目录
235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
701.二叉搜索树中的插入操作
450.删除二叉搜索树中的节点
235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
题目
235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
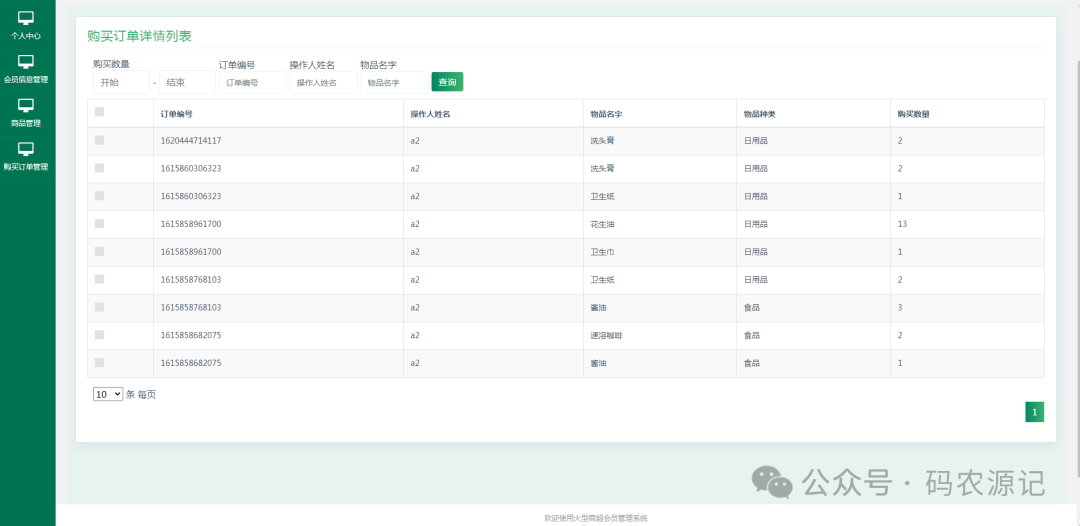
例如,给定如下二叉搜索树: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5]
示例1:
输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8
输出: 6
解释: 节点 2 和节点 8 的最近公共祖先是 6。
示例2:
输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4
输出: 2
解释: 节点 2 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是 2, 因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
说明:
- 所有节点的值都是唯一的。
- p、q 为不同节点且均存在于给定的二叉搜索树中。
思路
代码随想录:235.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
视频讲解:235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
类似于236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先 - 力扣(LeetCode),区别是本题为二叉搜索树,可以利用其特性进行解题。
从根节点向下遍历,有三种情况:
- 当前节点的值小于
q.val和p.val,说明目标节点在当前节点的右子树中。 - 当前节点的值大于
q.val和p.val,说明目标节点在当前节点的左子树中。 - 当前节点的值在
q.val和p.val之间,当前节点即为最近公共祖先。
本题使用递归法和迭代法都比较简单。
题解
递归法:
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val)
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if (root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val)
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
return root;
}
}
迭代法:
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val > p.val && cur.val > q.val) {
cur = cur.left;
} else if (cur.val < p.val && cur.val < q.val) {
cur = cur.right;
} else {
return cur;
}
}
return cur;
}
}
701.二叉搜索树中的插入操作
题目
701. 二叉搜索树中的插入操作 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点 root 和要插入树中的值 value ,将值插入二叉搜索树。 返回插入后二叉搜索树的根节点。 输入数据 保证 ,新值和原始二叉搜索树中的任意节点值都不同。
注意,可能存在多种有效的插入方式,只要树在插入后仍保持为二叉搜索树即可。 你可以返回 任意有效的结果 。
示例1:
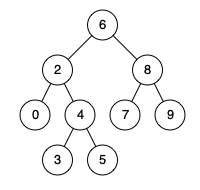
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 5
输出:[4,2,7,1,3,5]
解释:另一个满足题目要求可以通过的树是:

示例2:
输入:root = [40,20,60,10,30,50,70], val = 25
输出:[40,20,60,10,30,50,70,null,null,25]
示例3:
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3,null,null,null,null,null,null], val = 5
输出:[4,2,7,1,3,5]
提示:
- 树中的节点数将在
[0, 104]的范围内。 -108 <= Node.val <= 108- 所有值
Node.val是 独一无二 的。 -108 <= val <= 108- 保证
val在原始BST中不存在。
思路
代码随想录:701.二叉搜索树中的插入操作
视频讲解:701.二叉搜索树中的插入操作
根据二叉搜索树的特性向下遍历直到叶子节点即可。
题解
递归法:
class Solution {
public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
TreeNode node = new TreeNode();
if (root == null) {
node.val = val;
return node;
}
if (root.val < val) {
node = insertIntoBST(root.right, val);
if (root.right == null)
root.right = node;
} else if (root.val > val) {
node = insertIntoBST(root.left, val);
if (root.left == null)
root.left = node;
}
return root;
}
}
优化:
class Solution {
public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if (root == null) {
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(val);
return node;
}
if (root.val < val) {
root.right = insertIntoBST(root.right, val);
} else if (root.val > val) {
root.left = insertIntoBST(root.left, val);
}
return root;
}
}
迭代法:
class Solution {
public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if (root == null)
return new TreeNode(val);
TreeNode cur = root;
TreeNode pre = root;
while (cur != null) {
pre = cur;
if (cur.val < val) {
cur = cur.right;
} else if (cur.val > val) {
cur = cur.left;
}
}
if (pre.val < val) {
pre.right = new TreeNode(val);
} else {
pre.left = new TreeNode(val);
}
return root;
}
}
450.删除二叉搜索树中的节点
题目
450. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root 和一个值 key,删除二叉搜索树中的 key 对应的节点,并保证二叉搜索树的性质不变。返回二叉搜索树(有可能被更新)的根节点的引用。
一般来说,删除节点可分为两个步骤:
- 首先找到需要删除的节点;
- 如果找到了,删除它。
示例1:

