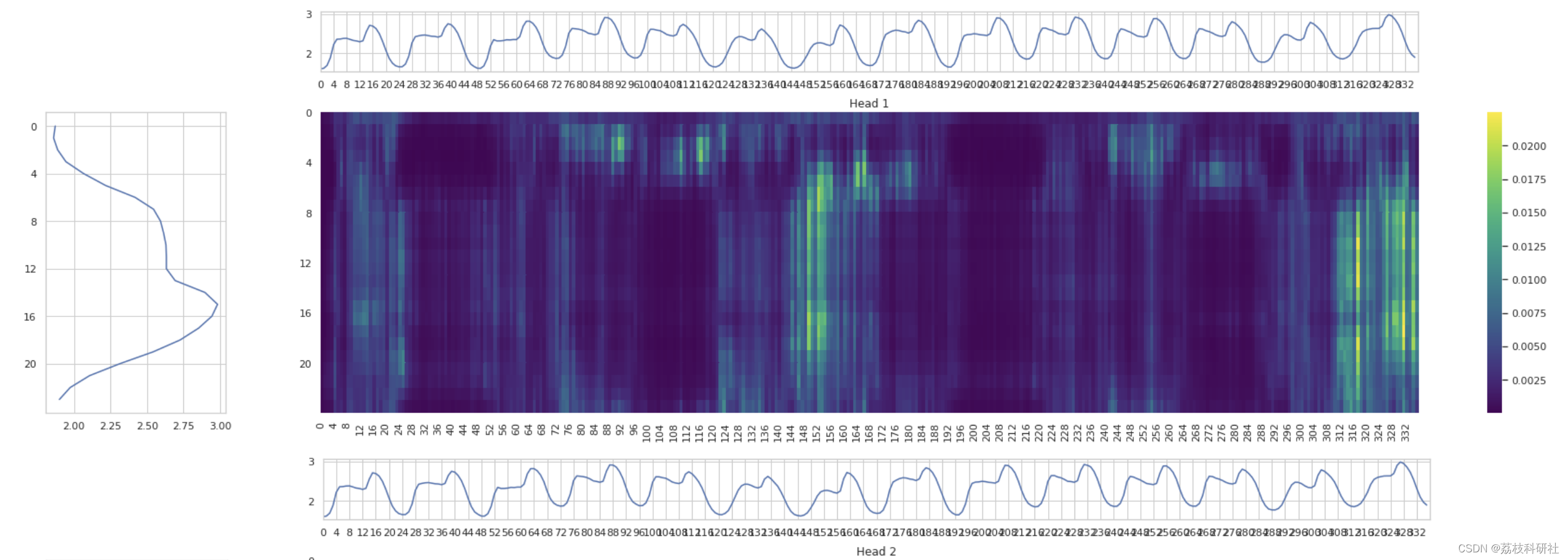
idx = -10
num_steps_display = timesteps_in
attention = attention_weights
attention = tf.squeeze(attention["decoder_layer1_block2"][idx:idx+1], axis=0)
for head in range(0, num_heads):
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(32,8))
spec = gridspec.GridSpec(ncols=90, nrows=100)
top_ax = fig.add_subplot(spec[0:15, 15:75])
left_ax = fig.add_subplot(spec[25:, 0:10])
right_ax = fig.add_subplot(spec[25:, 15:])
top_ax.plot(x_train[idx, :num_steps_display, 0])
top_ax.set_xlim([0, num_steps_display])
top_ax.set_xticks(range(0, num_steps_display, 4))
top_ax.set_xticklabels(range(0, num_steps_display, 4))
left_ax.plot(decoder_input[idx, :, 0], range(0, timesteps_out))
left_ax.set_yticks(range(0, timesteps_out, 4))
left_ax.set_yticklabels(range(0, timesteps_out, 4))
left_ax.invert_yaxis()
sns.heatmap(attention[head][:, :num_steps_display], cmap="viridis", ax=right_ax)
right_ax.set_xticks(range(0, num_steps_display, 4))
right_ax.set_xticklabels(range(0, num_steps_display, 4))
right_ax.set_yticks(range(0, timesteps_out, 4))
right_ax.set_yticklabels(range(0, timesteps_out, 4))
plt.title("Head {}".format(head+1))
plt.show()
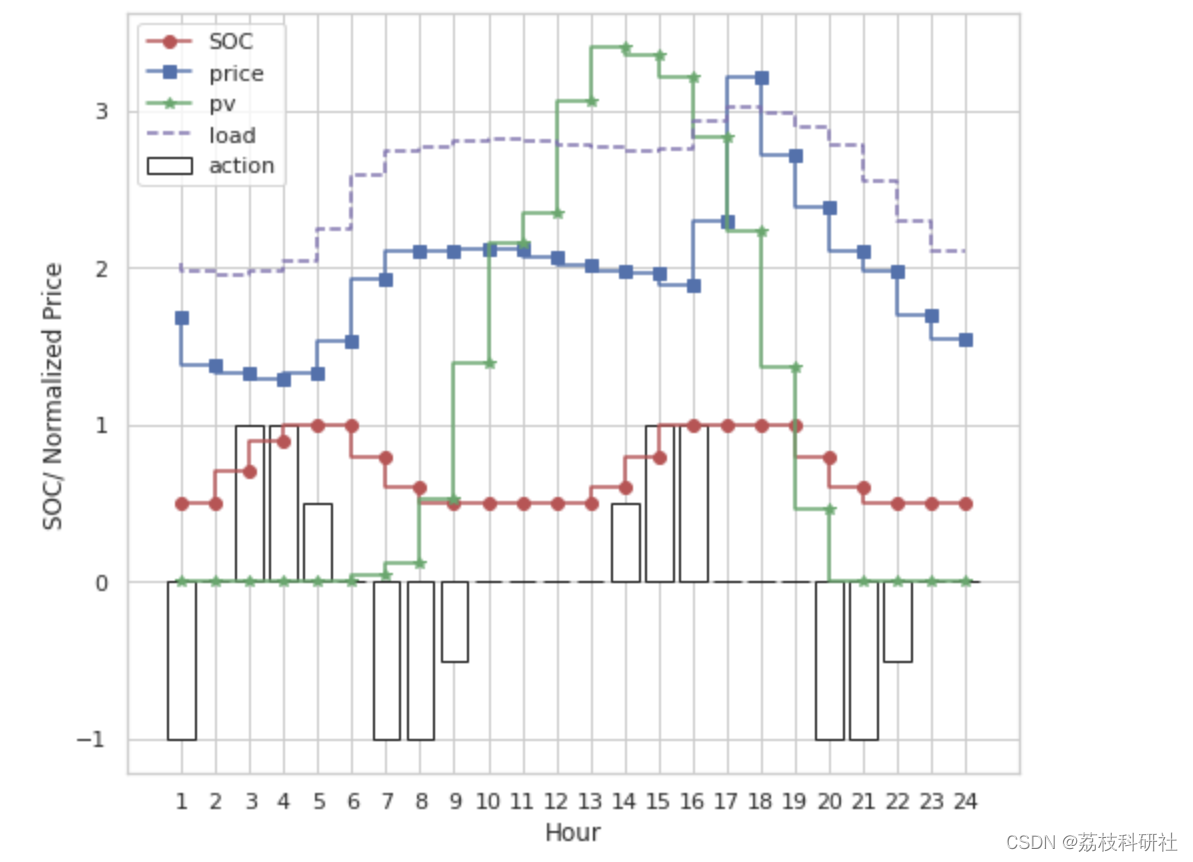
def get_resultplot(SOC_list, action_list, x, start_idx, end_idx):
hours = end_idx - start_idx
if hours == 24:
plt.figure(figsize = (8,7))
plt.xticks(range(0, 24), range(1, 25))
else:
plt.figure(figsize = (25,5))
