图论理论基础
https://www.programmercarl.com/kamacoder/%E5%9B%BE%E8%AE%BA%E7%90%86%E8%AE%BA%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80.html
98. 所有可达路径
(1)题目描述:



(2)解题思路:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
vector<vector<int>> result; // 收集符合条件的路径
vector<int> path; // 1节点到终点的路径
void dfs (const vector<list<int>>& graph, int x, int n) {
if (x == n) { // 找到符合条件的一条路径
result.push_back(path);
return;
}
for (int i : graph[x]) { // 找到 x指向的节点
path.push_back(i); // 遍历到的节点加入到路径中来
dfs(graph, i, n); // 进入下一层递归
path.pop_back(); // 回溯,撤销本节点
}
}
int main() {
int n, m, s, t;
cin >> n >> m;
// 节点编号从1到n,所以申请 n+1 这么大的数组
vector<list<int>> graph(n + 1); // 邻接表
while (m--) {
cin >> s >> t;
// 使用邻接表 ,表示 s -> t 是相连的
graph[s].push_back(t);
}
path.push_back(1); // 无论什么路径已经是从0节点出发
dfs(graph, 1, n); // 开始遍历
// 输出结果
if (result.size() == 0) cout << -1 << endl;
for (const vector<int> &pa : result) {
for (int i = 0; i < pa.size() - 1; i++) {
cout << pa[i] << " ";
}
cout << pa[pa.size() - 1] << endl;
}
}(3)总结:
1.该题目是深度优先搜索的一个简单应用。本题的关键是熟悉深搜模板,存储方式--本题采用邻接表存储,如下图所示。
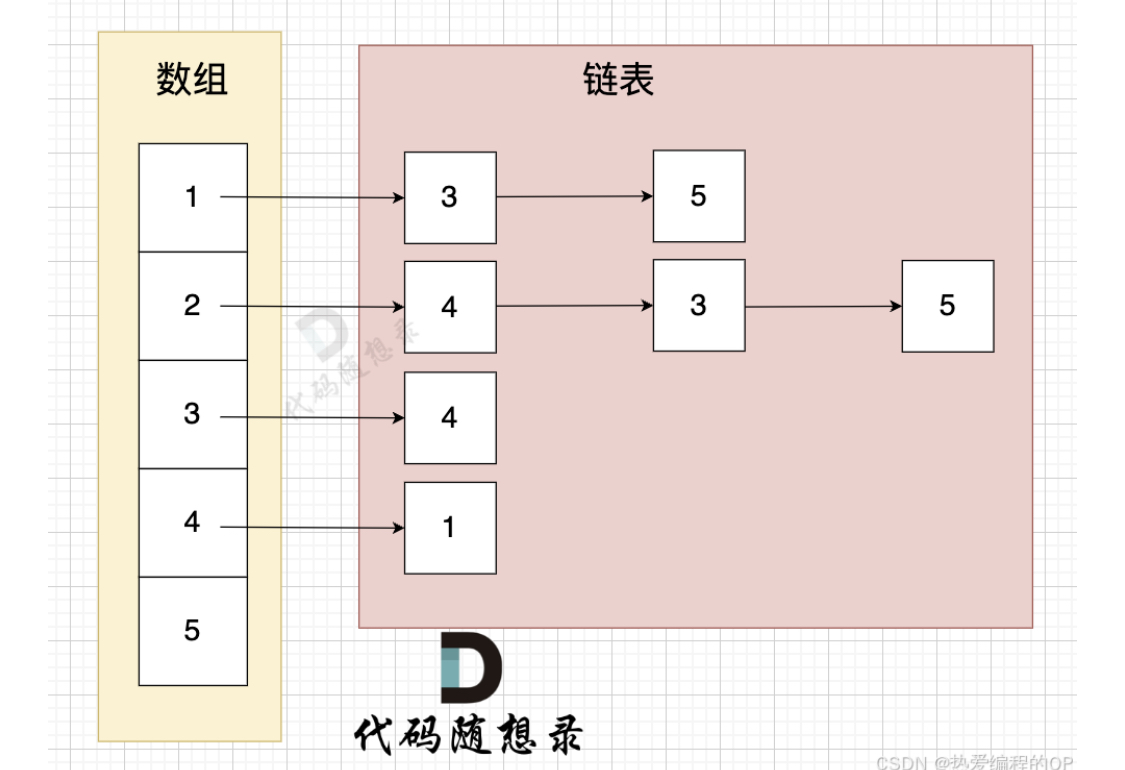
深搜理论基础
https://www.programmercarl.com/kamacoder/%E5%9B%BE%E8%AE%BA%E6%B7%B1%E6%90%9C%E7%90%86%E8%AE%BA%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80.html
1.深度优先搜索从起点到终点遇到搜索过的点或终点就通过回溯换一个方向继续搜索
2.回溯算法,其实就是dfs的过程,这里给出dfs的代码框架:
void dfs(参数) {
if (终止条件) {
存放结果;
return;
}
for (选择:本节点所连接的其他节点) {
处理节点;
dfs(图,选择的节点); // 递归
回溯,撤销处理结果
}
}广搜理论基础
https://www.programmercarl.com/kamacoder/%E5%9B%BE%E8%AE%BA%E6%B7%B1%E6%90%9C%E7%90%86%E8%AE%BA%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80.html
1.广度优先搜索以起点为中心向四周扩散
2.用一个方格地图,假如每次搜索的方向为 上下左右(不包含斜上方),那么给出一个start起始位
置,那么BFS就是从四个方向走出第一步。
代码实现中,只要能找到一个能保存我们要遍历过的元素的容器就可以。此处可以选择栈和队列。
由于广搜不考虑转圈搜索的顺序,因此当前栈和队列使用时没有区别。

int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 表示四个方向
// grid 是地图,也就是一个二维数组
// visited标记访问过的节点,不要重复访问
// x,y 表示开始搜索节点的下标
void bfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {
queue<pair<int, int>> que; // 定义队列
que.push({x, y}); // 起始节点加入队列
visited[x][y] = true; // 只要加入队列,立刻标记为访问过的节点
while(!que.empty()) { // 开始遍历队列里的元素
pair<int ,int> cur = que.front(); que.pop(); // 从队列取元素
int curx = cur.first;
int cury = cur.second; // 当前节点坐标
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { // 开始想当前节点的四个方向左右上下去遍历
int nextx = curx + dir[i][0];
int nexty = cury + dir[i][1]; // 获取周边四个方向的坐标
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 坐标越界了,直接跳过
if (!visited[nextx][nexty]) { // 如果节点没被访问过
que.push({nextx, nexty}); // 队列添加该节点为下一轮要遍历的节点
visited[nextx][nexty] = true; // 只要加入队列立刻标记,避免重复访问
}
}
}
}



