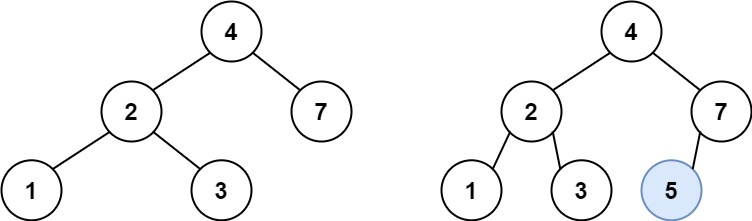
输入:root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], key = 3
输出:[5,4,6,2,null,null,7]
解释:给定需要删除的节点值是 3,所以我们首先找到 3 这个节点,然后删除它。
一个正确的答案是 [5,4,6,2,null,null,7], 如下图所示。
另一个正确答案是 [5,2,6,null,4,null,7]。

示例2:
输入: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], key = 0
输出: [5,3,6,2,4,null,7]
解释: 二叉树不包含值为 0 的节点
示例3:
输入: root = [], key = 0
输出: []
提示:
- 节点数的范围
[0, 104]. -105 <= Node.val <= 105- 节点值唯一
root是合法的二叉搜索树-105 <= key <= 105
思路
代码随想录:450.删除二叉搜索树中的节点
视频讲解:LeetCode:450.删除二叉搜索树中的节点
删除节点有四种情况:
- 没有找到目标节点
- 目标节点为叶子节点,直接删除,返回null
- 目标节点的左右孩子有一个为空,删除后返回不为空的孩子为根节点
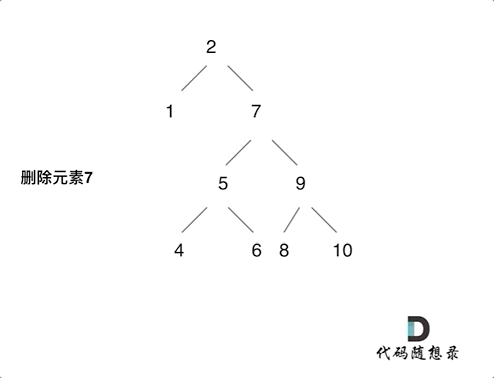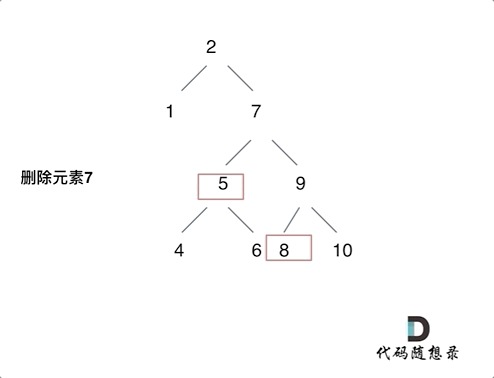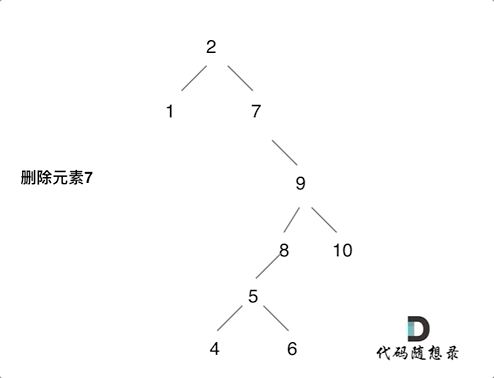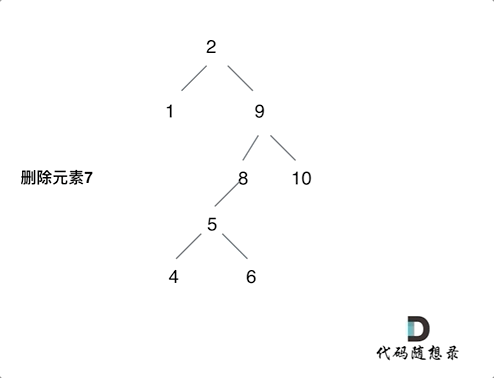
- 目标节点的左右孩子都不为空,删除后将左孩子放到右子树里面最左侧的叶子节点之下,返回右孩子为根节点
情况四如下图:
题解
递归法:
class Solution {
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if (root == null)
return null;
if (root.val == key) {
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return null;
if (root.left == null && root.right != null)
return root.right;
if (root.left != null && root.right == null)
return root.left;
if (root.left != null && root.right != null) {
TreeNode cur = root.right;
while (cur.left != null) {
cur = cur.left;
}
cur.left = root.left;
return root.right;
}
}
if (root.val < key) {
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key);
} else if (root.val > key) {
root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key);
}
return root;
}
}




![[MAUI]数据绑定和MVVM:MVVM的属性验证](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/22c9c9c9cf9242d6fe1f3d873a57e1c5.png#pic_center)