plt.xticks(range(0, end_idx-start_idx, 24), range(1, end_idx-start_idx+1, 24))
plt.step(range(0, hours), SOC_list[start_idx:end_idx], "ro-", label = "SOC")
plt.step(range(0, hours), x[start_idx:end_idx, 2], "bs-", label = "price")
plt.step(range(0, hours), x[start_idx:end_idx, 0], "g*-", label = "pv")
plt.step(range(0, hours), x[start_idx:end_idx, 1], "m--", label = "load")
plt.bar(range(0, hours), action_list[start_idx:end_idx],
facecolor = "w", edgecolor = "k", label = "action")
plt.ylabel("SOC/ Normalized Price")
plt.xlabel("Hour")
plt.legend(loc=2)
plt.show()
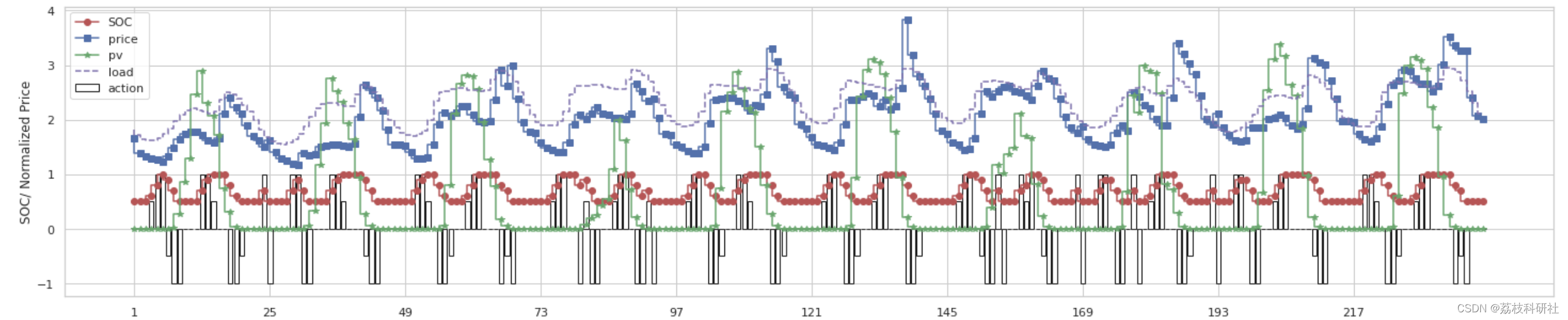
# Case 1 - Charged with PV not with grid to contain excess PV even the price is higher than average # Use the spare capacity to store PV # Not below the target SOC start_idx = len(SOC_list) - 192 end_idx = len(SOC_list) - 168 get_resultplot(SOC_list, action_list, x, start_idx, end_idx)
# Zoom of case 3
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize = (8,6))
#ax2 = ax.twinx()
ln1 = ax.step(range(0, 24), SOC_list[13079:13103], "ro-", label = "SOC")
ln2 = ax.bar(range(0, 24), action_list[13079:13103],
facecolor = "w", edgecolor = "k", label = "action")
ln3 = ax.axhline(y = 0.5, linestyle = "--", label = "target SOC")
ax.set_xlabel("Hour")
ax.set_ylabel("SOC")
lns = ln1 + [ln2] + [ln3]
labs = [l.get_label() for l in lns]
ax.legend(lns, labs, loc = 3)
plt.xticks(range(0, 24), range(1, 25))
plt.show()

其余详细部分见第4部分。
🎉3 参考文献
部分理论来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。